Structure Elucidation of Calyxoside B, a Bipolar Sphingolipid from a Marine Sponge Cladocroce sp. through the Use of Beckmann Rearrangement
Abstract
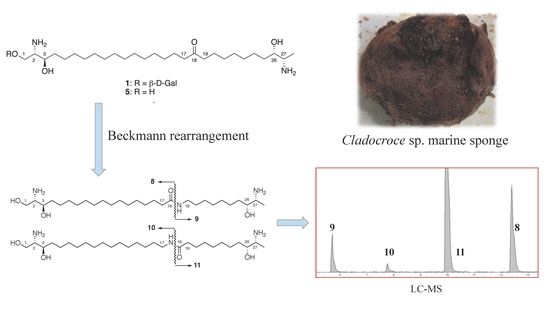
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Cytotoxic Constituents
2.2. Structure Elucidation
2.3. Biological Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Animal Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.3.1. Calyxoside B (1)
4.3.2. Calyxoside (2)
4.4. Determination of the Absolute Configuration of the Sugar Moiety
4.5. Preparation of 6 and 7
4.6. Modified Mosher’s Analysis
4.7. Preparation of 15
4.8. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.9. Analysis of Cytokine Production from Mouse Spleen Cells
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D.; Wei, L. Recent Advances in Deep-sea Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Takada, K.; Ise, Y.; Ohtsuka, S.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Microsclerodermins N and O, Cytotoxic Cyclic Peptides Containing a p-Ethoxy Phenyl Moiety from a Deep-Sea Marine Sponge Pachastrella sp. Tetrahedron 2020, 76, 130997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitora, Y.; Takada, K.; Ise, Y.; Woo, S.P.; Inoue, S.; Mori, N.; Takikawa, H.; Nakamukai, S.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Metachromins X and Y from a marine sponge Spongia sp. and their effects on cell cycle progression. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.-N.; Mattern, M.P.; Johnson, R.K.; Kingston, D.G.I. Structure and stereochemistry of a novel bioactive sphingolipid from a Calyx sp. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Guzzi, A.G.; Li, R.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Rhizochalins C and D from the Sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. A Rare threo-Sphingolipid and a Facile Method for Determination of the Carbonyl Position in r,ω-Bifunctionalized Ketosphingolipids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, Y.; Ishihara, K.; Yamamoto, H. Cyanuric Chloride as a Mild and Active Beckmann Rearrangement Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11240–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kashman, Y.; Kakisawa, H. High-field FT NMR application of Mosher’s method. The absolute configurations of marine terpenoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 4092–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.-P.; Pfander, H. Synthese und Strukturaufklarung von Merucathin und Pseudomerucathin. Zwei Inhaltstoffe von Cuthu edulis FORS. Helv. Chim. Acta 1986, 69, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, U.N.; Fusetani, N. Amaminols A and B, new bicyclic amino alcohols from an unidentified tunicate of the family Polyclinidae. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ueda, T.; Tomii, K.; Kouno, I. Facile discrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tashiro, T.; Mori, K. Fifteen Years since the Development of KRN7000—Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on Novel Glycosphingolipids Which Stimulate Natural Killer T Cells. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2010, 22, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Sekine-Kondo, E.; Tatayama, M.; Kasetthat, T.; Wongratanacheewin, S.; Watarai, H. New Genetically Manipulated Mice Provide Insights into the Development and Physiological Functions of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1671–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Molinski, T.F. Enantiodivergent Biosynthesis of the Dimeric Sphingolipid Oceanapiside from the Marine Sponge Oceanapia phillipensis. Determination of Remote Stereochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiratta, S.K.; Martin, W.D.; Hong, S.; Boesteanu, A.; Joyce, S.; Van Kaer, L. CD1d1 mutant mice are deficient in natural T cells that promptly produce IL-4. Immunity 1997, 6, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| No. | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC (Carbon Number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67.0, CH2 | 3.97 m | H-2 | 2, 1′ |
| 2 | 57.0, CH | 3.33 m | H-1, H-3 | |
| 3 | 70.3, CH | 3.76 m | H-2, H2-4 | |
| 4 | 34.2, CH2 | 1.46 m, 1.51 m | 5 | |
| 5 | 27.1, CH2 | 1.34 m, 1.53 m | ||
| 6–15 | 30.2–30.8, CH2 | 1.25–1.35 m | ||
| 16 | 24.9, CH2 | 1.54 m | H-17 | 17, 18 |
| 17 | 43.5, CH2 | 2.44 m | H-16 | 15, 16, 18 |
| 18 | 214.4, C | |||
| 19 | 43.5, CH2 | 2.44 m | H-20 | 18, 20, 21 |
| 20 | 24.9, CH2 | 1.54 m | H-19 | 18, 19 |
| 21–23 | 30.2–30.8, CH2 | 1.25–1.35 m | ||
| 24 | 26.3, CH2 | 1.38 m, 1.51 m | 25 | |
| 25 | 34.6, CH2 | 1.39 m, 1.54 m | 24 | |
| 26 | 73.2, CH | 3.42 m | H2-25, H-27 | |
| 27 | 53.4, CH | 3.08 m | H-26, H3-28 | 26, 28 |
| 28 | 16.0, CH3 | 1.25 d (6.7) | H-27 | 26, 27 |
| 1′ | 104.6, CH | 4.28 d (7.6) | H-2′ | 1 |
| 2′ | 72.4, CH | 3.52 dd (7.7) | H-1′, H-3′ | 1′, 3′ |
| 3′ | 74.8, CH | 3.48 dd (9.7, 3.3) | H-2′, H-4′ | 2′ |
| 4′ | 70.4, CH | 3.81 d (3.3) | H-3′ | 2′, 3′ |
| 5′ | 77.0, CH | 3.55 m | H2-6′ | 6′ |
| 6′a | 62.7, CH2 | 3.72 dd (11.4, 4.5) | H-5′, H-6′b | |
| 6′b | 3.76 m | H-5″, H-6′a | 5′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugawara, K.; Watarai, H.; Ise, Y.; Yokose, H.; Morii, Y.; Yamawaki, N.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Structure Elucidation of Calyxoside B, a Bipolar Sphingolipid from a Marine Sponge Cladocroce sp. through the Use of Beckmann Rearrangement. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060287
Sugawara K, Watarai H, Ise Y, Yokose H, Morii Y, Yamawaki N, Okada S, Matsunaga S. Structure Elucidation of Calyxoside B, a Bipolar Sphingolipid from a Marine Sponge Cladocroce sp. through the Use of Beckmann Rearrangement. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060287
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugawara, Kenji, Hiroshi Watarai, Yuji Ise, Hisayoshi Yokose, Yasuhiro Morii, Nobuhiro Yamawaki, Shigeru Okada, and Shigeki Matsunaga. 2021. "Structure Elucidation of Calyxoside B, a Bipolar Sphingolipid from a Marine Sponge Cladocroce sp. through the Use of Beckmann Rearrangement" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060287
APA StyleSugawara, K., Watarai, H., Ise, Y., Yokose, H., Morii, Y., Yamawaki, N., Okada, S., & Matsunaga, S. (2021). Structure Elucidation of Calyxoside B, a Bipolar Sphingolipid from a Marine Sponge Cladocroce sp. through the Use of Beckmann Rearrangement. Marine Drugs, 19(6), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060287