Phenolic Metabolites from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus puniceus A2 and Their Nrf2-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
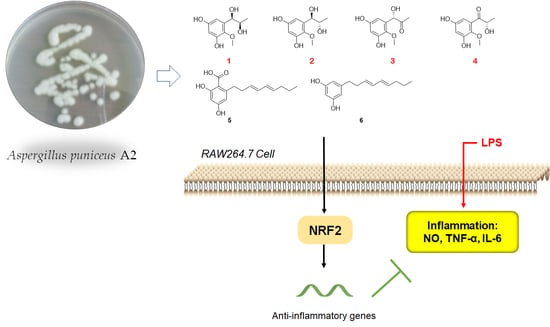
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material and Fermentation
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Preparation of (R)- and (S)-MPA Esters of 1, 2, and 4
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Cell Viability
3.7. Nitrite Determination
3.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
3.9. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, W.-Y.; Yi, J.; Chang, Y.-B.; Sun, C.-P.; Ma, X.-C. Recent studies on terpenoids in Aspergillus fungi: Chemical diversity, biosynthesis, and bioactivity. Phytochemistry 2022, 193, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Larsen, T.O. Chemodiversity in the genus Aspergillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7859–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.; Chen, J.; Kuron, G.; Hunt, V.; Huff, J.; Hoffman, C.; Rothrock, J.; Lopez, M.; Joshua, H.; Harris, E. Mevinolin: A highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, A.; Takahashi, C.; Matsushita, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Kawai, K.; Usami, Y.; Matsumura, E.; Inoue, M.; Ohishi, H.; Shingu, T. Fumiquinazolines, novel metabolites of a fungus isolated from a saltfish. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tian, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, J. Research status and development trends of natural products from marine microorganisms. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2021, 40, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Qi, S. Diketopiperazine-type alkaloids from a deep-sea-derived Aspergillus puniceus fungus and their effects on liver X receptor α. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Huang, Z.-H.; Ma, X.; Zheng, Z.-H.; Zhang, X.-X.; Lu, X.-H.; Qi, S.-H. Mycotoxins as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus puniceus SCSIO z021. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 107, 104571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-M.; Yao, F.-H.; Lu, X.-H.; Zhang, X.-X.; Luo, L.-X.; Liang, X.; Qi, S.-H. Isoquinoline Alkaloids as Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitors from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus puniceus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, F.; Seco, J.M.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R. Determining the absolute stereochemistry of secondary/secondary diols by 1H NMR: Basis and applications. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 3778–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.T.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saepua, S.; Kornsakulkarn, J.; Somyong, W.; Laksanacharoen, P.; Isaka, M.; Thongpanchang, C. Bioactive compounds from the scale insect fungus Conoideocrella tenuis BCC 44534. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypov, S.K.; Seco, J.M.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R. MTPA vs MPA in the determination of the absolute configuration of chiral alcohols by 1H NMR. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 8569–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhuang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Dong, Y. Varic acid analogues from fungus as PTP1B inhibitors: Biological evaluation and structure-activity relationships. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3382–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Chen, C.; Sun, W.; Zang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Zeng, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Phenolic C-Glycosides and Aglycones from Marine-Derived Aspergillus sp. and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, J.C.; Gilkeson, G.S. The biology of nitric oxide and other reactive intermediates in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 121, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, R.M.; Williams, J.A.; Shacter, E. Elevated interleukin 6 is induced by prostaglandin E2 in a murine model of inflammation: Possible role of cyclooxygenase-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.D.; Hauser, S.D.; McGarity, K.L.; Bremer, M.E.; Isakson, P.C.; Gregory, S.A. Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 reverses inflammation and expression of COX-2 and interleukin 6 in rat adjuvant arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Usatyuk, P.V.; Gorshkova, I.A.; He, D.; Wang, T.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Geyh, A.S.; Breysse, P.N.; Samet, J.M.; Spannhake, E.W. Regulation of COX-2 expression and IL-6 release by particulate matter in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, S.; Ogtata, Y.; Shimizu, E.; Yamazaki, M.; Furuyama, S.; Sugiya, H. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)-induced prostaglanding E2 release is mediated by the activation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription via NFκB in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 238, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.; Mahboubi, K.; Haider, A.; Li, I.; Ferreri, N.R. Cyclooxygenase-2 is required for tumor necrosis factor-α–and angiotensin II–mediated proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vomund, S.; Schäfer, A.; Parnham, M.J.; Brüne, B.; Von Knethen, A. Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petri, S.; Körner, S.; Kiaei, M. Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway: Key mediator in oxidative stress and potential therapeutic target in ALS. Neurol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 878030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledinos-Antón, N.; Fernández-Ginés, R.; Manda, G.; Cuadrado, A. Activators and inhibitors of NRF2: A review of their potential for clinical development. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9372182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 6.20, br s | 6.16, d (2.8) | 6.27, d (2.9) | 6.48, d (2.8) |
| 6 | 6.20, br s | 6.27, d (2.8) | 6.12, d (2.9) | 6.25, d (2.8) |
| 7 | 4.48, dd (6.5, 3.4) | 4.65, t (4.4) | 5.10, d (4.7) | |
| 8 | 3.60, m | 3.68, m | 4.76, quint (6.6) | |
| 9 | 0.87, d (6.4) | 0.95, d (6.3) | 2.03, s | 1.17, d (6.9) |
| 2-OCH3 | 3.62, s | 3.61, s | 3.63, s | 3.66, s |
| 3-OH | 9.07, s | 8.97, s | 9.27, s | 9.58, s |
| 5-OH | 8.86, s | 8.79, s | 9.03, s | 9.30, s |
| 7-OH | 4.94, d (3.4) | 4.79, d (4.4) | 5.59, d (4.7) | |
| 8-OH | 4.49, d (4.2) | 4.36, d (5.5) | 5.08, d (6.2) |
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 137.2, C | 137.3, C | 134.2, C | 132.8, C |
| 2 | 138.3, C | 138.2, C | 138.5, C | 139.0, C |
| 3 | 150.4, C | 150.2, C | 151.0, C | 151.5, C |
| 4 | 103.0, CH | 102.8, CH | 104.1, CH | 107.4, CH |
| 5 | 153.6, C | 153.4, C | 153.9, C | 153.9, C |
| 6 | 104.7, CH | 104.7, CH | 105.2, CH | 105.0, CH |
| 7 | 72.3, CH | 71.5, CH | 74.7, CH | 205.6, C |
| 8 | 71.2, CH | 69.9, CH | 208.3, C | 71.8, CH |
| 9 | 19.8, CH3 | 17.9, CH3 | 26.0, CH3 | 20.4, CH3 |
| 2-OMe | 60.5, CH3 | 60.4, CH3 | 60.6, CH3 | 61.4, CH3 |
| Genes | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | CGGCAAACATGACTTCAGGC | TCGATGCACAACTGGGTGAA |
| COX-2 | GCTGGAAAAGGTTCTTCTACG | AACCCAGGTCCTCGCTTA |
| Nrf2 | TCAGCGACAGAAGGACTAAG | AGGCATCTTGTTTGGAATG |
| β-actin | AGCCATGTACGTAGCCATCC | CTCTCAGCTGTGGTGGTGAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Niu, S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, G.; Cai, S.; Wu, J.; Hong, B. Phenolic Metabolites from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus puniceus A2 and Their Nrf2-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090575
He J, Wu X, Huang S, Wang J, Niu S, Chen M, Zhang G, Cai S, Wu J, Hong B. Phenolic Metabolites from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus puniceus A2 and Their Nrf2-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(9):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090575
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jianlin, Xin Wu, Shuhuan Huang, Juan Wang, Siwen Niu, Meixiang Chen, Gaiyun Zhang, Songyan Cai, Jingna Wu, and Bihong Hong. 2022. "Phenolic Metabolites from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus puniceus A2 and Their Nrf2-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effects" Marine Drugs 20, no. 9: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090575
APA StyleHe, J., Wu, X., Huang, S., Wang, J., Niu, S., Chen, M., Zhang, G., Cai, S., Wu, J., & Hong, B. (2022). Phenolic Metabolites from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus puniceus A2 and Their Nrf2-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Marine Drugs, 20(9), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090575