Purification and Characterization of a Biofilm-Degradable Dextranase from a Marine Bacterium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
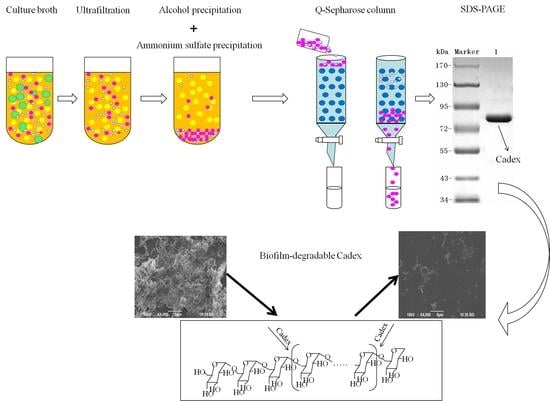
2.1. Purification of Dextranase
2.2. Characterization of Dextranase
2.2.1. Effects of pH and Temperature on Dextranase Activity
2.2.2. Enzymatic Stability
2.2.3. Effects of Metal Ions and Reagents on Dextranase Activity
2.2.4. Substrate Specificity and the Hydrolysis Products of Dextranase
2.3. Effects of Cadex on Biofilm
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Crude Dextranase Production
4.3. Purification of Dextranase
4.4. SDS-PAGE and Isoelectric Focusing
4.5. Enzyme Assay and Protein Measurement
4.6. Enzyme Properties
4.6.1. Effects of pH on Activity and Stability of Cadex
4.6.2. Effects of Temperature on Activity and Stability of Cadex
4.6.3. Effects of Metal Ions and Chemicals on Cadex Activity
4.6.4. Substrate Specificity
4.6.5. Products of Cadex Hydrolysis
4.7. Effects of Cadex on Biofilm
4.7.1. Biofilm Mass Assay
4.7.2. Effects of Cadex on Biofilm Formation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalikova, E.; Susi, P.; Korpela, T. Microbial dextran-hydrolyzing enzymes: Fundamentals and applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Wang, S.; Lu, M.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Hu, J. Optimization of four types of antimicrobial agents to increase the inhibitory ability of marine Arthrobacter oxydans KQ11 dextranase mouthwash. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Z. Purification and characterization of a novel marine Arthrobacter oxydans KQ11 dextranase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggleston, G.; Monge, A. Optimization of sugarcane factory application of commercial dextranases. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, G.; Wones, S. Application of dextranase in UK sugar beet factories. Zuckerindustrie 2011, 136, 780–783. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.-S.; Jeong, H.J.; Ko, J.-A.; Ryu, Y.B.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, W.S. Biochemical characterization of thermophilic dextranase from a thermophilic bacterium, Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushe, S.; Prakash, D.; Nawani, N.N.; Dhakephalkar, P.; Kapadnis, B. Biocatalytic potential of an alkalophilic and thermophilic dextranase as a remedial measure for dextran removal during sugar manufacture. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 115, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulas, A.K.; Cooper, J.M.; Grandison, A.S.; Rastall, R.A. Synthesis of isomaltooligosaccharides and oligodextrans in a recycle membrane bioreactor by the combined use of dextransucrase and dextranase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 88, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, E.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Gardarin, C.; Bridiau, N.; Maugard, T.; Strancar, A.; Michaud, P. Dextranase immobilization on epoxy CIM (R) disk for the production of isomaltooligosaccharides from dextran. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Ibarra-Junquera, V.; Escalante-Minakata, P.; Ornelas-Paz, J.d.J.; Osuna-Castro, J.A.; González-Potes, A. Kinetics and thermodynamic of the purified dextranase from Chaetomium erraticum. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2015, 122, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, P.H.; Hicks, M.A.; Goldman, M.; McCabe, R.M.; Fitzgerald, R.J. 3. Dispersion of dextranous bacterial plaques on human teeth with dextranase. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1971, 82, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.D.; Chung, S. Microfluidic approaches to bacterial biofilm formation. Molecules 2012, 17, 9818–9834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Alam, A.; Rani, M.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Hasnain, S.E. Biofilms: Survival and defense strategy for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ling, J.-Q.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.D. Physiological properties of Streptococcus mutans UA159 biofilm-detached cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 340, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, J.G.; Iorio, N.L.; Rodrigues, L.F.; Couri, M.L.; Farah, A.; Maia, L.C.; Antonio, A.G. Influence of a Brazilian wild green propolis on the enamel mineral loss and Streptococcus mutans’ count in dental biofilm. Arch. Oral Biol. 2016, 65, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, A.; Grobler, S.R.; Moola, M.H. The pH of various tooth-whitening products on the South African market. SADJ 2011, 66, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papaleo, E.; Tiberti, M.; Invernizzi, G.; Pasi, M.; Ranzani, V. Molecular determinants of enzyme cold adaptation: Comparative structural and computational studies of cold- and warm-adapted enzymes. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2011, 12, 657–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, R.; Giordano, D.; Riccio, A.; Prisco, G.D.; Verde, C. Cold-adapted bacteria and the globin case study in the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Mar Genom. 2010, 3, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Ni, X.; Chi, Z.; Ma, L.; Gao, L. Purification and characterization of an alkaline protease from the marine yeast Aureobasidium pullulans for bioactive peptide production from different sources. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Lu, M.; Fang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S. Screening, production, and characterization of dextranase from Catenovulum sp. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, J.; Tsuji, H.; Tsuru, D. Studies on mold dextranases 1. Penicillium luteum dextranase: Its production and some enzymatic properties. J. Biochem. 1971, 69, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.T.; Zhang, H.B.; Huang, L.J.; Hu, X.Q. Purification and characterization of extracellular dextranase from a novel producer, Hypocrea lixii F1002, and its use in oligodextran production. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Wu, M.; Hu, X.Q. Purification, characterization, and application of a thermostable dextranase from Talaromyces pinophilus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birol, H.; Damjanovic, D.; Setter, N. The purification and characterization of a dextranase from Lipomyces starkeyi. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 183, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wynter, C.V.A.; Chang, M.; Jersey, J.D.; Patel, B.; Inkerman, P.A.; Hamilton, S. Isolation and characterization of a thermostable dextranase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1997, 20, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleszczyńska, M.; Szczodrak, J.; Rogalski, J.; Fiedurek, J. Hydrolysis of dextran by Penicillium notatum dextranase and identification of final digestion products. Mycol. Res. 1997, 101, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.N.; Nguyen, T.B.P.; Mann, L.C. Purification and characterization of a dextranase from Sporothrix schenckii. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 170, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalikova, E.F.; Usanov, N.G. An insoluble colored substrate for dextranase assay. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2002, 38, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalikova, E.; Susi, P.; Usanov, N.; Korpela, T. Purification and properties of extracellular dextranase from a Bacillus sp. J. Chromatogr. B-Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003, 796, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, E.; Unno, T.; Ohba, M.; Okada, G. Purification and characterization of an isomaltotriose-producing endo-dextranase from a Fusarium sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.F.; Barrett, T.A.; Rd, C.R. Purification and partial characterization of the multicomponent dextranase complex of Streptococcus sobrinus and cloning of the dextranase gene. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.L.; Nam, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, N.; Kim, G.; Seo, E.S.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, D. Biochemical characterization of dextranase from Arthrobacter oxydans and its cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Zohra, R.R.; Aman, A.; Ansari, A.; Haider, M.S.; Qader, S.A. Purification, characterization and end product analysis of dextran degrading endodextranase from Bacillus licheniformis KIBGE-IB25. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, A.; Ishibashi, K.; Minato, S. The purification and characterization of the dextranase of Chaetomium gracile. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1981, 45, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, D.; Hiraoka, N.; Fukumoto, J. Studies on mold dextranases IV. Substrate specificity of Aspergillus carneus dextranase. J. Biochem. 1972, 71, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, M.; Ito, A. Studies on dextranase. III. Action patterns of dextranase from Penicillium funiculosum on substrate and inhibition on hydrolysis reaction by substrate analogues. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1974, 22, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonson, L.G.; Liberta, A.E.; Richardson, A. Characterization of an extracellular dextranase from Fusarium moniliforme. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 30, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Seo, M.Y.; Kang, H.K.; Atsuo, K.; Kim, D. Construction of a fusion enzyme of dextransucrase and dextranase: Application for one-step synthesis of isomalto-oligosaccharides. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2009, 44, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esawy, M.A.; Mansour, S.H.; Ahmed, E.F.; Hassanein, N.M.; El Enshasy, H.A. Characterization of Extracellular Dextranase from a Novel Halophilic Bacillus subtilis NRC-B233b a Mutagenic Honey Isolate under Solid State Fermentation. E-J. Chem. 2012, 9, 1494–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, K.; Deng, M.; Ram, E.; Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, L.; Ten Cate, J.M. Effect of arginine on the growth and biofilm formation of oral bacteria. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 82, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hao, J.; Sun, M. Cloning and characterization of a new cold-adapted and thermo-tolerant iota-carrageenase from marine bacterium Flavobacterium sp. YS-80-122. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespim, E.; Zanphorlin, L.M.; de Souza, F.H.M.; Diogo, J.A.; Gazolla, A.C.; Machado, C.B.; Figueiredo, F.; Sousa, A.S.; Nobrega, F.; Pellizari, V.H.; et al. A novel cold-adapted and glucose-tolerant GH1 beta-glucosidase from Exiguobacterium antarcticum B7. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Schinner, F. Properties of cold-adapted microorganisms and their potential role in biotechnology. J. Biotechnol. 1994, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, A.; Kikuchi, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yoshida, Y. The inhibitory effects of mushroom extracts on sucrose-dependent oral biofilm formation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Liu, B.L.; Zheng, X.H.; Huang, X.J.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Sun, D.Y.; Lin, B.R.; Zhou, G.X. Anandins A and B, two rare steroidal alkaloids from a marine Streptomyces anandii H41-59. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenkkeri, A.-M.H.; Pienihakkinen, K.; Hurme, S.; Alanen, P. The caries-preventive effect of xylitol/maltitol and erythritol/maltitol lozenges: Results of a double-blinded, cluster-randomized clinical trial in an area of natural fluoridation. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2012, 22, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, A.O.; Kannan, R.S.; Inglehart, M.R.; Rezende, C.T.; Sohn, W. Effect of 5% fluoride varnish application on caries among school children in rural Brazil: A randomized controlled trial. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2012, 40, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hild, E.; Brumbley, S.M.; O’Shea, M.G.; Nevalainen, H.; Bergquist, P.L. A Paenibacillus sp. dextranase mutant pool with improved thermostability and activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.N.; Cavalcante, T.T.; Araújo, A.X.; dos Santos, H.S.; Albuquerque, M.R.; Bandeira, P.N.; Da, C.R.; Cavada, B.S.; Teixeira, E.H. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm action of Casbane Diterpene from Croton nepetaefolius against oral bacteria. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 550–555. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Tong, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, W.; Kuang, R.; Wang, P.; Tian, Y.; Ni, L. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of pleurocidin against cariogenic microorganisms. Peptides 2011, 32, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Purification Step | Total Protein (mg) | Total Activity (U) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Purification (-Fold) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture broth | 80.6 | 6314.3 | 77.9 | 1 | 100 |
| 30 kDa ultrafiltration | 36.5 | 5973 | 163.5 | 2.1 | 94.6 |
| Alcohol precipitation | 20.9 | 4664.6 | 223.3 | 2.9 | 73.9 |
| Ammonium sulfate precipitation | 6.74 | 2303.9 | 341.6 | 4.4 | 36.5 |
| Ion exchange chromatography | 0.46 | 1069.5 | 2309 | 29.6 | 16.9 |
| Reagents | Relative Activity (%) (1 mM) | Relative Activity (%) (5 mM) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 100 ± 1.45 | 100 ± 0.71 |
| Ba2+ | 99.82 ± 0.51 | 97.73 ± 0.95 |
| NH4+ | 99.91 ± 1.23 | 77.8 ± 1.8 |
| Ca2+ | 97.46 ± 1.1 | 76.58 ± 2.96 |
| Mg2+ | 102.77 ± 2.27 | 104.47 ± 2.91 |
| K+ | 100.62 ± 3.69 | 91.87 ± 3.47 |
| Cu2+ | 1.97 ± 0.85 | 2.00 ± 1.11 |
| Fe3+ | 21.96 ± 1.67 | 0 |
| Zn2+ | 50.10 ± 1.92 | 2.47 |
| Li+ | 99.98 ± 0.4 | 90.53 ± 0.67 |
| Cd2+ | 41.14 ± 1.29 | 14.55 ± 1.65 |
| Ni2+ | 51.39 ± 1.35 | 21.35 ± 0.7 |
| Co2+ | 60.99 ± 2.32 | 29.00 ± 1.15 |
| Sr2+ | 103.75 ± 1.77 | 106.60 ± 1.89 |
| Reagents (w/v) | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Control | 100 ± 1.15 |
| 0.5% sodium lauryl sulfate | 7.31 ± 1.39 |
| 0.1% sodium fluoride | 93.8 ± 1.40 |
| 0.1% carboxybenzene | 102.2 ± 0.32 |
| 0.1% xylitol | 100.3 ± 0.50 |
| 5% ethanol | 105.5 ± 0.70 |
| Substrate | Main Linkages | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Dextran T20 | α-1,6 | 90.42 ± 0.25 |
| Dextran T40 | α-1,6 | 91.29 ± 0.67 |
| Dextran T70 | α-1,6 | 95.65 ± 1.55 |
| Dextran T500 | α-1,6 | 100 ± 1 |
| Soluble starch | α-1,4, α-1,6 | 4.93 ± 1.36 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | β-1,4 | 0 |
| Chitin | β-1,4 | 0 |
| Pullulan | α-1,4 | 0 |
| Time of Hydrolysis | Hydrolysis Productions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | |
| 15 min | 2.02 | 18.59 | 12.31 | 19.22 | 21.02 | 12.49 | 14.36 |
| 30 min | 1.95 | 17.75 | 12.03 | 19.13 | 21.01 | 13.1 | 15.03 |
| 1 h | 1.9 | 17.44 | 11.69 | 18.86 | 20.77 | 13.71 | 15.63 |
| 3 h | 1.94 | 16.74 | 11.25 | 18.57 | 21.05 | 14.53 | 15.92 |
| 5 h | 1.96 | 16.24 | 9.62 | 17.7 | 19.9 | 16.29 | 18.3 |
| Concentration of Penicillium Dextranase (U/mL) | Biofilm Inhibitory Rate a (%) | Concentration of Cadex (U/mL) | Biofilm Inhibitory Rate a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 27.46 ± 1.28 | 5 | 33.31 ± 0.99 |
| 10 | 39.44 ± 1.33 | 10 | 52.39 ± 1.21 |
| 15 | 50.2 ± 1.42 | 15 | 62.2 ± 0.92 |
| 20 | 63.13 ± 0.89 | 20 | 71.3 ± 0.69 |
| 25 | 73.42 ± 1.13 | 25 | 85.45 ± 0.70 |
| 30 | 82.16 ± 0.92 | 30 | 91.11 ± 0.83 |
| 40 | 89.34 ± 0.93 | 35 | 94.21 ± 1.13 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, W.; Cai, R.; Yan, W.; Lyu, M.; Fang, Y.; Wang, S. Purification and Characterization of a Biofilm-Degradable Dextranase from a Marine Bacterium. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020051
Ren W, Cai R, Yan W, Lyu M, Fang Y, Wang S. Purification and Characterization of a Biofilm-Degradable Dextranase from a Marine Bacterium. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(2):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Wei, Ruanhong Cai, Wanli Yan, Mingsheng Lyu, Yaowei Fang, and Shujun Wang. 2018. "Purification and Characterization of a Biofilm-Degradable Dextranase from a Marine Bacterium" Marine Drugs 16, no. 2: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020051
APA StyleRen, W., Cai, R., Yan, W., Lyu, M., Fang, Y., & Wang, S. (2018). Purification and Characterization of a Biofilm-Degradable Dextranase from a Marine Bacterium. Marine Drugs, 16(2), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020051