Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Lake Using Spectral Smoothing and Derivative Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection

| Dataset | Sample numbers | Minimum | Maximum | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 23 | 5.0 | 156.0 | 33.0 |
| 2005 | 21 | 4.0 | 98.0 | 29.0 |
| 2011 | 12 | 11.4 | 35.8 | 23.3 |
2.2. Spectral Smoothing and Spectral Derivative


2.3. Model Building and Accuracy Evaluation






2.4. Preprocessing of HJ1/HSI Data
3. Results and Discussion
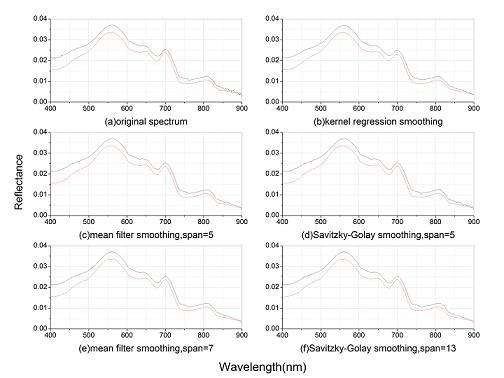
3.1. Spectral Smoothing

3.2. The Chl-a Estimation Model Based on the Spectral Derivative


3.3. Model Validation and Model Comparison


3.4. Estimation of Chl-a Based on HJ1/HSI Data

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Pitois, S.; Jackson, M.H.; Wood, B.J. Sources of the eutrophication problems associated with toxic algae: An overview. J. Environ Health 2001, 64, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Scherz, J.P. Development of a Practical Remote Sensing Water Quality Monitoring System. In Proceeding of 8th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2–6 October 1972.
- Johson, R.W.; Harris, R.C. Remote sensing for water quality and biological measurements in coastal waters. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1980, 46, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyendranath, S. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal, and other Optically-Complex, Waters; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Dartmouth, Canada, 2000; Report No. 3; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.Y. Weak Signal Detection, 2nd ed.; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 1994; pp. 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.N. Chemometrics in Analytical Chemistry; Sciences Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Demetriades-Shah, T.H.; Steven, M.D.; Clark, J.A. High resolution derivatives spectra in remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 33, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado-Torres, M.A. Evaluation and Development of Bio-optical Algorithms for Chlorophyll Retrieval in Western Puerto Rico. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Puerto Rico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goodin, D.G.; Han, L.; Fraser, R.N.; Rundquist, D.C.; Stebbins, W.A.; Schalles, J.F. Analysis of suspended solids in water using remotely sensed high resolution derivative spectra. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.H.; Rundquist, D.C. Comparison of NIR/RED ratio and first derivative of reflectance in estimating algal-chlorophyll concentration: A case study in a turbid reservoir. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H. Estimating chlorophyll-a concentration using first-derivative spectra in coastal water. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Q.; Tang, S.L.; Xing, Q.G.; Yang, J.K.; Zhan, H.G.; Shi, H.Y. A Derivative Spectrum Algorithm for Determination of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Pearl River Estuary. In Proceedings of Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007.
- Shi, H.Y.; Xing, Q.G.; Chen, C.Q.; Shi, P.; Tang, S.L. Using Second-Derivative Spectrum to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Estuarine Waters. In Proceedings of SPIE, Wuhan, China, 15–17 November 2007.
- Duan, H.T.; Ma, R.H.; Xu, J.P; Zhang, B. Comparison of different semi-empirical algorithms to estimate chlorophyll-a concentration in inland lake water. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Jiang, D.; Zhuang, D.F.; Fu, J.Y. Evaluation of hyperspectral indices for Chlorophyll-a concentration estimation in Tangxun Lake (Wuhan, China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2437–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Philpot, W. Derivative Analysis of Hyperspectral Data for Detecting Spectral Features. IGARSS’97. In Proceedings of 1997 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings. Remote Sensing—A Scientific Vision for Sustainable Development, Singapore, 3–8 August 1997.
- Chu, Z.L.; Yuan, H.F.; Lu, W.Z. Progress and application of spectral data pretreatment and wavelength selection methods in NIR analytical technique. Prog. Chem. 2004, 16, 528–542. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.C.; Wang, G.X.; Cheng, C.M. Noise removal in spectrum above water surface using Kernel regression smoothing. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 33, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q. Study prospect and evolution of eutrophication in lake Taihu. Shanghai Environ. Sci. 2001, 20, 263–265. [Google Scholar]
- Radiometric Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols, NASA/TM-2003-Ocean Optics Protocols For Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation, 4th ed.; Mueller, J.L.; Fargion, G.S.; McClain, C.R. (Eds.) Goddard Space Flight Space Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2003; Volume III.
- Yi, C. Kernel Smoothing Regression. 2008. Available online: www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/19195-kernel-smoothing-regression (accessed on 2 March 2011).
- Nadaraya, E.A. On Estimating Regression. Theor. Probab. Appl. 1964, 9, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Rundquist, D.C.; Liu, L.L.; Fraser, R.N.; Schalles, J.F. The spectral responses of algal chlorophyll in water with varying levels of suspended sediment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3707–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C. Towards a unified approach for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in both terrestrial vegetation and turbid productive waters. Geophys. Res. Lett 2003, 30, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimba, P.V.; Gitelson, A.A. Remote estimation of chlorophyll concentration inhypereutrophic aquatic systems: Model tuning and accuracy optimization. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.F.; Li, Y.M.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Lu, H. A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating chlorophyll a in highly turbid lakes: The case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanre, D.; Deuze, J.L. Second simulation of the satellite signal in the solar spectrum, 6S: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.F.R.; Doerffer, R.; Borstad, G.A. Interpretation of the 685 nm peak in water-leaving radiance spectra in terms of fluorescence, absorption and scattering, and its observation by MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A. The peak near 700 nm on reflectance spectra of algae and water: Relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll concentration. Int. J. Rem. Sens. 1992, 13, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.Z.; Lv, H.; Wei, Y.C. The Optical Characteristics of Taihu Lake and Its Color Remote Sensing; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, R.N. Hyperspectral remote sensing of turbidity and chlorophyll a among Nebraska Sand Hills lakes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 376. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.Q.; Hu, W.P.; Chen, W.M. Taihu Lake Water Environment Evolution Mechanism; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 248–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.X.; Song, L.R. Research of Formation Process and Its Environmental Characteristics of Cyanobacterial Bloom; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, D.; Han, X.Z.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Y.T.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L.J. Quantitative estimation of Taihu chlorophyll-a concentration using HJ-1A and 1B CCD imagery. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.; Wei, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Lake Using Spectral Smoothing and Derivative Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2979-2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10072979
Cheng C, Wei Y, Sun X, Zhou Y. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Lake Using Spectral Smoothing and Derivative Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013; 10(7):2979-2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10072979
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chunmei, Yuchun Wei, Xiaopeng Sun, and Yu Zhou. 2013. "Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Lake Using Spectral Smoothing and Derivative Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, no. 7: 2979-2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10072979
APA StyleCheng, C., Wei, Y., Sun, X., & Zhou, Y. (2013). Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Lake Using Spectral Smoothing and Derivative Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(7), 2979-2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10072979