Marine Natural Products with P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. P-Glycoprotein
1.2. Functions of P-gp
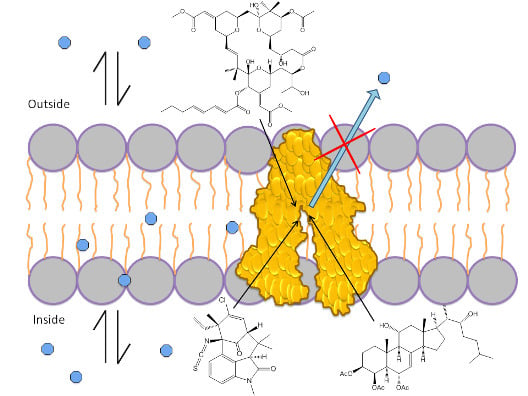
1.3. Mechanism of P-gp Efflux Function


1.4. Role of ATP in Protein Activation
- Promoting a conformational change in P-gp that blocks the ATP binding site and, subsequently, ATPase function;
- Promoting a conformational change in P-gp that enhances ATP binding, but concurrently blocks the substrate binding site;
- Inactivating the substrate binding site without inducing any conformational changes, e.g., stereo-isomers of cyclic hexapeptide inhibitors QZ59-RRR and QZ59-SSS [24].
1.5. Importance in Therapy
1.6. P-gp Inhibitors
| First Generation | Second generation | Third Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Verapamil Cyclosporine A Vincristine Reserpine Quinidine Tamoxifen Trifluoperazine | (R)-verapamil Valspodar (PSC-833) Dexniguldipine Elacridar (GF120918) Biricodar Dofequidar | Tariquidar (XR9576) Zosuquidar (LY335979) Laniquidar (R101933) ONT-093 (OC-144-093) Mitotane (NSC-38721) Annamycin |
| ATPase Activity | P-gp Expression | Competition for Binding Site | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitor | Stimulator | Down Regulator | Up Regulator | |
| Valspodar Tariquidar Elacridar ONT-093 | Verapamil Cyclosporine A Vincristine Quinidine Tamoxifen Toremifene Trifluoperazine Dexverapamil Biricodar | Verapamil Cyclosporine A Reserpine Toremifene Trifluoperazine Dexverapamil Valspodar | Vincristine | Verapamil Cyclosporine A Vincristine Reserpine Quinidine Valspodar Dexniguldipine Biricodar Elacridar Dofequidar Tariquidar Zosuquidar |
| P-gp Inhibitor | Phase | Trial | Protocols Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tariquidar (XR9576) | II | Tariquidar and Docetaxel to Treat Patients With Lung, Ovarian, Renal and Cervical Cancer | 03-C-0284, NCI-03-C-0284, NCT00072202, NCT00069160 |
| II | Surgery Plus Chemotherapy (Doxorubicin, Vincristine and Etoposide), Mitotane and Tariquidar to Treat Adrenocortical Cancer | 040011, 04-C-0011, NCT00071058 | |
| I | Study of XR9576 and Vinorelbine in Patients with Advanced Cancer | NCI-00-C-0044 | |
| I | Trial of Tariquidar (XR9576) in Combination with Doxorubicin, Vinorelbine or Docetaxel in Pediatric Patients with Solid Tumors | NCT00011414 | |
| Zosuquidar (LY335979) | III | Daunorubicin and Cytarabine ± Zosuquidar in Treating Older Patients with Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Refractory Anemia | CDR0000257122 E3999, U10CA021115, ECOG-E3999, NCT00046930 |
| II | Zosuquidar in Combination With Daunorubicin and Cytarabine in Patients Ages 55–75 with Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | KAN-979-01 NCT00129168 | |
| II | A Trial of Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin (GO) in Combination with Zosuquidar in Patients with CD33 Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia | KAN-979-02 NCT00233909 | |
| Laniquidar (R101933) | II | R101933 Combined with Chemotherapy in Treating Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer That Has Not Responded to Previous Chemotherapy | EORTC-10003-16004 EORTC-16004, ECSG-EORTC-16004, IDBBC-10003, NCT00028873 |
| Elacridar (GF120918) | I | A Phase I, Randomized, Open-Label, Parallel-Cohort, Dose-Finding Study of Elacridar (GF120918) in Combination with 2.0 mg Oral Topotecan in Cancer Patients | BCR10001 |
| Mitotane (NSC-38721) | III | Trial in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Adrenocortical Carcinoma Treatment (FIRM-ACT) | CO-ACT-001 NCT00094497 |
| II | Phase II Study of Continuous-Infusion DOX/VCR/VP-16 with Daily Oral Mitotane for Renal Cell Cancer | NCI-94-C-0156 | |
| II | Phase II Mitotane plus Cortisone Acetate/Fludrocortisone and ADR for Residual, Recurrent or Metastatic Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma | EST-1879 | |
| II | Phase II Study of Continuous-Infusion DOX/VCR/VP-16 with Daily Oral Mitotane Before and After Surgery in Patients with Adrenocortical Carcinoma | NCI-93-C-0200D NCI-93-C-0200B | |
| Annamycin | II | Chemotherapy in Treating Patients with Breast Cancer | CDR0000068486 NYU-9851, NCI-G01-1914, NCT00012129 |
2. Inhibitors from Marine Sources
| Inhibitor | Intracellular Accumulation of Substrates | ATPase Activity | Photoaffinity Labelling | Cell Line Tested | Drug with Enhanced Activity | P-gp Expression | Selective to MDR1 or ABCB1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sipholenol A | Increased | Stimulated | Inhibited | KB-C2, KB-V1 | colchicine, vinblastine, paclitaxel | Not altered | Yes |
| Lamellarin | Increased | xx | xx | P338/Schabel | doxorubicin, daunorubicin, vinblastine | xx | xx |
| Agosterol A | xx | xx | Inhibited | KB-C2 | colchicine | xx | No |
| ET-743 + | Increased | xx | Not inhibited. | KB-8-5, KB-C2 | doxorubicin, vincristine | Downregulated | xx |
| N-Methylwelwitin-dolinone C isothiocyanate | Increased | xx | Inhibited | NCI/ADR-RES | vinblastine, taxol, actinomycin D, daunomycin, colchicine | xx | xx |
| Parguerenes | Increased | xx | xx | SW620AD-300, HEK293/ABCB1, CEM/VLB100 | vinblastine, doxorubicin and paclitaxel | Not altered | No |
| Patellamide d | xx | xx | xx | CEM/VLB100 | vinblastine, colchicine and adriamycin | xx | xx |
| Kendarimide A | xx | xx | xx | KB-C2 | colchicine | xx | xx |
| Bryostatin 1 | Increased | xx | Inhibited | KB-C1, HeLa-MDR1-V185 | vinblastine, colchicine | xx | |
| ISA, ISA B | xx | xx | xx | KB/VJ300 | vincristine | xx | xx |
| Nocardioazines | xx | xx | xx | SW620AD-300 | doxorubicin | xx | xx |
| Discodermolide * | xx | xx | xx | SW620AD-300, A2780AD | xx | xx | No |
| Polyoxygenated steroids # | xx | xx | xx | KB-C2 | xx | xx | xx |
2.1. Inhibitors from Tunicates

2.2. Inhibitors from Sponge

2.3. Inhibitors from Cyanobacteria and Alga

2.4. Inhibitors from Bryozoans

2.5. Inhibitors from Corals
2.6. Inhibitors from Marine Bacteria
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharom, F.J. Multidrug Resistance Protein (P-Glycoprotein; MDR1). In Drug Transporters: Molecular Characterization and Role in Drug Disposition; You, G., Morris, M.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 223–262. [Google Scholar]
- Sharom, F.J. The P-glycoprotein multidrug transporter. Essays Biochem. 2011, 50, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, T.; Jaggi, M.; Khar, R.K.; Talegaonkar, S. Emerging significance of flavonoids as P-glycoprotein inhibitors in cancer chemotherapy. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 12, 46–78. [Google Scholar]
- Eckford, P.D.W.; Sharom, F.J. ABC efflux pump-based resistance to chemotherapy drugs. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2989–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordon-Cardo, C.; O’Brien, J.P.; Casals, D.; Rittman-Grauer, L.; Biedler, J.L.; Melamed, M.R.; Bertino, J.R. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.H.; Kim, R.B. Transporters and drug therapy: Implications for drug disposition and disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 78, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaut, F.; Tsuruo, T.; Hamada, H.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Willingham, M.C. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7735–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Lavasanifar, A. P-glycoprotein inhibition as a therapeutic approach for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F. Structure, function and regulation of P-glycoprotein and its clinical relevance in drug disposition. Xenobiotica 2008, 38, 802–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharom, F.J. ABC multidrug transporters: Structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics 2008, 9, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F.; Gottesman, M.M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.J.; Ferreira, M.J.U.; dos Santos, D.J.V.A. Molecular docking characterizes substrate-binding sites and efflux modulation mechanisms within P-glycoprotein. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, C.; Paine, S.W.; Littlewood, P. Can long range mechanical interaction between drugs and membrane proteins define the notion of molecular promiscuity? Application to P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance (MDR). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5112–5118. [Google Scholar]
- Aller, S.G.; Yu, J.; Ward, A.; Weng, Y.; Chittaboina, S.; Zhuo, R.; Harrell, P.M.; Trinh, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.; Urbatsch, I.L.; Chang, G. Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding. Science 2009, 323, 1718–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharom, F.J.; Yu, X.; Doige, C.A. Functional reconstitution of drug transport and ATPase activity in proteoliposomes containing partially purified P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24197–24202. [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar, S.V.; Dey, S.; Hrycyna, C.A.; Ramachandra, M.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 361–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F.; Linton, K.J. The ATP switch model for ABC transporters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siarheyeva, A.; Liu, R.; Sharom, F.J. Characterization of an asymmetric occluded state of P-glycoprotein with two bound nucleotides: Implications for catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7575–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauna, Z.E.; Ambudkar, S.V. Characterization of the catalytic cycle of ATP hydrolysis by human P-glycoprotein. The two ATP hydrolysis events in a single catalytic cycle are kinetically similar but affect different functional outcomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 11653–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Berridge, G.; Higgins, C.F.; Callaghan, R. The multi-drug resistance reversal agent SR33557 and modulation of vinca alkaloid binding to P-glycoprotein by an allosteric interaction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Tang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Xie, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, S.; Hu, L.; et al. Reversal of P-gp and MRP1-mediated multidrug resistance by H6, a gypenoside aglycon from Gynostemma pentaphyllum, in vincristine-resistant human oral cancer (KB/VCR) cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 696, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.F.; Wong, I.L.K.; Kan, J.W.Y.; Yan, C.S.W.; Chow, L.M.C.; Chan, T.H. Amine linked flavonoid dimers as modulators for P-glycoprotein-based multidrug resistance: Structure-activity relationship and mechanism of modulation. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanmahasathien, W.; Ohnuma, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Limtrakul, P. Biochemical mechanism of modulation of human P-glycoprotein by stemofoline. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Xia, D. Structure of a multidrug transporter: Crystal structures of a mammalian multidrug efflux pump bound to peptide inhibitors may reveal drug binding sites. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankatsing, S.U.C.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H.; Lange, J.M.A.; Prins, J.M. P-glycoprotein in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.M.; Volkman, S.K.; Thaithong, S.; Martin, R.K.; Kyle, D.E.; Milhous, W.K.; Wirth, D.F. Amplification of pfmdr1 associated with mefloquine and halofantrine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum from Thailand. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 57, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarro, F.; Chiquero, M.J.; Amador, M.V.; Légaré, D.; Ouellette, M.; Castanys, S. P-glycoprotein overexpression in methotrexate-resistant Leishmania tropica. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 47, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueiros, F.J.; Viola, J.P.B.; Gomes, F.C.A.; Farina, M.; Lins, U.; Bertho, A.L.; Wirth, D.F.; Lopes, U.G. Leishmania amazonensis: Multidrug resistance in vinblastine-resistant promastigotes is associated with rhodamine 123 efflux, DNA amplification, and RNA overexpression of a Leishmania mdr1 gene. Exp. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.C.O.; Castro-Pinto, D.B.; Ribeiro, G.A.; Berredo-Pinho, M.M.; Gomes, L.H.F.; da Silva Bellieny, M.S.; Goulart, C.M.; Echevarria, A.; Leon, L.L. P-glycoprotein efflux pump plays an important role in Trypanosoma cruzi drug resistance. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descoteaux, S.; Ayala, P.; Samuelson, J.; Orozco, E. Increase in mRNA of multiple Eh pgp genes encoding P-glycoprotein homologues in emetine-resistant Entamoeba histolytica parasites. Gene 1995, 164, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Bostian, K.A. Practical applications and feasibility of efflux pump inhibitors in the clinic—A vision for applied use. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Zgurskaya, H.I.; Totrov, M.; Watkins, W.J. Waltzing transporters and ‘the dance macabre’ between humans and bacteria. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppens, I.E.L.M.; Witteveen, E.O.; Jewell, R.C.; Radema, S.A.; Paul, E.M.; Mangum, S.G.; Beijnen, J.H.; Voest, E.E.; Schellens, J.H.M. A phase I, randomized, open-label, parallel-cohort, dose-finding study of elacridar (GF120918) and oral topotecan in cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3276–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, L.; Wagner, P.; Ibrahim, N.; Rivera, E.; Theriault, R.; Booser, D.; Symmans, F.W.; Wong, F.; Blumenschein, G.; Fleming, D.R.; et al. Phase II study of tariquidar, a selective P-glycoprotein inhibitor, in patients with chemotherapy-resistant, advanced breast carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 104, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malingré, M.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Rosing, H.; Koopman, F.J.; Jewell, R.C.; Paul, E.M.; Ten Bokkel Huinink, W.W.; Schellens, J.H.M. Co-administration of GF120918 significantly increases the systemic exposure to oral paclitaxel in cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer. 2001, 84, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Mayer, L.D. Multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer: Mechanisms, reversal using modulators of MDR and the role of MDR modulators in influencing the pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.V.S.; Ashokraj, Y.; Dey, C.S.; Panchagnula, R. P-glycoprotein inhibitors and their screening: A perspective from bioavailability enhancement. Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kokubu, N.; Charnick, S.B.; Naito, M.; Tsuruo, T.; Cohen, D. Interaction of cyclosporin derivatives with the ATPase activity of human P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.; Bates, S.E. Tariquidar (XR9576): A P-glycoprotein drug efflux pump inhibitor. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2007, 7, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapposelli, S.; Coi, A.; Imbriani, M.; Bianucci, A.M. Development of classification models for identifying “True” P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors through inhibition, ATPase activation and monolayer efflux assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6924–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.J.; Rodarte, J.C.; Benbatoul, K.D.; Romano, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Krane, S.; Moran, E.J.; Uyeda, R.T.; Dixon, R.; Guns, E.S.; et al. Discovery and characterization of OC144–093, a novel inhibitor of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2964–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Sharom, F.J.; Yu, X.; Chu, J.W.K.; Doige, C.A. Characterization of the ATPase activity of P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem. J. 1995, 308, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Kose, E.; Yasuda, S.; Ise, H.; Ikeda, U.; Ohmori, S. Determination of P-glycoprotein ATPase activity using luciferase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, G.Q. Interaction of multidrug resistance reversal agents with P-glycoprotein ATPase activity on blood-brain barrier. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002, 23, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Germann, U.A. Baculovirus-mediated expression of human multidrug resistance cDNA in insect cells and functional analysis of recombinant P-glycoprotein. Methods Enzymol. 1998, 292, 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, U.S.; Fine, R.L.; Scarborough, G.A. Antiestrogens and steroid hormones: Substrates of the human P-glycoprotein. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U.A.; Shlyakhter, D.; Mason, V.S.; Zelle, R.E.; Duffy, J.P.; Galullo, V.; Armistead, D.M.; Saunders, J.O.; Boger, J.; Harding, M.W. Cellular and biochemical characterization of VX-710 as a chemosensitizer: Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in vitro. Anticancer Drugs 1997, 8, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Fan, S.; Yang, Z.; Gao, F.; Chen, L.; Xiao, G.G.; Molnár, J.; Wang, Q. Down-regulation of P-glycoprotein is associated with resistance to cisplatin and VP-16 in human lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3593–3598. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.A.; Guo, J.J.; Cheng, J. Biomolecular mechanisms of cyclosporine A, tetrandrine and their combination on the reversion of multidrug resistance in human leukemia cell line. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2008, 28, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gréen, H.; Lotfi, K.; Zackrisson, A.L.; Peterson, C. Spontaneous reversal of P-Glycoprotein expression in multidrug resistant cell lines. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Masry, E.M.; Abou-Donia, M.B. Interaction of pyridostigmine bromide and N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide alone and in combination with P-glycoprotein expressed in Escherichia coli leaky mutant. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2006, 69, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.X.; Chen, B.A.; Cheng, J.; Ding, J.H.; Gao, F.; Gao, C.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, G.; Bao, W.; et al. Effect of tetrandrine, toremifene and their combination on the reversion of multidrug resistance of K562/A02 cell line. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2008, 16, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.Y.; Choi, B.H.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.H. Suppression of P-glycoprotein expression by antipsychotics trifluoperazine in adriamycin-resistant L1210 mouse leukemia cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 28, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickisch, G.H.; Noordzij, M.A.; Gaast, A.V.d.; Gebreamlack, P.; Köhrmann, K.U.; Mogler-Drautz, E.; Kupper, H.; Schröder, F.H. Dexverapamil to modulate vinblastine resistance in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 121, R11–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bark, H.; Choi, C.H. PSC833, cyclosporine analogue, downregulates MDR1 expression by activating JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 and suppressing NF-kappaB. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 65, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, M.M.; Safa, A.R.; Felsted, R.L.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I. Membrane vesicles from multidrug-resistant human cancer cells contain a specific 150- to 170-kDa protein detected by photoaffinity labeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3847–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Ramachandra, M.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M.; Ambudkar, S.V. Evidence for two nonidentical drug-interaction sites in the human P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10594–10599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friche, E.; Demant, E.J.; Sehested, M.; Nissen, N.I. Effect of anthracycline analogs on photolabelling of p-glycoprotein by [125I]iodomycin and [3H]azidopine: Relation to lipophilicity and inhibition of daunorubicin transport in multidrug resistant cells. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 67, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, S.; Cornwell, M.M.; Kuwano, M.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Most drugs that reverse multidrug resistance also inhibit photoaffinity labeling of P-glycoprotein by a vinblastine analog. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 33, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Jetté, L.; Murphy, G.F.; Leclerc, J.M.; Béliveau, R. Interaction of drugs with P-glycoprotein in brain capillaries. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J.; Gekeler, V.; Ise, W.; Noller, A.; Mitterdorfer, J.; Hofer, S.; Utz, I.; Gotwald, M.; Boer, R.; Glossmann, H.; et al. Mechanism of action of dexniguldipine-HCl (B8509-035), a new potent modulator of multidrug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyafil, F.; Vergely, C.; Du Vignaud, P.; Grand-Perret, T. In vitro and in vivo reversal of multidrug resistance by GF120918, an acridonecarboxamide derivative. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 4595–4602. [Google Scholar]
- Saeki, T.; Tsuruo, T.; Sato, W.; Nishikawsa, K. Drug resistance in chemotherapy for breast cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 56, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.; Stewart, A.J.; Dangerfield, W.; Okiji, S.; Liddle, C.; Bootle, D.; Plumb, J.A.; Templeton, D.; Charlton, P. In vitro and in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a novel potent modulator, XR9576. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig, A.H.; Shepard, R.L.; Cao, J.; Law, K.L.; Ehlhardt, W.J.; Baughman, T.M.; Bumol, T.F.; Starling, J.J. Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a potent cyclopropyldibenzosuberane modulator, LY335979. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar]
- Ekins, S.; Kim, R.B.; Leake, B.F.; Dantzig, A.H.; Schuetz, E.G.; Lan, L.B.; Yasuda, K.; Shepard, R.L.; Winter, M.A.; Schuetz, J.D.; et al. Application of three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships of P-glycoprotein inhibitors and substrates. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieiri, I. Functional significance of genetic polymorphisms in P-glycoprotein (MDR1, ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP, ABCG2). Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 27, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 144–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 237–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinehart, K.L.; Holt, T.G.; Fregeau, N.L.; Stroh, J.G.; Keifer, P.A.; Sun, F.; Li, L.H.; Martin, D.G. Ecteinascidins 729, 743, 745, 759A, 759B, and 770: Potent antitumor agents from the Caribbean tunicate Ecteinascidia turbinata. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 4512–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Forleo, D.A.; Gunawardana, G.P.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Koehn, F.E.; McConnell, O.J. Antitumor tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids from the colonial ascidian Ecteinascidia turbinata. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 4508–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, A.; Takebayashi, Y.; Ren, X.Q.; Miyashita, H.; Mori, S.; Akiyama, S.I.; Pommier, Y. Overcoming multidrug drug resistance in P-glycoprotein/MDR1-overexpressing cell lines by ecteinascidin 743. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, N.J.; Keam, S.J. Trabectedin: A review of its use in the management of soft tissue sarcoma and ovarian cancer. Drugs 2007, 67, 2257–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.J.; Faulkner, D.J.; He, C.H.; van Duyne, G.D.; Clardy, J. Metabolites of the marine prosobranch mollusk Lamellaria sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 5492–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, N.; Fenical, W.; van Duyne, G.D.; Clardy, J. New alkaloids of the lamellarin class from the marine ascidian Didemnum chartaceum (Sluiter, 1909). J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4570–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Carroll, A.R.; Pierens, G.K.; Quinn, R.J. New lamellarin alkaloids from the australian ascidian, Didemnum chartaceum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Butler, M.S.; Capon, R.J. Lamellarins O and P: New aromatic metabolites from the australian marine sponge Dendrilla cactos. Aust. J. Chem. 1994, 47, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Hobbs, L.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Capon, R.J. Lamellarins Q and R: New aromatic metabolites from an australian marine sponge, Dendrilla cactos. Aust. J. Chem. 1995, 48, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Bowden, B.F.; Coll, J.C. Studies of Australian ascidians. I. Six new lamellarin-class alkaloids from a colonial ascidian, Didemnum sp. Austr. J. Chem. 1993, 46, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Capon, R.J. Lamellarin-S: A new aromatic metabolite from an Australian Tunicate, Didemnum sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 711–713. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.V.R.; Faulkner, D.J.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Rao, M.R. New lamellarin alkaloids from an unidentified ascidian from the Arabian Sea. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 3457–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.V.R.; Rao, M.R.; Rhodes, D.; Hansen, M.S.T.; Rubins, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Faulkner, D.J. Lamellarin alpha 20-sulfate, an inhibitor of HIV-1 integrase active against HIV1 virus in cell culture. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, A.R.; García Grávalos, M.D.; Fernández Puentes, J.L. Polyaromatic alkaloids from marine invertebrates as cytotoxic compounds and inhibitors of multidrug resistance caused by P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, B.M.; Hawkins, C.J.; Lavin, M.F.; McCaffrey, E.J.; Parry, D.L.; van den Brenk, A.L.; Watters, D.J. New cyclic peptides with cytotoxic activity from the ascidian Lissoclinum patella. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.S.; Gehring, A.M.; Milne, J.C.; Belshaw, P.J.; Walsh, C.T. Thiazole and oxazole peptides: Biosynthesis and molecular machinery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1999, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.B.; Jacobs, R.S. A marine natural product, patellamide D, reverses multidrug resistance in a human leukemic cell line. Cancer Lett. 1993, 71, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Yoshioka, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Setiawan, A.; Murakami, N.; Chen, Z.S.; Sumizawa, T.; Akiyama, S.I.; Kobayashi, M. Agosterol A, a novel polyhydroxylated sterol acetate reversing multidrug resistance from a marine sponge of Spongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 6303–6306. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, S.; Chen, Z.S.; Higasiyama, K.; Setiawan, A.; Akiyama, S.; Kobayashi, M. Reversing effect of agosterol A, a spongean sterol acetate, on multidrug resistance in human carcinoma cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2001, 92, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S.; Aoki, S.; Komatsu, M.; Ueda, K.; Sumizawa, T.; Furukawa, T.; Okumura, H.; Ren, X.Q.; Belinsky, M.G.; Lee, K.; et al. Reversal of drug resistance mediated by multidrug resistance protein (MRP) 1 by dual effects of agosterol A on MRP1 function. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 93, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Gunasekera, M.; Longley, R.E.; Schulte, G.K. Discodermolide: A new bioactive polyhydroxylated lactone from the marine sponge Discodermia dissoluta. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 4912–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, R.E.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Faherty, D.; Mclane, J.; Dumont, F. Immunosuppression by discodermolide. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 696, 94–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kalesse, M. The chemistry and biology of discodermolide. ChemBioChem 2000, 1, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, R.J.; Giannakakou, P.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Longley, R.E.; Day, B.W.; Hamel, E. The microtubule-stabilizing agent discodermolide competitively inhibits the binding of paclitaxel (Taxol) to tubulin polymers, enhances tubulin nucleation reactions more potently than paclitaxel, and inhibits the growth of paclitaxel-resistant cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 613–622. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, A.; Miyamoto, T.; Higuchi, R.; Uchiumi, T.; Kuwano, M.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Structure of a novel multidrug resistance modulator, irciniasulfonic acid, isolated from a marine sponge, Ircinia sp. Tetrahedrom Lett. 2001, 42, 3335–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, C.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T. Irciniasulfonic acid B, a novel taurine conjugated fatty acid derivative from a Japanese marine sponge, Ircinia sp. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 5682–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Cao, L.; Matsui, K.; Rachmat, R.; Akiyama, S.I.; Kobayashi, M. Kendarimide A, a novel peptide reversing P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in tumor cells, from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7053–7059. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Laphookhieo, S.; Shi, Z.; Fu, L.W.; Akiyama, S.I.; Chen, Z.S.; Youssef, D.T.A.; van Soest, R.W.M.; El Sayed, K.A. Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by Sipholane triterpenoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Abraham, I.; Carvalho, P.; Kuang, Y.H.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Avery, M.A.; Chen, Z.S.; El Sayed, K.A. Sipholane triterpenoids: Chemistry, reversal of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance, and pharmacophore modeling. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Jain, S.; Kim, I.W.; Peng, X.X.; Abraham, I.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Fu, L.W.; El Sayed, K.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Chen, Z.S. Sipholenol A, a marine-derived sipholane triterpene, potently reverses P-glycoprotein (ABCB1)-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, I.; Jain, S.; Wu, C.P.; Khanfar, M.A.; Kuang, Y.; Dai, C.L.; Shi, Z.; Chen, X.; Fu, L.; Ambudkar, S.V.; et al. Marine sponge-derived sipholane triterpenoids reverse P-glycoprotein (ABCB1)-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.D.; Zilfou, J.T.; Stratmann, K.; Patterson, G.M.; Moore, R.E. Welwitindolinone analogues that reverse P-glycoprotein-mediated multiple drug resistance. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.C.; Sun, Y.L.; Salim, A.A.; Chen, Z.S.; Capon, R.J. Parguerenes: Marine red alga bromoditerpenes as inhibitors of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) in multidrug resistant human cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R. The Bryostatins. In Fortschritte der Chemie organischer Naturstoffe/Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Herz, W., Kirby, G.W., Steglich, W., Tamm, Ch., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; Volume 57, pp. 153–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mutter, R.; Wills, M. Chemistry and clinical biology of the bryostatins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 1841–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, A.S.; Smith, J.B.; Berkow, R.L. Bryostatin, an activator of the calcium phospholipid-dependent protein kinase, blocks phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, A.M.; George, M.A.; Pettit, G.R.; Rearick, J.I. Effects of bryostatins and retinoic acid on phorbol ester- and diacylglycerol-induced squamous differentiation in human tracheobronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 3990–3995. [Google Scholar]
- Spitaler, M.; Utz, I.; Hilbe, W.; Hofmann, J.; Grunicke, H.H. PKC-independent modulation of multidrug resistance in cells with mutant (V185) but not wild-type (G185) P-glycoprotein by bryostatin 1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. Polyhydroxylated steroids from the bamboo coral Isis hippuris. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, J.; Trianto, A.; Musman, M.; Issa, H.H.; Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Higa, T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J. New polyoxygenated steroids exhibiting reversal of multidrug resistance from the gorgonian Isis hippuris. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6259–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R.; Piggott, A.M.; Huang, X.C.; Capon, R.J. Nocardioazines: A novel bridged diketopiperazine scaffold from a marine-derived bacterium inhibits P-glycoprotein. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2770–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez, D.; Martinez-Luis, S. Marine Natural Products with P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor Properties. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 525-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010525
Lopez D, Martinez-Luis S. Marine Natural Products with P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor Properties. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(1):525-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010525
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez, Dioxelis, and Sergio Martinez-Luis. 2014. "Marine Natural Products with P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor Properties" Marine Drugs 12, no. 1: 525-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010525
APA StyleLopez, D., & Martinez-Luis, S. (2014). Marine Natural Products with P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor Properties. Marine Drugs, 12(1), 525-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010525