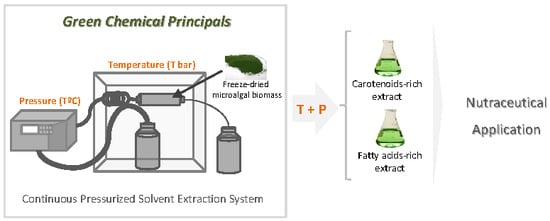
Gloeothece sp. as a Nutraceutical Source—An Improved Method of Extraction of Carotenoids and Fatty Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Biomass Amount Optimization
2.2. Solvent Flow-Rate Optimization
2.3. Temperature Optimization
2.4. Total Solvent Volume Optimization
Cycles of Solvent Recirculation
2.5. Comparison of Lab-Made CPSE System with Ultrasound Assisted Extraction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Microalga Source and Biomass Production
3.2. Continuous Pressurized Solvent Extraction
Extraction Conditions Optimization
3.3. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction
3.4. Antioxidant Scavenging Capacity Assessment of Extracts
3.4.1. ABTS+• Scavenging Capacity
3.4.2. DPPH• Scavenging Capacity
3.5. Compound Identification
3.5.1. Determination of Carotenoid Profile
3.5.2. Determination of Fatty Acid Profile
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementaly Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borowitzka, M.A. High-value products from microalgae—Their development and commercialisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.; Habib, B.; Parvin, M. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1034: A Review on Culture, Production and Use of Spirulina as Food for Humans and Feeds for Domestic Animals and Fish; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- García, J.L.; Vicente, M.; Galán, B. Microalgae, old sustainable food and fashion nutraceuticals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E.; Isambert, A. Commercial applications of microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alsenani, F.; Ahmed, F.; Schenk, P. Nutraceuticals from Microalgae. In Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods in Human Health and Disease Prevention; Bagchi, D., Preuss, H.G., Swaroop, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 673–684. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Malcata, F.X. Microalgae as sources of carotenoids. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro, H.M.; Guedes, A.C.; Malcata, F.X. Advances and perspectives in using microalgae to produce biodiesel. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3402–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Barbosa, C.R.; Amaro, H.M.; Pereira, C.I.; Xavier Malcata, F. Microalgal and cyanobacterial cell extracts for use as natural antibacterial additives against food pathogens. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, F.; Sanmartin, C.; Taglieri, I.; Nari, A.; Andrich, G.; Terzuoli, E.; Donnini, S.; Nicolella, C.; Zinnai, A. Development of Phenol-Enriched Olive Oil with Phenolic Compounds Extracted from Wastewater Produced by Physical Refining. Nutrients 2017, 9, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Malcata, F.X. Microalgae as sources of high added-value compounds—A brief review of recent work. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanthoor-Koopmans, M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Barbosa, M.J.; Eppink, M.H.M. Biorefinery of microalgae for food and fuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinnai, A.; Sanmartin, C.; Taglieri, I.; Andrich, G.; Venturi, F. Supercritical fluid extraction from microalgae with high content of LC-PUFAs. A case of study: Sc-CO2 oil extraction from Schizochytrium sp. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 116, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina Grima, E.; Belarbi, E.H.; Acien Fernandez, F.G.; Robles Medina, A.; Chisti, Y. Recovery of microalgal biomass and metabolites: Process options and economics. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 20, 491–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, M.C.; Campos, I.; Sanchez, J.F.; Acien, F.G.; Molina, E.; Fernandez-Sevilla, J.M. Recovery of lutein from microalgae biomass: Development of a process for Scenedesmus almeriensis biomass. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11761–11766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luengo, E.; Martinez, J.M.; Coustets, M.; Alvarez, I.; Teissie, J.; Rols, M.P.; Raso, J. A comparative study on the effects of millisecond- and microsecond-pulsed eectric field treatments on the permeabilization and extraction of pigments from Chlorella vulgaris. J. Membr. Biol. 2015, 248, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Theegala, C. Optimizing a continuous flow lipid extraction system (CFLES) used for extracting microalgal lipids. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, P.; Bhosle, D.; Janghel, A.; Deo, S.; Verma, C.; Kumar, S.S.; Agrawal, M.; Amit, N.; Sharma, M.; Giri, T.; Tripathi, D.K. Emerging Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) Techniques as an Innovative Green Technologies for the Effective Extraction of the Active Phytopharmaceuticals. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2015, 8, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Quintana, S.E.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T.; Garcia-Risco, M.R. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) as an Innovative Green Technology for the Effective Enrichment of Galician Algae Extracts with High Quality Fatty Acids and Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabias-Martínez, R.; Rodríguez-Gonzalo, E.; Revilla-Ruiz, P.; Hernández-Méndez, J. Pressurized liquid extraction in the analysis of food and biological samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1089, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, A.; Turner, C. Pressurized liquid extraction as a green approach in food and herbal plants extraction: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Valdés, A.; Ibrahim, O.H.M.; Suarez-Álvarez, S.; Ferragut, J.A.; Micol, V.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E.; García-Cañas, V. Pressurized liquid extraction of Neochloris oleoabundans for the recovery of bioactive carotenoids with anti-proliferative activity against human colon cancer cells. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denery, J.R.; Dragull, K.; Tang, C.S.; Li, Q.X. Pressurized fluid extraction of carotenoids from Haematococcus pluvialis and Dunaliella salina and kavalactones from Piper methysticum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 501, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Gião, M.S.; Malcata, F.X. Optimization of ABTS radical cation assay specifically for determination of antioxidant capacity of intracellular extracts of microalgae and cyanobacteria. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.; Jaime, L.; Martin-Alvarez, P.J.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibanez, E. Optimization of the extraction of antioxidants from Dunaliella salina microalga by pressurized liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5597–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieber, S.; Schober, S.; Mittelbach, M. Pressurized fluid extraction of polyunsaturated fatty acids from the microalga Nannochloropsis oculata. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 47, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taucher, J.; Baer, S.; Schwerna, P.; Hofmann, D.; Hümmer, M.; Buchholz, R.; Becker, A. Cell disruption and pressurized liquid extraction of carotenoids from microalgae. J. Thermodyn. Catal. 2016, 7, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibañez, E. Compressed fluids for the extraction of bioactive compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luthria, D.L. Influence of experimental conditions on the extraction of phenolic compounds from parsley (Petroselinum crispum) flakes using a pressurized liquid extractor. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, H.M.; Fernandes, F.; Valentao, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Malcata, F.X.; Guedes, A.C. Effect of solvent system on extractability of lipidic components of Scenedesmus obliquus (M2-1) and Gloeothece sp. on antioxidant scavenging capacity thereof. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6453–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, A.C.; Gião, M.S.; Seabra, R.; Ferreira, A.C.S.; Tamagnini, P.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; Malcata, F.X. evaluation of the antioxidant activity of cell extracts from microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, A.; Amaro, H.; Barbosa, C.; Dias Pereira, R.; Xavier Malcata, F. Fatty acid composition of several wild microalgae and cyanobacteria, with a focus on eicosapentaenoic, docosahexaenoic and α-linolenic acids for eventual dietary uses. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Guardia, M.; Armenta, S. Chapter 1—Origins of Green Analytical Chemistry. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Guardia, M.D.L., Armenta, S., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 57, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cooney, M.; Young, G.; Nagle, N. Extraction of Bio-oils from Microalgae. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2009, 38, 291–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.; King, J.W.; Mathiasson, L. Supercritical fluid extraction and chromatography for fat-soluble vitamin analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 936, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Gião, M.S.; Matias, A.A.; Nunes, A.V.M.; Pintado, M.E.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Malcata, F.X. Supercritical fluid extraction of carotenoids and chlorophylls a, b and c, from a wild strain of Scenedesmus obliquus for use in food processing. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Sánchez, M.D.; Fernandez-Sevilla, J.M.; Fernández, F.G.A.; García, M.C.C.; Grima, E.M. Supercritical fluid extraction of carotenoids from Scenedesmus almeriensis. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, R.; Gladman, B.; Danquah, M.K.; Webley, P.A. Oil extraction from microalgae for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, V.; Destaillats, F.; Juanéda, P.; Dionisi, F.; Lambelet, P.; Sébédio, J.-L.; Berdeaux, O. Thermal degradation of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids during deodorization of fish oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2006, 108, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime, L.; Rodríguez-Meizoso, I.; Cifuentes, A.; Santoyo, S.; Suarez, S.; Ibáñez, E.; Señorans, F.J. Pressurized liquids as an alternative process to antioxidant carotenoids extraction from Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Pereira, R.D.; Malcata, F.X. Effects of temperature and pH on growth and antioxidant content of the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerón, M.C.; García-Malea, M.C.; Rivas, J.; Acien, F.G.; Fernandez, J.M.; Del Río, E.; Guerrero, M.G.; Molina, E. Antioxidant activity of Haematococcus pluvialis cells grown in continuous culture as a function of their carotenoid and fatty acid content. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 74, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, K.H.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, C.Y.; Um, B.H.; Na, Y.R.; Pan, C.H. Effect of pressurized liquids on extraction of antioxidants from Chlorella vulgaris. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4756–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agamy, E.I. Bioactive Components in Camel Milk. In Bioactive Components in Milk and Dairy Products; Park, Y.W., Ed.; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 159–194. [Google Scholar]
- Nenadis, N.; Wang, L.-F.; Tsimidou, M.; Zhang, H.-Y. Estimation of Scavenging Activity of Phenolic Compounds Using the ABTS•+ Assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4669–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Torres, N.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Espinosa-Andrews, H.; Sánchez-Contreras, A.; Pacheco, N. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction for the Recovery of Phenolic Compounds from Vegetable Sources. Agronomy 2017, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Santoyo, S.; Jaime, L.; Avalo, B.; Cifuentes, A.; Reglero, G.; García-Blairsy Reina, G.; Señoráns, F.J.; Ibáñez, E. Comprehensive characterization of the functional activities of pressurized liquid and ultrasound-assisted extracts from Chlorella vulgaris. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lepage, G.; Roy, C.C. Improved recovery of fatty acid through direct transesterification without prior extraction or purification. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Z.; Vonshak, A.; Richmond, A. Effect of environmental conditions on fatty acid composition of the red alga Porphyridium cruentum: Correlation to growth rate. J. Phycol. 1988, 24, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 Q1 (1 mL·min−1);
Q1 (1 mL·min−1);  Q2 (2 mL·min−1);
Q2 (2 mL·min−1);  Q3 (3 mL·min−1) and
Q3 (3 mL·min−1) and  Q4 (4 mL·min−1); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI (trans-β-Apo-8′-carotenal), mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)
Q4 (4 mL·min−1); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI (trans-β-Apo-8′-carotenal), mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene; and (C) Antioxidant capacity expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in
β-carotene; and (C) Antioxidant capacity expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays.
DPPH• assays.
 Q1 (1 mL·min−1);
Q1 (1 mL·min−1);  Q2 (2 mL·min−1);
Q2 (2 mL·min−1);  Q3 (3 mL·min−1) and
Q3 (3 mL·min−1) and  Q4 (4 mL·min−1); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI (trans-β-Apo-8′-carotenal), mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)
Q4 (4 mL·min−1); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI (trans-β-Apo-8′-carotenal), mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene; and (C) Antioxidant capacity expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in
β-carotene; and (C) Antioxidant capacity expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays.
DPPH• assays.
 30 °C,
30 °C,  40 °C,
40 °C,  50 °C,
50 °C,  60 °C,
60 °C,  70 °C (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)
70 °C (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in
β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays.
DPPH• assays.
 30 °C,
30 °C,  40 °C,
40 °C,  50 °C,
50 °C,  60 °C,
60 °C,  70 °C (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)
70 °C (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoids content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6)  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in
β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9), obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays.
DPPH• assays.
 1F (12.5 mL),
1F (12.5 mL),  2F (12.5 mL),
2F (12.5 mL),  3F (125 mL); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of
3F (125 mL); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extract obtained in
β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extract obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
 1F (12.5 mL),
1F (12.5 mL),  2F (12.5 mL),
2F (12.5 mL),  3F (125 mL); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of
3F (125 mL); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extract obtained in
β-carotene; (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extract obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
 1C (4 min),
1C (4 min),  2C (8 min),
2C (8 min),  3C (12 min),
3C (12 min),  4C (16 min),
4C (16 min),  5C (20 min), (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI, mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of
5C (20 min), (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI, mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene); (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts obtained in
β-carotene); (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
 1C (4 min),
1C (4 min),  2C (8 min),
2C (8 min),  3C (12 min),
3C (12 min),  4C (16 min),
4C (16 min),  5C (20 min), (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI, mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of
5C (20 min), (bars for a common fatty acid, without a common superscript, are significantly different, p < 0.05); (B) Carotenoid content expressed in equivalent of PI, mgPI·mgE−1 (n = 6) of  Lutein and
Lutein and  β-carotene); (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts obtained in
β-carotene); (C) Antioxidant capacity of the extracts obtained in  ABTS+• and
ABTS+• and  DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).
DPPH• assays expressed in trolox equivalent (TE) per extract mass, µTE·mgE−1 (n = 9).

| Biomass (mg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 150 | ||
| Fatty acids (μgFA·mgB−1) | 14:0 | 5.4 ± 0.6 a | 4.9 ± 1.0 a | 4.4 ± 0.5 a |
| 16:0 | 24.6 ± 3.9 a | 23.0 ± 0.7 a | 23.3 ± 2.2 a | |
| 18:0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 a | 0.5 ± 0.1 a | 0.1 ± 0.0 a | |
| 18:1 n9 | 17.6 ± 3.0 a | 12.3 ± 3.7 a | 13.3 ± 2.5 a | |
| 18:2 n6 t | 19.8 ± 3.6 a | 14.6 ± 1.0 a | 18.8 ± 2.0 a | |
| 18:2 n6 c | 0.3 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.3 ± 0.0 a | |
| 18:3 n6 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 a | |
| 18:3 n3 | 36.6 ± 5.4 a,b | 27.1 ± 2.7 b | 39.3 ± 3.3 a | |
| Carotenoids (mgPI·mgB−1) | Lutein | 2.16 ± 0.14 | 1.15 ± 0.06 | 1.39 ± 0.18 |
| β-carotene | 0.16 ± 0.00 a | 0.13 ± 0.02 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | |
| Antioxidant capacity (mgTE·mgE−1. mgB−1) | ABTS+• | 129.4 ± 2.6 | 102.7 ± 8.0 | 70.1 ± 5.5 |
| DPPH• | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.4 a | 1.9 ± 0.5 a | |
| Extraction Methods Tested | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| UAE | Optimized Conditions of CPSE | ||
| Fatty acids (μgFA·mgE−1) | 14:0 | 9.9 ± 1.4 a | 10.0 ± 1.9 (5C) a |
| 16:0 | 38.5 ± 4.1 | 50.8 ± 2.5 (5C) | |
| 16:1 | 2.9 ± 0.2 a | 2.9 ± 1.5 (5C) a | |
| 18:0 | 0.9 ± 0.2 a | 1.5 ± 0.6 (5C) a | |
| 18:1 n9 | 23.5 ± 0.9 | 33.8 ± 8.7 (5C) * | |
| 18:2 n6 t | 18.8 ± 2.0 a | 23.8 ± 5.2 (5C) a | |
| 18:2 n6 c | 4.8 ± 0.1 a | 1.8 ± 1.1 (5C) a | |
| 18:3 n6 | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 1.3(5C) | |
| 18:3 n3 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 27.9 ± 4.2 (5C) | |
| Carotenoids (mgPI·mgE−1) | Lutein | 1.22 ± 0.18 | 2.9 ± 0.1 (3C) |
| β-Carotene | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 1.5 ± 0.1 (3C) | |
| Antioxidant capacity (µgTE·mgE−1) | ABTS+• | 121.6 ± 6.2 | 168.7 ± 4.3 (3C) |
| DPPH• | 395.1 ± 10.9 | 423.4 ± 10.6 (3C) | |
| Stage | Abbreviation | Condition Tested | Operating Conditions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Biomass | M50 | 50 mg DWbiomass | Q: 2 mL·min−1 T: 40 °C Vethanol: 150 mL |
| M100 | 100 mg DWbiomass | |||
| M150 | 150 mg DWbiomass | |||
| 2 | Flow | Q1 | 1 mL·min−1 | DWbiomass: 50 mg T: 60 °C Vethanol: 150 mL |
| Q2 | 2 mL·min−1 | |||
| Q3 | 3 mL·min−1 | |||
| Q4 | 4 mL·min−1 | |||
| 3 | Temperature | T30 | 30 °C | DWbiomass: 50 mg Q: 3 mL·min−1 Vethanol: 150 mL |
| T40 | 40 °C | |||
| T50 | 50 °C | |||
| T60 | 60 °C | |||
| T70 | 70 °C | |||
| 4 | Fractions of total solvent volume | 1F | 1st fraction of 12.5 mL | DWbiomass: 50 mg Q: 3 mL·min−1 T: 60 °C |
| 2F | 2nd fraction of 12.5 mL | |||
| 3F | 3rd fraction of 125 mL | |||
| Cycles of solvent recirculation | 1C (1F) | 1 cycle; 4 min | DWbiomass: 50 mg Q: 3 mL·min−1 T: 60 °C Vethanol: 12.5 mL | |
| 2C | 2 cycles; 8 min | |||
| 3C | 3 cycles; 12 min | |||
| 4C | 4 cycles; 16 min | |||
| 5C | 5 cycles; 20 min | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaro, H.M.; Guedes, A.C.; Preto, M.A.C.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Malcata, F.X. Gloeothece sp. as a Nutraceutical Source—An Improved Method of Extraction of Carotenoids and Fatty Acids. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090327
Amaro HM, Guedes AC, Preto MAC, Sousa-Pinto I, Malcata FX. Gloeothece sp. as a Nutraceutical Source—An Improved Method of Extraction of Carotenoids and Fatty Acids. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(9):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090327
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaro, Helena M., A. Catarina Guedes, Marco A. C. Preto, I. Sousa-Pinto, and F. Xavier Malcata. 2018. "Gloeothece sp. as a Nutraceutical Source—An Improved Method of Extraction of Carotenoids and Fatty Acids" Marine Drugs 16, no. 9: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090327
APA StyleAmaro, H. M., Guedes, A. C., Preto, M. A. C., Sousa-Pinto, I., & Malcata, F. X. (2018). Gloeothece sp. as a Nutraceutical Source—An Improved Method of Extraction of Carotenoids and Fatty Acids. Marine Drugs, 16(9), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090327