Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Roles of Microbial EPS in the Marine Environment
3. Structure and Production of EPS by Marine Bacteria
4. Marine EPS-Producing Microorganisms Isolated from
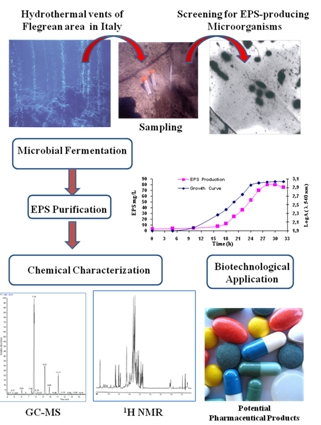
4.1. Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents, Volcanic and Hydrothermal Marine Areas, Shallow Submarine Thermal Springs
4.2. Cold Marine Environments: Deep-sea, Arctic and Antarctic Sea Ice
4.3. Hypersaline Marine Environment: Salt Lakes and Marine Salterns
4.4. Polychaete Annelid in Symbiotic Relationships
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Sutherland, IW. Microbial polysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Int. Dairy J 2001, 11, 663–674. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, IW. Bacterial exopolysaccharides. Adv. Microb. Phys 1972, 8, 143–213. [Google Scholar]
- MacCormick, CA; Harris, JE; Jay, AJ; Ridout, MJ; Colquhoun, IJ; Morris, VJ. Isolation and characterization of new extracellularpolysaccharide from an Acetobacter species. J. Appl. Bacteriol 1996, 81, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, IW. Biosynthesis of microbial exopolysaccharides. Adv. Microb. Phys 1982, 23, 79–150. [Google Scholar]
- Decho, AW. Barnes, M, Ed.; Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments: their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review; Aberdeen Univ Press: Aberdeen, UK, 1990; pp. 73–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wingender, J; Neu, TR; Flemming, H-C. Wingender, J, Neu, TR, Flemming, H-C, Eds.; What are bacterial extracellular polymer substances? In Microbial Extracellular Polymer Substance; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, M; Hedges, J; Benner, R. Major biochemical composition of dissolved high molecular weight organic matter in sea water. Mar.Chem 1996, 55, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfaardt, GM; Lawrence, JR; Korbe, DR. Wingender, J, Neu, TR, Flemming, H-C, Eds.; Function of EPS. In Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Characterization, Structure and Function; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 171–200. [Google Scholar]
- Alldredge, A. Interstitial dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations within sinking marine aggregates and their potential contribution to carbon flux. Limnol. Oceanogr 2000, 45, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Holmstrom, C; Kjelleberg, S. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol 1999, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Decho, AW; Herndl, GJ. Microbial activities and the transformation of organic matter within mucilaginous material. Sci. Total Environ 1995, 165, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso Nichols, CA; Guezennec, J; Bowman, JP. Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine environments with special consideration of the southern ocean, sea ice, and deep-sea Hydrothermal Vents: a review. Mar. Biotechnol 2005a, 7, 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Junge, K; Eicken, H; Deming, JW. Bacterial activity at −2 to −20 °C in Arctic Wintertime sea ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2004, 70, 550–557. [Google Scholar]
- Krembs, C; Eicken, H; Junge, K; Deming, JW. High concentrations of exopolymeric substances in Arctic winter sea ice: implication for the polar ocean carbon cycle and cryoprotection of diatoms. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2002, 49, 2163–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, BE; Hunt, JR. Advantages to microbes of growth in permeable aggregates in marine systems. Limnol. Oceanogr 1987, 32, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Loaec, M; Olier, R; Guezennec, J. Uptake of lead, cadmium and zinc by a novel bacterial exopolysaccharide. Water Res 1997, 31, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Loaec, M; Olier, R; Guezennec, J. Chelating properties of bacterial exopolysaccharides from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr. Polym 1998, 35, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wuertz, S; Muller, E; Spaeth, R; Pfleiderer, P; Flemming, H-C. Detection of heavy metals in bacterial biofilms and microbial floes with the fluorescent complexing agent Newport Green. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2000, 24, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso Nichols, C; Garon lardière, S; Bowman, JP; Nichols, PD; Gibson, JAE; Guézennec, J. Chemical characterization of exopolysaccharides from Antarctic marine bacteria. Microb. Ecol 2005b, 49, 578–589. [Google Scholar]
- Kenne, L; Lindberg, B. Aspinall, GO, Ed.; Bacterial polysaccharides. In The Polysaccharides; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 287–363. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, IW. Sanford, PA, Laskin, A, Eds.; Microbial exopolysaccharide synthesis. In Extracellular Microbial Polysaccharides; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; Volume 45, pp. 40–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, IW. Structure-function relationship in microbial exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv 1994, 12, 393–448. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhooren, PT; Vandamme, EJ. Biosynthesis, physiological role, use and fermentation process characteristics of bacterial exopolysaccharides. Rec. Res. Devel. Ferment. Bioeng 1998, 1, 253–299. [Google Scholar]
- Samain, E; Milas, M; Bozzi, L; Dubreucq, M; Rinaudo, M. Simultaneous production oft wo different gel-forming exopolysaccharides by an Alteromonas strain originating from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr. Polym 1997, 34, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, BE; Kjosbakken, J; Smithrod, O. Partial chemical and physical characterization of two extracellular polysaccharides produced by a marine, periphytic Pseudomonas sp. strain NCMB 2021. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1985, 50, 837–845. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, AS; Mody, K; Jha, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides - a perception. J. Bas. Microbiol 2007, 47, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, S-H; Lee, H-S; Park, S-H; Lee, H-K. Optimal conditions for the production of exopolysaccharide by marine microorganism Hahella chejuensis. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng 2000, 5, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, HK; Chun, J; Moon, EJ; Ko, SH; Lee, DS; Lee, HS; Bae, KS. Hahella chejuensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an extracellular-polysaccharide-producing marine bacterium. IJSEM 2001, 51, 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, A; Schiano Moriello, V; Esposito, E; Lama, L; Gambacorta, A; Nicolaus, B. Exopolysaccharide production by a new Halomonas strain CRSS isolated from saline lake Cape Russell in Antarctica growing on complex and defined media. Biotechnol. Lett 2004, 26, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, A; Esposito, E; Orlando, P; Lama, L; Giordano, A; de Appolonia, F; Nicolaus, B; Gambacorta, A. Halomonas alkaliantarctica sp. nov., isolated from saline lake Cape Russell in Antarctica, an alkalophilic moderately halophilic, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2007, 30, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada, E; Béjar, V; Del Moral, A; Ferrer, MR; Calvo, C; Llamas, I; Martinez-Checa, F; Arias, S; Ruiz-Garcìa, C; Martinez-Cánovas, J; Páez, R. Ventosa, A, Ed.; Moderately halophilic exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria. In Halophilic Microorganisms; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 297–314. [Google Scholar]
- Farres, J; Caminal, G; Lopez-Santin, J. Influence of phosphate on rhamnose-containing exopolysaccharide rheology and production by Klebsiella I-174. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 1997, 48, 522–527. [Google Scholar]
- Gorret, N; Maubois, JL; Engasser, JM; Ghoul, M. Study of the effects of temperature, pH and yeast extract on growth and exopolysaccharide production by Propionibacterium acidi-propionici on milk microfiltrate using a response surface methodology. J. Appl. Microbiol 2001, 90, 788–796. [Google Scholar]
- Schiano Moriello, V; Lama, L; Poli, A; Gugliandolo, C; Maugeri, TL; Gambacorta, A; Nicolaus, B. Production of exopolysaccharides from a thermophilic microorganism isolated from a marine hot spring in flegrean areas. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2003, 30, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Maugeri, TL; Gugliandolo, C; Caccamo, D; Panico, A; Lama, L; Gambacorta, A; Nicolaus, BA. Halophilic thermotolerant Bacillus isolated from a marine hot spring able to produce a new exopolysaccharide. Biotechnol. Lett 2002, 24, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Bozal, N; Tudela, E; Rossello-Mora, R; Lalucat, J; Guinea, J. Pseudoalteromonas antartica sp. nov., isolated from an Antarctica coastal environment. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1997, 47, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Raguénès, G; Pignet, P; Gauthier, G; Peres, A; Christen, R; Rougeaux, H; Barbier, G; Guezennec, J. Description of a new polymer-secreting bacterium from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent, Alteromonas macleodii subsp. fijiensis, and preliminary characterization of the polymer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1996, 62(1), 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, A. Dumitriu, S, Ed.; Screening of polysaccharide-producing microorganisms, factors influencing the production and recovery of microbial polysaccharides. In Polysaccharides-Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility; Marcel Dekker Inc. Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 275–296. [Google Scholar]
- Rougeaux, H; Guezennec, J; Carlson, RW; Kervarec, N; Pichon, R; Talaga, P. Structural determination of the exopolysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas strain HYD 721 isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Carbohydr. Res 1999a, 315, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Guezennec, JG. Deep-sea hydrothermal vents: a new source of innovative bacterial exopolysaccharides of biotechnological interest? J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2002, 29, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rougeaux, H; Talaga, P; Carlson, RW; Guerzennec, J. Structural studies of an exopolysaccharide produced by Alteromonas macleodii subsp. fijiensis originating from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Carbohydr. Res 1998, 312, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchetta, P; Guezennec, J. Surface thermodynamics of osteoblasts: relation between hydrophobicity and bone active biomaterials. Colloids Surf 2001, 22, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Colliec Jouault, S; Chevolot, L; Helley, D; Ratiskol, J; Bros, A; Sinquin, C; Roger, O; Fischer, A-M. Characterization, chemical modifications and in vitro anticoagulant properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by Alteromonas infernus. BBA 2001, 1528, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, MC; Lama, L; Improta, R; Esposito, E; Gambacorta, A; Nicolaus, B. Chemical composition of two exopolysaccharides from Bacillus thermoantarcticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1996, 62, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, EM; Trump, BF. Histologic fixative suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med 1976, 100, 405–414. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, M; Baba, M; Hirabayashi, K; Matsumoto, T; Suzuki, M; Suzuki, S; Shigeta, S; de Clercq, E. In vitro activity of mannan sulfate, a novel sulfated polysaccharide, against human immunodeficiency virus type I and other enveloped viruses. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infec. Dis 1989, 8, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Rinker, KD; Kelly, RM. Growth Physiology of the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus litoralis: Development of a Sulfur-Free Defined Medium, Characterization of an Exopolysaccharide, and Evidence of Biofilm Formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1996, 12, 4478–4485. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaus, B; Lama, L; Panico, A; Schiano Moriello, V; Romano, I; Gambacorta, A. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides excreted by thermophilic bacteria from shallow, marine hydrothermal vents of flegrean areas (Italy). Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2002, 25, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Gugliandolo, C; Maugeri, TL. Temporal variations of culturable mesophilic heterotrophic bacteria from a marine shallow hydrothermal vent of the island of Vulcano (Eolian Islands, Italy). Microb. Ecol 1998, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Guezennec, JG; Pignet, P; Raguenes, G; Deslandes, E; Lijour, Y; Gentric, E. Preliminary chemical characterization of unusual eubacterial exopolysaccharides of deep-sea origin. Carbohydr. Polym 1994, 24, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, M; Snoeck, R; Pauwels, R; de Clercq, E. Sulfated polysaccharides are potent and selective inhibitors of various enveloped viruses, including herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, vesicular stomatitis virus, and human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1988, 32, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, TK; Hayashi, M; Kojima, I. Calcium spirulan, an inhibitor of enveloped virus replication, from a blue-green alga Spirulina platensis. J. Nat. Prod 1996, 39, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, A; Gugliandolo, C; Stassi, G; Pavone, B; Iannello, D; Bisignano, G; Maugeri, TL. An exopolysaccharide produced by Geobacillus thermodenitrificans strain B3-72: Antiviral activity on immunocompetent cells. Immunol. Lett 2009, 123, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, A; Maugeri, TL; Pavone, B; Iannello, D; Gugliandolo, C; Bisignano, G. Antiviral and immunoregulatory effect of a novel exopolysaccharide from a marine thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis. Int. Immunopharmacol 2006, 6, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Rademacher, TW; Parekh, RB; Dwek, RA. Glycobiology. Ann. Rev. Biochem 1988, 57, 785–838. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, K; Zhu, L; Chen, L; Wang, PG; Zhang, Y. Structural characterization and ecological roles of a novel exopolysaccharide from the deep-sea psychrotolerant bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso Nichols, CA; Bowman, JP; Guezennec, J. Effects of incubation temperature on growth and production of exopolysaccharides by an Antarctic sea ice bacterium grown in batch culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2005c, 71, 3519–3523. [Google Scholar]
- Li, WW; Zhou, WZ; Zhang, YZ; Wang, J; Zhu, XB. Flocculation behavior and mechanism of an exopolysaccharide from the deep-sea psychrophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913. Bioresour. Technol 2008, 99(15), 6893–6899. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, HC; Wingender, J. Relevance of microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs)—Part I: structural and ecological aspects. Water Sci. Technol 2001, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Delille, D; Rosier, C. Seasonal changes of Antarctic marine bacterioplankton and sea ice bacterial assemblages. Pol. Biol 1996, 16, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso Nichols, CA; Garon, S; Bowman, JP; Raguénès, G; Guézennec, J. Production of exopolysaccharides by Antarctic marine bacterial isolates. J. Appl. Microbiol 2004, 96(5), 1057–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, MV; Lester, JN. Role of bacterial extracellular polymers in metal uptake in pure bacterial culture and activated sludge. Water Res 1982, 16, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, JG; Carpenter, SD; Deming, JW. Production of cryoprotectant extracellular polysaccharide substances (EPS) by the marine psychrophilic bacterium Colwellia psychrerythraeastrain 34H under extreme conditions. Can. J. Microbiol 2009, 55(1), 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Checa, F; Toledo, FL; Vilchez, R; Quesada, E; Calvo, C. Yield production, chemical composition, and functional properties of emulsifier H28 synthesized by Halomonas eurihalina strain H-28 in media containing various hydrocarbons. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2002, 58, 358–363. [Google Scholar]
- Pepi, M; Cesaro, A; Liut, G; Baldi, F. An antarctic psychrotrophic bacterium Halomonas sp. ANT-3b, growing on n-hexadecane, produces a new emulsifying glycolipid. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol 2005, 53, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, E. Microbial diversity as a source of useful biopolymers. J. Ind. Microbiol 1993, 11, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, RM. Biopolymers from marine prokaryotes. Mar. Biotechnol 1997, 15, 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, J; Meseguer, I; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Production of an extracellular polysaccharide by Haloferax mediterranei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1988, 10, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar]
- Parolis, H; Parolis, LAS; Boán, IF; Rodríguez-Valera, F; Widmalm, G; Manca, Mc; Jansson, P-E; Sutherland, IW. The structure of the exopolysaccharide produced by the halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei strain R4 (ATCC 33500). Carbohydr. Res 1996, 295, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, JH; Kim, SJ; Aan, SH; Lee, HK. Physicochemical and rheological properties of a novel emulsifier, EPS-R, produced by a marine bacterium Hahella chejuensis. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng 2004, 9, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Cambon-Bonavita, M-A; Raguénès, G; Jean, J; Vincent, P; Guezennec, J. A novel polymer produced by a bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete annelid. J. Appl. Microbiol 2002, 93, 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Dubreucq, G; Domon, B; Fournet, B. Structure determination of a novel uronic acid residue isolated from the exopolysaccharide produced by a bacterium originating from deep sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr. Res 1996, 290, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzi, L; Milas, M; Rinaudo, M. Characterization and solution properties of a new exopolysaccharide excreted by the bacterium Alteromonas sp. strain 1644. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 1996a, 18, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzi, L; Milas, M; Rinaudo, M. Solution and gel rheology of a new exopolysaccharide excreted by the bacterium Alteromonas sp. strain 1644. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 1996b, 18, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Raguénès, G; Christen, R; Guerzennec, J; Pignet, P; Barbier, G. Vibrio diabolicus sp. nov., a new polysaccharide-secreting organism isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete annelid, Alvinella pompejana. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1997, 47, 989–995. [Google Scholar]
- Rougeaux, H; Kervarec, N; Pichon, R; Guerzennec, J. Structure of the exopolysaccharide of Vibrio diabolicus isolated from a deep–sea hydrothermal vent. Carbohydr. Res 1999b, 322, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Colliec Jouault, S; Boisson-Vidal, C; Jozefonvicz, J. A low molecular weight fucoidan fraction from the brown seaweed Pelvetia canaliculata. J. Phytochem 1994, 35, 697–700. [Google Scholar]
- Nardella, A; Chaubet, F; Boisson-Vidal, C; Blondin, C; Durand, P; Jozefonvicz, J. Anticoagulant low molecular weight fucans produced by radical process and ion exchange chromatography of high molecular weight fucans extracted from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum. Carbohydr. Res 1996, 289, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Casu, B; Grazioli, G; Razi, N; Guerrini, M; Naggi, A; Torri, G; Oreste, P; Tursi, F; Zoppetti, G; Lindahl, U. Heparin-like compounds prepared by chemical modification of capsular polysaccharide from E.coli K5. Carbohydr. Res 1994, 263, 356–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchetta, P; Lagarde, N; Guezennec, J. A new bone-healing material: a hyaluronic acid-like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif. Tissue Int 2003a, 72, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchetta, P; Lagarde, N; Guezennec, J. Systematic effects on bone healing of a new hyaluronic acid-like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif. Tissue Int 2003b, 73, 232–236. [Google Scholar]


| Microorganisms | Source Environment | Description of EPS and Chemical Composition | Suggested Ecological Role and Biotechnological Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudoalteromonas strain 721 | Deep-sea hydrothermal vent | Octasaccharide repeating unit with two side chains, (Figure 1) | Gelling properties | [39,40] |
| Alteromonas macleodii subsp. fijiensis | Deep-sea hydrothermal vent, North Fijian Basin | Sulfated heteropolysaccharide, high uronic acids with pyruvate. The repeating unit is a branched hexasaccharide containing Glc, Man, Gal, GlcA, GalA, pyruvated mannose | Thickening agent in food- processing industry, biotoxification and waste- water treatment, bone healing, treatment of cardiovascular diseases | [16,17,37,41–43] |
| Thermococcus litoralis | Shallow submarine thermal spring | Man is the only monosaccharide | Biofilm formation | [47] |
| Geobacillus sp. strain 4004 | Sediment in marine hot spring near the seashore of Maronti, Ischia Island, Italy | A pentasaccharide repeating unit (two of them with a gluco-galacto configuration and three with a manno configuration. Gal:Man:GlcN:Arab (1.0:0.8:0.4:02) | Pharmaceutical application | [48] |
| Bacillus thermodenitrificans strain B3-72 | Water of a shallow hydrothermal vent, Vulcano Island, Italy | Trisaccharide repeating unit and a mannopyranosidic configuration. Man:Glc (1:0.2) | Immunomodulatory and antiviral activities | [49,53] |
| Bacillus licheniformis strain B3-15 | Water of a shallow marine hot spring, Vulcano Island, Italy | Man is the main monosaccharide. Tetrasaccharide repeating unit and a mannopyranosidic configuration | Antiviral activity | [35,54] |
| Microorganisms | Source environment | Description of EPS and Chemical composition | Suggested Ecological Role and Biotechnological Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudoalteromonas strain SM9913 | Deep-sea sediment in the Bohai Gulf, gulf of the Yellow Sea, China | Linear arrangement of α-(1→6) linkage of glucose with a high degree of acetylation | Flocculation behavior and bio-sorption capacity | [56,58] |
| Pseudoalteromonas strain CAM025 | Isolated from particles collected in melted Antarctic sea | Sulfated heteropolysaccharide, high levels of uronic acids with acetyl groups Glc:GalA:Rha:Gal (1:0.5:0.1:0.08) | Cryoprotection | [61] |
| Pseudoalteromonas strain CAM036 | Isolated from particles captured by a plankton net towed through the Southern Ocean | Sulfated heteropolysaccharide, high levels of uronic acids with acetyl and succinyl groups GalA:Glc:Man:GalNAc:Ara (1:0.8:0.84:0.36:0.13) | Trace metal binding | [61] |
| Colwellia psychrerythraea strain 34H | Arctic marine sediments | n.r. | Cryoprotection | [63] |
| Microorganisms | Source environment | Description of EPS and Chemical composition | Suggested ecological role and Potential Biotechnological Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haloferax mediterranei | Mediterranean Sea | →4)-β-D-GlcpNAcA- (1→6)-α-D-Manp- (1→4)-β-D-GlcpNAcA- 3-O-SO3--(1→ | Candidate in oil recovery, especially in oil deposits with high salinity concentrations | [68,69] |
| Hahella chejuensis | Marine sediment sample collected from Marado, Cheju Island, Republic of Korea | EPS named EPS-R Glc:Gal (0.68:1.0) | Biosurfactant and detoxification of polluted areas from petrochemical oils | [28] |
| Halomonas alkaliantarctica strain CRSS | Salt lake in Cape Russell in Antarctica | Glc:Fru:GlcN:GalN (1.0:0.7:0.3:trace) | High viscosity | [29,30] |
| Microorganisms | Source environment | Description of EPS and Chemical composition | Suggested ecological role and Potential Biotechnological Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alteromonas macleodii subsp. fijiensis biovar deepsane strain HYD657 | Isolated from epidermis of a polychaete annelid, Alvinella pompejana, hydrothermal vent of the East Pacific Rise | The repeating unit is an undesaccharide with three side-chains. Gal:Glc:Rha:Fuc:Man:GlcA:GalA:3-0-(1 carboxyethyl)-D-GlcA (1:0.42:0.85:0.5:0.42:0.5:0.5:0.5) | Cosmetics (patent PCT 94907582-4) | [71] |
| Alteromonas strain 1644 | Isolated from Alvinellidae collected near hydrothermal vent of the East Pacific Rise | Main chain of five sugars with a side chain of three sugars including a dicarboxylic acid. Glc:Gal:GlcA:3Lac-GlcA:GalA | Heavy metal binding | [73,74] |
| Vibrio diabolicus strain HE800 | Isolated from a Pompei worm tube collected from a deep-sea hydrothermal field of the East Pacific Rise | A linear tetrasaccharide repeating unit. Uronic acid :GlcN:GalN 1:0.5:0.5 →3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpA- (1→4)-β-D-GlcpA-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNAc- (1→ | Bone regeneration and cicatrizing material (patent US 7015206B2) | [75,76,80,81] |
| Alteromonas infernus strain 785 | Isolated from a fluid sample collected among a dense population of Riftia pachyptila in the proximity of an active hydrothermal vent, Guaymas basin (Gulf of California) | Glc:Gal:GlcA:GalA (1:1:0.7:0.4) | Anticoagulant activity | [43] |
© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Poli, A.; Anzelmo, G.; Nicolaus, B. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1779-1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061779
Poli A, Anzelmo G, Nicolaus B. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(6):1779-1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061779
Chicago/Turabian StylePoli, Annarita, Gianluca Anzelmo, and Barbara Nicolaus. 2010. "Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities" Marine Drugs 8, no. 6: 1779-1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061779
APA StylePoli, A., Anzelmo, G., & Nicolaus, B. (2010). Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities. Marine Drugs, 8(6), 1779-1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061779