Pyridine-2,6-Dithiocarboxylic Acid and Its Metal Complexes: New Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo -Lactamase-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
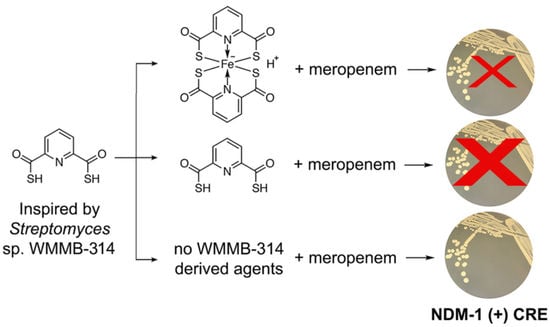
2.1. Identification, Synthesis and Evaluation of PDTC against Clinical CRE Isolates with Meropenem
2.2. Kinetic Evaluation of PDTC against Recombinant NDM-1
2.3. Synthesis and Kinetic Evaluation of PDTC Complexes against Recombinant NDM-1
2.4. Evaluation of PDTC Complexes against Clincal CRE Isolates with Meropenem
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents, Chemicals and Instrumentation
4.2. Purification and Identification of PDTC2-Fe
4.3. PDTC Synthesis
4.4. Mass Spectrometry of PDTC Complexes
4.5. NDM-1 Purification
4.6. Kinetic Data Collection
4.7. MIC Determinations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- Li, X.; Ye, H. Clinical and mortality risk factors in bloodstream infections with carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 2017, 6212910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daikos, G.L.; Tsaousi, S.; Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Anyfantis, I.; Psichogiou, M.; Argyropoulou, A.; Stefanou, I.; Sypsa, V.; Miriagou, V.; Nepka, M.; et al. Carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections: Lowering mortality by antibiotic combination schemes and the role of carbapenems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2322–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraenkel-Wandel, Y.; Raveh-Brawer, D.; Wiener-Well, Y.; Yinnon, A.M.; Assous, M.V. Mortality due to blakpc klebsiella pneumoniae bacteraemia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villegas, M.V.; Pallares, C.J.; Escandón-Vargas, K.; Hernández-Gómez, C.; Correa, A.; Álvarez, C.; Rosso, F.; Matta, L.; Luna, C.; Zurita, J.; et al. Characterization and clinical impact of bloodstream infection caused by carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae in seven latin american countries. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papadimitriou-Olivgeris, M.; Marangos, M.; Christofidou, M.; Fligou, F.; Bartzavali, C.; Panteli, E.S.; Vamvakopoulou, S.; Filos, K.S.; Anastassiou, E.D. Risk factors for infection and predictors of mortality among patients with kpc-producing klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections in the intensive care unit. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 46, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, H.J.; Pogue, J.M.; Kaye, K.S.; LaPlante, K.L. Treatment options for carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akajagbor, D.S.; Wilson, S.L.; Shere-Wolfe, K.D.; Dakum, P.; Charurat, M.E.; Gilliam, B.L. Higher incidence of acute kidney injury with intravenous colistimethate sodium compared with polymyxin b in critically ill patients at a tertiary care medical center. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giani, T.; Arena, F.; Vaggelli, G.; Conte, V.; Chiarelli, A.; Henrici De Angelis, L.; Fornaini, R.; Grazzini, M.; Niccolini, F.; Pecile, P.; et al. Large nosocomial outbreak of colistin-resistant, carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae traced to clonal expansion of an mgrb deletion mutant. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3341–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi Gonçalves, I.; Ferreira, M.L.; Araujo, B.F.; Campos, P.A.; Royer, S.; Batistão, D.W.; Souza, L.P.; Brito, C.S.; Urzedo, J.E.; Gontijo-Filho, P.P.; et al. Outbreaks of colistin-resistant and colistin-susceptible kpc-producing klebsiella pneumoniae in a brazilian intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 94, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, A.; Plasencia, V.; García, L.; Hidalgo, O.; Ayestarán, J.I.; Alberti, S.; Borrell, N.; Pérez, J.L.; Oliver, A. Characterization of a large outbreak by ctx-m-1-producing klebsiella pneumoniae and mechanisms leading to in vivo carbapenem resistance development. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Molecular epidemiology and mechanisms of carbapenem resistance in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4783–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; He, X.; Ding, F.; Wu, W.; Luo, Y.; Fan, B.; Cao, H. Overproduction of efflux pumps caused reduced susceptibility to carbapenem under consecutive imipenem-selected stress in. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 11, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.P.; Xu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Fang, Y.P.; Shen, J.L. Overexpression of mexab-oprm efflux pump in carbapenem-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Dortet, L.; Iorga, B.I. Structural and functional aspects of class a carbapenemases. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1006–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docquier, J.D.; Mangani, S. Structure-function relationships of class d carbapenemases. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palzkill, T. Metallo-β-lactamase structure and function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1277, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Giske, C.G.; Cho, H.S.; Sundman, K.; Lee, K.; Walsh, T.R. Characterization of a new metallo-β-lactamase gene, blandm-1, and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from india. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5046–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tracking Cre. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/hai/organisms/cre/trackingcre.html (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- Tehrani, K.H.M.E.; Martin, N.I. Β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations: An update. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 1439–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linciano, P.; Cendron, L.; Gianquinto, E.; Spyrakis, F.; Tondi, D. Ten years with new delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (ndm-1): From structural insights to inhibitor design. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xu, Y.; Xia, Q.; Bai, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; He, D.; Xie, N.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Simplified captopril analogues as ndm-1 inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Tang, M.L.; Yu, L.; Liang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, F.; Yu, J.M.; Sun, X. Novel mercapto propionamide derivatives with potent new delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 inhibitory activity and low toxicity. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brem, J.; van Berkel, S.S.; Zollman, D.; Lee, S.Y.; Gileadi, O.; McHugh, P.J.; Walsh, T.R.; McDonough, M.A.; Schofield, C.J. Structural basis of metallo-β-lactamase inhibition by captopril stereoisomers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brem, J.; Cain, R.; Cahill, S.; McDonough, M.A.; Clifton, I.J.; Jiménez-Castellanos, J.C.; Avison, M.B.; Spencer, J.; Fishwick, C.W.; Schofield, C.J. Structural basis of metallo-β-lactamase, serine-β-lactamase and penicillin-binding protein inhibition by cyclic boronates. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cendron, L.; Quotadamo, A.; Maso, L.; Bellio, P.; Montanari, M.; Celenza, G.; Venturelli, A.; Costi, M.P.; Tondi, D. X-ray crystallography deciphers the activity of broad-spectrum boronic acid β-lactamase inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnc, A.; Brem, J.; Hinchliffe, P.; Calvopiña, K.; Panduwawala, T.D.; Lang, P.A.; Kamps, J.J.A.G.; Tyrrell, J.M.; Widlake, E.; Saward, B.G.; et al. Bicyclic boronate vnrx-5133 inhibits metallo- and serine-β-lactamases. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8544–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, A.M.; Reid-Yu, S.A.; Wang, W.; King, D.T.; De Pascale, G.; Strynadka, N.C.; Walsh, T.R.; Coombes, B.K.; Wright, G.D. Aspergillomarasmine a overcomes metallo-β-lactamase antibiotic resistance. Nature 2014, 510, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.Y.; Thomas, P.W.; Stewart, A.C.; Bergstrom, A.; Cheng, Z.; Miller, C.; Bethel, C.R.; Marshall, S.H.; Credille, C.V.; Riley, C.L.; et al. Dipicolinic acid derivatives as inhibitors of new delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7267–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.W.; Cammarata, M.; Brodbelt, J.S.; Fast, W. Covalent inhibition of new delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (ndm-1) by cefaclor. Chembiochem 2014, 15, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, J.; Wan, S.; Chan, K.F.; So, P.K.; He, D.; Chan, E.W.; Chan, T.H.; Wong, K.Y.; Tao, J.; Chen, S. Ebselen as a potent covalent inhibitor of new delhi metallo-β-lactamase (ndm-1). Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9543–9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vraspir, J.M.; Butler, A. Chemistry of marine ligands and siderophores. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Chemistry and biology of siderophores from marine microbes. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carmichael, J.R.; Zhou, H.; Butler, A. A suite of asymmetric citrate siderophores isolated from a marine shewanella species. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 198, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, C.D.; Butler, A. Ambiguity of nrps structure predictions: Four bidentate chelating groups in the siderophore pacifibactin. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Nolan, E.M. Beyond iron: Non-classical biological functions of bacterial siderophores. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 6320–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schalk, I.J.; Hannauer, M.; Braud, A. New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2844–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Chen, W.H.; Bruner, S.D. Microbial siderophore-based iron assimilation and therapeutic applications. Biometals 2016, 29, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockels, W.; Römer, A.; Budzikiewicz, H. An fe(ii) complex of pyridine-2,6-di-(monothiocarboxylic acid) - a novel bacterial metabolic product-sciencedirect. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 3341–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.A.; Paszczynski, A.; Gordon-Wylie, S.W.; Jeedigunta, S.; Lee, C.H.; Crawford, R.L. Carbon tetrachloride dechlorination by the bacterial transition metal chelator pyridine-2,6-bis(thiocarboxylic acid). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.A.; Leach, L.; Morales, S.; Austin, P.R.; Hartwell, H.J.; Kaplan, B.; Forker, C.; Meyer, J.M. Physiological and molecular genetic evaluation of the dechlorination agent, pyridine-2,6-bis(monothiocarboxylic acid) (pdtc) as a secondary siderophore of pseudomonas. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, L.H.; Morris, J.C.; Lewis, T.A. The role of the siderophore pyridine-2,6-bis (thiocarboxylic acid) (pdtc) in zinc utilization by pseudomonas putida dsm 3601. Biometals 2007, 20, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebat, J.L.; Paszczynski, A.J.; Cortese, M.S.; Crawford, R.L. Antimicrobial properties of pyridine-2,6-dithiocarboxylic acid, a metal chelator produced by pseudomonas spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3934–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cortese, M.S.; Paszczynski, A.; Lewis, T.A.; Sebat, J.L.; Borek, V.; Crawford, R.L. Metal chelating properties of pyridine-2,6-bis(thiocarboxylic acid) produced by pseudomonas spp. And the biological activities of the formed complexes. Biometals 2002, 15, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, D.M.; Yang, Y.; Wildey, M.J.; Bush, K.; Lee, M.D. Inhibition of metallo-beta-lactamases by pyridine monothiocarboxylic acid analogs. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laatsch, H. Antibase; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.W.; Zheng, M.; Wu, S.; Guo, H.; Liu, D.; Xu, D.; Fast, W. Characterization of purified new delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 10102–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Sun, L.Y.; Gao, H.; Kang, P.W.; Li, J.Q.; Zhen, J.B.; Yang, K.W. Identification of cisplatin and palladium(ii) complexes as potent metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors for targeting carbapenem-resistant. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.B.; Crans, D.C. Solid-to-solid oxidation of a vanadium (iv) to a vanadium (v) compound: Chemisty of a sulfur-containing siderophore. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 9144–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, H.J. Windnmr: Dynamic nmr spectra for windows. J. Chem. Educ. 1995, 72, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tropea, J.E.; Cherry, S.; Waugh, D.S. Expression and purification of soluble his6-tagged tev protease. In Methods in Molecular Biology: High Throughput Protein Expression; Doyle, S.A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 498. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaund, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the expasy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill, F., III.; Wikler, M.; Alder, J.; Dudley, M.; Eliopoulos, G.; Ferraro, M.J.; Hardy, D.; Hecht, D.; Hindler, J.; Patel, J.; et al. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 9th ed.; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]





| Complex | E. coli 2692 | E. coli BAA-2452 | K. pneumonieae BAA-2146 |
|---|---|---|---|
| No PDTC or Complex | 64 a | 20 a | 64 a |
| PDTC2-Fe | 16 a | 2 a | 20 a |
| PDTC2-Co | 28 a | 4 a | 32 a |
| PDTC-Ni | 16 a | 2 a | 32 a |
| PDTC-Zn | 64 c | 12 c | 64 b |
| PDTC (no metal) | 8 b | 1 b | 8 b |
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| pNIC-Fwd | CGCATGGCCGATAAGTTACGTTAAacggtctccagtaaaggt |
| pNIC-Rev | CCCGATAGTTGGACGAATTTCACCggattggaagtacaggttctc |
| NDM1-Fwd | accgagaacctgtacttccaatccGGTGAAATTCGTCCAACTATC |
| NDM1-Rev | gtatccacctttactggagaccgtTTAACGTAACTTATCGGCCA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomas, C.S.; Braun, D.R.; Olmos, J.L., Jr.; Rajski, S.R.; Phillips, G.N., Jr.; Andes, D.N.; Bugni, T.S., Jr. Pyridine-2,6-Dithiocarboxylic Acid and Its Metal Complexes: New Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo -Lactamase-1. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060295
Thomas CS, Braun DR, Olmos JL Jr., Rajski SR, Phillips GN Jr., Andes DN, Bugni TS Jr. Pyridine-2,6-Dithiocarboxylic Acid and Its Metal Complexes: New Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo -Lactamase-1. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(6):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060295
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomas, Chris S., Doug R. Braun, Jose Luis Olmos, Jr., Scott R. Rajski, George N. Phillips, Jr., David N. Andes, and Tim S. Bugni, Jr. 2020. "Pyridine-2,6-Dithiocarboxylic Acid and Its Metal Complexes: New Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo -Lactamase-1" Marine Drugs 18, no. 6: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060295
APA StyleThomas, C. S., Braun, D. R., Olmos, J. L., Jr., Rajski, S. R., Phillips, G. N., Jr., Andes, D. N., & Bugni, T. S., Jr. (2020). Pyridine-2,6-Dithiocarboxylic Acid and Its Metal Complexes: New Inhibitors of New Delhi Metallo -Lactamase-1. Marine Drugs, 18(6), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060295