Exploring the Role of the Food Environment on Food Shopping Patterns in Philadelphia, PA, USA: A Semiquantitative Comparison of Two Matched Neighborhood Groups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Block Selection
2.2. Survey Methodology
2.3. Analysis of Survey Data
3. Results and Discussion
| Unfavorable: no major food stores (½-mile) | Favorable: many major food sources (½-mile) | p-value a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size (n) | 25 | 25 | ||
| Mean household size (SD b) c | 2.92 (1.29) | 3.08 (1.41) | p = 0.6774 | |
| Mean number adults (SD) | 2.16 (0.90) | 2.52 (1.36) | p = 0.2752 | |
| Mean number of children (SD) | 0.76 (1.05) | 0.56 (0.71) | p = 0.4355 | |
| Car Ownership | ||||
| We don’t drive | 16% | 12% | ||
| We only use car share | 0% | 8% | ||
| One | 48% | 48% | ||
| More than one | 36% | 31% | p = 0.7237 | |
| Home Ownership | ||||
| Rental Unit | 24% | 36% | ||
| Owner Occupied | 76% | 64% | p = 0.5380 | |
| Length of time in current residence | ||||
| Less than a year | 8% | 44% | ||
| Between 1 and 2 years | 0% | 0% | ||
| Between 2 and 5 years | 28% | 24% | ||
| Between 5 and 10 years | 12% | 12% | ||
| More than 10 years | 52% | 20% | p = 0.0178 * | |
| How safe feel in neighborhood | ||||
| Very Safe | 12% | 20% | ||
| Safe | 56% | 64% | ||
| Varies by time of day | 32% | 16% | ||
| Not very safe | 0% | 0% | ||
| Not safe at all | 0% | 0% | p = 0.4155 | |
| Race | ||||
| Black | 12% | 4% | ||
| White | 68% | 84% | ||
| Asian/South Asian/Pacific Islander | 4% | 4% | ||
| AIAN d | 0% | 0% | ||
| Black and White | 12% | 4% | ||
| White and AIAN | 0% | 4% | ||
| Other | 4% | 0% | p = 0.5605 | |
| Hispanic/Latino | 0% | 8% | p = 0.4898 | |
| US Citizens | 100% | 92% | p = 0.4898 | |
| Employment | ||||
| Full-time employment | 56% | 68% | ||
| Part-time employment | 16% | 4% | ||
| Unemployed, actively seeking | 4% | 0% | ||
| Unemployed, not actively seeking | 8% | 4% | ||
| Retired | 12% | 0% | ||
| Student | 4% | 24% | p = 0.0538 | |
| Education | ||||
| Less than high school | 0% | 0% | ||
| High school or equivalent | 8% | 0% | ||
| Some college/associates | 20% | 16% | ||
| Bachelors | 40% | 28% | ||
| Graduate or professional degree | 32% | 56% | p = 0.2490 | |
| Income | ||||
| Less than $20,000 | 16% | 16% | ||
| $20,000–$50,000 | 28% | 20% | ||
| $50,000–$100,000 | 24% | 16% | ||
| More than $100,000 | 32% | 48% | p = 0.6956 | |
| Self-Reported Health | ||||
| Poor | 0% | 0% | ||
| Fair | 8% | 0% | ||
| Good | 28% | 12% | ||
| Very Good | 28% | 48% | ||
| Excellent | 36% | 40% | p = 0.2139 | |
3.1. Food Environment Perceptions
3.2. Food Shopping Patterns
| Both street segments combined | Unfavorable: no major food stores (½-mile) | Favorable: many major food sources (½-mile) | p-value a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIG FOOD SHOPPING TRIPS (n) | 39 | 21 | 18 | ||
| Frequency of shopping trips | |||||
| Never | 22.0% | 16.0% | 28.0% | ||
| Every month | 20.0% | 20.0% | 20.0% | ||
| Every two weeks | 22.0% | 20.0% | 24.0% | ||
| Every week | 22.0% | 32.0% | 12.0% | ||
| More than once a week | 4.0% | 0.0% | 8.0% | ||
| Other | 10.0% | 12.0% | 8.0% | p = 0.4360 | |
| Distance to store in miles | |||||
| Mean, (SD b) Median | 3.02 (3.08) 2.13 | 2.50 (1.29) 2.40 | 3.59 (4.25) 1.83 | p = 0.3110 | |
| Mode of transportation to store | |||||
| Walk | 7.0% | 4.2% | 10.5% | ||
| Drive | 79.1% | 70.8% | 89.5% | ||
| Bicycle | 4.7% | 8.3% | 0.0% | ||
| Public Transportation | 4.7% | 8.3% | 0.0% | ||
| Other | 4.7% | 8.3% | 0.0% | p = 0.2735 | |
| Why chose mode of transportation | |||||
| Distance | 26.7% | 29.7% | 21.7% | ||
| Convenience | 35.0% | 29.7% | 43.4% | ||
| Cost | 8.3% | 10.8% | 4.3% | ||
| Weather | 8.3% | 8.1% | 8.6% | ||
| Children accompanying | 15.0% | 13.5% | 17.4% | ||
| Other | 8.3% | 8.1% | 8.7% | p = 0.8498 | |
| Time of shopping trip | |||||
| Morning (prior to 12 pm) | 20.5% | 14.3% | 27.8% | ||
| Early Afternoon (12 pm to 3 pm) | 20.5% | 23.8% | 16.7% | ||
| Late Afternoon (3 pm to 5 pm) | 33.3% | 33.3% | 33.3% | ||
| Evening (5 pm to 8 pm) | 23.1% | 28.6% | 16.7% | ||
| Night (after 8 pm) | 2.6% | 0.0% | 5.6% | p = 0.6812 | |
| Pattern of shopping | |||||
| Completely separate trip | 64.1% | 71.4% | 55.6% | ||
| On the way to/from work | 5.1% | 4.8% | 5.6% | ||
| As part of a chain of several errands | 25.6% | 14.3% | 38.9% | ||
| Other | 5.1% | 9.5% | 0.0% | p = 0.1918 | |
| SMALL FOOD SHOPPING TRIPS (n) | 113 | 52 | 61 | ||
| Frequency of shopping trips | |||||
| Never | 2.0% | 0.0% | 4.0% | ||
| Once a month | 6.0% | 12.0% | 0.0% | ||
| A few times a month | 2.0% | 4.0% | 0.0% | ||
| Once a week | 32.0% | 32.0% | 32.0% | ||
| A few times a week | 54.0% | 48.0% | 60.0% | ||
| Every day | 4.0% | 4.0% | 4.0% | p = 0.4360 | |
| Distance to store in miles | |||||
| Mean, (SD) Median | 1.10 (1.17) 0.93 | 1.53 (1.34) 1.38 | 0.73 (0.85) 0.35 | p = 0.0003 ** | |
| Mode of transportation to store | |||||
| Walk | 41.5% | 12.9% | 54.6% | ||
| Drive | 32.0% | 40.0% | 24.7% | ||
| Bicycle | 11.6% | 8.6% | 14.3% | ||
| Public Transportation | 15.0% | 24.3% | 6.5% | p = 0.0004 ** | |
| Why chose mode of transportation | |||||
| Distance | 28.4% | 26.2% | 30.1% | ||
| Convenience | 42.8% | 40.8% | 45.1% | ||
| Cost | 5.2% | 2.9% | 7.7% | ||
| Weather | 10.3% | 12.6% | 7.7% | ||
| Children accompanying | 6.2% | 7.8% | 4.4% | ||
| Other | 7.2% | 9.7% | 4.4% | p = 0.2662 | |
| Category | Description | Examples | Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convenience | Specifically referred to convenience |
| 30 |
| Price or Cost | Referred to cheap, price, cost, or bulk shopping |
| 31 |
| Quality and Freshness | Referred to the quality or freshness of products, including words like “best” and “good” |
| 33 |
| Geographic Location | Referred to proximity or closeness to home, schools, work, or other shopping locations |
| 43 |
| Selection | Referred to the breadth of stuff offered at the store, selection, or variety. Includes comments about organic selection |
| 38 |
| Social Reasons | Either referring to the social nature of a specific location (staff friendliness, social gathering spot) or to a social movement that is supported by choosing this store (i.e., organic, local) |
| 25 |
| Miscellaneous | Anything that did not fit into the other 6 categories. Usually item, individual or store specific |
| 38 |
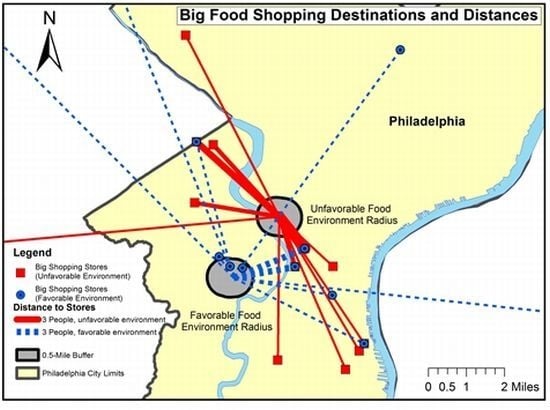
3.3. Distance Traveled

3.4. Multivariate Factors in Distance Traveled

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Giskes, K.; van Lenthe, F.; Avendano-Pabon, M.; Brug, J. A systematic review of environmental factors and obesogenic dietary intakes among adults: Are we getting closer to understanding obesogenic environments? Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e95–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Glass, T.A.; Curriero, F.C.; Stewart, W.F.; Schwartz, B.S. The built environment and obesity: A systematic review of the epidemiologic evidence. Health Place 2010, 16, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, R.A.; Reedy, J.; Morrissette, M.A.; Lytle, L.A.; Yaroch, A.L. Measures of the food environment: A compilation of the literature, 1990–2007. Amer. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 36, S124–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morland, K.B.; Evenson, K.R. Obesity prevalence and the local food environment. Health Place 2009, 15, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papas, M.A.; Alberg, A.J.; Ewing, R.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Gary, T.L.; Klassen, A.C. The built environment and obesity. Epidemiologic Rev. 2007, 29, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, L.M.; Auld, M.C.; Chaloupka, F.J.; O’Malley, P.M.; Johnston, L.D. Associations between access to food stores and adolescent body mass index. Amer. J. Prev. Med. 2007, 33, S301–S307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagami, S.; Cohen, D.A.; Finch, B.K.; Asch, S.M. You are where you shop: Grocery store locations, weight, and neighborhoods. Amer. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 31, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morland, K.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Wing, S. Supermarkets, other food stores, and obesity: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Amer. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 30, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, K.; Sallis, J.F.; Saelens, B.E.; Frank, L.D. Healthy nutrition environments: Concepts and measures. Amer. J. Health Promot. 2005, 19, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morland, K.; Wing, S.; Roux, A.D. The contextual effect of the local food environment on residents’ diets: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Amer. J. Public Health 2002, 92, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone-Heinonen, J.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Kiefe, C.I.; Shikany, J.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Popkin, B.M. Fast food restaurants and food stores: longitudinal associations with diet in young to middle-aged adults: The CARDIA study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, A.; Hankins, S.; Jilcott, S. Measures of the consumer food store environment: A systematic review of the evidence 2000–2011. J. Commun. Health 2011, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, C.; Chaix, B. The influence of geographic life environments on cardiometabolic risk factors: A systematic review, a methodological assessment and a research agenda. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Charreire, H.; Casey, R.; Salze, P.; Simon, C.; Chaix, B.; Banos, A.; Badariotti, D.; Weber, C.; Oppert, J.M. Measuring the food environment using geographical information systems: A methodological review. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, K.; Timperio, A.F.; Crawford, D.A. Understanding environmental influences on nutrition and physical activity behaviors: Where should we look and what should we count? Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2006, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez Roux, A.V. Invited commentary: Places, people, and health. Amer. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiekermann, K.; Wegener, M. Freedom from the Tyranny of Zones: Towards New GIS-Based Spatial Models. In Spatial Models and GIS: New Potential and New Models; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zenk, S.N.; Schulz, A.J.; Matthews, S.A.; Odoms-Young, A.; Wilbur, J.; Wegrzyn, L.; Gibbs, K.; Braunschweig, C.; Stokes, C. Activity space environment and dietary and physical activity behaviors: A pilot study. Health Place 2011, 17, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarloos, D.; Kim, J.E.; Timmermans, H. The built environment and health: Introducing individual space-time behavior. Int. J. Environ. Res.Public Health 2009, 6, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEntee, J.; Agyeman, J. Towards the development of a GIS method for identifying rural food deserts: Geographic access in Vermont, USA. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchincloss, A.H.; Diez Roux, A.V. A new tool for epidemiology: The usefulness of dynamic-agent models in understanding place effects on health. Amer. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.; Witten, K.; Bartie, P. Neighbourhoods and health: A GIS approach to measuring community resource accessibility. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2006, 60, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.P. Analysis of human spatial behavior in a GIS environment: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Geograph. Syst. 2000, 2, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.P.; Murray, A.T.; O’Kelly, M.E.; Tiefelsdorf, M. Recent advances in accessibility research: Representation, methodology and applications. J. Geograph. Syst. 2003, 5, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestens, Y.; Lebel, A.; Daniel, M.; Thériault, M.; Pampalon, R. Using experienced activity spaces to measure foodscape exposure. Health Place 2010, 16, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilcott, S.B.; Moore, J.B.; Wall-Bassett, E.D.; Liu, H.; Saelens, B.E. Association between travel times and food procurement practices among female supplemental nutrition assistance program participants in eastern North Carolina. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2011, 43, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Karpyn, A.; McLaughlin, J.; Chilton, M.; Glanz, K. How far do low-income parents travel to shop for food? Empirical evidence from two urban neighborhoods. Urban Geogr. 2011, 32, 712–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northridge, M.E.; Sclar, E.D.; Biswas, P. Sorting out the connections between the built environment and health: A conceptual framework for navigating pathways and planning healthy cities. J. Urban Health 2003, 80, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M.; Giles-Corti, B.; Yaroch, A.L.; Cummins, S.; Frank, L.D.; Huang, T.T; Lewis, L.B. Work group IV: Future directions for measures of the food and physical activity environments. Amer. J. Prevent. Med. 2009, 36, S182–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.; Flood, V.M.; Yeatman, H. Measuring local food environments: An overview of available methods and measures. Health Place 2011, 17, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.A.; Bell, B.A. Access to healthful foods among an urban food insecure population: Perceptions versus reality. J. Urban Health 2009, 86, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.; Frank, L.; Sallis, J.F.; Saelens, B.; Glanz, K.; Chapman, J. Predictors of trips to food destinations. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, A.A.; Townshend, T.G.; Alvanides, S. Obesogenic Environments: Complexities, Perceptions and Objective Measures; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley, N.; Warm, D.; Margetts, B.; Whelan, A. Assessing the impact of improved retail access on diet in a “food desert”: A preliminary report. Urban Studies 2002, 39, 2061–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, S.; Petticrew, M.; Higgins, C.; Findlay, A.; Sparks, L. Large scale food retailing as an intervention for diet and health: Quasi-experimental evaluation of a natural experiment. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2005, 59, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokols, D. Social ecology and behavioral medicine: Implications for training, practice, and policy. Behav. Med. 2000, 26, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery, R.W.; Baxter, J.; McGuire, M.; Linde, J. Are fast food restaurants an environmental risk factor for obesity? Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2006, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Sallis, J.F.; Norman, G.J.; Saelens, B.E.; Harris, S.K.; Kerr, J.; Rosenberg, D.; Durant, N.; Glanz, K. Community food environment, home food environment, and fruit and vegetable intake of children and adolescents. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2012, 44, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.A.; Burgoine, T.; Greenhalgh, F.; Stamp, E.; Tyrrell, R. The foodscape: Classification and field validation of secondary data sources. Health Place 2010, 16, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timperio, A.F.; Ball, K.; Roberts, R.; Andrianopoulos, N.; Crawford, D.A. Children’s takeaway and fast-food intakes: Associations with the neighbourhood food environment. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.A.; Detwiler, J.E.; Burton, L.M. Geo-ethnography: Coupling geographic information analysis techniques with ethnographic methods in urban research. Cartographica 2005, 40, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, A.A.; Sharkey, J.; Samuel-Hodge, C.D.; Jones-Smith, J.; Folds, M.C.; Cai, J.; Ammerman, A.S. Perceived and objective measures of the food store environment and the association with weight and diet among low-income women in North Carolina. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, A.F.; Rigby, S.; Betterley, C.; Park, S.; Kurtz, H.; Johnson, M.A.; Lee, J.S. Store type and demographic influence on the availability and price of healthful foods, Leon County, Florida, 2008. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2011, 8, p. A140. Available online: www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2011/nov/10_0231.htm (accessed on 10 October 2012).
- Latham, J.; Moffat, T. Determinants of variation in food cost and availability in two socioeconomically contrasting neighbourhoods of Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Health Place 2007, 13, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, D.; Kouba, J. A comparison of the availability and affordability of a market basket in two communities in the Chicago area. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 837–845. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.; Filomena, S.; Morland, K. Analysis of fruit and vegetable cost and quality among racially segregated neighborhoods in Brooklyn, New York. J. Hunger Environ. Nutr. 2010, 5, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosler, A.S.; Rajulu, D.T.; Ronsani, A.E.; Fredrick, B.L. Peer reviewed: Assessing retail fruit and vegetable availability in urban and rural underserved communities. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2008, 5, p. A123. Available online: www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2008/oct/07_0169.htm (accessed on 10 October 2012).
- Caldwell, E.M.; Kobayashi, M.M.; DuBow, W.M.; Wytinck, S.M. Perceived access to fruits and vegetables associated with increased consumption. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 12, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, A.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Griffin, L.; Thomas, N.; Glanz, K. The value of conducting door-to-door surveys. Int. J. Soc. Res. Meth. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirsch, J.A.; Hillier, A. Exploring the Role of the Food Environment on Food Shopping Patterns in Philadelphia, PA, USA: A Semiquantitative Comparison of Two Matched Neighborhood Groups. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 295-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10010295
Hirsch JA, Hillier A. Exploring the Role of the Food Environment on Food Shopping Patterns in Philadelphia, PA, USA: A Semiquantitative Comparison of Two Matched Neighborhood Groups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013; 10(1):295-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10010295
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirsch, Jana A., and Amy Hillier. 2013. "Exploring the Role of the Food Environment on Food Shopping Patterns in Philadelphia, PA, USA: A Semiquantitative Comparison of Two Matched Neighborhood Groups" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, no. 1: 295-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10010295
APA StyleHirsch, J. A., & Hillier, A. (2013). Exploring the Role of the Food Environment on Food Shopping Patterns in Philadelphia, PA, USA: A Semiquantitative Comparison of Two Matched Neighborhood Groups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(1), 295-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10010295