New Glycosylated Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
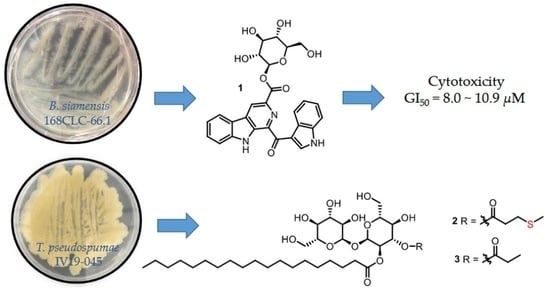
3.2. Bacterial Strain, Fermentation, and Isolation of 1 and 4–6 from Bacillus siamensis 168CLC-66.1
3.3. Bacterial Strain, Fermentation, and Isolation of 2 and 3 from Tsukamurella pseudospumae IV19-045
3.4. Acid Hydrolysis and Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Glucose
3.5. Cytotoxicity Test by SRB Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elshahawi, S.I.; Shaaban, K.A.; Kharel, M.K.; Thorson, J.S. A comprehensive review of glycosylated bacterial natural products. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7591–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hug, J.J.; Krug, D.; Müller, R. Bacteria as genetically programmable producers of bioactive natural products. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.; Cooper, M.A. Aminoglycoside antibiotics in the 21st century. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirst, H.A. Milestones in Drug Therapy. Macrolide Antibiotics; Schönfeld, W., Kirst, H.A., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2002; Chapter 1; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hulst, M.B.; Grocholski, T.; Neefjes, J.J.C.; van Wezel, G.P.; Metsä-Ketelä, M. Anthracyclines: Biosynthesis, engineering and clinical applications. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 814–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, R.; Huang, Q.; Rensing, C.; Raza, W.; Shen, Q. Antibacterial Compounds-Macrolactin Alters the Soil Bacterial Community and Abundance of the Gene Encoding PKS. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Xu, S.; Bao, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, Y.; Cui, Q.; Li, W. An effective strategy for identification of highly unstable bacillaenes. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3340–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tareq, F.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, H.J. Ieodoglucomides A and B from a Marine-Derived Bacterium Bacillus licheniformis. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Cai, J.; Su, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; Tao, H. Glycosylated Natural Products From Marine Microbes. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kügler, J.H.; Muhle-Goll, C.; Kühl, B.; Kraft, A.; Heinzler, R.; Kirschhöfer, F.; Henkel, M.; Wray, V.; Luy, B.; Brenner-Weiss, G.; et al. Trehalose lipid biosurfactants produced by the actinomycetes Tsukamurella spumae and T. pseudospumae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8905–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volbrecht, E.; Heckmann, R.; Wray, V.; Nimtz, M.; Lang, S. Production and structure elucidation of di-and oligosaccharide lipids (biosurfactans) from Tsukamurella sp. nov. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paściak, M.; Kaczyński, Z.; Lindner, B.; Holst, O.; Gamian, A. Immunochemical studies of trehalose-containing major glycolipid from Tsukamurella pulmonis. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irlinger, B.; Bartsch, A.; Krämer, H.J.; Mayser, P.; Steglich, W. New Tryptophan Metabolites from Cultures of the Lipophilic Yeast Malassezia furfur. Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 1472–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, D.C.; Prebble, D.W.; Er, S.; Hayton, J.B.; Robertson, L.P.; Avery, V.M.; Domanskyi, A.; Kiefel, M.J.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Carroll, A.R. α-Synuclein Aggregation Inhibitory Prunolides and a Dibrominated β-Carboline Sulfamate from the Ascidian Synoicum prunum. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, K.; Roman, M.; Fenical, W. The macrolactins, a novel class of antiviral and cytotoxic macrolides from a deep-sea marine bacterium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 7519–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.S.; Ye, W.C.; Wang, Z.T.; Che, C.T.; Zhou, R.H.; Xu, G.J.; Xu, L.S. β-Carboline alkaloids from Hypodematium squamuloso-pilosum. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 1807–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-K.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Choi, B.-W.; Kang, J.S.; Ngoc, N.T.D.; Van, T.T.T.; Shin, H.J. New Ophiobolin Derivatives from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus and Their Cytotoxicities against Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 135.7, C | 2′ | 9.62, s | 140.1, CH | |
| 3 | 139.0, C | 3′ | 115.9, C | ||
| 4 | 8.96, s | 121.1, CH | 3′a | 128.9, C | |
| 4a | 132.8, C | 4′ | 8.57, d (8.5) | 122.7, CH | |
| 4b | 124.1, C | 5′ | 7.25, ovl | 123.4, CH | |
| 5 | 8.21, d (7.7) | 122.2, CH | 6′ | 7.25, ovl | 123.3, CH |
| 6 | 7.34, t (7.4) | 122.2, CH | 7′ | 7.46, d (8.1) | 112.8, CH |
| 7 | 7.61, t (7.5) | 130.4, CH | 7′a | 137.5, C | |
| 8 | 7.76, d (8.1) | 113.9, CH | 1″ | 5.93, d (8.1) | 96.7, CH |
| 8a | 143.4, C | 2″ | 3.76, t (8.5) | 74.4, CH | |
| 9a | 138.1, C | 3″ | 3.64, t (8.7) | 78.2, CH | |
| 10 | 188.4, C | 4″ | 3.58, m | 71.2, CH | |
| 11 | 166.0, C | 5″ | 3.58, m | 79.0, CH | |
| 6″ | 3.96, d (12.4) 3.82, dd (12.3, 4.6) | 62.4, CH2 |
| 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | |
| 1 | 5.30, d (3.6) | 93.0, CH | 5.30, d (3.6) | 93.0, CH |
| 2 | 4.88, dd (10.3, 3.7) | 71.9, CH | 4.87, dd (10.3, 3.7) | 72.1, CH |
| 3 | 5.51, m | 74.3, CH | 5.49, m | 73.9, CH |
| 4 | 3.63, m | 69.6, CH | 3.63, m | 69.6, CH |
| 5 | 4.01, ddd (10.0, 4.6, 2.2) | 73.7, CH | 4.01, ddd (10.0, 4.6, 2.2) | 73.7, CH |
| 6 | 3.82, m 3.81, m | 61.9, CH2 | 3.82, m 3.73, m | 62.0, CH2 |
| 1′ | 5.10, d (3.7) | 95.9, CH | 5.10, d (3.7) | 95.9, CH |
| 2′ | 3.49, dd (9.8, 3.8) | 73.0, CH | 3.50, dd (9.8, 3.7) | 73.0, CH |
| 3′ | 3.77, m | 74.6, CH | 3.78, m | 74.6, CH |
| 4′ | 3.35, m | 71.6, CH | 3.34, dd (12.2, 6.1) | 71.6, CH |
| 5′ | 3.66, m | 74.2, CH | 3.66, m | 74.3, CH |
| 6′ | 3.70, m 3.66, m | 62.5, CH2 | 3.71, m 3.66, m | 62.4, CH2 |
| 1″ | 173.1, C | 175.5, C | ||
| 2″ | 2.65, m | 35.4, CH2 | 2.36, m | 28.4, CH2 |
| 3″ | 2.73, m | 29.9, CH2 | 1.12, t (7.6) | 9.5, CH3 |
| 5″ | 2.10, s | 15.4, CH3 | ||
| 1‴ | 174.6, C | 174.4, C | ||
| 2‴ | 2.37, m | 35.0, CH2 | 2.34, m | 34.9, CH2 |
| 3‴ | 1.57, m | 25.8, CH2 | 1.56, m | 25.9, CH2 |
| 4‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.3, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.2, CH2 |
| 5‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.5, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.4, CH2 |
| 6‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.6, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.5, CH2 |
| 7‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.6, CH2 |
| 8‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.7, CH2 |
| 9‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 10‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 11‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 12‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 13‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 14‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 15‴ | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 30.8, CH2 |
| 16‴ | 1.30, ovl | 33.1, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 33.1, CH2 |
| 17‴ | 1.30, ovl | 23.7, CH2 | 1.30, ovl | 23.7, CH2 |
| 18‴ | 0.90, t (7.0) | 14.4, CH3 | 0.90, t (7.0) | 14.4, CH3 |
| Cell Line a | GI50, μM | ADR b |
|---|---|---|
| HCT-15 | 10.9 | 0.13 |
| NUGC-3 | 9.8 | 0.16 |
| NCI-H23 | 10.2 | 0.14 |
| ACHN | 10.1 | 0.17 |
| PC-3 | 8.8 | 0.17 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 8.0 | 0.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anh, C.V.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, H.-S.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Heo, C.-S.; Shin, H.J. New Glycosylated Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070464
Anh CV, Kang JS, Lee H-S, Trinh PTH, Heo C-S, Shin HJ. New Glycosylated Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(7):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070464
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnh, Cao Van, Jong Soon Kang, Hwa-Sun Lee, Phan Thi Hoai Trinh, Chang-Su Heo, and Hee Jae Shin. 2022. "New Glycosylated Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria" Marine Drugs 20, no. 7: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070464
APA StyleAnh, C. V., Kang, J. S., Lee, H. -S., Trinh, P. T. H., Heo, C. -S., & Shin, H. J. (2022). New Glycosylated Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria. Marine Drugs, 20(7), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070464