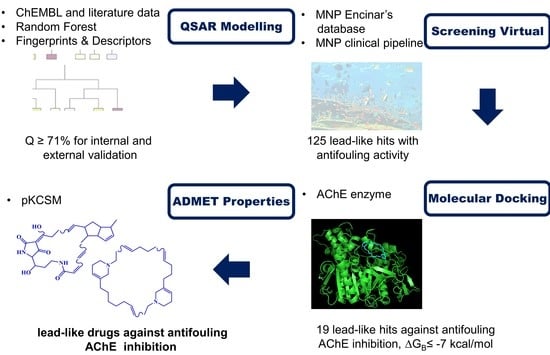
Predicting Antifouling Activity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Marine-Derived Compounds Using a Computer-Aided Drug Design Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Space of the Antifouling Model
2.2. Establishment of QSAR Classification Model
2.3. Analysis of Fingerprints and Descriptors Identified as Relevant for Modeling the Antifouling Activity
2.4. Application of the In Silico Antifouling QSAR Model in Virtual Screening
2.5. Molecular Docking against AChE Enzyme
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sets/Selection of Training and Test Sets
3.2. Calculation of Descriptors
3.3. Selection of Descriptors and Optimization of QSAR Models
3.4. Class Balancer
3.5. Machine Learning (ML) Methods
3.5.1. Random Forest (RF)
3.5.2. Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
3.5.3. Deep Learning Multilayer Perceptron Networks (dMLP)
3.6. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magin, C.M.; Cooper, S.P.; Brennan, A.B. Non-toxic antifouling strategies. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.P.; Bendick, J.A.; Holm, E.R.; Hertel, W.M. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.P. Effects of coating roughness and biofouling on ship resistance and powering. Biofouling 2007, 23, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.P.; Walker, J.M.; Steppe, C.N.; Flack, K.A. Impact of diatomaceous biofilms on the frictional drag of fouling-release coatings. Biofouling 2015, 31, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B. Biomimetics: Lessons from nature—An overview. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 2009, 367, 1445–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ware, C.; Berge, J.; Sundet, J.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Coutts, A.D.M.; Jelmert, A.; Olsen, S.M.; Floerl, O.; Wisz, M.S.; Alsos, I.G. Climate change, non-indigenous species and shipping: Assessing the risk of species introduction to a high-Arctic archipelago. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashton, G.V.; Davidson, I.C.; Geller, J.; Ruiz, G.M. Disentangling the biogeography of ship biofouling: Barnacles in the Northeast Pacific. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettengill, J.B.; Wendt, D.E.; Schug, M.D.; Hadfield, M.G. Biofouling likely serves as a major mode of dispersal for the polychaete tubeworm Hydroides elegans as inferred from microsatellite loci. Biofouling 2007, 23, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piola, R.F.; Johnston, E.L. The potential for translocation of marine species via small-scale disruptions to antifouling surfaces. Biofouling 2008, 24, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Prabowo, R.E.; Ohshiro, Y.; Shimono, T.; Jones, D.; Kawai, H.; Otani, M.; Oshino, A.; Inagawa, S.; Akaya, T.; et al. The introduction to Japan of the Titan barnacle, Megabalanus coccopoma (Darwin, 1854) (Cirripedia: Balanomorpha) and the role of shipping in its translocation. Biofouling 2009, 25, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonak, S.; Pangam, P.; Giriyan, A.; Hawaldar, K. Implications of the ban on organotins for protection of global coastal and marine ecology. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S96–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, J.A.; Callow, M.E. Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, C.M.; Brennan, A.B. Bio-Inspired Antifouling Strategies. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2012, 42, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, L.D.; Stokes, K.R.; Walsh, F.C.; Wood, R.J.K. Modern approaches to marine antifouling coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 3642–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othmani, A.; Bunet, R.; Bonnefont, J.L.; Briand, J.F.; Culioli, G. Settlement inhibition of marine biofilm bacteria and barnacle larvae by compounds isolated from the Mediterranean brown alga Taonia atomaria. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.; Ba-akdah, M.A.; Al-Sofyani, A.A. Natural antifouling compound production by microbes associated with marine macroorganisms—A review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 21, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, J.R.; Vasconcelos, V. Natural antifouling compounds: Effectiveness in preventing invertebrate settlement and adhesion. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.-Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-review: Marine natural products and their synthetic analogs as antifouling compounds: 2009-2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Fusetani, N. Natural products as antifouling compounds: Recent progress and future perspectives. Biofouling 2010, 26, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.; Dahms, H.U.; Qian, P.Y. Inhibition of biofouling by marine microorganisms and their metabolites. Biofouling 2006, 22, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Wu, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Xu, Y. Mini-Review: Antifouling Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Analogs. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, S.-H.; Ma, X. Antifouling Compounds from Marine Invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahms, H.U.; Dobretsov, S. Antifouling Compounds from Marine Macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodie, L.W.K.; Sepcic, K.; Turk, T.; Frangez, R.; Svenson, J. Natural cholinesterase inhibitors from marine organisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1053–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworjanyn, S.A.; de Nys, R.; Steinberg, P.D. Chemically mediated antifouling in the red alga Delisea pulchra. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 318, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, J.J.; Ballard, T.E.; Huigens, R.W., III; Melander, C. Synthesis and screening of an oroidin library against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, C.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Ballard, T.E.; Richards, J.J.; Huigens, R.W., III; Cavanagh, J. Evaluation of dihydrooroidin as an antifouling additive in marine paint. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2009, 63, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trepos, R.; Cervin, G.; Hellio, C.; Pavia, H.; Stensen, W.; Stensvag, K.; Svendsen, J.-S.; Haug, T.; Svenson, J. Antifouling Compounds from the Sub-Arctic Ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria: Synoxazolidinones A and C, Pulmonarins A and B, and Synthetic Analogues. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjogren, M.; Goransson, U.; Johnson, A.L.; Dahlstrom, M.; Andersson, R.; Bergman, J.; Jonsson, P.R.; Bohlin, L. Antifouling activity of brominated cyclopeptides from the marine sponge Geodia barretti. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Hong, Y.K.; Baek, H.H.; Shin, H.W.; Kim, M.S. Isolation and Structural Determination of the Antifouling Diketopiperazines from Marine-Derived Streptomyces praecox 291-11. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Dobretsov, S.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Hung, O.S.; Qian, P.-Y. Antifouling diketopiperazines produced by a deep-sea bacterium, Streptomyces fungicidicus. Biofouling 2006, 22, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Davo, A.; Dias, T.; Gomes, S.E.; Rodrigues, S.; Parera-Valadezl, Y.; Borralho, P.M.; Pereira, F.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Santos-Sanches, I.; Gaudencio, S.P. The Madeira Archipelago As a Significant Source of Marine-Derived Actinomycete Diversity with Anticancer and Antimicrobial Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauermeister, A.; Pereira, F.; Grilo, I.R.; Godinho, C.C.; Paulino, M.; Almeida, V.; Gobbo-Neto, L.; Prieto-Davo, A.; Sobral, R.G.; Lopes, N.P.; et al. Intra-clade metabolomic profiling of MAR4 Streptomyces from the Macaronesia Atlantic region reveals a source of anti-biofilm metabolites. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.; Almeida, J.R.; Paulino, M.; Grilo, I.R.; Macedo, H.; Cunha, I.; Sobral, R.G.; Vasconcelos, V.; Gaudencio, S.P. Antifouling Napyradiomycins from Marine -Derived Actinomycetes Streptomyces aculeolatus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruz, S.; Gomes, S.E.; Borralho, P.M.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Gaudencio, S.P.; Pereira, F. In Silico HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cell-Based Models En Route to the Discovery of Lead-Like Anticancer Drugs. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, T.; Gaudencio, S.P.; Pereira, F. A Computer-Driven Approach to Discover Natural Product Leads for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Don Duy, N.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, G.; Mayhudin, N.A.; Mitova, M.I.; Sun, L.; van der Sar, S.; Blunt, J.W.; Cole, A.L.J.; Ellis, G.; Laatsch, H.; Munro, M.H.G. Evolving trends in the dereplication of natural product extracts: New methodology for rapid, small-scale investigation of natural product extracts. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, D.; Davis, R.A.; Campitelli, M.; Ebdon, J.; Quinn, R.J. Drug-like Properties: Guiding Principles for the Design of Natural Product Libraries. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudencio, S.P.; Pereira, F. A Computer-Aided Drug Design Approach to Predict Marine Drug-Like Leads for SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibition. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Le, X.; Li, L.; Ju, Y.C.; Lin, Z.X.; Gu, Q.; Xu, J. Discovering New Agents Active against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus with Ligand-Based Approaches. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.; Aires-de-Sousa, J. Computational Methodologies in the Exploration of Marine Natural Product Leads. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, F. Have marine natural product drug discovery efforts been productive and how can we improve their efficiency? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llanos, M.A.; Gantner, M.E.; Rodriguez, S.; Alberca, L.N.; Bellera, C.L.; Talevi, A.; Gavernet, L. Strengths and Weaknesses of Docking Simulations in the SARS-CoV-2 Era: The Main Protease (Mpro) Case Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3758–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Moreira, J.; Pereira, D.; Pereira, S.; Antunes, J.; Palmeira, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Cidade, H. Potential of synthetic chalcone derivatives to prevent marine biofouling. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.R.; Palmeira, A.; Campos, A.; Cunha, I.; Freitas, M.; Felpeto, A.B.; Turkina, M.V.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; et al. Structure-Antifouling Activity Relationship and Molecular Targets of Bio-Inspired(thio)xanthones. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Svenson, J.; Sepicic, K.; Trembleau, L.; Engqvist, M.; Andersen, J.H.; Jaspars, M.; Stensvag, K.; Haug, T. Isolation and Synthesis of Pulmonarins A and B, Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from the Colonial Ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, J.; Zhang, M.Q. Molecular modelling and QSAR of reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2000, 7, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munoz-Torrero, D. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors as Disease-Modifying Therapies for Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 2433–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabshahi, H.J.; Trobec, T.; Foulon, V.; Hellio, C.; Frangez, R.; Sepcic, K.; Cahill, P.; Svenson, J. Using Virtual AChE Homology Screening to Identify Small Molecules With the Ability to Inhibit Marine Biofouling. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 762287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, C.W. PaDEL-Descriptor: An Open Source Software to Calculate Molecular Descriptors and Fingerprints. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V. Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volumes 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Catto, M.; Pisani, L.; de la Mora, E.; Belviso, B.D.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Pinto, A.; De Palma, A.; Denora, N.; Caliandro, R.; Colletier, J.-P.; et al. Chiral Separation, X-ray Structure, and Biological Evaluation of a Potent and Reversible Dual Binding Site AChE Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Software News and Update AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guedes, I.A.; Barreto, A.M.S.; Marinho, D.; Krempser, E.; Kuenemann, M.A.; Sperandio, O.; Dardenne, L.E.; Miteva, M.A. New machine learning and physics-based scoring functions for drug discovery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, D.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; De Veij, M.; Felix, E.; Magarinos, M.P.; Mosquera, J.F.; Mutowo, P.; Nowotka, M.; et al. ChEMBL: Towards direct deposition of bioassay data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D930–D940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selzer, P.; Ertl, P. Identification and classification of GPCR ligands using self-organizing neural networks. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2005, 24, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Fartaria, R.; Latino, D.A.R.S.; Qu, X.; Campos, T.; Zhao, T.; Aires-de-Sousa, J. A QSPR approach for the fast estimation of DFT/NBO partial atomic charges. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2014, 134, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. 2014. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Jain, S.; Kotsampasakou, E.; Ecker, G.F. Comparing the performance of meta-classifiers-a case study on selected imbalanced data sets relevant for prediction of liver toxicity. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2018, 32, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random forest: A classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. J. Chem. Inform. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F.K. GitHub, Seattle, WA, USA. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/fchollet/keras (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Clusters 1 | # 2 (Active Class) | Average MW (Da) 3 | Average ALogP 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tr | Te | Tr | Te | Tr | Te | |
I—acyclic derivative | 11 (11) | 0 (0) | 361.65 | 0 | 2.86 | 0 |
II—O-heterocyclic derivative | 28 (9) | 3 (1) | 328.09 | 334.64 | 3.18 | 3.22 |
III—N-heterocyclic derivative | 19 (14) | 1 (0) | 363.92 | 493.04 | 2.50 | 3.65 |
IV—terpenoid derivative | 22 (5) | 6 (3) | 264.64 | 341.76 | 3.00 | 4.49 |
V—diketopiperazine derivative | 15 (10) | 3 (2) | 392.54 | 415.15 | 3.06 | 3.10 |
VI—chalcone derivative | 16 (3) | 0 (0) | 352.37 | 0 | 4.56 | 0 |
| VII—miscellaneous | 16 (5) | 1 (0) | 1164.53 | 975.69 | −0.88 | −1.57 |
| Descriptors (#) | TP 1 | TN 2 | FN 3 | FP 4 | SE 5 | SP 6 | Q 7 | MCC 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACCS (166) 9 | 41 | 51 | 16 | 19 | 0.719 | 0.729 | 0.724 | 0.446 |
| Sub (307) 9 | 41 | 53 | 16 | 17 | 0.719 | 0.757 | 0.740 | 0.476 |
| PubChem (881) 9 | 43 | 48 | 14 | 22 | 0.754 | 0.686 | 0.717 | 0.438 |
| CDK (1024) 9 | 42 | 47 | 15 | 23 | 0.737 | 0.671 | 0.701 | 0.406 |
| ExtCDK (1024) 9 | 41 | 49 | 16 | 21 | 0.719 | 0.700 | 0.709 | 0.417 |
| 1D&2D (1376) | 40 | 53 | 17 | 17 | 0.702 | 0.757 | 0.732 | 0.459 |
| Model | # | SE 1 | SP 2 | Q 3 | MCC 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub + RDF | 691 | 0.667 | 0.714 | 0.693 | 0.380 |
| Selection 5 | 50 | 0.667 | 0.714 | 0.693 | 0.380 |
| Selection 5 | 100 | 0.684 | 0.757 | 0.724 | 0.442 |
| Selection 5 | 150 | 0.702 | 0.786 | 0.748 | 0.489 |
| Selection 5 | 200 | 0.684 | 0.757 | 0.724 | 0.442 |
| ExtCDK + RDF | 1408 | 0.667 | 0.743 | 0.709 | 0.410 |
| Selection 5 | 12 | 0.754 | 0.729 | 0.740 | 0.481 |
| Selection 5 | 25 | 0.737 | 0.786 | 0.764 | 0.523 |
| Selection 5 | 50 | 0.702 | 0.771 | 0.740 | 0.474 |
| Selection 5 | 100 | 0.684 | 0.771 | 0.732 | 0.457 |
| 1D&2D + RDF | 1760 | 0.719 | 0.714 | 0.717 | 0.432 |
| Selection 5 | 50 | 0.807 | 0.800 | 0.803 | 0.605 |
| Selection 5 | 100 | 0.825 | 0.786 | 0.803 | 0.607 |
| Selection 5 | 150 | 0.807 | 0.800 | 0.803 | 0.605 |
| Selection 5 | 200 | 0.842 | 0.786 | 0.811 | 0.625 |
| Selection 5 | 250 | 0.772 | 0.800 | 0.787 | 0.571 |
| Model | SE 1 | SP 2 | Q 3 | MCC 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.667 | 0.750 | 0.714 | 0.417 |
| SVM | 0.830 | 0.500 | 0.643 | 0.344 |
| dMLP | 0.670 | 0.750 | 0.714 | 0.417 |
| Cluster | # | SE 1 | SP 2 | Q 3 | MCC 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | |||||
| I | 11 | 1.000 | - | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| II | 28 | 0.889 | 0.789 | 0.821 | 0.640 |
| III | 19 | 1.000 | 0.400 | 0.842 | 0.574 |
| IV | 22 | 0.800 | 0.941 | 0.909 | 0.741 |
| V | 15 | 0.900 | 0.000 | 0.600 | - |
| VI | 16 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.813 | - |
| VII | 16 | 0.400 | 0.812 | 0.688 | 0.234 |
| All | 0.842 | 0.786 | 0.811 | 0.625 | |
| Test set | |||||
| II | 3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| III | 1 | - | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| IV | 6 | 0.333 | 1.000 | 0.667 | 0.447 |
| V | 3 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.667 | - |
| VII | 1 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | - |
| All | 0.667 | 0.750 | 0.713 | 0.417 | |
| CAS | Chemical Structure | Name/Structural Category | Natural Source | Prob_A | ∆GB (kcal/mol) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147362-39-8 |  | cylindramide/lactam | marine sponge 2 | 0.684 | −11.3 |
| 126622-63-7 |  | haliclamine B/macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 3 | 0.682 | −8.2 |
| 126622-64-8 |  | haliclamine A/macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 3 | 0.682 | −7.8 |
| 156310-18-8 |  | ingamine B/macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 4 | 0.682 | −7.8 |
| 155944-26-6 |  | madangamines A/macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 4 | 0.694 | −7.7 |
| 105305-54-2 |  | serain 3/ macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 5 | 0.686 | −7.5 |
| 142677-10-9 |  | chondriamide B/indole | red alga 6 | 0.682 | −7.5 |
| 134029-43-9 |  | nortopsentin A/indole | marine sponge 7 | 0.702 | −7.3 |
| 134029-44-0 |  | nortopsentin B/indole | marine sponge 7 | 0.698 | −7.3 |
| 134029-45-1 |  | nortopsentin C/indole | marine sponge 7 | 0.700 | −7.3 |
| 105418-77-7 |  | serain 1/ macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 5 | 0.686 | −7.2 |
| 142677-09-6 |  | chondriamide A/indole | red alga 6 | 0.682 | −7.2 |
| 223596-72-3 |  | isobromodeoxytopsent/ indole | marine sponge 8 | 0.680 | −7.2 |
| 134779-34-3 |  | nortopsentin D/indole | marine sponge 7 | 0.688 | −7.1 |
| 157536-35-1 |  | keramaphidin B/macrocyclic alkaloid | marine sponge 9 | 0.684 | −7.1 |
| 59697-14-2 |  | nemertelline/ pyridine | marine worm 10 | 0.680 | −7.0 |
| positive control |  | synoxazolidinone A | - | - | −6.5 |
| positive control |  | synoxazolidinone C | - | - | −6.7 |
| positive control |  | donepezil | - | - | −6.5 |
| negative control |  | phenolic | - | - | −5.1 |
| Hyperparameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Initializer | Glorot uniform |
| Number of hidden layers | 2 |
| Number of neurons in the 1st and 2nd layers | 200 |
| Number of neurons in the 3rd | 2 |
| Activation 1st–2nd layers | Relu |
| Activation 3rd layer | Sigmoid |
| Batch size | 36 |
| Optimizer | Adadelta |
| Loss | Binary crossentropy |
| Epochs | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaudêncio, S.P.; Pereira, F. Predicting Antifouling Activity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Marine-Derived Compounds Using a Computer-Aided Drug Design Approach. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020129
Gaudêncio SP, Pereira F. Predicting Antifouling Activity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Marine-Derived Compounds Using a Computer-Aided Drug Design Approach. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020129
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaudêncio, Susana P., and Florbela Pereira. 2022. "Predicting Antifouling Activity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Marine-Derived Compounds Using a Computer-Aided Drug Design Approach" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020129
APA StyleGaudêncio, S. P., & Pereira, F. (2022). Predicting Antifouling Activity and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Marine-Derived Compounds Using a Computer-Aided Drug Design Approach. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020129