Symbioses of Cyanobacteria in Marine Environments: Ecological Insights and Biotechnological Perspectives
Abstract
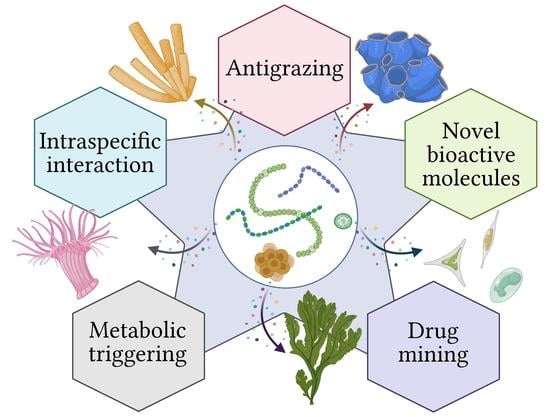
:1. Introduction: Cyanobacteria and Their Symbiotic Associations
2. Protists
3. Macroalgae and Seagrasses
4. Sponges
5. Cnidarians
6. Ascidians and Other Tunicates
7. Metabolic Interactions Involved in Symbiosis of Cyanobacteria
8. Bioprospecting of Cyanobacteria Symbioses
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, T.L.F.; Poulin, R. Parasitism, commensalism, and mutualism: Exploring the many shades of symbioses. Vie Milieu 2008, 58, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Microbial symbiosis in marine sponges. J. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, R.W. Impacts of shading on sponge-cyanobacteria symbioses: A comparison between host-specific and generalist associations. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.P.; Mazel, C.H.; Gorbunov, M.Y.; Falkowski, P.G. Discovery of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria in corals. Science 2004, 305, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, F.; Schmitt, F.; Leutenegger, A.; Ivanchenko, S.; D’Angelo, C.; Salih, A.; Maslakova, S.; Bulina, M.; Schirmbeck, R.; Nienhaus, G.U.; et al. Contributions of host and symbiont pigments to the coloration of reef corals. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1102–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wegley, L.; Edwards, R.; Rodriguez-Brito, B.; Liu, H.; Rohwer, F. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community associated with the coral Porites astreoides. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2707–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.D.; Ainsworth, T.D.; Gates, R.D.; Takabayashi, M. Diazotrophic bacteria associated with Hawaiian Montipora corals: Diversity and abundance in correlation with symbiotic dinoflagellates. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 371, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakirev, E.S.; Pavlyuchkov, V.A.; Ayala, F.J. DNA variation and symbiotic associations in phenotypically diverse sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16218–16223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tianero, M.D.B.; Kwan, J.C.; Wyche, T.P.; Presson, A.P.; Koch, M.; Barrows, L.R.; Bugni, T.S.; Schmidt, E.W. Species specificity of symbiosis and secondary metabolism in ascidians. ISME J. 2015, 9, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauermeister, A.; Branco, P.C.; Furtado, L.C.; Jimenez, P.C.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; da Cruz Lotufo, T.M. Tunicates: A model organism to investigate the effects of associated-microbiota on the production of pharmaceuticals. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2018, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Torres, J.P.; Ammon, M.A.; Marett, L.; Teichert, R.W.; Reilly, C.A.; Kwan, J.C.; Hughen, R.W.; Flores, M.; Tianero, M.D.; et al. A bacterial source for mollusk pyrone polyketides. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhukova, N.V.; Eliseikina, M.G. Symbiotic bacteria in the nudibranch mollusk Dendrodoris nigra: Fatty acid composition and ultrastructure analysis. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distel, D.L.; Altamia, M.A.; Lin, Z.; Shipway, J.R.; Han, A.; Forteza, I.; Antemano, R.; Limbaco, M.G.J.P.; Teboe, A.G.; Dechavez, R.; et al. Discovery of chemoautotrophic symbiosis in the giant shipworm Kuphus polythalamia (Bivalvia: Teredinidae) extends wooden-steps theory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3652–E3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bird, C.; Darling, K.F.; Russell, A.D.; Davis, C.V.; Fehrenbacher, J.; Free, A.; Wyman, M.; Ngwenya, B.T. Cyanobacterial endobionts within a major marine planktonic calcifier (Globigerina bulloides, Foraminifera) revealed by 16S rRNA metabarcoding. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bird, C.; Darling, K.; Russell, A.; Davis, C.; Fehrenbacher, J.; Free, A.; Wyman, M.; Ngwenya, B. 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding reveals a potential metabolic role for intracellular bacteria in a major marine planktonic calcifier (Foraminifera). Biogeosci. Discuss. 2016, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.A.; Raina, J.B.; Kahlke, T.; Seymour, J.R.; Suggett, D.J. Defining the core microbiome of the symbiotic dinoflagellate, Symbiodinium. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.A.; Zehr, J.P. Characterization of diatom-cyanobacteria symbioses on the basis of nifH, hetR and 16S rRNA sequences. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1913–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.A.; O’Mullan, G.D. Nitrogen-fixing and nitrifying symbioses in the marine environment. In Nitrogen in the Marine Environment; Capone, D.G., Bronk, D.A., Mulholland, M.R., Carpenter, E.J., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK, 2008; pp. 1197–1218. ISBN 9780123725226. [Google Scholar]
- Cardini, U.; Bednarz, V.N.; Naumann, M.S.; van Hoytema, N.; Rix, L.; Foster, R.A.; Al-Rshaidat, M.M.D.; Wild, C. Functional significance of dinitrogen fixation in sustaining coral productivity under oligotrophic conditions. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20152257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, M.; Bednarz, V.N.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. Diazotrophs: Overlooked key players within the coral symbiosis and tropical reef ecosystems? Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grube, M.; Seckbach, J.; Muggia, L.; Hrouzek, P. Secondary metabolites produced by Cyanobacteria in symbiotic associations. In Algal and Cyanobacteria Symbioses; World Scientific Publishing Europe Ltd.: London, UK, 2017; pp. 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasalainen, U.; Fewer, D.P.; Jokela, J.; Wahlsten, M.; Sivonen, K.; Rikkinen, J. Cyanobacteria produce a high variety of hepatotoxic peptides in lichen symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5886–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodgers, G.A.; Stewart, W.D.P. The cyanophyte-hepatic symbiosis I. Morphology and physiology. New Phytol. 1977, 78, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaimera, A.; Helfrichb, E.J.N.; Hinrichsc, K.; Guljamowc, A.; Ishidab, K.; Hertweck, C.; Dittmann, E. Nostopeptolide plays a governing role during cellular differentiation of the symbiotic cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chlipala, G.E.; Mo, S.; Orjala, J. Chemodiversity in freshwater and terrestrial Cyanobacteria—A source for Drug Discovery. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1654–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampa, A.; Gagunashvili, A.N.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Morinaka, B.I.; Daolio, C.; Godejohann, M.; Miao, V.P.W.; Piel, J.; Andrésson, Ó.S. Metagenomic natural product discovery in lichen provides evidence for a family of biosynthetic pathways in diverse symbioses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usher, K.M.; Bergman, B.; Raven, J.A. Exploring cyanobacterial mutualisms. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2007, 38, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, K.M. The ecology and phylogeny of cyanobacterial symbionts in sponges. Mar. Ecol. 2008, 29, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, M.; Hass, H.; Kerp, H.; Taylor, T.N.; Agerer, R.; Dotzler, N. Endophytic cyanobacteria in a 400-million-yr-old land plant: A scenario for the origin of a symbiosis? Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2009, 153, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-associated microorganisms: Evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esteves-Ferreira, A.A.; Cavalcanti, J.H.F.; Vaz, M.G.M.V.; Alvarenga, L.V.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Araújo, W.L. Cyanobacterial nitrogenases: Phylogenetic diversity, regulation and functional predictions. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, D.G.; Duggan, P.S.; Jackson, O. Cyanobacterial symbioses. In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Whitton, B.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 593–647. ISBN 9789400738553. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Li, T.; Jenkins, J.; Hu, Y.; Brueck, C.L.; Pei, H.; Betenbaugh, M.J. Evidence for a mutualistic relationship between the cyanobacteria Nostoc and fungi Aspergilli in different environments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6413–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenkoornhuyse, P.; Quaiser, A.; Duhamel, M.; Le Van, A.; Dufresne, A. The importance of the microbiome of the plant holobiont. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.C.G.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. Metaorganisms as the new frontier. Zoology 2011, 114, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mutalipassi, M.; Fink, P.; Maibam, C.; Porzio, L.; Buia, M.C.; Gambi, M.C.; Patti, F.P.; Scipione, M.B.; Lorenti, M.; Zupo, V. Ocean acidification alters the responses of invertebrates to wound-activated infochemicals produced by epiphytes of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 530–531, 151435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L.-A. Aquatic chemical ecology: New directions and challenges for the future. In Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems; Brönmark, C., Hansson, L.-A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 272–278. ISBN 9780199583096. [Google Scholar]
- Dierking, K.; Pita, L. Receptors mediating host-microbiota communication in the metaorganism: The invertebrate perspective. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devassy, R.P.; El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Al-Sofyani, A.A.; Crosby, M.P.; Al-Aidaroos, A.M. Seasonality and latitudinal variability in the diatom-cyanobacteria symbiotic relationships in the coastal waters of the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Symbiosis 2019, 78, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, A.; Nylander, J.A.A.; Foster, R.A. The genetic diversity and evolution of diatom-diazotroph associations highlights traits favoring symbiont integration. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stancheva, R.; Lowe, R.; Lowe, R. Diatom symbioses with other photoautotroph. In Diatoms: Fundamentals and Applications; Seckbach, J., Gordon, R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 225–244. ISBN 978-1-119-37021-5. [Google Scholar]
- Padmakumar, K.B.; Cicily, L.; Shaji, A.; Maneesh, T.P.; Sanjeevan, V.N. Symbiosis between the stramenopile protist Solenicola setigera and the diatom Leptocylindrus mediterraneus in the North Eastern Arabian Sea. Symbiosis 2012, 56, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, K.R.; Bentham, W.N. A novel symbiosis between a cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp., an aplastidic protist, Solenicola setigera, and a diatom, Leptocylindrus mediterraneus, in the open ocean. Mar. Biol. 1998, 132, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagino, K.; Onuma, R.; Kawachi, M.; Horiguchi, T. Discovery of an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium UCYN-A in Braarudosphaera bigelowii (Prymnesiophyceae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupke, A.; Musat, N.; LaRoche, J.; Mohr, W.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.I.; Kuypers, M.M.M.; Foster, R.A. In situ identification and N2 and C fixation rates of uncultivated cyanobacteria populations. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripp, H.J.; Bench, S.R.; Turk, K.A.; Foster, R.A.; Desany, B.A.; Niazi, F.; Affourtit, J.P.; Zehr, J.P. Metabolic streamlining in an open-ocean nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium. Nature 2010, 464, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.P.; Bench, S.R.; Carter, B.J.; Hewson, I.; Niazi, F.; Shi, T.; Tripp, H.J.; Affourtit, J.P. Globally distributed uncultivated oceanic N2-fixing cyanobacteria lack oxygenic photosystem II. Science 2008, 322, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.W.; Foster, R.A.; Krupke, A.; Carter, B.J.; Musat, N.; Vaulot, D.; Kuypers, M.M.M.; Zehr, J.P. Unicellular Cyanobacterium symbiotic with a single-celled eukaryotic alga. Science 2012, 337, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.A.; Zehr, J.P. Diversity, genomics, and distribution of phytoplankton-cyanobacterium single-cell symbiotic associations. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.A.; Collier, J.L.; Carpenter, E.J. Reverse transcription PCR amplification of cyanobacterial symbiont 16S rRNA sequences from single non-photosynthetic eukaryotic marine planktonic host cells. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.A.; Carpenter, E.J.; Bergman, B. Unicellular cyanobionts in open ocean dinoflagellates, radiolarians, and tintinnids: Ultrastructural characterization and immuno-localization of phycoerythrin and nitrogenase. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Miyashita, H.; Iseki, M.; Adachi, K.; Mimuro, M. Chlorophyll d in an epiphytic cyanobacterium of red algae. Science 2004, 303, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, P.; Smith, T.B.; Wartian, M.J. Epiphytic cyanobacteria maintain shifts to macroalgal dominance on coral reefs following ENSO disturbance. Ecology 2006, 87, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.B.; Smith, A.G. Exploring mutualistic interactions between microalgae and bacteria in the omics age. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 26, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, G.; Paerl, H.W. Nitrogen fixation by blue-green algae associated with the siphonous green seaweed Codium decorticatum: Effects on ammonium uptake. Mar. Biol. 1981, 61, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Mohanraju, R. Epiphytic bacterial communities in seagrass meadows of oligotrophic waters of Andaman Sea. Open Access Libr. J. 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Jaffé, R.; Anderson, W.T.; Jochem, F.J. Importance of seagrass as a carbon source for heterotrophic bacteria in a subtropical estuary (Florida Bay). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uku, J.; Björk, M.; Bergman, B.; Díez, B. Characterization and comparison of prokaryotic epiphytes associated with three East African seagrasses. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, C.; Albertano, P.; Bruno, L.; Montinari, M.; Rizzi, M.; Vigliotta, G.; Pagliara, P. Identification and characterization of a new Halomicronema species (Cyanobacteria) isolated from the Mediterranean marine sponge Petrosia ficiformis (Porifera). Fottea 2012, 12, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliara, P.; Barca, A.; Verri, T.; Caroppo, C. The marine sponge Petrosia ficiformis harbors different cyanobacteria strains with potential biotechnological application. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaci, L.; Sara, M. Associazione fra la cianoficea Aphanocapsa feldmanni e alcune Demospongie marine. Bolletino di Zoologia 1964, 31, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arillo, A.; Bavestrello, G.; Burlando, B.; Sarà, M. Metabolic integration between symbiotic cyanobacteria and sponges: A possible mechanism. Mar. Biol. 1993, 117, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unson, M.D.; Faulkner, D.J. Cyanobacterial symbiont biosynthesis of chlorinated metabolites from Dysidea herbacea (Porifera). Experientia 1993, 49, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unson, M.D.; Holland, N.D.; Faulkner, D.J. A brominated secondary metabolite synthesized by the cyanobacterial symbiont of a marine sponge and accumulation of the crystalline metabolite in the sponge tissue. Mar. Biol. 1994, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R.A.; Kavlekar, D.P.; LokaBharathi, P.A. Marine drugs from sponge-microbe association—A review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kvennefors, E.C.E.; Roff, G. Evidence of cyanobacteria-like endosymbionts in Acroporid corals from the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2009, 28, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lema, K.A.; Willis, B.L.; Bourne, D.G. Amplicon pyrosequencing reveals spatial and temporal consistency in diazotroph assemblages of the Acropora millepora microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 3345–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lema, K.A.; Willis, B.L.; Bourneb, D.G. Corals form characteristic associations with symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3136–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lema, K.A.; Bourne, D.G.; Willis, B.L. Onset and establishment of diazotrophs and other bacterial associates in the early life history stages of the coral Acropora millepora. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4682–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.P.; Tseng, C.H.; Chen, C.A.; Tang, S.L. The dynamics of microbial partnerships in the coral Isopora palifera. ISME J. 2011, 5, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Försterra, G.; Häussermann, V. Unusual symbiotic relationships between microendolithic phototrophic organisms and azooxanthellate cold-water corals from Chilean fjords. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 370, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesser, M.P.; Falcón, L.I.; Rodríguez-Román, A.; Enríquez, S.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Iglesias-Prieto, R. Nitrogen fixation by symbiotic cyanobacteria provides a source of nitrogen for the scleractinian coral Montastraea cavernosa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 346, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, R.V.; Willner-Hall, D.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Desnues, C.; Edwards, R.A.; Angly, F.; Dinsdale, E.; Kelly, L.; Rohwer, F. Metagenomic analysis of stressed coral holobionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2148–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, F.; Breitbart, M.; Jara, J.; Azam, F.; Knowlton, N. Diversity of bacteria associated with the Caribbean coral Montastraea franksi. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, F.; Seguritan, V.; Azam, F.; Knowlton, N. Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, R.R. Photoadaptations of the Caribbean colonial ascidian-cyanophyte symbiosis Trididemnum solidum. Biol. Bull. 1986, 170, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, E. Ascidian photosymbiosis: Diversity of cyanobacterial transmission during embryogenesis. Genesis 2015, 53, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, P.L.; Fidler, A.E.; Hopkins, G.A.; Wood, S.A. Geographically conserved microbiomes of four temperate water tunicates. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donia, M.S.; Fricke, W.F.; Partensky, F.; Cox, J.; Elshahawi, S.I.; White, J.R.; Phillippy, A.M.; Schatz, M.C.; Piel, J.; Haygood, M.G.; et al. Complex microbiome underlying secondary and primary metabolism in the tunicate-Prochloron symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1423–E1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkinson, C.S.; Carpenter, E.J.; Capone, D.G. Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. Estuaries 1985, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.P.; Stochaj, W.R. Photoadaptation and protection against active forms of oxygen in the symbiotic procaryote Prochloron sp. and its ascidian host. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kühl, M.; Behrendt, L.; Staal, M.; Cristescu, S.M.; Harren, F.J.M.; Schliep, M.; Larkum, A.W.D. Reactive oxygen production induced by near-infrared radiation in three strains of the Chl d-containing cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina. F1000Research 2013, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sings, H.L.; Bible, K.C.; Rinehart, K.L. Acyl tunichlorins: A new class of nickel chlorins isolated from the Caribbean tunicate Trididemnum solidum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10560–10565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Opinion: Hijacking exogenous signals to generate new secondary metabolites during symbiotic interactions. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, J.M. Endosymbiosis and eukaryotic cell evolution. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R911–R921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Katz, M.E.; Knoll, A.H.; Quigg, A.; Raven, J.A.; Schofield, O.; Taylor, F.J.R. The evolution of modern eukaryotic phytoplankton. Science 2004, 305, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seymour, J.R.; Amin, S.A.; Raina, J.B.; Stocker, R. Zooming in on the phycosphere: The ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decelle, J.; Colin, S.; Foster, R.A. Photosymbiosis in marine planktonic protists. In Marine Protists: Diversity and Dynamics; Ohtsuka, S., Suzaki, T., Horiguchi, T., Suzuki, N., Not, F., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 465–500. ISBN 9784431551300. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, R.A.; Kuypers, M.M.M.; Vagner, T.; Paerl, R.W.; Musat, N.; Zehr, J.P. Nitrogen fixation and transfer in open ocean diatom-cyanobacterial symbioses. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janson, S. Cyanobacteria in symbiosis with diatoms. In Cyanobacteria in Symbiosis; Rai, A.N., Bergman, B., Rasmussen, U., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-1-4020-0777-4. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Foster, R.A. Marine cyanobacterial symbioses. In Cyanobacteria in Symbiosis; Rai, A.N., Bergman, B., Rasmussen, U., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 10–17. ISBN 0306480050. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.W.; Zehr, J.P. Cellular interactions: Lessons from the nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 2013, 49, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.A.; Reis, A. Microalgal symbiosis in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5839–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Koch, F.; Gobler, C.J. Most harmful algal bloom species are vitamin B1 and B12 auxotrophs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20756–20761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, S.; Lyu, S.; An, Y.; Lu, J.; Gjermansen, C.; Schramm, A. Microalgae–bacteria symbiosis in microalgal growth and biofuel production: A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmermann, E. Die Algenflora der Sandwich-Inseln. Ergebnisse einer Reise nach dem Pacific, H. Schauinsland 1896/97. Engler Bot. Jb. 1905, 34, 607–663. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, J.A.; Foster, R.A.; Tripp, H.J.; Carter, B.J.; Zehr, J.P.; Villareal, T.A. Genomic deletions disrupt nitrogen metabolism pathways of a cyanobacterial diatom symbiont. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Janson, S. Intracellular cyanobacterial symbionts in the marine diatom Climacodium frauenfeldianum (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Cabello, A.M.; Salazar, G.; Sánchez-Baracaldo, P.; Lima-Mendez, G.; Hingamp, P.; Alberti, A.; Sunagawa, S.; Bork, P.; De Vargas, C.; et al. Cyanobacterial symbionts diverged in the late Cretaceous towards lineage-specific nitrogen fixation factories in single-celled phytoplankton. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Muñoz-Marín, M.d.C.; Turk-Kubo, K.A.; Royo-Llonch, M.; Farnelid, H.; Acinas, S.G.; Zehr, J.P. UCYN-A3, a newly characterized open ocean sublineage of the symbiotic N2-fixing cyanobacterium Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.; Carter, B.J.; Turk-Kubo, K.; Malfatti, F.; Azam, F.; Zehr, J.P. Genetic diversity of the unicellular nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria UCYN-A and its Prymnesiophyte host. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 3238–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.P.; Waterbury, J.B.; Turner, P.J.; Montoya, J.P.; Omoregie, E.; Steward, G.F.; Hansen, A.; Karl, D.M. Unicellular cyanobacteria fix N2 in the subtropical north Pacific Ocean. Nature 2001, 412, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisander, P.H.; Beinart, R.A.; Hewson, I.; White, A.E.; Johnson, K.S.; Carlson, C.A.; Montoya, J.P.; Zehr, J.P. Unicellular cyanobacterial distributions broaden the oceanic N2 fixation domain. Science 2010, 327, 1512–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalera, L.; Reguera, B.; Takishita, K.; Yoshimatsu, S.; Koike, K.; Koike, K. Cyanobacterial endosymbionts in the benthic dinoflagellate Sinophysis canaliculata (Dinophysiales, Dinophyceae). Protist 2011, 162, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, O.; Mayama, S.; Matsuoka, A. Host-symbiont associations of polycystine Radiolaria: Epifluorescence microscopic observation of living Radiolaria. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2003, 49, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, I.A.N. Symbionts of the tropical dinophysiales (Dinophyceae). Ophelia 1991, 33, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnelid, H.; Tarangkoon, W.; Hansen, G.; Hansen, P.J.; Riemann, L. Putative N2-fixing heterotrophic bacteria associated with dinoflagellate-cyanobacteria consortia in the low-nitrogen Indian Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 61, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuasa, T.; Horiguchi, T.; Mayama, S.; Matsuoka, A.; Takahashi, O. Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of cyanobacterial symbionts in Dictyocoryne profunda (polycystine radiolaria). Symbiosis 2012, 57, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.; Matsuoka, A. Endocytoplasmic microalgae and bacteroids within the central capsule of the radiolarian Dictyocoryne truncatum. Symbiosis 1992, 12, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo, S.; Miyashita, H.; Murakami, A.; Takeyama, H.; Tsuchiya, T.; Mimuro, M. Molecular detection of epiphytic Acaryochloris spp. on marine macroalgae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7912–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armitage, A.R.; Frankovich, T.A.; Fourqurean, J.W. Variable responses within epiphytic and benthic microalgal communities to nutrient enrichment. Hydrobiologia 2006, 569, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankovich, T.A.; Armitage, A.R.; Wachnicka, A.H.; Gaiser, E.E.; Fourqurean, J.W. Nutrient effects on seagrass epiphyte community structure in Florida bay. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uku, J.; Björk, M. The distribution of epiphytic algae on three Kenyan seagrass species. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2001, 67, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamisi, M.I.; Lyimo, T.J.; Muruke, M.H.S.; Bergman, B. Nitrogen fixation by epiphytic and epibenthic diazotrophs associated with seagrass meadows along the Tanzanian coast, Western Indian Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Issa, A.A.; Abd-Alla, M.H.; Ohyam, T. Nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria: Future prospect. In Advances in Biology and Ecology of Nitrogen Fixation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobara, S.; McCalley, C.; Koba, K.; Giblin, A.E.; Weiss, M.S.; Gettel, G.M.; Shaver, G.R. Nitrogen fixation in surface soils and vegetation in an arctic tundra watershed: A key source of atmospheric nitrogen. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2006, 38, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruocco, N.; Mutalipassi, M.; Pollio, A.; Costantini, S.; Costantini, M.; Zupo, V. First evidence of Halomicronema metazoicum (Cyanobacteria) free-living on Posidonia oceanica leaves. PLoS ONE 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Vives, C.; Taboada, S.; Leiva, C.; Busch, K.; Hentschel, U.; Riesgo, A. On the way to specificity—Microbiome reflects sponge genetic cluster primarily in highly structured populations. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 4412–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkema, D.; de Caralt, S.; Morillo, J.A.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Smidt, H.; Uriz, M.J. Similar sponge-associated bacteria can be acquired via both vertical and horizontal transmission. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3807–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: Love and other relationships. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, C.R. Microbial associations in sponges. III. Ultrastructure of the in situ associations in coral reef sponges. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R.; Fay, P. Nitrogen fixation in coral reef sponges with symbiotic Cyanobacteria. Nature 1979, 279, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R. Net primary productivity in coral reef sponges. Science 1983, 219, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usher, K.M.; Kuo, J.; Fromont, J.; Sutton, D.C. Vertical transmission of cyanobacterial symbionts in the marine sponge Chondrilla australiensis (Demospongiae). Hydrobiologia 2001, 461, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, V.; Mutalipassi, M.; Ruocco, N.; Glaviano, F.; Pollio, A.; Langellotti, A.L.; Romano, G.; Costantini, M. Distribution of toxigenic Halomicronema spp. In adjacent environments on the island of ischia: Comparison of strains from thermal waters and free living in Posidonia oceanica meadows. Toxins 2019, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Britstein, M.; Cerrano, C.; Burgsdorf, I.; Zoccarato, L.; Kenny, N.J.; Riesgo, A.; Lalzar, M.; Steindler, L. Sponge microbiome stability during environmental acquisition of highly specific photosymbionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3593–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindler, L.; Huchon, D.; Avni, A.; Ilan, M. 16S rRNA phylogeny of sponge-associated cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4127–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erwin, P.M.; Thacker, R.W. Cryptic diversity of the symbiotic cyanobacterium Synechococcus spongiarum among sponge hosts. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 2937–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaby, B.M.; Hentsche, U. Draft genome sequences of Candidatus Synechococcus spongiarum, cyanobacterial symbionts of the mediterranean sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00268-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thacker, R.W.; Starnes, S. Host specificity of the symbiotic cyanobacterium Oscillatoria spongeliae in marine sponges, Dysidea spp. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, S.E.; Blum, J.E.; Leichter, J.J.; Pawlik, J.R. Bleaching of the giant barrel sponge Xestospongia muta in the Florida Keys. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarà, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Cattaneo-vietti, R.; Cerrano, C. Endosymbiosis in sponges: Relevance for epigenesis and evolution. Symbiosis 1998, 25, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara, P.; Caroppo, C. Cytotoxic and antimitotic activities in aqueous extracts of eight cyanobacterial strains isolated from the marine sponge Petrosia ficiformis. Toxicon 2011, 57, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, D.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E.; Gkelis, S. Sponges-cyanobacteria associations: Global diversity overview and new data from the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstantinou, D.; Mavrogonatou, E.; Zervou, S.K.; Giannogonas, P.; Gkelis, S. Bioprospecting sponge-associated marine Cyanobacteria to produce bioactive compounds. Toxins 2020, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, D.M.; Pfitzner, J.; Trott, L.A. Deposition and cycling of carbon and nitrogen in carbonate mud of the lagoons of Arlington and Sudbury Reefs, Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2006, 25, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, R.E.; Alberts, J.; D’Elia, C.; Kinzie, R.A.; Pomeroy, L.R.; Sottile, W.; Wiebe, W.; Marsh, J.A.; Helfrich, P.; Maragos, J.; et al. The metabolism of some coral reef communities: A team study of nutrient and energy flux at Eniwetok. Bioscience 1972, 22, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, K.L.; DuPaul, W.D.; Wlebe, W.; Sottile, W.; Johannes, R.E.; Wiebe, W.; Sottile, W.; Johannes, R.E. Enewetak (Eniwetok) Atoll: Aspects of the nitrogen cycle on a coral reef. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marubini, F.; Davies, P.S. Nitrate increases zooxanthellae population density and reduces skeletogenesis in corals. Mar. Biol. 1996, 127, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furla, P.; Allemand, D.; Shick, J.M.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Richier, S.; Plantivaux, A.; Merle, P.L.; Tambutté, S. The symbiotic anthozoan: A physiological chimera between alga and animal. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, M.M.; Sebens, K.P. Ingestion and assimilation of nitrogen from benthic sediments by three species of coral. Mar. Biol. 2004, 145, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.M.; Lipschultz, F.; Sebens, K.P. Particulate matter ingestion and associated nitrogen uptake by four species of scleractinian corals. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlbrèque, F.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. Heterotrophy in tropical scleractinian corals. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Witting, J.; Tambutté, E.; Sebens, K.P. Effect of natural zooplankton feeding on the tissue and skeletal growth of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Coral Reefs 2003, 22, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, V.N.; Grover, R.; Maguer, J.F.; Fine, M.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. The assimilation of diazotroph-derived nitrogen by scleractinian corals depends on their Metabolic Status. MBio 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benavides, M.; Houlbreque, F.; Camps, M.; Lorrain, A.; Grosso, O.; Bonnet, S. Diazotrophs: A non-negligible source of nitrogen for the tropical coral Stylophora pistillata. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimes, N.E.; Johnson, W.R.; Torralba, M.; Nelson, K.E.; Weil, E.; Morris, P.J. The Montastraea faveolata microbiome: Ecological and temporal influences on a Caribbean reef-building coral in decline. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimes, N.E.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Weil, E.; Zhou, J.; Morris, P.J. Microbial functional structure of Montastraea faveolata, an important Caribbean reef-building coral, differs between healthy and yellow-band diseased colonies. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchka, M.E.; Hewson, I.; Harvell, C.D. Coral-associated bacterial assemblages: Current knowledge and the potential for climate-driven impacts. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissimov, J.; Rosenberg, E.; Munn, C.B. Antimicrobial properties of resident coral mucus bacteria of Oculina patagonica. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 292, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, K.B. Regulation of microbial populations by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 322, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnit-Orland, M.; Sivan, A.; Kushmaro, A. Antibacterial activity of Pseudoalteromonas in the coral holobiont. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypien, K.L.; Ward, J.R.; Azam, F. Antagonistic interactions among coral-associated bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, K.B.; Smith, G.W. Microbial communities of coral surface mucopolysaccharide layers. In Coral Health and Disease; Rosenberg, E., Loya, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 259–264. ISBN 978-3-642-05863-9. [Google Scholar]
- Guppy, R.; Bythell, J.C. Environmental effects on bacterial diversity in the surface mucus layer of the reef coral Montastraea faveolata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 328, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, A.M. Changes in Bacterial Communities, Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics on Coral Surfaces Following Mortality: Potential Implications for Reef Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Queensland, St. Lucia, QLD, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Reshef, L.; Koren, O.; Loya, Y.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. The coral probiotic hypothesis. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ainsworth, T.D.; Krause, L.; Bridge, T.; Torda, G.; Raina, J.B.; Zakrzewski, M.; Gates, R.D.; Padilla-Gamiño, J.L.; Spalding, H.L.; Smith, C.; et al. The coral core microbiome identifies rare bacterial taxa as ubiquitous endosymbionts. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.J.; Croquer, A.; Bythell, J.C. Bacterial assemblages differ between compartments within the coral holobiont. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, S.H.; Fine, M.; Kühl, M. Light microclimate of endolithic phototrophs in the scleractinian corals Montipora monasteriata and Porites cylindrica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, J.M.; Cairns, S.D. Cold-water corals in a changing ocean. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 7, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavaleye, M.; Duineveld, G.; Lundälv, T.; White, M.; Guihen, D.; Kiriakoulakis, K.; Wolff, G.A. Cold water corals on the Tisler reef preliminary observations on the dynamic reef environment. Oceanography 2009, 22, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, C.E.; Larsson, A.I.; Veuger, B.; Middelburg, J.J.; Van Oevelen, D. Opportunistic feeding on various organic food sources by the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Mueller, C.E.; Veuger, B.; Larsson, A.I.; Form, A.; Van Oevelen, D. Discovery of symbiotic nitrogen fixation and chemoautotrophy in cold-water corals. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neulinger, S.C.; Järnegren, J.; Ludvigsen, M.; Lochte, K.; Dullo, W.C. Phenotype-specific bacterial communities in the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia) and their implications for the coral’s nutrition, health, and distribution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7272–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellogg, C.A.; Lisle, J.T.; Galkiewicz, J.P. Culture-independent characterization of bacterial communities associated with the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2294–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Försterra, G.; Beuck, L.; Häussermann, V.; Freiwald, A. Shallow-water Desmophyllum dianthus (Scleractinia) from Chile: Characteristics of the biocoenoses, the bioeroding community, heterotrophic interactions and (paleo)-bathymetric implications. In Cold-Water Corals and Ecosystems; Freiwald, A., Roberts, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 937–977. ISBN 978-3-540-24136-2. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter, D.; Zscharnack, B.; Krisch, H. Transfer of photoassimilates from endolithic algae to coral tissue. Naturwissenschaften 1995, 82, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradoville, M.R.; White, A.E.; Letelier, R.M. Physiological response of Crocosphaera watsonii to enhanced and fluctuating carbon dioxide conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabir, T.; Dhanya, V.; Jesmi, Y.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Saravanane, N.; Gupta, G.V.M.; Hatha, A.A.M. Occurrence and distribution of a Diatom-Diazotrophic Cyanobacteria association during a Trichodesmium bloom in the southeastern Arabian Sea. Int. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Fu, F.X.; Zhang, Y.; Warner, M.E.; Feng, Y.; Portune, K.; Bernhardt, P.W.; Mulholland, M.R. CO2 control of Trichodesmium N2 fixation, photosynthesis, growth rates, and elemental ratios: Implications for past, present, and future ocean biogeochemistry. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, D.; Kranz, S.A.; Kim, J.M.; Morel, F.M.M. Ocean acidification slows nitrogen fixation and growth in the dominant diazotroph Trichodesmium under low-iron conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3094–E3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rädecker, N.; Meyer, F.W.; Bednarz, V.N.; Cardini, U.; Wild, C. Ocean acidification rapidly reduces dinitrogen fixation associated with the hermatypic coral Seriatopora hystrix. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 511, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glasl, B.; Herndl, G.J.; Frade, P.R. The microbiome of coral surface mucus has a key role in mediating holobiont health and survival upon disturbance. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fermé, C.; Mateos, M.V.; Szyldergemajn, S.; Corrado, C.S.; Zucca, E.; Extremera, S.; Gianni, A.M.; Vandermeeren, A.; Ribrag, V. Aplidin® (Plitidepsin) activity In peripheral T-Cell lymphoma (PTCL): Final results. Blood 2010, 116, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.M.; Mandrekar, S.; Sanford, B.L.; Geyer, S.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Dohner, K.; Thiede, C.; Marcucci, G.; Lo-Coco, F.; Klisovic, R.B.; et al. The multi-kinase inhibitor midostaurin (M) prolongs survival compared with placebo (P) in combination with daunorubicin (D)/cytarabine (C) induction (ind), high-dose C consolidation (consol), and as maintenance (maint) therapy in newly diagnosed acute mye. Blood 2015, 126, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levis, M.; Ravandi, F.; Wang, E.S.; Baer, M.R.; Perl, A.; Coutre, S.; Erba, H.; Stuart, R.K.; Baccarani, M.; Cripe, L.D.; et al. Results from a randomized trial of salvage chemotherapy followed by lestaurtinib for patients with FLT3 mutant AML in first relapse. Blood 2011, 117, 3294–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saif, M.W.; Diasio, R.B. Edotecarin: A novel topoisomerase I inhibitor. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2005, 5, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.W.; Donia, M.S. Life in cellulose houses: Symbiotic bacterial biosynthesis of ascidian drugs and drug leads. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z. Advances in marine symbiotic cyanobacteria. In Handbook on Cyanobacteria: Biochemistry, Biotechnology and Applications; Gault, P.M., Marler, H.J., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 464–472. ISBN 9781607410928. [Google Scholar]
- López-Legentil, S.; Turon, X.; Espluga, R.; Erwin, P.M. Temporal stability of bacterial symbionts in a temperate ascidian. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sings, H.L.; Rinehart, K.L. Compounds produced from potential tunicate-blue-green algal symbiosis: A review. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 17, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukimoto, M.; Nagaoka, M.; Shishido, Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Nishisaka, F.; Matsumoto, S.; Harunari, E.; Imada, C.; Matsuzaki, T. Bacterial production of the tunicate-derived antitumor cyclic depsipeptide didemnin B. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2329–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Kersten, R.D.; Nam, S.J.; Lu, L.; Al-Suwailem, A.M.; Zheng, H.; Fenical, W.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Moore, B.S.; Qian, P.Y. Bacterial biosynthesis and maturation of the didemnin anti-cancer agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8625–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, K.; Yamada, L.; Satou, Y.; Azuma, J.I.; Satoh, N. The evolutionary origin of animal cellulose synthase. Dev. Genes Evol. 2004, 214, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehal, P.; Satou, Y.; Campbell, R.K.; Chapman, J.; Degnan, B.; De Tomaso, A.; Davidson, B.; Di Gregorio, A.; Gelpke, M.; Goodstein, D.M.; et al. The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: Insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science 2002, 298, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grube, M.; Seckbach, J.; Muggia, L.; Small, D.P.; Bishop, C.D. Trade-Offs of symbiotic relationships between aquatic hosts and algae in a changing world. In Algal and Cyanobacteria Symbioses; World Scientific Publishing Europe Ltd.: London, UK, 2017; pp. 241–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacalli, T.C. Protochordate body plan and the evolutionary role of larvae: Old controversies resolved? Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, D.J. Ascidian toxins with potential for drug development. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luesch, H.; Harrigan, G.; Goetz, G.; Horgen, F. The cyanobacterial origin of potent anticancer agents originally isolated from Sea Hares. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 9, 1791–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, J.C.; Elhai, J. Regulation of cellular differentiation in filamentous Cyanobacteria in free-living and plant-associated symbiotic growth states. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 94–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meeks, J.C. Symbiotic interactions between Nostoc punctiforme, a multicellular cyanobacterium, and the hornwort Anthoceros punctatus. Symbiosis 2003, 35, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Meeks, J.C. Physiological adaptations in nitrogen-fixing Nostoc–plant symbiotic associations. In Prokaryotic Symbionts in Plants; Pawlowski, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 181–205. ISBN 978-3-540-75460-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, F.C.Y.; Meeks, J.C. Establishment of a functional symbiosis between the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme and the bryophyte Anthoceros punctatus requires genes involved in nitrogen control and initiation of heterocyst differentiation. Microbiology 2002, 148, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, M.; Rasmussen, U.; Bergman, B. Cyanobacterial chemotaxis to extracts of host and nonhost plants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A.M.; Rasmussen, U.; Bateman, K.; Huss-Danell, K.; Lindwall, S.; Bergman, B. Arabinogalactan proteins are expressed at the symbiotic interface in root nodules of Alnus spp. New Phytol. 2002, 155, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, H.; Galun, M.; Ott, S.; Jahns, H.M.; Fleminger, G. Cephalodia of the lichen Peltigera aphthosa (L.) Willd. Specific recognition of the compatible photobiont. Symbiosis 2000, 29, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Rikkinen, J. Cyanolichens: An evolutionary overview. In Cyanobacteria in Symbiosis; Rai, A.N., Bergman, B., Rasmussen, U., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 31–72. ISBN 978-0-306-48005-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sacristán, M.; Millanes, A.M.; Legaz, M.E.; Vicente, C. A lichen lectin specifically binds to the α-1,4-polygalactoside moiety of urease located in the cell wall of homologous algae. Plant Signal. Behav. 2006, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, E.L.; Wong, F.C.Y.; Meeks, J.C. DNA binding properties of the HrmR protein of Nostoc punctiforme responsible for transcriptional regulation of genes involved in the differentiation of hormogonia. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ungerer, J.L.; Pratte, B.S.; Thiel, T. Regulation of fructose transport and its effect on fructose toxicity in Anabaena spp. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 8115–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, D.G.; Duggan, P.S. Signalling in cyanobacteria–Plant symbioses. In Signaling and Communication in Plant Symbiosis; Baluska, S., Perotto, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 93–121. ISBN 9783642209666. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, K.; Tripathi, J.K.; Pareek, A.; Sharma, D.K. Growth and secretome analysis of possible synergistic interaction between green algae and cyanobacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.L.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Carrapiço, F. Volatile compounds from the symbiotic system Azolla filiculoides-Anabaena azollae bacteria. Plant Biosyst. 2009, 143, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, G.; Baldi, F.; Renzone, G.; Gallo, M.; Cordaro, A.; Scaloni, A.; Puglia, A.M. Adaptative biochemical pathways and regulatory networks in Klebsiella oxytoca BAS-10 producing a biotechnologically relevant exopolysaccharide during Fe(III)-citrate fermentation. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafner, C.; Jung, K.; Schüürmann, G. Effects of trichloroacetic acid on the nitrogen metabolism of Pinus sylvestris—A 13C/15N tracer study. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Mazmanian, S.K. Innate immune recognition of the microbiota promotes host-microbial symbiosis. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Clarke, T.B. The regulation of host defences to infection by the microbiota. Immunology 2017, 150, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenstiel, P.; Philipp, E.E.R.; Schreiber, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. Evolution and function of innate immune receptors—Insights from marine invertebrates. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bufe, B.; Zufall, F. The sensing of bacteria: Emerging principles for the detection of signal sequences by formyl peptide receptors. Biomol. Concepts 2016, 7, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J.; Goldsworthy, S.M.; Barnes, A.A.; Eilert, M.M.; Tcheang, L.; Daniels, D.; Muir, A.I.; Wigglesworth, M.J.; Kinghorn, I.; Fraser, N.J.; et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11312–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steindler, L.; Schuster, S.; Ilan, M.; Avni, A.; Cerrano, C.; Beer, S. Differential gene expression in a marine sponge in relation to its symbiotic state. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demay, J.; Bernard, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Marie, B. Natural products from cyanobacteria: Focus on beneficial activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Jokela, J.; Herfindal, L.; Wahlsten, M.; Sinkkonen, J.; Permi, P.; Fewer, D.P.; Døskeland, S.O.; Sivonen, K. 4-Methylproline guided natural product discovery: Co-occurrence of 4-hydroxy- and 4-methylprolines in nostoweipeptins and nostopeptolides. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, E.J.N.; Piel, J. Biosynthesis of polyketides by trans-AT polyketide synthases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 231–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narquizian, R.; Kocienski, P.J. The pederin family of antitumor agents: Structures, synthesis and biological activity. In The Role of Natural Products In Drug Discovery; Mulzer, J., Bohlmann, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 25–56. ISBN 978-3-662-04042-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Nishimura, S.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Horinouchi, S.; Yoshida, M. Inhibition of protein synthesis and activation of stress-activated protein kinases by onnamide A and theopederin B, antitumor marine natural products. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, E.J.; Lacroix, C. Microbe-microbe interactions in mixed culture food fermentations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavšić, M.; Terzic, S.; Ahel, M.; Van Den Berg, C.M.G. Folic acid in coastal waters of the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 53, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, K.E.; Lawrence, A.D.; Holzer, A.; Kudahl, U.J.; Sasso, S.; Kräutler, B.; Scanlan, D.J.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Cyanobacteria and Eukaryotic algae use different chemical variants of vitamin B12. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, S.; Novak, A.C.; Sydney, E.B.; Soccol, V.T.; Carvalho, J.C.; Pandey, A.; Noseda, M.D.; Tholozan, J.L.; Lorquin, J.; Soccol, C.R. Co-culture of microalgae, cyanobacteria, and macromycetes for exopolysaccharides production: Process preliminary optimization and partial characterization. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, E.W.; Nelson, J.T.; Rasko, D.A.; Sudek, S.; Eisen, J.A.; Haygood, M.G.; Ravel, J. Patellamide A and C biosynthesis by a microcin-like pathway in Prochloron didemni, the cyanobacterial symbiont of Lissoclinum patella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7315–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Coll, J.C.; Bourne, D.J.; MacLeod, J.K.; Zabriskie, T.M.; Ireland, C.M.; Bowden, B.F. Patellins 1-6 and trunkamide A: Novel cyclic hexa-, hepta- and octa-peptides from colonial ascidians, Lissoclinum sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.P.; Liu, L.N.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.C. Factors that effect antioxidant activity of c-phycocyanins from Spirulina platensis. J. Food Biochem. 2005, 29, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.N.; Sonani, R.R.; Jakharia, K.; Bhastana, B.; Patel, H.M.; Chaubey, M.G.; Singh, N.K.; Madamwar, D. Antioxidant activity and associated structural attributes of Halomicronema phycoerythrin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Huang, B. Photosensitization of phycocyanin extracted from Microcystis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Implication of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2012, 117, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattarayan, D.; Rajarajan, D.; Ayyanar, S.; Palanichamy, R.; Subbiah, R. C-phycocyanin suppresses transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition in human epithelial cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, B.; Chu, X.M.; Lv, C.Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Yang, P. Molecular mechanism of inhibitory effects of C-phycocyanin combined with all-trans-retinoic acid on the growth of HeLa cells in vitro. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 5619–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, W.; Yang, R.; Zhang, E.; Ying, J.; Xu, T.; Yi, H.; et al. Spirulina phycocyanin induces differential protein expression and apoptosis in SKOV-3 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam, R.; Suresh, V.; Princy, W.A.; Rajkumar, M.; Senthilkumar, N.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rengasamy, R.; Anbazhagan, C.; Kaveri, K.; Kannan, S. C-Phycocyanin from Oscillatoria tenuis exhibited an antioxidant and in vitro antiproliferative activity through induction of apoptosis and G 0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Cheng, N.; Lin, L.; Zhang, C. Inhibitory effect of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis on the growth of human leukemia K562 cells. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Lin, C.; Pan, R.; Zhou, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, E.; Ren, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of phycocyanin inhibitory effects on SKOV-3 cell proliferation. Gene 2016, 585, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Ji, H.; Li, B. C-Phycocyanin exerts anti-cancer effects via the MAPK signaling pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shridhar, D.M.P.; Mahajan, G.B.; Kamat, V.P.; Naik, C.G.; Parab, R.R.; Thakur, N.R.; Mishra, P.D. Antibacterial activity of 2-(2′,4′-dibromophenoxy)-4,6- dibromophenol from Dysidea granulosa. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehraus, S.; König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Woerheide, G. Leucamide A: A new cytotoxic heptapeptide from the Australian sponge Leucetta microraphis. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 4989–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, D.; Kim, D.W.; Park, H.S. Cyclic peptides: Promising scaffolds for biopharmaceuticals. Genes 2018, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, D.; Burgoyne, D.L.; Rettig, S.J.; Andersen, R.J.; Fathi-Afshar, Z.R.; Allen, T.M. The isolation of majusculamide C from the sponge Ptilocaulis trachys collected in Enewetak and determination of the absolute configuration of the 2-methyl-3-aminopentanoic acid residue. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.E. Cyclic peptides and depsipeptides from cyanobacteria: A review. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1996, 16, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahila, N.K.; Prakash, S.; Manikandan, B.; Ravindran, J.; Prabhu, N.M.; Kannapiran, E. Bio-prospecting of coral (Porites lutea) mucus associated bacteria, Palk Bay reefs, Southeast coast of India. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.E.; Bythell, J.C. Perspectives on mucus secretion in reef corals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 296, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liyanage, T.D.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Edirisinghe, S.L.; Nikapitiya, C.; Heo, G.J.; de Zoysa, M.; Whang, I. Biological activity of porcine gastric mucin on stress resistance and immunomodulation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosic, N.N. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Making the foundation for organic personalised sunscreens. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheewinthamrongrod, V.; Kageyama, H.; Palaga, T.; Takabe, T.; Waditee-Sirisattha, R. DNA damage protecting and free radical scavenging properties of mycosporine-2-glycine from the Dead Sea cyanobacterium in A375 human melanoma cell lines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 164, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 34, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, P.F.; Dunlap, W.C.; Battershill, C.N.; Jaspars, M. Shotgun cloning and heterologous expression of the patellamide gene cluster as a strategy to achieving sustained metabolite production. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, E.; Turon, X.; López-Legentil, S.; Erwin, P.M.; Hirose, M. First records of didemnid ascidians harbouring Prochloron from Caribbean Panama: Genetic relationships between Caribbean and Pacific photosymbionts and host ascidians. Syst. Biodivers. 2012, 10, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.W.; Sudek, S.; Haygood, M.G. Genetic evidence supports secondary metabolic diversity in Prochloron spp., the cyanobacterial symbiont of a tropical ascidian. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, C.; Scheuer, P.J. Ulicyclamide and ulithiacyclámide, two new small peptides from a marine tunicate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 5688–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, R.; Dahiya, S.; Fuloria, N.K.; Kumar, S.; Mourya, R.; Chennupati, S.V.; Jankie, S.; Gautam, H.; Singh, S.; Karan, S.K.; et al. Natural bioactive thiazole-based peptides from marine resources: Structural and pharmacological aspects. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Vasconcelos, V. Cyanobactins from cyanobacteria: Current genetic and chemical state of knowledge. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6910–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donia, M.S.; Hathaway, B.J.; Sudek, S.; Haygood, M.G.; Rosovitz, M.J.; Ravel, J.; Schmidt, E.W. Natural combinatorial peptide libraries in cyanobacterial symbionts of marine ascidians. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donia, M.S.; Fricke, W.F.; Ravel, J.; Schmidt, E.W. Variation in tropical reef symbiont metagenomes defined by secondary metabolism. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichota, A.; Gwozdzinski, K. Anticancer activity of natural compounds from plant and marine environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Sheng, J.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, X.K.; Sun, M. Antitumor peptides from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1840–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCauley, E.P.; Piña, I.C.; Thompson, A.D.; Bashir, K.; Weinberg, M.; Kurz, S.L.; Crews, P. Highlights of marine natural products having parallel scaffolds found from marine-derived bacteria, sponges, and tunicates. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 504–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Amaral, S.C.; Santos, A.V.; da Cruz Schneider, M.P.; da Silva, J.K.R.; Xavier, L.P. Determination of volatile organic compounds and antibacterial activity of the amazonian cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain GFB01. Molecules 2020, 25, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Host | Cyanobacteria | Interaction | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microalgae (or photosynthetic protists) | |||
| Bacillariophyta—Rhizosolenia, Hemiaulus, Guinardia and Chaetoceros | Richelia intracellularis and Calothrix rhizosoleniae | Nitrogen fixing | [18,40] |
| Bacillariophyta—Climacodium frauenfeldianum | Crocosphaera watsonii | Nitrogen fixing | [41] |
| Bacillariophyta—Streptotheca and Neostrepthotheca | Crocosphaera watsonii | Nitrogen fixing | [42] |
| Solenicola setigera and Bacillariophyta—Leptocylindrus mediterraneus | Synechoccus sp. | Nitrogen fixing and photosynthesis | [43,44] |
| Haptophyta—Braarudosphaera bigelowii | Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa | Nitrogen fixing. Cyanobacterium lack in oxygen-evolving photosystem II (PSII), RuBisCo for CO2 fixation, and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) | [45,46,47,48,49] |
| Non-photosynthetic protists | |||
| Dinoflagellates | Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus | Nitrogen fixing | [50,51] |
| Tintinnids, Dinoflagellates, Radiolarians, | Synechococcus | Nitrogen fixing | [51,52] |
| Macroalgae | |||
| Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis | Acaryochloris marina | Not reported | [53] |
| Acanthophora spicifera | Lynbya sp. | Nutrient supply | [54] |
| Codium decorticatum | Calothrix, Anabaena and Phormidium | Nitrogen fixing | [55,56] |
| Seagrasses | |||
| Thalassia testudinum | unidentified | Carbon fixation | [57,58] |
| Cymodocea rotundata | Calothrix, Anabaena | Nitrogen fixing | [59] |
| Sponge | |||
| Petrosia ficiformis | Halomicronema metazoicum | Not reported | [60] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Halomicronema cf. metazoicum | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Cyanobium sp. | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Synechococcus sp. | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Pseudoanabaena sp. 1 | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Pseudoanabaena sp. 2 | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Leptolyngbya ectocarpi | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Undetermined Oscillatoriales | Production of secondary metabolites | [61] |
| Petrosia ficiformis | Aphanocapsa feldmannii | Food supply | [62,63] |
| Chondrilla nucula | Not classified | Feeding | [63] |
| Dysidea herbacea | Oscillatoria spongeliae | Defensive ecological role—production of toxic compounds | [64,65] |
| Leucetta microraphis | Not classified | Defensive ecological role—production of toxic compounds | [66] |
| Ptilocaulis trachys | Not classified | Defensive ecological role—production of toxic compounds | [66] |
| Cnidaria | |||
| Acropora hyacintus and A. cytherea | Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus | Nitrogen fixing | [67] |
| Montastraea cavernosa | Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus | Nitrogen Fixing and Photoprotective or photosynthesis | [4] |
| Acropora millepora | Not classified | Nitrogen Fixing | [68,69,70] |
| Porites astreoides | Chroococcales, Nostocales, Oscillatoriales and Prochlorales | Nitrogen Fixing | [6] |
| Acropora muricata | Not classified | Not reported | [69] |
| Pocillopora damicornis | Not classified | Not reported | [69] |
| Isopora palifera | Chroococcidiopsis - Chroococcales | Nitrogen Fixing | [71] |
| Montipora flabellate and M. capitate | Fischerella UTEX1931; Trichodesmium sp.; Lyngbya majuscule; Cyanothece sp.; Gloeothece sp.; Synechocystis sp.; Myxosarcina sp.; Leptolyngbya boryana; Chlorogloeopsis sp.; Calothrix sp.; Tolypothrix sp.; Nostoc sp.; Anabaena sphaerica. | Nitrogen Fixing | [7] |
| Desmophyllum dianthus | Plectonema terebrans | Opportunistic feeding strategy | [72] |
| Caryophyllia huinayensis | Plectonema terebrans | Not reported | [72] |
| M. cavernosa, M. franksi and Diploria and Porites genus | Anabaena, Synechococcus, Spirulina, Trichodesmium, Lyngbya, Phormidium and Chroococcales cyanobacterium | Nitrogen Fixing Photoprotective compounds | [4,73,74,75,76] |
| Ascidians | |||
| Didemnum, Lissoclinum, Diplosoma and Trididemnum | Prochloron and Synechocystis | Secondary metabolites production | [77,78] |
| Botryllus schlosseri and Botrylloides leachii | Synechococcus related | Secondary metabolites production | [79] |
| Lissoclinum patella | Prochloron didemmi | Carbon and ammonia fixing; Oxidative stress protection | [80,81,82] |
| Lissoclinum patella | Acaryochloris marina | Not reported | [83] |
| Trididemnum solidum | Synechocystis trididemni | Production of biologically active molecules | [84,85] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mutalipassi, M.; Riccio, G.; Mazzella, V.; Galasso, C.; Somma, E.; Chiarore, A.; de Pascale, D.; Zupo, V. Symbioses of Cyanobacteria in Marine Environments: Ecological Insights and Biotechnological Perspectives. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040227
Mutalipassi M, Riccio G, Mazzella V, Galasso C, Somma E, Chiarore A, de Pascale D, Zupo V. Symbioses of Cyanobacteria in Marine Environments: Ecological Insights and Biotechnological Perspectives. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040227
Chicago/Turabian StyleMutalipassi, Mirko, Gennaro Riccio, Valerio Mazzella, Christian Galasso, Emanuele Somma, Antonia Chiarore, Donatella de Pascale, and Valerio Zupo. 2021. "Symbioses of Cyanobacteria in Marine Environments: Ecological Insights and Biotechnological Perspectives" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040227
APA StyleMutalipassi, M., Riccio, G., Mazzella, V., Galasso, C., Somma, E., Chiarore, A., de Pascale, D., & Zupo, V. (2021). Symbioses of Cyanobacteria in Marine Environments: Ecological Insights and Biotechnological Perspectives. Marine Drugs, 19(4), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040227