Probing the Interactions of Sulfur-Containing Histidine Compounds with Human Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Kinetics of GGT Inhibition by 5-Thiohistidine
2.2. Mechanism of Inactivation of GGT by Sulfur-Containing Compounds and Cytotoxicity
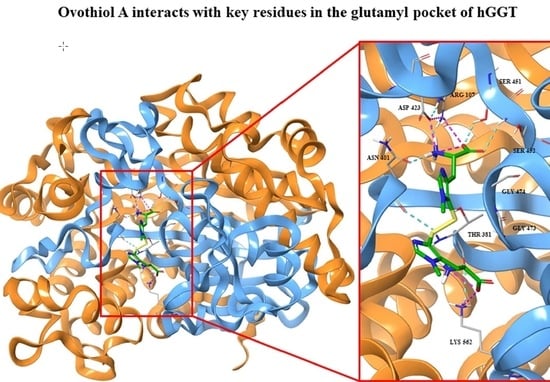
2.3. Docking Studies
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. GGT Activity, Kinetic Studies and Data Analysis
4.2. Time-Dependent Inhibition of hGGT by Thiohistidine Compounds
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.4. Molecular Docking of Thiohistidines into the GGT Active Site
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seebeck, F.P. Thiohistidine biosynthesis. CHIMIA Int. J. Chem. 2013, 67, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, C.; Bauer, T.; Surek, B.; Schömig, E.; Gründemann, D. Cyanobacteria produce high levels of ergothioneine. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1766–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebeck, F.P. In vitro reconstruction of mycobacterial ergothioneine biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepwong, P.; Giri, A.; Sasaki, F.; Fukui, R.; Ohshima, T. Mycobial enhancement of ergothioneine by submerged cultivation of edible mushroom mycelia and its application as an antioxidative compound. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ey, J.; Schömig, E.; Taubert, D. Dietary sources and antioxidant effects of ergothioneine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6466–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründemann, D.; Harlfinger, S.; Golz, S.; Geerts, A.; Lazar, A.; Berkels, R.; Jung, N.; Rubbert, A.; Schömig, E. Discovery of the ergothioneine transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5256–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.M.Y.; Cheah, I.K.-M.; Yew, T.S.K.; Halliwell, B. Distribution and accumulation of dietary ergothioneine and its metabolites in mouse tissues. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunshausen, A.; Seebeck, F.P. Identification and characterization of the first ovothiol biosynthetic enzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1757–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman-Reimer, S.; Duhe, R.J.; Stockman, B.J.; Selman, B.R. l-1-N-Methyl-4-mercaptohistidine disulfide, a potential endogenous regulator in the redox control of chloroplast coupling factor-I in Dunaliella. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, E.C.; Trick, M.; Hill, L.; Rejzek, M.; Dusi, R.G.; Hamilton, C.J.; Zimba, P.V.; Henrissat, B.; Field, R.A. The transcriptome of Euglena gracilis reveals unexpected metabolic capabilities for carbohydrate and natural product biochemistry. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 2808–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, I.; Migliaccio, O.; D’Aniello, S.; Merlino, A.; Napolitano, A.; Palumbo, A. Shedding light on ovothiol biosynthesis in marine metazoans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, I.; Seebeck, F.P. On ovothiol biosynthesis and biological roles: From life in the ocean to therapeutic potential. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spies, H.S.; Steenkam, D.J. Thiols of intracellular pathogens. Identification of ovothiol A in Leishmania donovani and structural analysis of a novel thiol from Mycobacterium bovis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 224, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, A.; Castellano, I.; Napolitano, A. Ovothiol: A potent natural antioxidant from marine organisms. In Blue Biotechnology: Production and Use of Marine Molecules; Barre, S., Bates, S.S., Eds.; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, C.A. A scent of therapy: Pharmacological implications of natural products containing redox-active sulfur atoms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, I.; Di Tomo, P.; Di Pietro, N.; Mandatori, D.; Pipino, C.; Formoso, G.; Napolitano, A.; Palumbo, A.; Pandolfi, A. Anti-inflammatory activity of marine ovothiol A in an in vitro model of endothelial dysfunction induced by hyperglycemia. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 2087373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, M.; D’Argenio, G.; Lembo, V.; Palumbo, A.; Castellano, I. Antifibrotic Effect of Marine Ovothiol in an In Vivo Model of Liver Fibrosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 5045734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Russo, M.; Castellano, I.; Napolitano, A.; Palumbo, A. Ovothiol isolated from sea urchin oocytes induces autophagy in the Hep-G2 cell line. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4069–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, M.; Russo, M.; Masullo, M.; Palumbo, A.; Russo, G.L.; Castellano, I. Sulfur-containing histidine compounds inhibit gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in human cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 14603–14614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, I.; Merlino, A. γ-Glutamyltranspeptidases: Sequence, structure, biochemical properties, and biotechnological applications. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3381–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, I.; Merlino, A. Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidases: Structure and Function. In SpringerBriefs in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hanigan, M.H. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: Redox regulation and drug resistance. Adv. Cancer. Res. 2014, 122, 103–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hanigan, M.H.; Frierson, H.F., Jr.; Swanson, P.E.; De Young, B.R. Altered expression of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in human tumors. Hum. Pathol. 1999, 30, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompella, A.; De Tata, V.; Paolicchi, A.; Zunino, F. Expression of gamma-glutamyltransferase in cancer cells and its significance in drug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, A.; Franzini, M.; Paolicchi, A.; Pompella, A. Gamma-glutamyltransferase of cancer cells at the crossroads of tumor progression, drug resistance and drug targeting. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Watanabe, B.; Hiratake, J.; Tanaka, R.; Ohkita, M.; Matsumura, Y. Preventive effect of GGsTop, a novel and selective γ-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor, on ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 339, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzova, M.; Jean, J.C.; Hughey, R.P.; Brown, L.A.; Cruikshank, W.W.; Hiratake, J.; Joyce-Brady, M. Inhibiting lung lining fluid glutathione metabolism with GGsTop as a novel treatment for asthma. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.B.; Chen, Y.; Wickham, S.; Heroux, A.; Cahill, K.; Hanigan, M.H.; Mooers, B.H. Novel insights into eukaryotic γ-glutamyltranspeptidase 1 from the crystal structure of the glutamate-bound human enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31902–31913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzyan, S.S.; Burgett, A.W.; Heroux, A.; Smith, C.A.; Mooers, B.H.; Hanigan, M.H. Human gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase 1: Structures of the free enzyme, inhibitor-bound tetrahedral transition states, and glutamate-bound enzyme reveal novel movement within the active site during catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 17576–17586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, S.S.; Meister, A. Serine-borate complex as a transition-state inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4806–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzyan, S.S.; Cook, P.F.; Heroux, A.; Hanigan, M.H. Structure of 6-diazo-5-oxo-norleucine-bound human gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase 1, a novel mechanism of inactivation. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.D.; Sant, M.E.; Christopherson, R.I. Cytotoxic mechanisms of glutamine antagonists in mouse L1210 leukemia. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 11377–11381. [Google Scholar]
- Lherbet, C.; Keillor, J.W. Probing the stereochemistry of the active site of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase using sulfur derivatives of l-glutamic acid. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Hiratake, J.; Tachi, N.; Suzuki, H.; Kumagai, H.; Sakata, K. Gamma-(Monophenyl) phosphono glutamate analogues as mechanism-based inhibitors of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6043–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Hiratake, J.; Kamiyama, A.; Sakata, K. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of gamma-phosphono diester analogues of glutamate as highly potent inhibitors and active site probes of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 1432–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiyama, A.; Nakajima, M.; Han, L.; Wada, K.; Mizutani, M.; Tabuchi, Y.; Kojima-Yuasa, A.; Matsui-Yuasa, I.; Suzuki, H.; Fukuyama, K.; et al. Phosphonate-based irreversible inhibitors of human γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT). GGsTop is a non-toxic and highly selective inhibitor with critical electrostatic interaction with an active-site residue Lys562 for enhanced inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 5340–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, Y.; Takeuchi, I.; Terada, H.; Makino, K. Therapeutic Effect of GGsTop, Selective Gamma-glutamyl Transpeptidase Inhibitor, on a Mouse Model of 5-Fluorouracil-induced Oral Mucositis. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.B.; West, M.B.; Cook, P.F.; Hanigan, M.H. A novel, species-specific class of uncompetitive inhibitors of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9059–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westley, A.M.; Westley, J. Enzyme inhibition in open systems. Superiority of uncompetitive agents. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5347–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Tipton, K.F. Assessment of enzyme inhibition: a review with examples from the development of monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitory drugs. Molecules 2017, 22, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milito, A.; Brancaccio, M.; D’Argenio, G.; Castellano, I. Natural sulfur-containing compounds: an alternative therapeutic strategy against liver fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daunay, S.; Lebel, R.; Farescour, L.; Yadan, J.C.; Erdelmeier, I. Short protecting-group-free synthesis of 5-acetylsulfanyl-histidines in water: Novel precursors of 5-sulfanyl-histidine and its analogues. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 10473–10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Sollitto, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Castellano, I. The complex evolutionary history of sulfoxide synthase in ovothiol biosynthesis. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 20191812, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo, P.; Cariati, L.; Desiderio, D.; Sgammato, R.; Lamberti, A.; Arcone, R.; Salerno, R.; Nardi, M.; Masullo, M.; Oliverio, M. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of donepezil-like compounds as ache and bace-1 inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shaw, D.E.; Shelley, M.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein-Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Time (min) | eqGGT | DTT | ovo | 5-thio | DTT + ovo | DTT + 5-thio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100% | 93% | 39% | 33% | 94% | 86% |
| 30 | 100% | 89% | 60% | 47% | 83% | 71% |
| 60 | 100% | 72% | 72% | 59% | 73% | 60% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milito, A.; Brancaccio, M.; Lisurek, M.; Masullo, M.; Palumbo, A.; Castellano, I. Probing the Interactions of Sulfur-Containing Histidine Compounds with Human Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120650
Milito A, Brancaccio M, Lisurek M, Masullo M, Palumbo A, Castellano I. Probing the Interactions of Sulfur-Containing Histidine Compounds with Human Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(12):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120650
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilito, Alfonsina, Mariarita Brancaccio, Michael Lisurek, Mariorosario Masullo, Anna Palumbo, and Immacolata Castellano. 2019. "Probing the Interactions of Sulfur-Containing Histidine Compounds with Human Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase" Marine Drugs 17, no. 12: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120650
APA StyleMilito, A., Brancaccio, M., Lisurek, M., Masullo, M., Palumbo, A., & Castellano, I. (2019). Probing the Interactions of Sulfur-Containing Histidine Compounds with Human Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase. Marine Drugs, 17(12), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120650