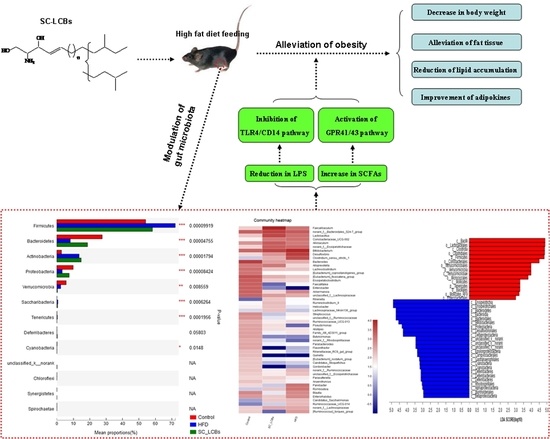
Long-Chain Bases from Sea Cucumber Alleviate Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. SC-LCBs Alleviated Obesity
2.2. SC-LCBs Inhibited Hyperglycemia
2.3. SC-LCBs Reduced Lipids Accumulation
2.4. SC-LCBs Regulated Serum Adipokines
2.5. SC-LCBs Modulated Gut Microbiota
2.6. SC-LCBs Regulated Secondary Metabolites of Gut Microbiota
2.7. SC-LCBs Inhibited LPS-Dependent Pathway and Activated SCFAs-Dependent Patyway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of SC-LCBs
4.2. Animal Experimental Design
4.3. OGTT
4.4. Blood Glucose and Lipids Measurement
4.5. Hepatic Lipids Analysis
4.6. Adiokines Measurement
4.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.8. Serum and Fecal LPS Determination
4.9. Fecal SCFAs Detection
4.10. Fecal DNA Extraction
4.11. Intestinal Microbiota Analysis
4.12. Western Blotting
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cecchini, M.; Sassi, F.; Lauer, J.A.; Lee, Y.Y.; Guajardo-Barron, V.; Chisholm, D. Tackling of unhealthy diets, physical inactivity and obesity: Health effects and cost-effectiveness. Lancet 2010, 376, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and diabetes: The increased risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, D.K.; Renuka, P.M.; Shandilya, U.K.; Dhewa, T.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, S.; Puniya, A.K.; Shukla, P. Gut microbiota modulation and its relationship with obesity using prebiotic fibers and probiotics: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Tena, M.; Alegria, A.; Lagarda, M.; Venema, K. Impact of plant sterols enrichment dose on gut microbiota from lean and obese subjects using TIM-2 in vitro fermentation model. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, S.; Venema, K. Gut microbiota and obesity: Involvement of the adipose tissue. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Teng, C.; Kalyanam, N.; Ho, C.; Pan, M. Garcinol reduces obesity in high-fat-diet-fed mice by modulating gut microbiota composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1970025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Ning, G.; Hong, J.; Liu, R. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract ameliorates inflammation and adiposity by modulating gut microbiota in high-fat diet mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Duan, M.; Liu, Y.; Luo, T.; Ma, N.; Song, S.; Ai, C. The beneficial effects of Gracilaria lemaneiformis polysaccharides on obesity and the gut microbiota in high fat diet-fed mice. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Lobley, G.E.; Holtrop, G.; Ince, J.; Johnstone, A.M.; Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Human colonic microbiota associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schafer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in line and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Han, X.; Zhan, J.; You, Y.; Huang, W. Vanillin alleviates high fat diet-induced obesity and improve the gut microbiota composition. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, M.J.; Aviello, G.; Ross, A.W.; Walker, A.W.; Barrett, P.; Morgan, P.J. Diet induced obesity is independent of metabolic endotoxemia and TLR4 signalling, but markedly increases hypothalamic expression of the acute phase protein, SerpinA3N. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Chang, X.; Qi, K. Short chain fatty acids prevent gigh-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice by regulating G Protein-coupled receptors and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Beneficial effects of ginger on prevention of obesity through modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Y.; Ai, C.; Wang, L.; Wen, C.; Yang, J.; Song, S.; Liu, X. Sulfated polysaccharide from sea cucumber and its depolymerized derivative prevent obesity in association with modification of gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Y.; Ai, C.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Liu, X. Sulfated polysaccharide from sea cucumber modulates the gut microbiota and its metabolites in normal mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Mao, G.; Wu, T.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Tian, D.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S. A fucoidan from sea cucumber Pearsonothuria graeffei with well-repeated structure alleviates gut microbiota dysbiosis and metabolic syndromes in HFD-fed mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5371–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, X.; Yan, X.; Su, L. Anti-inflammation effects of fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from Acaudina molpadioides by altering gut microbiota in obese mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, S.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods-a review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1761–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Z.; Sugawara, T.; Hirata, T. Sphingoid bases from sea cucumber induce apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells through p-AKT and DR5. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Song, Y.; Tao, S.; Cong, P.; Wang, X.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Structure of sphingolipids from sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa and structure-specific cytotoxicity against human HepG2 cells. Lipids 2016, 51, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z.; Leng, K.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Sea cucumber cerebrosides and long-chain bases from Acaudina molpadioides protect against high fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3428–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Long-chain bases from sea cucumber mitigate endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in obesity mice. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Long-chain bases from Cucumaria frondosa inhibit adipogenesis and regulate lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1735–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, P. Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.C.; lément, K. Gut microbiota and obesity: Concepts relevant to clinical care. Eur. J. Int. Med. 2018, 48, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; An, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Alterations of bile acids and gut microbiota in obesity Induced by High Fat Diet in Rat Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.P.; Gratz, S.W.; Sheridan, P.O.; Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H. The influence of diet on the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Mao, G.; Wu, T.; Lin, D.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Tian, D.; Chai, W.; Lindhardt, R.J.; et al. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from Isostichopus badionotus alleviates metabolic syndromes and gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by high-fat and high-fructose diet. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cheng, G.; Li, Q.; Jiao, S.; Feng, C.; Zhao, X.; Yin, H.; Du, Y.; Liu, H. Chitin oligosaccharide modulates gut microbiota and attenuates high-fat-diet-induced metabolic syndrome in mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W.; Yang, X.; Yu, J. Intake of total saponins and polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum affects the gut microbiota in diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2017, 26, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Chiba, Y.; Wang, C.; Yamashiro, Y. The effects of the Lactobacillus casei strain on obesity in children: A pilot study. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaprakasam, S.; Prasad, P.D.; Singh, N. Benefits of short-chain fatty acids and their receptors in inflammation and carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 164, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Org, E.; Blum, Y.; Kasela, S.; Mehrabian, M.; Kuusisto, J.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Wang, Z.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Hazen, S.L.; et al. Relationships between gut microbiota, plasma metabolites and metabolic syndrome traits in the METSIM cohort. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Wang, R.; Peng, Y.; Li, X. Effects of a homogeneous polysaccharide from Sijunzi decoction on human intestinal microbes and short chain fatty acids in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol 2018, 224, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, A. Contributions of colonic short-chain fatty acid receptors in energy homeostasis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2014, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, H.J.; de Goffau, M.C. The human gut microbiota. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Yadava, K.; Sichelstiel, A.K.; Sprenger, N.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Blanchard, C.; Junt, T.; Nicod, L.P.; Harris, N.L.; et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influence s allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, B.O.; Kwak, Y.S. Perspectives on the therapeutic potential of short-chain fatty acid receptors. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, J.; Kasubuchi, M.; Nakajima, A.; Kimura, I. Anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects of free fatty acid receptors. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 236, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Verotta, L.; Panzella, L.; Antenucci, S.; Calvenzani, V.; Tomay, F.; Petroni, K.; Caneva, E.; Napolitano, A. Fermented pomegranate wastes as sustainable source of ellagic acid: Antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory action, and controlled release under simulated digestion conditions. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Possemiers, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Guiot, Y.; Everard, A.; Rottier, O.; Geurts, L.; Naslain, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Lambert, D.M.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009, 58, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, H.; Zou, L.; Li, X. Insulin sensitivity-enhancing activity of phlorizin is associated with lipopolysaccharide decrease and gut microbiota changes in obese and type 2diabetes (db/db) mice. J. Agric. Chem. 2016, 64, 7502–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersoug, L.G.; Møller, P.; Loft, S. Role of microbiota-derived lipopolysaccharide in adipose tissue inflammation, adipocyte size and pyroptosis during obesity. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Duan, J.; Xue, C.; Feng, T.; Dong, P.; Sugawara, T.; Hirata, T. Analysis and comparison of glucocerebroside species from three edible sea cucumbers using liquid chromatography-ion trap-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12246–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.; Su, L. Fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides improves insulin resistance by altering gut microbiota dysfunction. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Control | HFD | SC-LCBs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum LPS (IU/mL) | 0.83 ± 0.07 | 3.50 ± 0.45 ## | 2.26 ± 0.32 * |
| Fecal LPS (µg/g feces) | 5.04 ± 0.70 | 11.3 ± 0.9 ## | 8.53 ± 0.77 ** |
| Fecal acetate (mmol/L) | 16.8 ± 1.6 | 7.49 ± 0.82 ## | 12.5 ± 1.2 ** |
| Fecal propionate (mmol/L) | 6.38 ± 0.67 | 3.50 ± 0.44 ## | 5.07 ± 0.55 * |
| Fecal butyrate (mmol/L) | 1.46 ± 0.11 | 0.68 ± 0.04 ## | 1.33 ± 0.14 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Yang, H. Long-Chain Bases from Sea Cucumber Alleviate Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080455
Hu S, Xu Y, Gao X, Li S, Jiang W, Liu Y, Su L, Yang H. Long-Chain Bases from Sea Cucumber Alleviate Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080455
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shiwei, Yangli Xu, Xiang Gao, Shijie Li, Wei Jiang, Yu Liu, Laijin Su, and Huicheng Yang. 2019. "Long-Chain Bases from Sea Cucumber Alleviate Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiota" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080455
APA StyleHu, S., Xu, Y., Gao, X., Li, S., Jiang, W., Liu, Y., Su, L., & Yang, H. (2019). Long-Chain Bases from Sea Cucumber Alleviate Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080455