New Hippolide Derivatives with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne
Abstract
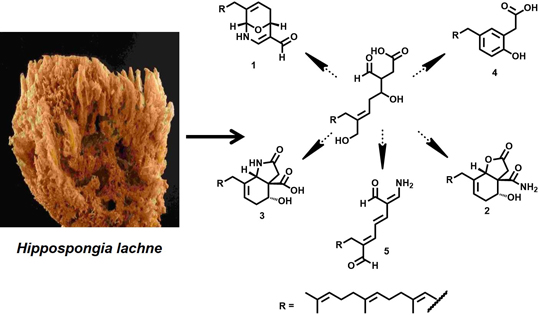
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
| Carbon | 1 a | 2 a | 3 b | 4 b | 5 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 186.5 CH | 174.5 qC | 178.5 qC | 181.9 qC | 190.2 CH |
| 2 | 117.3 qC | 33.9 CH2 | 30.4 CH2 | 42.0 CH2 | 108.0 CH |
| 3 | 146.5 CH | 53.1 qC | 58.6 qC | 123.3 qC | 151.8 qC |
| 4 | 65.6 CH | 67.8 CH | 67.4 CH | 153.5 qC | 139.7 CH |
| 5 | 31.0 CH2 | 29.8 CH2 | 31.5 CH2 | 117.0 CH | 114.2 CH |
| 6 | 120.1 CH | 122.2 CH | 119.7 CH | 128.2 CH | 150.9 CH |
| 7 | 134.8 qC | 135.1 qC | 138.8 qC | 134.5 qC | 138.2 qC |
| 8 | 33.0 CH2 | 33.2 CH2 | 31.9 CH2 | 35.4 CH2 | 24.5 CH2 |
| 9 | 26.0 CH2 | 25.7 CH2 | 26.8 CH2 | 30.5 CH2 | 27.4 CH2 |
| 10 | 124.0 CH | 123.1 CH | 123.6 CH | 123.9 CH | 123.5 CH |
| 11 | 135.7 qC | 136.2 qC | 136.0 qC | 135.8 qC | 136.1 qC |
| 12 | 39.7 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 | 39.9 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 |
| 13 | 26.6 CH2 | 26.6 CH2 | 26.7 CH2 | 26.8 CH2 | 26.7 CH2 |
| 14 | 123.2 CH | 124.0 CH | 124.1 CH | 124.4 CH | 124.2 CH |
| 15 | 126.2 qC | 135.0 qC | 135.1 qC | 135.1 qC | 135.0 qC |
| 16 | 39.7 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 | 39.9 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 |
| 17 | 26.8 CH2 | 26.7 CH2 | 26.7 CH2 | 26.9 CH2 | 26.8 CH2 |
| 18 | 124.4 CH | 124.3 CH | 124.4 CH | 124.6 CH | 124.4 CH |
| 19 | 131.4 qC | 131.4 qC | 131.3 qC | 131.4 qC | 131.3 qC |
| 20 | 25.7 CH3 | 25.7 CH3 | 25.7 CH3 | 25.7 CH3 | 25.7 CH3 |
| 21 | 17.7 CH3 | 17.7 CH3 | 17.7 CH3 | 17.7 CH3 | 17.7 CH3 |
| 22 | 16.0 CH3 | 16.0 CH3 | 16.0 CH3 | 16.0 CH3 | 16.0 CH3 |
| 23 | 16.2 CH3 | 16.1 CH3 | 16.1 CH3 | 16.0 CH3 | 16.1 CH3 |
| 24 | 76.9 CH | 79.7 CH | 70.8 CH | 130.9 CH | 194.2 CH |
| 25 | 175.2 qC | 182.9 qC |
| Position | 1 a | 2 a | 3 b | 4 b | 5 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.97, s | 9.75, d (3.5) | |||
| 2 | 2.93, d (18.0); 2.77, d (18.0) | 2.69, s | 3.53, s | ||
| 3 | 7.13, d (5.6) | 7.70, dt (3.5, 11.5) | |||
| 4 | 5.03, d (5.0) | 4.21, dd (7.0, 1.8) | 4.22, dd (9.5, 3.6) | 6.64, d (14.7) | |
| 5 | 2.64, dd (5.0, 20.0) 2.12, m | 2.46, m; 2.29, m | 2.39, m; 2.06, m | 6.78, d (8.0) | 6.66, m |
| 6 | 5.66, d (5.0) | 5.74, t (3.9) | 5.35, t (3.9) | 6.93, d (8.0) | 6.86, d (11.0) |
| 8 | 1.99, m | 2.19, m | 2.06, m | 2.51, t (8.0) | 2.39, t (7.5) |
| 9 | 2.13, m | 2.17, m | 2.06, m | 2.22, m | 2.12, m |
| 10 | 5.11, m | 5.09, m | 5.10, m | 5.17, t (6.8) | 5.16, t (7.5) |
| 12 | 1.97, m | 1.97, m | 2.69, m | 1.98, m | 1.96, m |
| 13 | 2.05, m | 2.07, m | 2.06, m | 2.06, m | 2.05, m |
| 14 | 5.10, m | 5.09, m | 5.10, m | 5.11, t (6.8) | 5.11, t (6.8) |
| 16 | 1.97, m | 1.97, m | 1.98, m | 1.98, m | 1.95, m |
| 17 | 2.05, m | 2.07, m | 2.06, m | 2.06, m | 2.05, m |
| 18 | 5.08, m | 5.09, m | 5.10, m | 5.10, t (6.3) | 5.09, t (6.5) |
| 20 | 1.68, s | 1.68, s | 1.68, s | 1.68, s | 1.68, s |
| 21 | 1.60, s | 1.60, s | 1.59, s | 1.60, s | 1.60, s |
| 22 | 1.60, s | 1.60, s | 1.59, s | 1.60, s | 1.58, s |
| 23 | 1.60, s | 1.60, s | 1.59, s | 1.57, s | 1.60, s |
| 24 | 5.06, d (4.1) | 5.14, s | 4.58, s | 6.89, br s | 9.37, s |
| 25 | |||||
| OH c | 4.99, br s | 11.04, s; 4.02, br s | |||
| NH | 5.78, br s (in CDCl3) | 7.56 c, s; 7.26, s | 5.42 c, d (7.5) | 8.20 c, m |





3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
 +67° (c 0.120, MeOH); CD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε) 219 (3.40), 266 (−0.80), 297 (2.77) nm; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 210 (1.68), 233 (1.64), 282 (1.56) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3369, 2926, 1596, 1448, 1212, 1067, 840, 673 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 392.2567 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C24H35NO2Na+, 392.2560).
+67° (c 0.120, MeOH); CD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε) 219 (3.40), 266 (−0.80), 297 (2.77) nm; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 210 (1.68), 233 (1.64), 282 (1.56) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3369, 2926, 1596, 1448, 1212, 1067, 840, 673 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 392.2567 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C24H35NO2Na+, 392.2560). −15° (c 0.10, MeOH); CD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε) 189 (−3.48), 196 (5.71) nm; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 190 (3.30) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3427, 2924, 1773, 1671, 1377, 1189, 1097, 981 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; 1H NMR data (in DMSO): δH 7.56 (1H, s, NH), 7.26 (1H, s, NH), 5.54 (1H, br s, H-24), 4.99 (1H, br s, OH), 5.14 (1H, m, H-6), 4.10 (1H, m, H-4); HRESIMS m/z 438.2619 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C25H37NO4Na+, 438.2615).
−15° (c 0.10, MeOH); CD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε) 189 (−3.48), 196 (5.71) nm; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 190 (3.30) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3427, 2924, 1773, 1671, 1377, 1189, 1097, 981 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; 1H NMR data (in DMSO): δH 7.56 (1H, s, NH), 7.26 (1H, s, NH), 5.54 (1H, br s, H-24), 4.99 (1H, br s, OH), 5.14 (1H, m, H-6), 4.10 (1H, m, H-4); HRESIMS m/z 438.2619 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C25H37NO4Na+, 438.2615). −10° (c 0.12, MeOH); CD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε) 184 (−3.30), 198 (4.39) nm; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 195 (3.84), 223 (1.48) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3434, 2923, 1712, 1374, 1199, 1038, 742 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; 1H NMR data (in DMSO): δH 11.04 (1H, s, OH), 5.42 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 5.22 (1H, m, H-6), 4.30 (1H, br s, H-24), 4.02 (1H, br s, OH), 3.86 (1H, m, H-4); HRESIMS m/z 438.2622 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C25H37NO4Na+, 438.2615).
−10° (c 0.12, MeOH); CD (MeOH) λmax (∆ε) 184 (−3.30), 198 (4.39) nm; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 195 (3.84), 223 (1.48) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3434, 2923, 1712, 1374, 1199, 1038, 742 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 and Table 2; 1H NMR data (in DMSO): δH 11.04 (1H, s, OH), 5.42 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, NH), 5.22 (1H, m, H-6), 4.30 (1H, br s, H-24), 4.02 (1H, br s, OH), 3.86 (1H, m, H-4); HRESIMS m/z 438.2622 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C25H37NO4Na+, 438.2615).3.4. PTP1B Inhibitory Assay
3.5. Computational Details of Calculated ECD
3.6. Preparation of MTPA Esters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, R.; Zeng, L.F.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.Y. Small molecule tools for functional interrogation of protein tyrosine phosphatases. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 731–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.S.; Liang, L.F.; Guo, Y.W. Natural products possessing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitory activity found in the last decades. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1217–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, K.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H. Hyrtiosal, a PTP1B inhibitor from the marine sponge Hyrtios erectus, shows extensive cellular effects on PI3K/AKT activation, glucose transport, and TGFbeta/Smad2 signaling. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 30, 237–323. [Google Scholar]
- Bialy, L.; Waldmann, H. Inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases: Next-generation drugs? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 3814–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Sumilat, D.A.; Kanno, S.I.; Ukai, K.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Ishikawa, M.; Mangindaan, R.E.; Namikoshi, M. A polybromodiphenyl ether from an Indonesian marine sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea and its chemical derivatives inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, an important target for diabetes treatment. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 730–735. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Guo, Y.W. A novel sesquiterpene quinone from Hainan sponge Dysidea villosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Huang, X.J.; Yang, J.S.; Yang, F.; Piao, S.J.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; Ye, W.C.; Yao, X.S.; Chen, W.S.; et al. Dysidavarones A–D, new sesquiterpene quinones from the marine sponge Dysidea avara. Org. Lett. 2011, 14, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Naitoh, K.; Sasaki, T.; Shigemori, H. Metachromins D–H, new cytotoxic sesquiterpenoids from the Okinawan marine sponge Hippospongia metachromia. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 5773–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.H. New sesquiterpene hydroquinones from a Taiwanese marine sponge, Hippospongia metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Wang, W.; Ukai, K.; Nakazawa, T.; Mochizuki, M. A sesquiterpene quinone, 5-Epi-smenospongine, promotes TNF-alpha production in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Cheng, J.F.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Metachromins A and B, novel antineoplastic sesquiterpenoids from the Okinawan sponge Hippospongia cf. metachromia. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 2855–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musman, M.; Ohtani, I.I.; Nagaoka, D.; Tanaka, J.; Higa, T. Hipposulfates A and B, new sesterterpene sulfates from an Okinawan sponge, Hippospongia cf. metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, T.H.; Yang, S.H.; Shin, H.J.; Shin, J.; Oh, K.B. Sesterterpene sulfates as isocitrate lyase inhibitors from tropical sponge Hippospongia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2483–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Lu, H.Y.; Yang, F.; Jiao, W.H.; Yi, Y.H.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Hippolides A–H, acyclic manoalide derivatives from the marine sponge Hippospongia lachne. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort, S.J.; Atkin, D.; Hobbs, L.; Capon, R.J. Hippospongins A–F: New furanoterpenes from a Southern Australian marine sponge Hippospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.S.; Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Collins, K.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Novel sesterterpenoid and norsesterterpenoid RCE-protease inhibitors isolated from the marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 4801–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.J.; Song, Y.L.; Jiao, W.H.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.F.; Chen, W.S.; Han, B.N.; Lin, H.W. Hippolachnin A, a new antifungal polyketide from the South China Sea sponge Hippospongia lachne. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3526–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berova, N.; di Bari, L.; Pescitelli, G. Application of electronic circular dichroism in configurational and conformational analysis of organic compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, M.; Imperatore, C.; D’Aniello, F.; Aiello, A. Meroterpenes from marine invertebrates: Structures, occurrence, and ecological implications. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1602–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.P.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y. Sesterterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hamann, M.T. Atkamine: A new pyrroloiminoquinone scaffold from the cold water Aleutian Islands Latrunculia sponge. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Piao, S.-J.; Jiao, W.-H.; Yang, F.; Yi, Y.-H.; Di, Y.-T.; Han, B.-N.; Lin, H.-W. New Hippolide Derivatives with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4096-4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074096
Piao S-J, Jiao W-H, Yang F, Yi Y-H, Di Y-T, Han B-N, Lin H-W. New Hippolide Derivatives with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(7):4096-4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074096
Chicago/Turabian StylePiao, Shu-Juan, Wei-Hua Jiao, Fan Yang, Yang-Hua Yi, Ying-Tong Di, Bing-Nan Han, and Hou-Wen Lin. 2014. "New Hippolide Derivatives with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne" Marine Drugs 12, no. 7: 4096-4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074096
APA StylePiao, S. -J., Jiao, W. -H., Yang, F., Yi, Y. -H., Di, Y. -T., Han, B. -N., & Lin, H. -W. (2014). New Hippolide Derivatives with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Marine Drugs, 12(7), 4096-4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074096