Tetrodotoxin Sensitivity of the Vertebrate Cardiac Na+ Current
Abstract
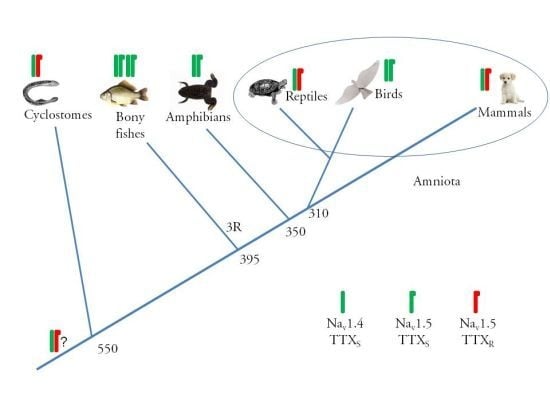
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. TTX-Sensitivity of the Vertebrate Cardiac INa
2.2. Alpha Subunit Composition of the Cardiac Na+ Channels
2.3. Amino Acid Sequence of the TTX Binding Site in Domain I
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals
4.2. Patch-Clamp Recording of INa
4.3. Cloning of TTX Binding Area of Cardiac Na+ Channels
4.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
Acknowledgments
References
- Lopreato, G.F.; Lu, Y.; Southwell, A.; Atkinson, N.S.; Hillis, D.M.; Wilcox, T.P.; Zakon, H.H. Evolution and divergence of sodium channel genes in vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7588–7592. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, A.E.; Jost, M.C.; Lu, Y.; Taylor, A.D.; Zakon, H.H.; Ribera, A.B. Gene dublications and evolution of vertebrate voltage-gated sodium channels. J. Mol. Evol 2006, 63, 208–221. [Google Scholar]
- Widmark, J.; Sundström, G.; Ocampo Daza, D.; Larhammar, D. Differential evolution of voltage-gated sodium channels in tetrapods and teleost Fishes. Mol. Biol. Evol 2011, 28, 859–871. [Google Scholar]
- Zakon, H.H.; Jost, M.C.; Lu, Y. Expansion of voltage-dependent Na+ channel gene family in early tetrapods coincided with the emergence of terrestriality and increased brain complexity. Mol. Biol. Evol 2011, 28, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Plummer, N.W.; Meisler, M.H. Evolution and diversity of mammalian sodium channel genes. Genomics 1999, 57, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Satin, J.; Kyle, J.W.; Chen, M.; Bell, P.; Cribbs, L.L.; Fozzard, H.A.; Rogart, R.B. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science 1992, 256, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Soong, T.W.; Venkatesh, B. Adaptive evolution of tetrodotoxin resistance in animals. Trends Genet 2006, 22, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Leffler, A.; Herzog, R.; Dib-Hajj, S.; Waxman, S.; Cummins, T. Pharmacological properties of neuronal TTX-resistant sodium channels and the role of a critical serine pore residue. Pflugers Arch 2005, 451, 454–463. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, Y.; Matsumoto, G.; Hanyu, Y. TTX resistivity of Na+ channel in newt retinal neuron. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1997, 240, 651–656. [Google Scholar]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Nishimoto, K.; Nitanai, Y.; Isemura, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Yasumoto, T. Binding properties of 3H-PbTx-3 and 3H-saxitoxin to brain membranes and to skeletal muscle membranes of pufferfish Fugu pardalis and the primary structure of a voltage-gated Na+ channel alpha-subunit (fMNa1) from skeletal muscle of F. pardalis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2000, 267, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Geffeney, S.; Brodie, E.D.; Ruben, P.C.; Brodie, E.D. Mechanisms of adaptation in a predator-prey arms race: TTX-resistant sodium channels. Science 2002, 297, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Jost, M.C.; Hillis, D.M.; Lu, Y.; Kyle, J.W.; Fozzard, H.A.; Zakon, H.H. Toxin-resistant sodium channels: parallel adaptive evolution across a complete gene family. Mol. Biol. Evol 2008, 25, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Sivilotti, L.; Okuse, K.; Akopian, A.N.; Moss, S.; Wood, J.N. A single serine residue confers tetrodotoxin insensitivity on the rat sensory-neuron-specific sodium channel SNS. FEBS Lett 1997, 409, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Tyrrell, L.; Escayg, A.; Wood, P.M.; Meisler, M.H.; Waxman, S.G. Coding sequence, genomic organization, and conserved chromosomal localization of the mouse gene Scn11a encoding the sodium channel NaN. Genomics 1999, 59, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Tarr, M.; Trank, J.W. An assessment of the double sucrose-gap voltage clamp technique as applied to frog atrial muscle. Biophys. J 1974, 14, 627–643. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka, K. Does the maximum upstroke velocity of the action potential (Vmax) represent available sodium conductance in frog ventricular cells? Jpn. J. Physiol 1987, 37, 585–599. [Google Scholar]
- Vornanen, M. Sarcolemmal Ca influx through L-type Ca channels in ventricular myocytes of a teleost fish. Am. J. Physiol 1997, 272, R1432–R1440. [Google Scholar]
- Haverinen, J.; Hassinen, M.; Vornanen, M. Fish cardiac sodium channels are tetrodotoxin sensitive. Acta Physiol 2007, 191, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, J.C.; Doyle, D.D.; Barr, L. Sodium channels in vertebrate hearts. Three types of saxitoxin binding sites in heart. Bioch. Biophys. Acta 1984, 775, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, M.; Best, P.M.; Reuter, H. Voltage-dependent action of tetrodotoxin in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature 1976, 263, 344–345. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, C.J.; Bean, B.P.; Colatsky, T.J.; Tsien, R.W. Teterodotoxin block of sodium channels in rabbit Purkinje fibers. J. Gen. Physiol 1981, 78, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, T.; Pappano, A.J. Ontogenetic increase of the maximal rate of rise of the chick embryonic heart action potential. Relationship to voltage, time, and tetrodotoxin. Circ. Res 1979, 44, 358–367. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, N.C.; Fozzard, H. Tetrodotoxin sensitivity in the developing and adult chick heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol 1981, 13, 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Rogart, R.B.; Regan, L.J.; Dziekan, L.C.; Galper, J.B. Identification of two sodium channel subtypes in chick heart and brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Blechschmidt, S.; Haufe, V.; Benndorf, K.; Zimmer, T. Voltage-gated Na+ channel transcript patterns in the mammalian heart are species-dependent. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol 2008, 98, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Sidow, A. Gen(om)e duplications in the evolution of early vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 1996, 6, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Kuraku, S.; Meyer, A.; Kuratani, S. Timing of Genome Duplications Relative to the Origin of the Vertebrates: Did Cyclostomes Diverge before or after? Mol. Biol. Evol 2009, 26, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zakon, H.H.; Jost, M.C.; Zwickl, D.J.; Lu, Y.; Hillis, D.M. Molecular evolution of Na+ channels in teleost fishes. Integrative Zoology 2009, 4, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin—Distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, E.D.I.; Brodie, E.D.J. Tetrodotoxin resistance in garter snakes: an evolutionary response of pradator to dangerous prey. Evolution 1990, 44, 651–659. [Google Scholar]
- Haverinen, J.; Vornanen, M. Temperature acclimation modifies Na+ current in fish cardiac myocytes. J. Exp. Biol 2004, 207, 2823–2833. [Google Scholar]
- Hassinen, M.; Paajanen, V.; Haverinen, J.; Eronen, H.; Vornanen, M. Cloning and expression of cardiac Kir2.1 and Kir2.2 channels in thermally acclimated rainbow trout. Am. J. Physiol 2007, 292, R2328–R2339. [Google Scholar]






| Target Gene | Primers for the First PCR | Primers for the Second PCR |
|---|---|---|
| ccSCN4A | F: ATGGCDMSCATKCTCCCTCC R: GCCATGGCNACCACVGCSAGGAT | F: ATGGCDMSCATKCTCCCTCC R: AGGTAGAARGAVCCCAGRAAKATGA |
| ccSCN5A | F: TCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: GCCATGGCNACCACVGCSAGGAT | F: TTCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: AGGTAGAARGAVCCCAGRAAKATGA |
| lfSCN1A, −4A, −5A, −8A | F: TCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: GCCATGGCNACCACVGCSAGGAT | F: TTCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: AGGTAGAARGAVCCCAGRAAKATGA |
| lfSCN4A | F: TGCTTGTCATCGCATGTTTT R: CCACATGGTCTCGATCCACT | F: TCATGACSCARGACTMCTGG R: CCACATGGTCTCGATCCACT |
| lfSCN5A | F: CCTTAAAACGTTCCGAGTGC R: CCACATGGTCTCGATCCACT | F: TCATGACSCARGACTMCTGG R: CCACATGGTCTCGATCCACT |
| llSCN4A llSCN5A | F: TCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: GCCATGGCNACCACVGCSAGGAT | F: TTCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: AGGTAGAARGAVCCCAGRAAKATGA |
| xlSCN4A xlSCN5A | F: TCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: GCCATGGCNACCACVGCSAGGAT | F: TTCCTHCGRGACCCVTGGAAYTGGCT R: AGGTAGAARGAVCCCAGRAAKATGA |
| Target Gene | Primer Sequences | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| ccSCN4A | F: CAACAGTGATAACCTGACCA R: GGTTCGCTGGGTTTTCAATA | 102 |
| ccSCN5A | F: CCTTCAGACAACAGCAGCAC R: CTTGGCTCCTTCCACTTTGA | 105 |
| ccDnaJA2 | F: GGACTTGTACGACCGTTATGG R:CGCCAAAGATATGGGAAAAGAT | 93 |
| lfSCN1A | F: AGTTCAACGAGACCGTCGAG R: CCACACAGGAGAGCATCCTT | 100 |
| lfSCN4A | F: TGCTTGTCATCGCATGTTTT R: CCACGGAAATGGTTTTCAAC | 98 |
| lfSCN5A | F: CCTTAAAACGTTCCGAGTGC R: GAGCTTTTTCACCGACTGGA | 99 |
| lfSCN8A | F: CGCTACCAAACGTCTCGTTC R: CCCTTGACTTCCCAGACGTA | 103 |
| lfDnaJA2 | F: AGCCCCATGGACATATTTGA R: GCCCACAGACAACTGGTGTA | 96 |
| llSCN4A | F: AACGACAGCCTTGGTGATGT R: TCTGGCCGTTTCGGTAGTAG | 103 |
| llSCN5A | F: AACGCCTCCTTCTACTGCAA R: AACGCATCCTTGGCTCCTT | 101 |
| llDnaJA2 | F: CCCGAGAAGAAGGAGCTGTA R: CCGAAGATGTGGGAGAAGAT | 101 |
| omSCN4A | F: CAGCAACAGTACGTGGGACT R: CAGAAGCGTTTCCACAGAGA | 101 |
| omSCN5A | F: ACACCCTCAACACCAACACA R: CGCTCCCTCCACTTTGTAGT | 104 |
| omSCN8A | F: GGAGCTCCATGAACGACTTC R: CTTCCCTGCATCTTGTCCAT | 101 |
| omDnaJA2 | F: TTGTAATGGAGAAGGTGAGG R: TGGGCCGCTCTCTTGTATGT | 233 |
| xlSCN4A | F: CAACAGTACCTTAAACGCCACA R: TAGGCATCCCAGTCAATGGT | 105 |
| xlSCN5A | F: ATTTCAATGCGACCCAGATG R: CCGTCCTTGTGGTAGATGTT | 106 |
| xlDnaJA2 | F: GTCGCAATGGGAGAAGAAGA R: CTTGCTGAGCTGAAGTTTGG | 101 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vornanen, M.; Hassinen, M.; Haverinen, J. Tetrodotoxin Sensitivity of the Vertebrate Cardiac Na+ Current. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2409-2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9112409
Vornanen M, Hassinen M, Haverinen J. Tetrodotoxin Sensitivity of the Vertebrate Cardiac Na+ Current. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(11):2409-2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9112409
Chicago/Turabian StyleVornanen, Matti, Minna Hassinen, and Jaakko Haverinen. 2011. "Tetrodotoxin Sensitivity of the Vertebrate Cardiac Na+ Current" Marine Drugs 9, no. 11: 2409-2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9112409
APA StyleVornanen, M., Hassinen, M., & Haverinen, J. (2011). Tetrodotoxin Sensitivity of the Vertebrate Cardiac Na+ Current. Marine Drugs, 9(11), 2409-2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9112409