Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering
Abstract
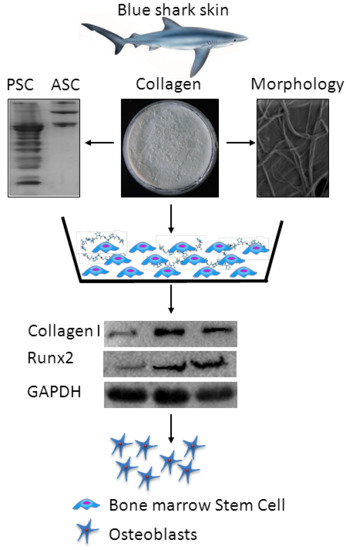
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hydroxyproline and Collagen Content of Raw Materials
2.2. Amino Acid Content
2.3. Molecular Weight Analysis
2.4. Viscosity and Solubility
2.5. UV Absorbance
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7. Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
2.8. Thermal Properties
2.9. Morphalogical Characteristics
2.10. Effect of Collagen on Bone Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Extraction, Purification, and Total Collagen Content of Fish Collagen
3.2. Molecular Mass by SDS-PAGE and Amino Acid Profile
3.3. Viscosity and Solubility
3.4. Absorbance UV Maxima and FTIR Spectra
3.5. RP-HPLC
3.6. Thermal Stability
3.7. Morphological Analysis
3.8. Effect of Collagen on Osteoblastogenesis
3.8.1. Cell Culture
3.8.2. Osteogenic Differentiation
3.8.3. Proliferation Assay
3.8.4. mRNA Expression
3.8.5. Immunocytochemistry
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeevithan, E.; Bao, B.; Bu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, W. Type II collagen and gelatin from silvertip shark (Carcharhinus albimarginatus) cartilage: Isolation, purification, physicochemical and antioxidant properties. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3852–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Isolation and characterisation of acid and pepsin-solubilised collagens from the skin of Brownstripe red snapper (Lutjanus vitta). Food Chem. 2005, 93, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; You, C.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Feng, Z.; Sun, H.; Gao, C.; Han, C. The roles of knitted mesh-reinforced collagen-chitosan hybrid scaffold in the one-step repair of full-thickness skin defects in rats. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7822–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, N.; Hatta, K.; Nakanishi, T. 3D-culture system for heart regeneration and cardiac medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 895967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, M. Novel cell-scaffold interactions encountered in tissue engineering: Contractile behavior of musculoskeletal connective tissue cells. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, H.; Yunoki, S.; Kondo, E.; Ikoma, T.; Tanaka, J.; Yasuda, K. In vivo biological responses and bioresorption of tilapia scale collagen as a potential biomaterial. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.; Yeon, K.S.; Chun, T.; Byun, H.J.; Lee, Y.M. Collagen scaffolds derived from a marine source and their biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, T.; Ueno, M.; Goto, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Doi, M.; Akiyama, K.; Yamauchi, S. Immunostimulation effect of jellyfish collagen. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevithan, E.; Jingyi, Z.; Bao, B.; Shujun, W.; JeyaShakila, R.; Wu, W.H. Biocompatibility assessment of type-II collagen and its polypeptide for tissue engineering: Effect of collagen’s molecular weight and glycoprotein content on tumor necrosis factor (Fas/Apo-1) receptor activation in human acute T-lymphocyteleukemia cell line. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14236–14246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Jeevithan, E.; Bao, B.; Wang, S.; Gao, K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.H. Structural characterization, in-vivo acute systemic toxicity assessment and in-vitro intestinal absorption properties of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin acid and pepsin solublilized type I collagen. Process. Biochem. 2016, 51, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.P.; Dunn, M.G.; Zawadsky, J.P.; Tria, A.J.; Silver, F.H. Regeneration of Achilles tendon with a collagen tendon prosthesis: Results of a one year implantation study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1991, 73, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.G.; Tria, A.J.; Bechler, J.R.; Ochner, R.S.; Zawadsky, J.P.; Kato, Y.P.; Silver, F.H. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using a composite collagenous prosthesis. A biomechanical and histologic study in rabbits. Am. J. Sports Med. 1992, 20, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevithan, E.; Sanchez, C.; De Val, J.E.M.S.; Henrotin, Y.; Wang, S.; Motaung, K.S.C.M.; Guo, R.; Wang, C.; Robinson, J.; Regenstein, J.M.; et al. Cross-talk between primary osteocytes and bone marrow macrophages for osteoclastogenesis upon collagen treatment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5318. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Diogo, G.S.; Senra, E.L.; Pirraco, R.P.; Canadas, R.F.; Fernandes, E.M.; Serra, J.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Sotelo, C.G.; Marques, A.P.; González, P.; et al. Marine collagen/apatite composite scaffolds envisaging hard tissue applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Characterisation of acid-soluble collagen from skin and bone of bigeye snapper (Pricanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilages of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum) and blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and characterization of thermostable collagen from the marine eel-fish (Evenchelys macrura). Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.; Osatomi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Osako, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Hara, K. Biochemical properties of acid-soluble collagens extracted from the skins of underutilised fishes. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Moody, M.W.; Portier, R.J.; Bell, J.; Schexnayder, M.A.; Losso, J.N. Biochemical properties of black drum and sheepshead seabream skin collagen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8088–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Q.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, H. Characterization of collagen from the skin of Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.A.; O’Brien, W.D., Jr. Modified assay for determination of hydroxyproline in a tissue hydrolyzate. Clin. Chim. Acta 1980, 104, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, H. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilage of Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Process. Biochem. 2014, 49, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Characterisation of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.O.; Lin, C.W.; Sheu, M.T. Characterization of collagen isolation and application of collagen gel as a drug carrier. J. Control. Release 1997, 44, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W. Proteins. In Mechanism and Theory in Food Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.T.; Li, G.Y. Isolation and characterization of collagens from the skin of largefinlongbarbel catfish (Mystus macropterus). Food Chem. 2009, 115, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, K.M.; Pollot, B.E.; Clem, W.C.; Phipps, M.C.; Sawyer, A.A.; Culpepper, B.K.; Bellis, S.L. The effect of collagen I mimetic peptides on mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and differentiation, and on bone formation at hydroxyapatite surfaces. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1898–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Harvey, E.J.; Chua, M.; Chen, B.P.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, A.; Wang, H.; Henderson, J.E. MSC-seeded dense collagen scaffolds with a bolus dose of VEGF promote healing of large bone defects. Eur. Cells Mater. 2013, 26, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.H.; Lai, W.F.; Chang, S.F.; Wong, C.C.; Fan, C.Y.; Fang, C.L.; Tsai, Y.H. The effect of type II collagen on MSC osteogenic differentiation and bone defect repair. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2680–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuckwell, D.S.; Ayad, S.; Grant, M.E.; Takigawa, M.; Humphries, M.J. Conformation dependence of integrin-type II collagen binding Inability of collagen peptides to support alpha 2 beta 1 binding, and mediation of adhesion to denatured collagen by a novel alpha 5 beta 1-fibronectin bridge. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergman, I.; Loxley, R. Two improved and simplified methods for the spectrophotometric determination of hydroxyproline. Anal. Chem. 1963, 35, 1961–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yongshi, B.; Jeevithan, E.; Jingyi, Z.; Bin, B.; Ruihua, G.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Jeya Shakila, R.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Joe, M.R.; Wenhui, W. Immunological effects of collagen and collagen peptide from blue shark cartilage on 6T-CEM cells. Process. Biochem. 2017, 57, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Rochdi, A.; Foucat, L.; Renou, J.P. NMR and DSC studies during thermal denaturation of collagen. Food Chem. 2000, 69, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Amino Acids | ASC | PSC |
|---|---|---|
| Glycine | 392.44 | 387.12 |
| Alanine | 144.59 | 130.88 |
| Proline | 132.98 | 124.46 |
| Hydroxyproline | 80.45 | 98.28 |
| Glutamic acid | 69.23 | 71.50 |
| Aspartic acid | 36.73 | 40.51 |
| Arginine | 28.64 | 26.25 |
| Leucine | 24.44 | 13.83 |
| Serine | 21.75 | 26.25 |
| Lysine | 14.84 | 15.95 |
| Phenylalanine | 13.63 | 14.02 |
| Methionine | 10.17 | 12.03 |
| Threonine | 10.04 | 8.19 |
| Histidine | 5.39 | 6.65 |
| Valine | 7.61 | 8.38 |
| Isoleucine | 3.79 | 9.38 |
| S.No | Primers Name | Primers Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | 5′-TCC TGA CCA AAA ACC TCA AAG G-3′ |
| 5′-TGC TTC ATG CAG AGC CTG C-3′ | ||
| 2 | Osteocalcin | 5′-CTC ACA GAT GCC AAG CCC-3′ |
| 5′-CCA AGG TAG CGC CGG AGT CT-3′ | ||
| 3 | Collagen 1 alpha 1 (Col1a1) | 5′-GCG AAG GCA ACA GTC GCT-3′ |
| 5′-CTT GGT GGT TTT GTA TTC GAT GAC-3′ | ||
| 4 | Runx2 | 5′-CCA CCA CTC ACT ACC ACA CG-3′ |
| 5′-TCA GCG TCA ACA CCA TCA TT-3′ | ||
| 5 | Beta-actin | 5′-CTG GCA CCA CAC CTT CTA CA-3′ |
| 5′-GGT ACG ACC AGA GGC ATA CA-3′ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elango, J.; Lee, J.W.; Wang, S.; Henrotin, Y.; De Val, J.E.M.S.; M. Regenstein, J.; Lim, S.Y.; Bao, B.; Wu, W. Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100350
Elango J, Lee JW, Wang S, Henrotin Y, De Val JEMS, M. Regenstein J, Lim SY, Bao B, Wu W. Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(10):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100350
Chicago/Turabian StyleElango, Jeevithan, Jung Woo Lee, Shujun Wang, Yves Henrotin, José Eduardo Maté Sánchez De Val, Joe M. Regenstein, Sun Young Lim, Bin Bao, and Wenhui Wu. 2018. "Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering" Marine Drugs 16, no. 10: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100350
APA StyleElango, J., Lee, J. W., Wang, S., Henrotin, Y., De Val, J. E. M. S., M. Regenstein, J., Lim, S. Y., Bao, B., & Wu, W. (2018). Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering. Marine Drugs, 16(10), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100350