Cyanobacterial Metabolite Calothrixins: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Biological Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Marine Natural Products
1.2. Cyanobacteria

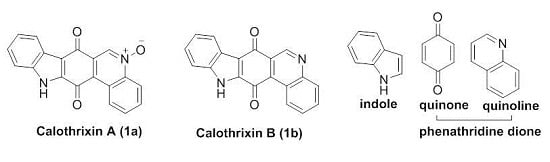
1.3. Calothrixins

2. Synthesis of Calothrixins
| Research Group | Year | Ring Closure | Key Step | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velu et al. | 2014 | B | Mn(OAc)3 mediated oxidative free radical reaction | [36] |
| Ishikura et al. | 2011 & 2012 | C | Palladium catalyzed tandem cyclization/cross-coupling | [37,38] |
| Dethe et al. | 2014 | C | LTA mediated rearrangement of o-hydroxy aryl hydrazone | [39] |
| Nagarajan et al. | 2014 | C | Friedel-Crafts hydroxyalkylation and directed o-lithiation | [40] |
| Mal et al. | 2014 | C | The anionic annulation of MOM-protected furoindolone | [41] |
| Kusurkar et al. | 2012 | D | Two one pot reaction sequences: a nucleophilic substitution and reduction | [42] |
| Nagarajan et al. | 2013 | D | Pd catalyzed intramolecular cross-coupling reaction via C–H activation | [43] |
| Mohanakrishnan et al. | 2014 | D | Electrocyclization of 2-nitroarylvinyl-3-phenylsulfonylvinylindole | [44] |
| Kumar et al. | 2014 | D | Pd mediated intramolecular C-X/C-H cross coupling reactions | [45] |
| Hibino et al. | 2012 | D | Allene mediated electrocyclic reaction of the 6π-electron system | [46] |
| Mohanakrishnan et al. | 2013 | C & D | FeCl3 mediated domino reaction of enamines | [47] |
2.1. Formation of Indole (Rings A and B) as the Last Step in the Construction of the Indolo[3,2-j]Phenanthridine Framework
Velu’s Synthesis

2.2. Ring C Closure as the Last Step in the Construction of the Indolo[3,2-j]Phenanthridine Framework
2.2.1. Ishikura’s Synthesis

2.2.2. Dethe’s Synthesis

2.2.3. Nagarajan’s Synthesis

2.2.4. Mal’s Synthesis

2.3. Ring D Closure as the Last Step in the Construction of the Indolo[3,2-j]Phenanthridine Framework
2.3.1. Kusurkar’s Synthesis

2.3.2. Nagarajan’s Synthesis

2.3.3. Mohanakrishnan’s Synthesis

2.3.4. Kumar’s Synthesis


2.3.5. Hibino’s Synthesis

2.4. Simultaneous Closure of Rings C and D
Mohanakrishnan’s Synthesis

3. Bioactivities of Calothrixins
3.1. Antiparasitic Activity
| Compound | IC50 against FCR-3 Strain (nM) | Compound | IC50 against FCR-3 Strain (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 185 |  | 120 |
 | 380 |  | 490 |
 | 380 |  | 220 |
 | 320 |  | 640 |
 | 250 |  | 330 |
 | 180 |
3.2. Anticancer Activity
| Compound | Structure | IC50 for Cytotoxicity | IC50 for Apoptosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calothrixin A |  | 1.6 µM | 0.6 µM |
| Menadione |  | 4.7 µM | 12 µM |
| Compound | Structure | EC50 (µM) HeLa Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Calothrixin A |  | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Calothrixin B |  | 0.24 ± 0.04 |
| N-MOM-calothrixin B |  | 0.42 ± 0.02 |
| Ellipticine quinone |  | 0.15 ± 0.09 |
| N-MOM-ellipticine quinone |  | 0.37 ± 0.08 |
| Benzocarbazoledione |  | 0.43 ± 0.01 |
| N-MOM-Benzocarbazoledione |  | 1.6 ± 1.0 |
| Menadione |  | 3.7 ± 0.3 |
| Uncyclized precursor to benzocarbazoledione |  | >50 |
| Uncyclized precursor to N-MOM-benzocarbazoledione |  | >50 |
| Compound | Structure | EC50 (µM) HeLa Cells | EC50 (µM) P388 Cells | EC50 (µM) CV-1 Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calothrixin B |  | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 9 ± 2 | 2.4 ± 0.7 |
| Indolophenanthrene-7,13-dione |  | 1.5 ± 0.3 | >50 | >50 |
| Benzocarbzoledione |  | 1.8 ± 0.1 | >50 | >50 |
| Carbazole-1,4-dione |  | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| Murrayaquinone |  | 13 ± 1 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 10 ± 2 |
| 2-Methylcarbazoledione |  | 7 ± 1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.4 |
| Isoquinoline-5,8-dione |  | 12 ± 1 | 9 ± 2 | >50 |
| Compound | Structure | IC50 (µM) in CEM Leukemia Cells | % Topo I DNA Cleavage at 5 µM | % NaCl Induced Reversibility at 5 µM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camptothecin |  | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 100 | 100 |
| Calothrixin A |  | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 18 | 17 |
| Calothrixin B |  | 1.05 ± 0.30 | 13 | 16 |
| N-methycalothrixin B |  | 5.13 ± 0.72 | 11 | 13 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AcCl | Acetyl chloride |
| Ac2O | Acetic anhydride |
| AcOEt | Ethyl acetate |
| AcOH | Acetic acid |
| AIBN | Azobisisobutyronitrile |
| AlCl3 | Aluminum chloride |
| BEt3 | Triethylborane or triethylboron |
| BF3.OEt2 | Boron trifluoride diethyl etherate |
| CAN | Ceric ammonium nitrate |
| CCl4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| CH2Cl2 | Dichloromethane |
| CH3CN | Acetonitrile |
| COSY | Correlation spectroscopy |
| c-PC | c-Phycocyanin |
| CSA | Camphorsulfonic acid |
| CuI | Copper(I) iodide |
| (CuOTf)2.toluene | Trifluoromethanesulfonate toluene complex |
| DMAP | 4-Dimethylaminopyridine |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| DMP | Dess-Martin periodinane |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DoM | Directed o-metalation |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| Et2NH | Diethylamine |
| Et3SiH | Triethylsilane |
| FeCl3 | Iron(III) chloride |
| HCO2H | Formic acid |
| HDACs | Histone deacetylases |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| K2CO3 | Potassium carbonate |
| LDA | Lithium diisopropylamide |
| LiTMP | Lithium tetramethylpiperidide |
| LTA | Lead tetracetate |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| Mn(OAc)3 | Manganese triacetate |
| MOM | Methoxymethyl protecting group |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NaCNBH3 | Sodium cyanoborohydride |
| NaH | Sodium hydride |
| NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| NaOMe | Sodium methoxide |
| NBS | N-bromosuccinimide |
| n-BuLi | n-Butyllithium |
| NH2NH2.H2O | Hydrazine hydrate solution |
| Pb(OAc)4 | Lead(IV) acetate |
| PCC | Pyridinium chlorochromate |
| Pd/C | Palladium on carbon |
| PdCl2(PPh3)2 | Bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride |
| Pd2(dba)3 | Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0) |
| Pd(dppf)Cl2 | [1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene] dichloropalladium(II) |
| Pd(OAc)2 | Palladium acetate |
| Pd(TFA)2 | palladium(II) trifluoroacetate |
| PhCN | Benzonitrile |
| (PhSe)2 | Diphenyl diselenide |
| PMB | p-Methoxybenzyl |
| PMBCl | p-Methoxybenzyl chloride |
| P(o-tol)3 | Tri(o-tolyl)phosphine |
| POCl3 | Phosphoryl chloride |
| PPh3 | Triphenylphosphine |
| p-TSA | p-Toluenesulfonic acid |
| PTT | Polytrimethylene terephthalate |
| rac-BINAP | Racemic 2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TBAD | Bis(tetrabutylammonium) dichromate |
| TBHP | Tert-butyl hydroperoxide |
| Tf2O | Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| THP | Tetrahydropyran |
| TMG | 1,1,3,3-Tetramethylguanidine |
| TMP | 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine |
| TMSI | Trimethylsilyl iodide |
References
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reen, F.J.; Gutierrez-Barranquero, J.A.; Dobson, A.D.; Adams, C.; O’Gara, F. Emerging concepts promising new horizons for marine biodiscovery and synthetic biology. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2924–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawadogo, W.R.; Boly, R.; Cerella, C.; Teiten, M.H.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. A survey of marine natural compounds and their derivatives with anti-cancer activity reported in 2012. Molecules 2015, 20, 7097–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.K.; Alkon, D.L. Bryostatin-1: Pharmacology and therapeutic potential as a CNS drug. CNS Drug Rev. 2006, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Kang, K.H.; Sivakumar, K.; Li-Chan, E.C.; Oh, H.M.; Kim, S.K. Marine actinobacteria: An important source of bioactive natural products. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardellina, J.H., II; Moore, B.S. Richard E. Moore (1933–2007). J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchett, G.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: From impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects. Toxins 2013, 5, 1896–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, C.; Ramos, V.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V. Methods to detect cyanobacteria and their toxins in the environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8073–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabdulkhakov, A.G.; Dontsova, M.V. Structural studies on photosystem II of cyanobacteria. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehringer, M.M.; Wannicke, N. Climate change and regulation of hepatotoxin production in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobotka, R. Making proteins green; biosynthesis of chlorophyll-binding proteins in cyanobacteria. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 119, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, R.B.; Suseela, M.R. Cyanobacteria: Potential candidates for drug discovery. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowska, N.; Szelag-Wasielewska, E. Toxic picoplanktonic cyanobacteria—Review. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1497–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijffels, R.H.; Kruse, O.; Hellingwerf, K.J. Potential of industrial biotechnology with cyanobacteria and eukaryotic microalgae. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Suzuki, J.; Onda, Y.; Fujino, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Doi, T. Total synthesis and conformational analysis of apratoxin C. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 8000–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Cowley, E.S.; Sikorska, J.; Shaala, L.A.; Ishmael, J.E.; Youssef, D.T.; McPhail, K.L. Apratoxin H and apratoxin A sulfoxide from the red sea cyanobacterium moorea producens. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.; Luesch, H. Systematic chemical mutagenesis identifies a potent novel apratoxin A/E hybrid with improved in vivo antitumor activity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T. Synthesis of the biologically active natural product cyclodepsipeptides apratoxin A and its analogues. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T.; Numajiri, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. Solid-phase total synthesis of (−)-apratoxin A and its analogues and their biological evaluation. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, C.; Sammet, B.; Sewald, N. Recent approaches for the synthesis of modified cryptophycins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Jimenez, G.M.; Burgos-Hernandez, A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with anticancer potential: Sources from marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 963–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajula, P.K.; Asthana, J.; Panda, D.; Chakraborty, T.K. A synthetic dolastatin 10 analogue suppresses microtubule dynamics, inhibits cell proliferation, and induces apoptotic cell death. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Hogan, F.; Toms, S. Antineoplastic agents. 592. Highly effective cancer cell growth inhibitory structural modifications of dolastatin 10. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maderna, A.; Doroski, M.; Subramanyam, C.; Porte, A.; Leverett, C.A.; Vetelino, B.C.; Chen, Z.; Risley, H.; Parris, K.; Pandit, J.; et al. Discovery of cytotoxic dolastatin 10 analogues with N-terminal modifications. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10527–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.A.; Hillman, D.W.; Fishkin, P.A.; Krook, J.E.; Tan, W.W.; Kuriakose, P.A.; Alberts, S.R.; Dakhil, S.R. Phase II trial of dolastatin-10 in patients with advanced breast cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2005, 23, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVita, M.D.; Evens, A.M.; Rosen, S.T.; Greenberger, P.A.; Petrich, A.M. Multiple successful desensitizations to brentuximab vedotin: A case report and literature review. J. Nat. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014, 12, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Nademanee, A.; Masszi, T.; Agura, E.; Holowiecki, J.; Abidi, M.H.; Chen, A.I.; Stiff, P.; Gianni, A.M.; Carella, A.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression (AETHERA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, H.; Salvador, L.A.; Serrano, P.E.; Kwan, J.C.; Zeller, S.L.; Chen, Q.Y.; Ryu, S.; Liu, Y.; Byeon, S.; et al. Evaluation of class I HDAC isoform selectivity of largazole analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3728–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Ren, X.; Jin, J.; Su, S.B. Largazole, an inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases, attenuates inflammatory corneal neovascularization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Riegsecker, S.; Beamer, M.; Rahman, A.; Bellini, J.V.; Bhansali, P.; Tillekeratne, L.M. Largazole, a class I histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 270, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhansali, P.; Hanigan, C.L.; Casero, R.A.; Tillekeratne, L.M. Largazole and analogues with modified metal-binding motifs targeting histone deacetylases: Synthesis and biological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7453–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhansali, P.; Hanigan, C.L.; Perera, L.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; Tillekeratne, L.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of largazole analogues with modified surface recognition cap groups. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, E.; Zhang, K. Comprehensive analysis for histone acetylation of human colon cancer cells treated with a novel HDAC inhibitor. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickards, R.W.; Rothschild, J.M.; Willis, A.C.; de Chazal, N.M.; Kirk, J.; Kirk, K.; Saliba, K.J.; Smith, G.D. Calothrixins A and B, novel pentacyclic metabolites from calothrix cyanobacteria with potent activity against malaria parasites and human cancer cells. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13513–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choshi, T.; Hibino, S. Progress towards the total synthesis of the bioactive calothrixins A and B. Heterocycles 2009, 77, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Nguyen, T.; Pomilio, I.; Vitale, M.C.; Velu, S.E. Total synthesis of calothrixins A and B via oxidative radical reaction of cyclohexenone with aminophenanthridinedione. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 5928–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Ikeda, T.; Choshi, T.; Hibino, S.; Hatae, N.; Toyata, E.; Yanada, R.; Ishikura, M. Total synthesis of calothrixins A and B by palladium-catalyzed tandem cyclization/cross-coupling reaction of indolylborate. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5018–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Ikeda, T.; Yanada, R.; Ishikura, M. Concise total synthesis of calothrixins A and B. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3356–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethe, D.H.; Murhade, G.M. Diversity-oriented synthesis of calothrixins and ellipticines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 6953–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, N.; Nagarajan, R. Total synthesis of ellipticine quinones, olivacine, and calothrixin B. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mal, D.; Roy, J.; Biradha, K. Regiodivergent and short total synthesis of calothrixins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8196–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, S.M.; Gawade, R.L.; Puranik, V.G.; Kusurkar, R.S. An efficient total synthesis of calothrixin B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 2894–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, N.; Nagarajan, R. Total synthesis of calothrixin A and B via C–H activation. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 2802–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, V.; Muthu Ramalingam, B.; Mohanakrishnan, A.K. Total synthesis of calothrixin B and its analogs. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyaperumal, S.A.; Banerjee, S.; Syam Kumar, U.K. Palladium mediated intramolecular multiple C-X/C-H cross coupling and C–H activation: Synthesis of carbazole alkaloids calothrixin B and murrayaquinone A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 6105–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Choshi, T.; Hourai, M.; Zamami, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Abe, T.; Ishikura, M.; Hatae, N.; Iwamura, T.; Tohyama, S.; et al. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of calothrixins A and B, and their N-alkyl derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4762–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, B.M.; Saravanan, V.; Mohanakrishnan, A.K. Synthesis of calothrixins and its analogs using FeCl3-mediated domino reaction protocol. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3726–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.-P.; Tsai, A.I. Oxidative free radical reactions between 2-amino-1,4-benzoquinones and carbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 11911–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-P.; Wu, Y.-L. A novel oxidative free radical reaction between 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone and β-enamino carbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chuang, C.-P. Cerium salts in the oxidative free radical reactions between 2-amino-1,4-naphthoquinones and β-dicarbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7625–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, D.; Senapati, B.K.; Pahari, P. A new synthetic route to indoloquinones: Formal synthesis of ellipticine. Synlett 2005, 6, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, N.T.; Rickards, R.W.; Rothschild, J.M.; Smith, G.D. Allelopathic actions of the alkaloid 12-epi-hapalindole e isonitrile and calothrixin a from cyanobacteria of the genera fischerella and calothrix. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, N.T.; Stewart, P.R.; Smith, G.D. Inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase by the cyanobacterial metabolites 12-epi-hapalindole E isonitrile and calothrixin A. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 196, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.X.; Smith, G.D.; Waring, P. Human cancer cell (Jurkat) killing by the cyanobacterial metabolite calothrixin A. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, N.; Klonowski-Stumpe, H.; Han, B.; Haussinger, D.; Niederau, C. Menadione induces both necrosis and apoptosis in rat pancreatic acinar AR4-2J cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.L.; Trush, M.A.; Penning, T.M.; Dryhurst, G.; Monks, T.J. Role of quinones in toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, P.H.; Chai, C.L.; Heath, G.A.; Mahon, P.J.; Smith, G.D.; Waring, P.; Wilkes, B.A. Synthesis, electrochemistry, and bioactivity of the cyanobacterial calothrixins and related quinones. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4958–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, P.H.; Chai, C.L.; Le Guen, M.; Smith, G.D.; Waring, P. Structure-activity delineation of quinones related to the biologically active calothrixin B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Q.A.; Lu, J.; Hecht, S.M. Calothrixins, a new class of human DNA topoisomerase I poisons. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.K.; Liu, L.F. Tumor cell death induced by topoisomerase-targeting drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Nijampatnam, B.; Dutta, S.; Velu, S.E. Cyanobacterial Metabolite Calothrixins: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010017
Xu S, Nijampatnam B, Dutta S, Velu SE. Cyanobacterial Metabolite Calothrixins: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Su, Bhavitavya Nijampatnam, Shilpa Dutta, and Sadanandan E. Velu. 2016. "Cyanobacterial Metabolite Calothrixins: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Biological Evaluation" Marine Drugs 14, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010017
APA StyleXu, S., Nijampatnam, B., Dutta, S., & Velu, S. E. (2016). Cyanobacterial Metabolite Calothrixins: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Marine Drugs, 14(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010017