Methylthio-Aspochalasins from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
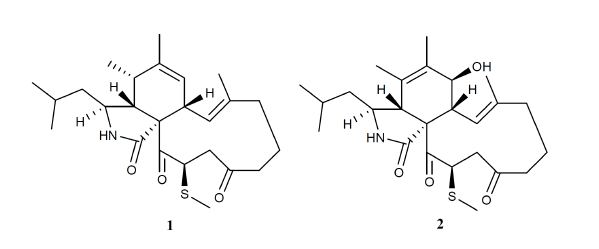
2. Results and Discussion

| NO. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13C | 1H (mult., J in Hz) | 13C | 1H (mult., J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 177.2 | 174.7 | ||
| 3 | 52.7 | 3.17 (m) | 56.2 | 3.25 (m) |
| 4 | 54.1 | 2.55 (brs) | 50.3 | 3.21 (s) |
| 5 | 37.2 | 2.55 (brs) | 127.0 | |
| 6 | 141.8 | 131.6 | ||
| 7 | 126.5 | 5.30 (brs) | 69.4 | 3.88 (d, 9.6) |
| 8 | 46.2 | 3.00 (m) | 49.1 | 2.36 (t,10.4) |
| 9 | 66.1 | 59.6 | ||
| 10 | 49.9 | 1.21,( m), 1.47 ( m) | 45.5 | 1.22,( m), 1.47 ( m) |
| 11 | 14.0 | 1.28 (d, 6.8) | 17.7 | 1.74 (s) |
| 12 | 20.1 | 1.80 (s) | 13.9 | 1.74 (s) |
| 13 | 125.2 | 6.29 (d, 10.8) | 121.4 | 6.22 (d,10.8) |
| 14 | 138.9 | 144.7 | ||
| 15 | 41.9 | 2.19 (brd, 8.0), 1.96 (td,12.0, 4.0) | 41.3 | 2.19 (m), 2.24 (m) |
| 16 | 19.8 | 2.29 (dd, 18.0,8.0 ), 1.56 (m) | 19.2 | 2.32 (m), 2.24 (m) |
| 17 | 40.2 | 2.70 (dd, 10.4, 18.6), 2.26 (m) | 40.0 | 2.69 (dd,10.4, 18.0), 2.17 (m) |
| 18 | 208.1 | 205.1 | ||
| 19 | 44.4 | 2.65 (dd,11.6,2.4), 3.00 (m) | 44.1 | 3.08 (t,11.6), 2.57 (dd,11.6,2.0m) |
| 20 | 46.0 | 5.03 (dd,12.8,2.4) | 44.2 | 4.77 (dd,12.4,2.0) |
| 21 | 200.5 | 196.2 | ||
| 22 | 25.7 | 1.69 (m) | 24.8 | 1.62 (m) |
| 23 | 21.9 | 0.94 (d,6.8) | 21.5 | 0.90 (d,6.8) |
| 24 | 24.2 | 0.92 (d,6.8) | 23.3 | 0.89 (d,6.8) |
| 25 | 15.1 | 1.36 (brs) | 15.6 | 1.45 (brs) |
| 26 | 10.8 | 1.85 (s) | 10.9 | 1.84 (s) |


3. Experimental
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungus Material and Compound Isolation
3.3. Cytotoxicity against Cancer Cell Lines
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Abbreviations
| ESI-HRMS | Electron Spray Ionization-High Resolution Mass Spectrum |
| DEPT | Distortionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer |
| HMBC | Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Correlation |
| COSY | Correlation Spectroscopy |
| HMQC | Heteronuclear Multiple Quantum Correlation |
| NOESY | Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement Spectroscopy |
| MM2 | Minimize Model |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mostafa, E.; Rateb, R.E. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 290–334. [Google Scholar]
- Cafaro, M.J. Baltomyces, a new genus of gut-inhabiting fungus in an isopod. Mycologia 1999, 91, 517–519. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.M. Legerioides, a new genus of Harpellales in isopods and other Trichomycetes from New England, USA. Mycologia 1999, 91, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Cafaro, M.J. Gut fungi of isopods: The genus Palavascia. Mycologia 2000, 92, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, M.; Danko, J.P.; Pennings, S.C.; Danford, A.R.; Ziegler, A.; Uglow, R.F.; Carefoot, T.H. Hepatopancreatic endosymbionts in coastal isopods (Crustacea: Isopoda), and their contribution to digestion. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 955–963. [Google Scholar]
- Roa, J.J.H.; Virella, C.R; Cafaro, M.J. First survey of arthropod gut fungi and associates from Vieques, Puerto Rico. Mycologia 2009, 101, 896–903. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, N.; Barber, P.H.; Weisz, J.B. Episymbiotic microbes as food and defence for marine isopods: Unique symbioses in a hostile environment. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, R.H.; Xu, H.; Cui, J.T.; Ge, H.M.; Tan, R.X. Neuraminidase Inhibitors from marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces seoulensis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Holtzel, A.; Schmid, D.G.; Nicholson, G.J.; Krastel, P.; Zeeck, A.; Gebhardt, K.; Fiedler, H.P.; Jung, G. Aspochalamins A–D and aspochalasin Z produced by the endosymbiotic Fungus Aspergillus niveus LU 9575. II. Structure elucidation. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2004, 57, 715–720. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.J.; Shao, C.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, K.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Sun, X.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive phenylalanine derivatives and cytochalasins from the soft coral-derived fungus, Aspergillus elegans. Mar Drugs 2013, 11, 2054–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.J.; Zhu, T.J.; Wei, H.J.; Zhang, G.J.; Wang, H.; Gu, Q.Q. Spicochalasin A and New Aspochalasins from the Marine-Derived Fungus Spicaria elegans. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 18, 3045–3051. [Google Scholar]
- Tomikawa, T.; Shin-Ya, K.; Seto, H.; Okusa, N.; Kajiura, T.; Hayakawa, Y. Structure of aspochalasin H, a new member of the aspochalasin family. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2002, 55, 666–668. [Google Scholar]
- Tomikawa, T.; Shin-Ya, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Miyajima, A.; Seto, H.; Hayakawa, Y. Selective cytotoxicity and stereochemistry of aspochalasin D. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2001, 54, 379–381. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Ui, H.; Shiomi, K.; Masuma, R.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhang, C.G.; Zhang, X.W.; Tanaka, Y.; Omura, S. Two new components of the aspochalasins produced by Aspergillus sp. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1997, 50, 919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, K.S.; Ernst, K. Metabolites of microorganisms, the aspochalasins A, B, C, and D. Helv. Chim. Acta 1979, 62, 1501–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Kohno, J.; Nonaka, N.; Nishio, M.; Ohnuki, T.; Kawano, K.; Okuda, T.; Komatsubara, S. TMC-169, a new antibiotic of the aspochalasin group produced by Aspergillus flavipes. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1999, 52, 575–577. [Google Scholar]
- Naruse, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Murata, S.; Sawada, Y.; Fukagawa, Y.; Oki, T. Aspochalasin E, a new antibiotic isolated from a fungus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1993, 46, 679–681. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.X.; Wijeratne, E.M.; Bigelow, D.; Pierson, L.S., 3rd; VanEtten, H.D.; Gunatilaka, A.A. Aspochalasins I, J, and K: Three new cytotoxic cytochalasans of Aspergillus flavipes from the rhizosphere of Ericameria laricifolia of the Sonoran Desert. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 328–332. [Google Scholar]
- Rochfort, S.; Ford, J.; Ovenden, S.; Wan, S.S.; George, S.; Wildman, H.; Tait, R.M.; Meurer-Grimes, B.; Cox, S.; Coates, J.; Rhodes, D. A novel aspochalasin with HIV-1 integrase inhibitory activity from Aspergillus flavipes. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2005, 58, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Q. Aspochalasin U, a moderate TNF-alpha inhibitor from Aspergillus sp. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2012, 65, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, S.J.; Yun, B.S.; Ryoo, I.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, K.H.; Yoo, I.D. Aspochalasin I, a melanogenesis inhibitor from Aspergillus sp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.B.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Yang, H.O.; Lee, K.R.; Kwon, H.C. Glionitrin B, a Cancer Invasion Inhibitory Diketopiperazine Produced by Microbial Coculture. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2309–2312. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A. Purification and Characterization of a New l-Methioninase from Solid Cultures of Aspergillus flavipes. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ding, W.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Methylthio-Aspochalasins from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5124-5131. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12105124
Liu Y, Zhao S, Ding W, Wang P, Yang X, Xu J. Methylthio-Aspochalasins from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(10):5124-5131. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12105124
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ying, Shizhe Zhao, Wanjing Ding, Pinmei Wang, Xianwen Yang, and Jinzhong Xu. 2014. "Methylthio-Aspochalasins from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp." Marine Drugs 12, no. 10: 5124-5131. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12105124
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhao, S., Ding, W., Wang, P., Yang, X., & Xu, J. (2014). Methylthio-Aspochalasins from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Marine Drugs, 12(10), 5124-5131. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12105124