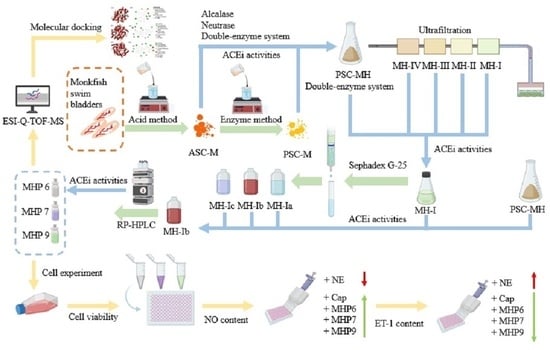
Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Collagen from Swim Bladders of Monkfish (L. litulon)
2.1.1. Proximate Composition Analysis
2.1.2. Amino Acid Analysis of ASC-M and PSC-M
2.1.3. Electrophoretic Patterns of ASC-M and PSC-M
2.1.4. Ultraviolet (UV) Absorption Spectrums of ASC-M and PSC-M
2.2. Preparation of ACEi Peptides from Collagen Hydrolysates of Monkfish Swim Bladders
2.2.1. Preparation of Collagen Hydrolysates of Monkfish Swim Bladders
2.2.2. Preparation of ACEi Peptides from PSC-MHs
2.3. Sequences and MW Determination of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9
2.4. IC50 Values and Molecular Docking Analysis of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9
2.5. Effects of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9 on HUVECs
2.5.1. Effects of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9 on Viability of HUVECs
2.5.2. Effects of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9 on Production of NO and ET-1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Extraction of Collagens from Monkfish Swim Bladders
3.3. Characterization of ASC-M and PSC-M
3.3.1. Proximate and Amino Acid Analysis
3.3.2. SDS-PAGE Patterns of ASC-M and PSC-M
3.3.3. UV Absorption Analysis
3.4. Preparation of Hydrolysates of ASC-M and PSC-M
3.5. Preparation of ACEi Peptides from PSC-MH
3.6. Determination of ACEi Activity
3.7. Sequence Identification of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9
3.8. Molecular Docking Experiments on MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9
3.9. Effects of MHP6, MHP7 and MHP9 on HUVECs
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Stankus, A. State of world aquaculture 2020 and regional reviews: FAO webinar series. FAO Aquaculture 429 Newsletter, 1 May 2021; 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Qiu, Y.T.; Chi, C.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, B. Gelatin from cartilage of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii): Characterization and protective function on ultraviolet-A injured human skin fibroblasts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 925407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozogul, F.; Cagalj, M.; Šimat, V.; Ozogul, Y.; Tkaczewska, J.; Hassoun, A.; Kaddour, A.A.; Kuley, E.; Rathod, N.B.; Phadke, G.G. Recent developments in valorisation of bioactive ingredients in discard/seafood processing by-products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 559–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Qiu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Novel antioxidant collagen peptides of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) cartilages: The preparation, characterization, and cytoprotection of H2O2-damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siahaan, E.A.; Agusman; Pangestuti, R.; Shin, K.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Potential cosmetic active ingredients derived from marine by-products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.M.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack tuna milt: Purification, identification, and cytoprotection on H2O2 damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Process Biochem. 2022, 113, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.-M.; Li, L.-Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Twelve antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) roe prepared by flavourzyme: Purification, sequence identification, and activity evaluation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 813780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.B.; Chi, C.F.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, B. Physicochemical properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the cartilage of Siberian sturgeon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31427–31438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; He, Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the scales of miiuy croaker (Miichthys Miiuy). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mienaltowski, M.D.E. Structure, physiology, and biochemistry of collagens. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 802, 5–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.-H.; Chi, C.-F.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, B. Preparation, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the swim bladders of Miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Q.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; Ding, G.F. Preparation and characterization of acid and pepsin-soluble collagens from scales of croceine and redlip croakers. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. Collagen of extracellular matrix from marine invertebrates and its medical applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslan, S.N.H.; Li, C.X.; Shapawi, R.; Mokhtar, R.A.M.; Noordin, W.N.M.; Huda, N. Extraction and characterization of bioactive fish by-product collagen as promising for potential wound healing agent in pharmaceutical applications: Current trend and future perspective. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 9437878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G.F.; Wu, C.W. Characterization of acid-soluble collagen from the skin of hammerhead shark (Sphyrna lewini). Food Biochem. 2014, 38, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, X.R.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Gelatins and antioxidant peptides from Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) skins: Purification, characterization, and cytoprotection on ultraviolet-A injured human skin fibroblasts. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.-W.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-M.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Bioactive peptides from Skipjack tuna cardiac arterial bulbs: Preparation, identification, antioxidant activity, and stability against thermal, pH, and simulated gastrointestinal digestion treatments. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Hu, X.-M.; Cai, W.-W.; Wang, Y.-M.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Bioactive peptides from Skipjack tuna cardiac arterial bulbs (II): Protective function on UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells through antioxidant and anti-apoptotic Mmechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Liu, Y.; Guo, D.; Li, B.; He, H. Collagen peptides from crucian skin improve calcium bioavailability and structural characterization by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8847–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Characterization and wound healing evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geahchan, S.; Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Marine Collagen: A promising biomaterial for wound healing, skin anti-aging, and bone regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yu, K.; Kang, M.; Wang, Q.; Liao, W.; Liang, P.; Liu, G.; Cao, Y.; Miao, J. Identification and functional analysis of three novel osteogenic peptides isolated from tilapia scale collagen hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162 Pt A, 111993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Xie, W.; Jin, T.; Xu, D.; Liu, L. Cod (Gadus) skin collagen peptide powder reduces inflammation, restores mucosal barrier function, and inhibits fibrosis in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 316, 116728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S. Bioactive peptides derived from crimson snapper and in vivo anti-aging effects on fat diet-induced high fat Drosophila melanogaster. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liao, B.; He, H. Antioxidant and anti-freezing peptides from salmon collagen hydrolysate prepared by bacterial extracellular protease. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.L.; Costa-Gouveia, J.; Vieira de Castro, J.; Sotelo, C.G.; Vázquez, J.A.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Torrado, E.; Neves, N.; Reis, R.L.; Castro, A.G.; et al. Study of the immunologic response of marine-derived collagen and gelatin extracts for tissue engineering applications. Acta. Biomater. 2022, 141, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, B. High Fischer ratio oligopeptides from hard-shelled mussel: Preparation and hepatoprotective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Pan, N.; Xu, M.; Su, Y.; Qiao, K.; Chen, B.; Zheng, B.; Xiao, M.; Liu, Z. ACE inhibitory peptide from skin collagen hydrolysate of Takifugu bimaculatus as potential for protecting HUVECs injury. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, V.; Goswami, B. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 524, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, S.K.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Pan, X.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Seventeen novel angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of Mytilus edulis: Isolation, identification, molecular docking study, and protective function on HUVECs. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7831–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Ge, M.X.; Wu, H.W.; Zheng, S.L.; Zheng, H.Y.; Wang, B. Production, identification, in silico analysis, and cytoprotection on H2O2-induced HUVECs of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Skipjack tuna roes. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1197382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, S.K.; Zheng, S.L.; Chi, C.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, B. Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from tuna byproducts-milts: Preparation, characterization, molecular docking study, and antioxidant function on H2O2-damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 957778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikkam, V.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O.N.; Mathai, M.L. A review of potential marine-derived hypotensive and anti-obesity peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abachi, S.; Bazinet, L.; Beaulieu, L. Antihypertensive and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from fish as potential cardioprotective compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Vo, T.S.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. Angiotensin- I- converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Pacific cod skin gelatin using ultrafiltration membranes. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.Q.; Luo, Q.B.; Suo, S.K.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Preparation, characterization, and cytoprotective effects on HUVECs of fourteen novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of tuna processing by-products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 868681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.-L.; Luo, Q.-B.; Suo, S.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, molecular docking study and protective function on HUVECs of novel ACE inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna muscle. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.; Abdul, N.R. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE-I) inhibition and antioxidant peptide from a Squilla species. Protein Pept. Lett. 2021, 28, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qin, S.; Li, W. Purification and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptide derived from Alaska pollack skins. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.-T.; Matanjun, P.; Budiman, C.; Shapawi, R.; Lee, J.-S. Novel peptide sequences with ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities derived from the heads and bones of hybrid groupers (Epinephelus lanceolatus × Epinephelus fuscoguttatus). Foods 2022, 11, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Suo, S.K.; Zheng, S.L.; Wang, B. Isolation, identification, molecular docking analysis, and cytoprotection of seven novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from miiuy croaker byproducts-swim bladders. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 977234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-A.; Tsai, J.-S.; Chen, G.-W. Preparation and identification of novel antihypertensive peptides from the in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of marine Cobia skin hydrolysates. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Eight antihypertensive peptides from the protein hydrolysate of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): Isolation, identification, and activity evaluation on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Deng, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Deng, S.G.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle. Food Res. Int. 2014, 55, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Miao, B.; Cao, H.; Tian, X.; Shen, L.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Ding, Y. Monkfish (Lophius litulon) peptides ameliorate high-fat-diet-induced nephrotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation via regulation of intestinal Flora. Molecules 2023, 28, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Wu, M.F.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhu, W.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Eighteen novel bioactive peptides from monkfish (Lophius litulon) swim bladders: Production, identification, antioxidant activity and stability. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-F.; Xi, Q.-H.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wang, W.-Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from monkfish swim bladders: Ameliorating NAFLD in vitro by suppressing lipid accumulation and oxidative stress via regulating AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Yang, F.; Yao, S.; Bi, L.; Jiang, G.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y. Effects of low molecular weight peptides from monkfish (Lophius litulon) roe on immune response in immunosuppressed mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 929105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from the protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle: Purification, identification, and cytoprotective function on HepG2 cells damage by H2O2. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, G.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, F.; Yang, Z. Using collagen peptides from the skin of monkfish (Lophius litulon) to ameliorate kidney damage in high-fat diet fed mice by regulating the Nrf2 pathway and NLRP3 signaling. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 798708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Regenstein, J.; Su, X. In vitro and in vivo anti-oxidation and anti-fatigue effect of monkfish liver hydrolysate. Food Biosci. 2017, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, P. Structural properties, anti-fatigue and immunological effect of low molecular weight peptide from Monkfish. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 105, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.K.; Suresh, P.V. Physico-chemical characteristics and fibril-forming capacity of carp swim bladder collagens and exploration of their potential bioactive peptides by in silico approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewdang, O.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewmanee, T.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of collagens from the swim bladders of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Chem. 2014, 155, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative study on molecular characteristics of acid soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of seabass (Lates calcarifer). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Dong, W.; Liang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Extraction and characterization of pepsin- and acid-soluble collagen from the swim bladders of Megalonibea fusca. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.T.; Li, G.Y.; Shi, B.; Miao, Y.Q.; Wu, X.H. Isolation and partial characterization of pepsin-soluble collagen from the skin of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, X.-R.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) scales: Preparation, identification and activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Structural, functional, rheological, and biological properties of the swim bladder collagen extracted from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). LWT 2022, 153, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Cortes-Santiago, Y.; López, L.M. Comparison of collagen characteristic from the skin and swim bladder of Gulf corvina (Cynoscion othonopterus). Tissue Cell 2021, 72, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; True, C.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Fernández-Velasco, D.A.; López, L.M. Swim bladder of farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A source of value-added collagen. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Liao, W.; Wu, J. Molecular interactions, bioavailability, and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems. A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; He, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Lu, A.; Che, T.; Shen, S. Purification identification and function analysis of ACE inhibitory peptide from Ulva prolifera protein. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Han, Q.; Koyama, T.; Ishizaki, S. Preparation, purification and characterization of antibacterial and ACE inhibitory peptides from head protein hydrolysate of Kuruma shrimp, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Molecules 2023, 28, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ulaah, S. Isolation, purification and the anti-hypertensive effect of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from Ruditapes philippinarum fermented with Bacillus natto. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5230–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Lan, X.; Yaseen, M.; Wu, S.; Feng, X.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Liao, A.; Liao, D.; Sun, L. Purification, characterization and evaluation of inhibitory mechanism of ACE inhibitory peptides from pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) meat protein hydrolysate. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, Y.; Toji, K.; Katsukura, S.; Morikawa, R.; Uji, T.; Yasui, H.; Shimizu, T.; Kishimura, H. Characterization of ACE inhibitory peptides prepared from Pyropia pseudolinearis protein. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Luo, Q.; Hong, H.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y. Novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide identified from Arthrospira platensis protein and stability against thermal/pH treatments and simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; Wei, J. A novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide from rice bran protein: Biochemical characterization and molecular docking study. LWT 2017, 75, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, T.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhao, M.; Su, G. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.X.; Song, C.C.; Liu, X.T.; Qiao, B.W.; Song, S.; Fu, Y.H. ACE inhibitory activities of two peptides derived from Volutharpa ampullacea perryi hydrolysate and their protective effects on H2O2 induced HUVECs injury. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Ma, Z.; Ramachandran, M.; De Souza, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.W. ACE inhibitory peptide KYIPIQ derived from yak milk casein induces nitric oxide production in HUVECs and diffuses via a transcellular mechanism in Caco-2 monolayers. Process Biochem. 2020, 99, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Cai, S.; Ryu, B.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Qian, Z. An ACE inhibitory peptide from Isochrysis zhanjiangensis exhibits antihypertensive effect via anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis in HUVEC and hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 92, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, X.R.; Wang, B. High Fischer ratio oligopeptides determination from Antartic krill: Preparation, peptides profiles, and in vitro antioxidant activity. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-R.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Qiu, Y.-T.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Preparation and characterization of gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) bone stimulated by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Zhao, G.-X.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from collagen hydrolysate of redlip croaker (Pseudosciaena polyactis) scales: Preparation, characterization, and cytoprotective effects on H2O2-damaged HepG2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Proximate Compositions (% Dry Weight) | Yield on Dry Weight Basis (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Protein | Fat | Ash | ||
| Swim bladders | 76.95 ± 3.68 a | 20.06 ± 1.09 a | 1.71 ± 0.14 a | 0.32 ± 0.03 a | |
| ASC-M | 4.51 ± 0.19 b | 93.68 ± 3.51 b | 0.37 ± 0.05 b | 1.02 ± 0.34 b | 4.27 ± 0.22 |
| PSC-M | 4.49 ± 0.35 b | 95.87 ± 2.89 b | 0.34 ± 0.03 b | 0.74 ± 0.26 c | 9.54 ± 0.51 |
| Amino Acid | ASC-M | PSC-M | Collagen from Calf Skins (CSC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyproline | 87.3 | 85.7 | 95.1 |
| Aspartic acid/asparagine | 45.9 | 43.8 | 45.7 |
| Threonine | 23.6 | 24.9 | 18.4 |
| Glycine | 325.2 | 314.9 | 330.6 |
| Glutamine/glutamic acid | 88.6 | 87.1 | 75.9 |
| Proline | 105.2 | 102.9 | 121.5 |
| Serine | 25.9 | 26.3 | 33.2 |
| Isoleucine | 16.6 | 15.1 | 11.4 |
| Alanine | 99.3 | 97.6 | 119.7 |
| Cysteine | 0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Valine | 23.7 | 26.5 | 21.5 |
| Methionine | 5.8 | 4.5 | 6.1 |
| Arginine | 47.8 | 52.3 | 51.0 |
| Leucine | 32.5 | 29.4 | 23.4 |
| Tyrosine | 4.5 | 6.6 | 3.7 |
| Hydroxylysine | 8.2 | 10.9 | 7.7 |
| Tryptophan | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lysine | 32.6 | 38.5 | 26.5 |
| Histidine | 7.5 | 9.4 | 5.3 |
| Phenylalanine | 19.8 | 23.6 | 3.3 |
| Total | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 |
| Imino acid | 192.5 | 188.6 | 216.6 |
| RT (min) | Amino Acid Sequence | Observed MW/Theoretical MW (Da) | ACEi Activity (IC50, mg/mL) | Affinity (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHP6 | 10.08 | SEGPK | 516.5/516.6 | 0.63 | −7.3 |
| MHP7 | 12.68 | FDGPY | 597.6/597.6 | 0.94 | −10.9 |
| MHP9 | 14.91 | SPGPW | 542.6/542.6 | 0.71 | −9.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.-D.; Xi, Q.-H.; Kong, J.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100516
Hu Y-D, Xi Q-H, Kong J, Zhao Y-Q, Chi C-F, Wang B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(10):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100516
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yu-Dong, Qing-Hao Xi, Jing Kong, Yu-Qin Zhao, Chang-Feng Chi, and Bin Wang. 2023. "Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation" Marine Drugs 21, no. 10: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100516
APA StyleHu, Y. -D., Xi, Q. -H., Kong, J., Zhao, Y. -Q., Chi, C. -F., & Wang, B. (2023). Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation. Marine Drugs, 21(10), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100516