In Vitro Insights into the Role of 7,8-Epoxy-11-Sinulariolide Acetate Isolated from Soft Coral Sinularia siaesensis in the Potential Attenuation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of Cytotoxicity of Esa
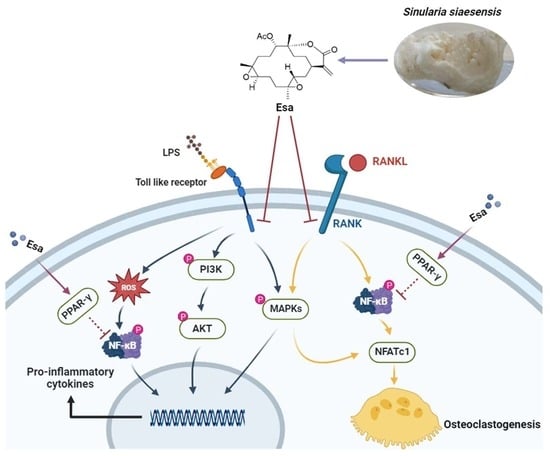
2.2. Esa Inhibited the Messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) and Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Proteins in RAW264.7 Cells
2.3. Esa Reduced Reactive Oxygen Species Levels in RAW264.7 Cells
2.4. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Was Repressed by Treatment with Esa
2.5. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases (PI3K) Signaling Pathways of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Activation Were Suppressed by Treatment with Esa
2.6. Esa inhibited Osteoclastogenesis
2.7. Esa Inhibited Receptor Activator for Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Cascades in RAW264.7 Cells and Promoted Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (PPAR-γ) Protein Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) Assay
4.4. Production Level of Nitric Oxide (NO) in Cell Supernatants
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Measurement
4.7. Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP) Staining
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Jung, H.-Y.; Park, J.-I.; Jang, Y.-J.; Ahn, J.; Kim, K.-N. Effect of Ishophloroglucin A Isolated from Ishige okamurae on In Vitro Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.S.; Oh, Y.R.; Kang, E.H.; Khang, G.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, Y.J. Fucoxanthin suppresses osteoclastogenesis via modulation of MAP kinase and Nrf2 signaling. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzmann, M.N. The role of inflammatory cytokines, the RANKL/OPG axis, and the immunoskeletal interface in physiological bone turnover and osteoporosis. Scientifica 2013, 2013, 125705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Ren, F.; Ye, Y.; Wang, F.; Zheng, C.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, M. The macrophage-osteoclast axis in osteoimmunity and osteo-related diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummuri, D.; Guntuku, L.; Challa, V.S.; Ramavat, R.N.; Naidu, V.G.M. Abietic acid attenuates RANKL induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammation associated osteolysis by inhibiting the NF-KB and MAPK signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, T.; Lin, S.; Cui, L. Antiosteoporotic effects of Alpinia officinarum Hance through stimulation of osteoblasts associated with antioxidant effects. J. Orthop. Translat. 2016, 4, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Cheng, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y. Shear stress inhibits IL-17A-mediated induction of osteoclastogenesis via osteocyte pathways. Bone 2017, 101, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellucci, R.; Terenzi, R.; Kanis, J.; Kress, H.; Mediati, R.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Brandi, M.L. Understanding osteoporotic pain and its pharmacological treatment. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, M.; Adami, G.; Adami, S.; Viapiana, O.; Gatti, D. Safety issues and adverse reactions with osteoporosis management. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewiecki, E.M. Safety of long-term bisphosphonate therapy for the management of osteoporosis. Drugs 2011, 71, 791–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.K. The gastrointestinal tolerability and safety of oral bisphosphonates. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2002, 1, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recker, R.R.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Miller, P.D.; Reiffel, J. Safety of bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S22–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, I.R.; Green, J.R.; Lyles, K.W.; Reid, D.M.; Trechsel, U.; Hosking, D.J.; Black, D.M.; Cummings, S.R.; Russell, R.G.G.; Eriksen, E.F. Zoledronate. Bone 2020, 137, 115390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.-L.; Wang, Y.; He, X.-W.; Xie, M.-M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zou, Z.-B.; Yang, L.-H.; Xu, R. Penidihydrocitrinins A–C: New Polyketides from the Deep-Sea-Derived Penicillium citrinum W17 and Their Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Osteoporotic Bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gu, Y.-C.; Su, M.-Z.; Guo, Y.-W. Chemistry and bioactivity of secondary metabolites from South China Sea marine fauna and flora: Recent research advances and perspective. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 3062–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-T.; Yu, D.-D.; Su, M.-Z.; Luo, H.; Cao, J.-G.; Liang, L.-F.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y.-W. Structurally diverse diterpenes from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-D.; Yu, D.-D.; Su, M.-Z.; Gu, Y.-C.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.-W. New Antibacterial Diterpenoids from the South China Sea Soft Coral Klyxum molle. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.W.; Chang, F.R.; McPhail, A.T.; Lee, K.H.; Wu, Y.C. New cembranolide analogues from the formosan soft coral Sinularia flexibilis and their cytotoxicity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2003, 17, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.J.; Sung, Y.; Park, K.H.; Oh, E.; Park, C.; Son, Y.J.; Kang, H. Austalides, Osteoclast Differentiation Inhibitors from a Marine-Derived Strain of the Fungus Penicillium rudallense. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Cao, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Im, D.S.; Yoo, J.-W.; Jung, J.H. The in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory effects of a phthalimide PPAR-γ agonist. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Murata, K.; Ito, S.; Suzuki, A.; Terao, C.; Ishie, S.; Umemoto, A.; Murotani, Y.; Nishitani, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; et al. Role of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 in Metabolically Integrating Osteoclast Differentiation and Inflammatory Bone Resorption Through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α and E2F1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Yin, J.; Bai, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Urolithin A suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and postmenopausal osteoporosis by, suppresses inflammation and downstream NF-κB activated pyroptosis pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Inoue, K.; Du, Y.; Baker, S.J.; Reddy, E.P.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Zhao, B. TGFβ reprograms TNF stimulation of macrophages towards a non-canonical pathway driving inflammatory osteoclastogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Lu, L.J.; Wang, J.J.; Ma, S.Y.; Xu, B.L.; Lin, R.; Chen, Q.S.; Ma, Z.G.; Mo, Y.L.; Wang, D.T. Tubson-2 decoction ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis complicated with osteoporosis in CIA rats involving isochlorogenic acid A regulating IL-17/MAPK pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z. Coixol Suppresses NF-κB, MAPK Pathways and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S.; Xing, R.; Yan, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, W. 20-Hydroxy-3-Oxolupan-28-Oic Acid Attenuates Inflammatory Responses by Regulating PI3K⁻Akt and MAPKs Signaling Pathways in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2019, 24, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattaruolo, L.; Carullo, G.; Brindisi, M.; Mazzotta, S.; Bellissimo, L.; Rago, V.; Curcio, R.; Dolce, V.; Aiello, F.; Cappello, A.R. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Flavanones from Glycyrrhiza glabra L. (licorice) Leaf Phytocomplexes: Identification of Licoflavanone as a Modulator of NF-kB/MAPK Pathway. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Pan, F.; Jiao, Y. Crocin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway activation. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.Z.; He, L.G.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tao, L.; Li, X.J.; Liu, S.W. Aconine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing NF-κB and NFATc1 activation and DC-STAMP expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Liu, K.; Peng, S.; Liu, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, X. Anti-Osteoclastogenic and Antibacterial Effects of Chlorinated Polyketides from the Beibu Gulf Coral-Derived Fungus Aspergillus unguis GXIMD 02505. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Wu, F.; Shi, Z.; He, B.; Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Yan, S. Dehydrocostus lactone attenuates osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast-induced bone loss by modulating NF-κB signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5762–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lin, X.; Wu, Z.; Su, Y.; Liang, J.; Chen, R.; Yang, X.; Hou, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Pristimerin Protects Against OVX-Mediated Bone Loss by Attenuating Osteoclast Formation and Activity via Inhibition of RANKL-Mediated Activation of NF-κB and ERK Signaling Pathways. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zong, S.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Protocatechualdehyde Inhibits the Osteoclast Differentiation of RAW264.7 and BMM Cells by Regulating NF-κB and MAPK Activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Zhong, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tang, W.; Li, D.; Shi, J.; Lu, A.; Yang, H.; Geng, D.; et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Aging 2020, 12, 21706–21729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasan, H.; Terkawi, M.A.; Matsumae, G.; Ebata, T.; Tian, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Nishida, Y.; Yokota, S.; Garcia-Martin, F.; Abd Elwakil, M.M.; et al. Inhibitory role of Annexin A1 in pathological bone resorption and therapeutic implications in periprosthetic osteolysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Bi, F.; Xu, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, J.; Han, X.; Guo, W. PPAR-γ activation promotes xenogenic bioroot regeneration by attenuating the xenograft induced-oxidative stress. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, F. Bavachinin selectively modulates PPAR γ and maintains bone homeostasis in Type 2 Diabetes. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4457–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Lian, N. Overexpression of SENP3 promotes PPAR-γ transcription through the increase of HIF-1α stability via SUMO2/3 and participates in molecular mechanisms of osteoporosis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2023, 577, 112014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassumi, M.Y.; Silva-Filho, V.J.; Campos-Júnior, J.C.; Vieira, S.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; Alves, P.M.; Alves, J.B.; Kawai, T.; Gonçalves, R.B.; Napimoga, M.H. PPAR-γ agonist rosiglitazone prevents inflammatory periodontal bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E.; Mo, S.; Lee, H.S.; Jeon, M.; Song, J.S.; Choi, H.J.; Cho, H.; Kang, C.M. Deferoxamine Reduces Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis in Avulsed Teeth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orabona, C.; Orecchini, E.; Volpi, C.; Bacaloni, F.; Panfili, E.; Pagano, C.; Perioli, L.; Belladonna, M.L. Crocus sativus L. Petal Extract Inhibits Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis in RAW 264.7 Cell Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Prime Code | Prime Sequence (5’–3) |
|---|---|
| IL-6 forward | CTCCCAACAGACCTGTCTATAC |
| IL-6 reverse | CCATTGCACAACTCTTTTCTCA |
| IL-1β forward | CACTACAGGCTCCGAGATGAACAAC |
| IL-1β reverse | TGTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTGTAC |
| GAPDH forward | CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT |
| GAPDH reverse | GAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, L.-M.; Yu, D.-D.; Su, M.-Z.; Cui, L.; Guo, Y.-W. In Vitro Insights into the Role of 7,8-Epoxy-11-Sinulariolide Acetate Isolated from Soft Coral Sinularia siaesensis in the Potential Attenuation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020095
Ke L-M, Yu D-D, Su M-Z, Cui L, Guo Y-W. In Vitro Insights into the Role of 7,8-Epoxy-11-Sinulariolide Acetate Isolated from Soft Coral Sinularia siaesensis in the Potential Attenuation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(2):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020095
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Lin-Mao, Dan-Dan Yu, Ming-Zhi Su, Liao Cui, and Yue-Wei Guo. 2024. "In Vitro Insights into the Role of 7,8-Epoxy-11-Sinulariolide Acetate Isolated from Soft Coral Sinularia siaesensis in the Potential Attenuation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis" Marine Drugs 22, no. 2: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020095
APA StyleKe, L.-M., Yu, D.-D., Su, M.-Z., Cui, L., & Guo, Y.-W. (2024). In Vitro Insights into the Role of 7,8-Epoxy-11-Sinulariolide Acetate Isolated from Soft Coral Sinularia siaesensis in the Potential Attenuation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis. Marine Drugs, 22(2), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020095