Fucoxanthin-Containing Cream Prevents Epidermal Hyperplasia and UVB-Induced Skin Erythema in Mice
Abstract
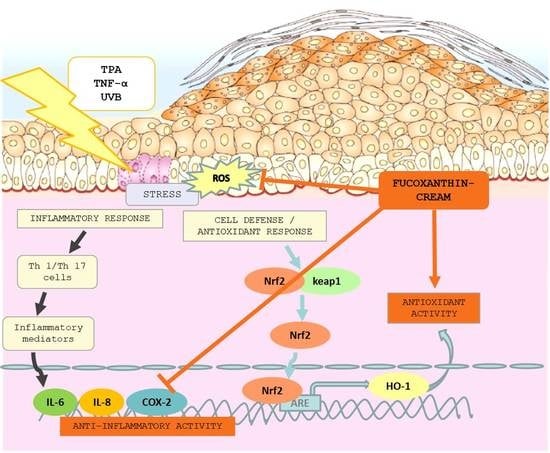
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of FX on Cell Viability
2.2. Effects of FX on TNF-α Production in LPS-Stimulated THP-1 Macrophages and IL-6 and IL-8 Production in TNF-α-Stimulated HaCaT Human Keratinocytes
2.3. In Vitro Permeation Studies of BC from Different Topical Formulations
2.4. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies of FX-Containing Cream
2.5. Topical Application of FX-Containing Cream Decreases Skin Inflammation and Hyperplasia on the Murine TPA-Induced Model
2.6. FX Protects Human HaCaT Keratinocytes against UVB-Caused Damage
2.7. Topical Application of FX-Containing Cream Protects against UVB-Induced Skin Erythema in SKH-1 Hairless Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Determination of TNF-α Production
4.4. Determination of IL-6 and IL-8 Production
4.5. Preparation of Topical Formulations
4.6. In Vitro Permeation Studies from Topical Formulations
4.7. Animals
4.8. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies from Creams
4.9. TPA-Induced Epidermal Hyperplasia Model and Treatments
4.10. MPO Activity
4.11. Histological Study
4.12. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.13. UVB Irradiation of HaCaT Keratinocytes
4.14. Analysis of Intracellular LDH Activity
4.15. Intracellular ROS Scavenging Activity
4.16. Determination of IL-6 Production in UVB-Exposed HaCaT Keratinocytes
4.17. UVB-Induced Erythema in Hairless Mice
4.18. Dermatoscope Measurements
4.19. Western Blot Assay
4.20. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | β-carotene |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DCF | 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein |
| DCF-DA | dichlorofluorescein diacetate |
| DCFH-DA | 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| Dex | dexamethasone |
| FX | fucoxanthin |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase-1 |
| IL | interleukin |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SRB | sulforhodamine B |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TPA | 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate |
| UV | ultraviolet |
References
- Fernández-García, E. Function Skin protection against UV light by dietary antioxidants. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1994–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijsten, T. Atopic dermatitis and comorbidities: Added value of comprehensive dermatoepidemiology. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.H.; Norval, M.; Byrne, S.N.; Rhodes, L.E. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation in the modulation of human diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2018, 14, 421058260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, F.; Martin, J.; Wulff, B.; Stoner, G.; Tober, K.; Oberyszyn, T.; Kusewitt, D.; Van Buskirk, A. Topical treatment with black raspberry extract reduces cutaneous UVB-induced carcinogenesis and inflammation. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthon, J.-Y.; Nachat-Kappes, R.; Bey, M.; Cadoret, J.-P.; Renimel, I.; Filaire, E. Marine algae as attractive source to skin care. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.G.; Burgess, J.G. The promise of marine molecules as cosmetic active ingredients. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, A.; Basirnejad, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Bolhassani, A. Carotenoids: Biochemistry, pharmacology and treatment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1290–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, J.; Wang, X.; Kong, R.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. Fucoxanthin: A promising medicinal and nutritional ingredient. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 723515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, N.; Gemello, E.; Gammone, M.A.; de Girolamo, M.; Ficoneri, C.; Riccioni, G. Fucoxantin: A treasure from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.J.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, I.K.; Baek, S.Y.; Kim, Y.W. Fucoxanthin, the constituent of Laminaria japonica, triggers AMPK-mediated cytoprotection and autophagy in hepatocytes under oxidative stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Yao, C.W.; Cha, J.W.; Hyun, J.W. Fucoxanthin enhances the level of reduced glutathione via the Nrf2-mediated pathway in human keratinocytes. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4214–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urikura, I.; Sugawara, T.; Hirata, T. Protective effect of fucoxanthin against UVB-induced skin photoaging in hairless mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, H.; Tanaka, J.; Shan, S.-J.; Maoka, T. Anti-pigmentary activity of fucoxanthin and its influence on skin mRNA expression of melanogenic molecules. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Tanaka, K.; Higashiguchi, N.; Okawa, H.; Yamada, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Taira, S.; Aoyama, T.; Takanishi, M. Protective and therapeutic effects of fucoxanthin against sunburn caused by UV irradiation. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 132, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwah, H.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Permeation enhancer strategies in transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Kim, J.-C. Chemical stability and skin permeation of fucoxanthin-loaded microemulsions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Kim, J.-C. In vivo anti-obesity efficacy of fucoxanthin-loaded emulsions stabilized with phospholipid. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 46, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, J.V.; Praça, F.S.G.; Bentley, M.V.L.B.; Gaspar, L.R. Trans-resveratrol and beta-carotene from sunscreens penetrate viable skin layers and reduce cutaneous penetration of UV-filters. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arasa, J.; Martos, P.; Terencio, M.C.; Valcuende-Cavero, F.; Montesinos, M.C. Topical application of the adenosine A2A receptor agonist CGS-21680 prevents phorbol-induced epidermal hyperplasia and inflammation in mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Luna, A.; Talero, E.; Terencio, M.C.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M.; de los Reyes, C.; Motilva, V.; Ávila-Román, J. Topical Application of Glycolipids from isochrysis galbana prevents epidermal hyperplasia in mice. Mar. Drugs 2017, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatoniene, J.; Masteikova, R.; Davalgiene, J.; Peciura, R.; Gauryliene, R.; Bernatoniene, R.; Majiene, D.; Lazauskas, R.; Civinskiene, G.; Velziene, S.; et al. Topical application of calendula officinalis (L.): Formulation and evaluation of hydrophilic cream with antioxidant activity. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 868–877. [Google Scholar]
- Sirerol, J.A.; Feddi, F.; Mena, S.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Sirera, P.; Aupí, M.; Pérez, S.; Asensi, M.; Ortega, A.; Estrela, J.M. Topical treatment with pterostilbene, a natural phytoalexin, effectively protects hairless mice against UVB radiation-induced skin damage and carcinogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, W.; Sies, H. β-Carotene and other carotenoids in protection from sunlight 1–3. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-N.; Heo, S.-J.; Yoon, W.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Ahn, G.; Yi, T.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J. Fucoxanthin inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Vale, D.L.; Steffen, V.S.; Vicentini, F.T.M.C.; Vignoli, J.A.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A.; Casagrande, R. Trans-chalcone added in topical formulation inhibits skin inflammation and oxidative stress in a model of ultraviolet B radiation skin damage in hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 171, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Chai, J.-K.; Hu, Q.; Yu, Y.-H.; Ma, L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Li, B.-L.; Zhang, D.-H. Transdermal permeation of drugs with differing lipophilicity: Effect of penetration enhancer camphor. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 507, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahamongkol, H.; Bellantone, R.A.; Stagni, G.; Plakogiannis, F.M. Permeation study of five formulations of alpha-tocopherol acetate through human cadaver skin. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 56, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Goindi, S.; Mehta, S.D. Preparation and evaluation of dermal delivery system of griseofulvin containing vitamin E-TPGS as penetration enhancer. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 0–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taofiq, O.; González-Paramás, A.; Barreiro, M.; Ferreira, I. Hydroxycinnamic acids and their derivatives: cosmeceutical significance, challenges and future perspectives, a review. Molecules 2017, 22, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Funayama, K.; Miyashita, K. Effect of medium-chain triacylglycerols on anti-obesity effect of fucoxanthin. J. Oleo Sci. 2007, 56, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laihia, J.K.; Taimen, P.; Kujari, H.; Leino, L. Topical cis-urocanic acid attenuates oedema and erythema in acute and subacute skin inflammation in the mouse. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, G.K.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2012, 7, 385–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikai, K. Psoriasis and the arachidonic acid cascade. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1999, 21, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, R.M.; Montesinos, M.C.; Navalón, P.; Payá, M.; Terencio, M.C. NF-κB and STAT3 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in psoriasis: In vitro and in vivo effects of BTH. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Kwon, S.H.; Chun, Y.S.; Gu, M.Y.; Yang, H.O. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of fucoxanthin via inhibition of Akt/NF-κB and MAPKs/AP-1 pathways and activation of PKA/CREB pathway in lipopolysaccharide-activated BV-2 Microglial. Cells Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.J.; Xie, Z.P.; Lu, Z.W.; Tan, Z.B.; Bi, Y.M.; Xie, L.P.; Wu, Y.T.; Zhang, W.T.; Liu-Kot, K.; Liu, B.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and immune response regulation of Si-Ni-San in 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin dysfunction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 222, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.P.; Hou, Y.H. First evidence for the anti-inflammatory activity of fucoxanthin in high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice and the antioxidant functions in PC12 cells. Inflammation 2014, 37, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar, T.; Leshem, Y.A.; Hanifin, J.M.; Nedorost, S.T.; Lio, P.A.; Paller, A.S.; Block, J.; Simpson, E.L. (the National Eczema Association Task Force) A systematic review of topical corticosteroid withdrawal (“steroid addiction”) in patients with atopic dermatitis and other dermatoses. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saewan, N.; Jimtaisong, A. Natural products as photoprotection. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, P.; Szabó, É.; Hegedus, C.; Haskó, G.; Gergely, P.; Bai, P.; Virág, L. 3-Aminobenzamide protects primary human keratinocytes from UV-induced cell death by a poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation independent mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leerach, N.; Yakaew, S.; Phimnuan, P.; Soimee, W.; Nakyai, W.; Luangbudnark, W.; Viyoch, J. Effect of Thai banana (Musa AA group) in reducing accumulation of oxidation end products in UVB-irradiated mouse skin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 168, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.-J.; Jeon, Y.-J. Protective effect of fucoxanthin isolated from Sargassum siliquastrum on UV-B induced cell damage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2009, 95, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Piao, M.J.; Keum, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Hyun, J.W. Fucoxanthin protects cultured human keratinocytes against oxidative stress by blocking free radicals and inhibiting apoptosis. Biomol. Ther. 2013, 21, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanekura, T.; Higashi, Y.; Kanzaki, T. Inhibitory effects of 9-cis-retinoic acid and pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate on cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression and cell growth in human skin squamous carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2000, 161, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, P.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Váradi, J.; Fenyvesi, F.; Róka, E.; Juhász, B.; Varga, B.; Bombicz, M.; Priksz, D.; Bácskay, I.; et al. Efficacy of pre- and post-treatment by topical formulations containing dissolved and suspended silybum marianum against UVB-induced oxidative stress in guinea pig and on HaCaT keratinocytes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Li, L. Skin-derived precursors against UVB-induced apoptosis via Bcl-2 and Nrf2 upregulation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6894743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M.; Uchi, H.; Mitoma, C.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Chiba, T.; Ito, T.; Nakahara, T.; Tsuji, G. Antioxidants for healthy skin: The emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptors and nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2. Nutrients 2017, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, I.; Cao, M.; Su, Z.-Y.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y.; Fang, M.; Kong, A.-N. Fucoxanthin elicits epigenetic modifications, Nrf2 activation and blocking transformation in mouse skin JB6 P+ cells. AAPS J. 2018, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeetha, R.K.; Bhaskar, N.; Baskaran, V. Comparative effects of beta-carotene and fucoxanthin on retinol deficiency induced oxidative stress in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 331, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De los Reyes, C.; Ortega, M.J.; Rodríguez-Luna, A.; Talero, E.; Motilva, V.; Zubía, E. Molecular characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of galactosylglycerides and galactosylceramides from the microalga isochrysis galbana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Celesti, L.; Murratzu, C.; Corsi, S.; Furlanetto, S.; Corti, P. In vitro studies of simulated percutaneous absorption: influence of artificial membrane impregnation agent. Acta Technol. Leg. Med. 1993, 4, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Maestrelli, F.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M.; Mura, P. Preparation and characterisation of liposomes encapsulating ketoprofen-cyclodextrin complexes for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirri, M.; Maestrelli, F.; Mennini, N.; Mura, P. Combined use of bile acids and aminoacids to improve permeation properties of acyclovir. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pinto, J.M.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M. Effect of cholesterol and ethanol on dermal delivery from DPPC liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.D.S. Increased cutaneous wound healing effect of biodegradable liposomes containing madecassoside: preparation optimization, in vitro dermal permeation, and in vivo bioevaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grisham, M.B.; Benoit, J.N.; Granger, D.N. Assessment of leukocyte involvement during ischemia and reperfusion of intestine. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talero, E.; Alvarez de Sotomayor, M.; Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Motilva, V. Vascular contribution of adrenomedullin to microcirculatory improvement in experimental colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Fang, J.-Y.; Yang, C.; Chan, C.-M.; Wu, N.-L.; Kang, S.-W.; Hung, C.-F. Protective effects of myricetin against ultraviolet-B-induced damage in human keratinocytes. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhulst, C.; Coiffard, C.; Coiffard, L.J.M.; Rivalland, P.; De Roeck-Holtzhauer, Y. In vitro correlation between two colorimetric assays and the pyruvic acid consumption by fibroblasts cultured to determine the sodium laurylsulfate cytotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1998, 39, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Joseph, J.A. Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.J.; Piao, M.J.; Zhang, R.; Choi, Y.H.; Chae, S.; Hyun, J.W. Photo-protection by 3-bromo-4, 5-dihydroxybenzaldehyde against ultraviolet B-induced oxidative stress in human keratinocytes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 83, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta-Ono, Y.; Ueno, H.; Ueda, N.; Kato, K.; Yoshioka, T. Investigation into the dosage of dietary sphingomyelin concentrate in relation to the improvement of epidermal function in hairless mice. Anim. Sci. J. 2012, 83, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimori, Y.; Edwards, C.; Pearse, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Kawai, M.; Marks, R. Degenerative alterations of dermal collagen fiber bundles in photodamaged human skin and UVB-irradiated hairless mouse skin: Possible effect on decreasing skin mechanical properties and appearance of wrinkles. Soc. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Hong, C.T.; Chiu, W.T.; Fang, J.Y. In vitro and in vivo evaluations of topically applied capsaicin and nonivamide from hydrogels. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 224, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talero, E.; Bolivar, S.; Ávila-Román, J.; Alcaide, A.; Fiorucci, S.; Motilva, V. Inhibition of chronic ulcerative colitis-associated adenocarcinoma development in mice by VSL#3. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]








| Formulation | % Permeation (180 min) | Flux (Jss) (μg/cm2·min) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cream | 68.38 | 0.1159 | 0.9795 |
| Ointment | 47.31 | 0.0548 | 0.9704 |
| Hydrogel | 25 | 0.0383 | 0.9403 |
| Control | 100 | 0.1350 | 0.9862 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Luna, A.; Ávila-Román, J.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Cózar, M.J.; Rabasco, A.M.; Motilva, V.; Talero, E. Fucoxanthin-Containing Cream Prevents Epidermal Hyperplasia and UVB-Induced Skin Erythema in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100378
Rodríguez-Luna A, Ávila-Román J, González-Rodríguez ML, Cózar MJ, Rabasco AM, Motilva V, Talero E. Fucoxanthin-Containing Cream Prevents Epidermal Hyperplasia and UVB-Induced Skin Erythema in Mice. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(10):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100378
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Luna, Azahara, Javier Ávila-Román, María Luisa González-Rodríguez, María José Cózar, Antonio M Rabasco, Virginia Motilva, and Elena Talero. 2018. "Fucoxanthin-Containing Cream Prevents Epidermal Hyperplasia and UVB-Induced Skin Erythema in Mice" Marine Drugs 16, no. 10: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100378
APA StyleRodríguez-Luna, A., Ávila-Román, J., González-Rodríguez, M. L., Cózar, M. J., Rabasco, A. M., Motilva, V., & Talero, E. (2018). Fucoxanthin-Containing Cream Prevents Epidermal Hyperplasia and UVB-Induced Skin Erythema in Mice. Marine Drugs, 16(10), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100378