Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Numerical Analysis
2.3.1. Enrichment Factor
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3.3. Human Health Risk Assessment
- (1)
- Non-carcinogenic risk assessment:
- (2)
- Carcinogenic risk assessment:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distribution of TopSoil Metals
3.2. Source Appointment of Heavy Metal Elements
3.2.1. The Enrichment of Heavy Metal Elements
3.2.2. Principal Component Analysis
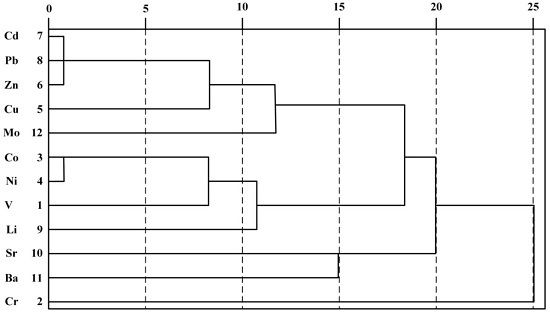
3.2.3. Clustering Analysis
3.3. Human Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.; Hou, H.; Shangguan, Y.; Li, F. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.B.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.L.; Hou, H. Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: Levels, sources and spatial distribution. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Int. J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Mei, Y.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of trace metals in urban soils in Wuhan, central China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Andrade, M.L.; Vega, F.A. Origin and spatial distribution of metals in urban soils. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lv, Y.; Shen, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Hu, S.; Zhou, X. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of Hankou region in Wuhan, China. In Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 740–750. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Pan, L.; Feng, X. Effect of land use type on metals accumulation and risk assessment in soil in the peri-urban area of Beijing, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Zeng, M.; Zhou, M. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in roadside soils based on voronoi diagram: A case study of Wuhan city. In Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 732–739. [Google Scholar]
- Ordóñez, A.; Álvarez, R.; De Miguel, E.; Charlesworth, S. Spatial and temporal variations of trace element distribution in soils and street dust of an industrial town in NW Spain: 15 years of study. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, S.X.; Yan, B.; Yang, F.; Li, N.; Xiao, X.M.; Fu, J.M. Spatial distribution of heavy metal contamination in soils near a primitive e-waste recycling site. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Hu, Q.; Yang, R.; Tang, H.; Li, M.; Huang, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Canonical correspondence analysis of soil heavy metal pollution, microflora and enzyme activities in the Pb–Zn mine tailing dam collapse area of Sidi village, SW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbana, T.A.; Ramadan, M.A.; Gaber, H.M.; Bahnassy, M.H.; Kishk, F.M.; Selim, H.M. Heavy metals accumulation and spatial distribution in long term wastewater irrigated soils. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Myrna, H.P.H.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; et al. Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 2013, 192, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.K.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, C.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, Y.; He, L.Y. Source apportionment of heavy metals in soils using multivariate statistics and geostatistics. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Malik, R.N.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Qadir, A. Enrichment, risk assessment, and statistical apportionment of heavy metals in tannery-affected areas. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartan, G.; Taşpınar, F.; Toröz, İ. Assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils and their source apportionment: A Turkish district survey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, Z.; Qureshi, B.A. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soil of Karachi, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 20, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, M.; Song, J.; Luo, F.; Han, L.; Li, C.; Dong, M. Assessment of human health risk for an area impacted by a large-scale metallurgical refinery complex in Hunan, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 21, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, E.; Iribarren, I.; Chacon, E.; Ordonez, A.; Charlesworth, S. Risk-based evaluation of the exposure of children to trace elements in playgrounds in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere 2007, 66, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around a smelter in Changqing town of Baoji City. Environ. Eng. 2015, 33, 121–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.R.; Lei, Y.Q.; Zhou, Q.L.; Wang, C.; Pan, J.C. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in environmental samples around electroplating factories and the health risk assessment. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 3447–3456. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, X.W.; Huang, L.; Zhuang, S.K.; Shi, C.Q.; Yin, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.J. Pollution level and health risk of heavy metals in dust from city parks of Xi’an. Int. J. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2015, 28, 5–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zoller, W.H.; Gladney, E.S.; Duce, R.A. Atmospheric concentrations and sources of trace metals at the South Pole. Science 1974, 183, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Bao, Z.Y.; Tang, J.H. Application of the enrichment factor in evaluating of heavy metals contamination in the environmental geochemistry. Geo Sci. Technol. Inf. 2006, 25, 65–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.X.; Li, K.; Li, M.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.; Cheng, X. Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical elements in urban soil in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 265–306. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhan, J.; Jiang, A. Environmental quality and sources of heavy metals in the topsoil based on multivariate statistical analyses: A case study in Laiwu City, Shandong Province, China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Peng, X.; Chen, G.; Xu, J.; Shi, G.L.; Zhang, Y.C.; Feng, Y.C. Insights into the chemical characterization and sources of PM2.5 in Beijing at a 1-h time resolution. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukumaran, M.; Devarayan, K. Evaluation of water quality of Kaveri River in Tiruchirappalli district, Tamil Nadu by principal component analysis. Curr. World Environ. 2016, 11, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinelli, A.; Sacchi, E.; Mallen, L. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, C.L.; Zereini, F.; Püttmann, W. Metal and metalloid accumulation in cultivated urban soils: A medium-term study of trends in Toronto, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C. Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Cheung, S.C.; Iain, T. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Part A; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 1.
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment; Part A; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Volume 1.
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Part E; Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 1.
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, S.; Chen, X. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of the coal mining city, Huainan, East China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variation Range | Degree of Contamination |
|---|---|
| EF ≤ 1 | No enrichment |
| 1 < EF ≤ 2 | Minimal enrichment |
| 2 < EF ≤ 5 | Moderate enrichment |
| 5 < EF ≤ 20 | Significant enrichment |
| 20 < EF ≤ 40 | Very high enrichment |
| EF > 40 | Extraordinary high enrichment |
| Parameter | IRing (mg·d−1) | IRinh (m3·d−1) | CF(mg·kg−1) | EF (d·a−1) | ED (a) | SA (cm2) | AF (mg·cm−1·d−1) | ABS | PEF (m3·kg−1) | BW (kg) | AT (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 100 | 15 | 1 × 10−6 | 87.5 | 6 | 5700 | 0.2 | 0.001 | 1.36 × 109 | 55.9 | ED × 365 (non-carcinogen) 70 × 365 (carcinogen) |
| Element | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RfDing | 7 × 10−3 | 3 × 10−3 | 2 × 10−2 | 2 × 10−2 | 4 × 10−2 | 3 × 10−1 | 1 × 10−3 | 3.5 × 10−3 | 5 × 10−3 |
| RfDinh | 7 × 10−3 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 5.71 × 10−6 | 2.06 × 10−2 | 4.02 × 10−2 | 3 × 10−1 | 1 × 10−3 | 3.52 × 10−3 | 4.95 × 10−3 |
| RfDder | 7 × 10−5 | 6 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−2 | 5.40 × 10−3 | 1.2 × 10−2 | 6 × 10−2 | 1 × 10−5 | 5.25 × 10−4 | 1.9 × 10−3 |
| SFinh | - | 42 | 9.8 | 0.84 | - | 6.3 | - | - |
| Element | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Li | Sr | Ba | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 99.27 | 147.84 | 11.94 | 38 | 66.8 | 221.77 | 0.93 | 66.28 | 38.5 | 387.94 | 796.73 | 2.24 |
| Min | 52.63 | 50.8 | 7.62 | 15.06 | 19.73 | 54.2 | 0.17 | 19.51 | 17.11 | 191 | 534.5 | 0.57 |
| Mean | 75.48 | 75.36 | 10.16 | 25.09 | 38.68 | 126.22 | 0.44 | 34.4 | 28.07 | 291 | 612.59 | 1.16 |
| Beijing’s Background | 71 | 58 | 10 | 25 | 20 | 58 | 0.09 | 19 | 26 | 271 | 598 | 0.6 |
| National Background | 87 | 73 | 13 | 29 | 24 | 68 | 0.11 | 23 | 37 | 156 | 495 | 0.7 |
| Element | Average Enrichment Coefficient | Contamination Classification Proportion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF ≤ 1 | 1 < EF ≤ 2 | 2 < EF ≤ 5 | 5 < EF ≤ 20 | ||
| V | 1.29 | 0.00% | 100.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Cr | 1.58 | 0.00% | 91.43% | 8.57% | 0.00% |
| Co | 1.23 | 0.00% | 100.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Ni | 1.22 | 11.43% | 88.57% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Cu | 2.35 | 0.00% | 38.64% | 61.36% | 0.00% |
| Zn | 2.64 | 0.00% | 25.71% | 68.57% | 5.71% |
| Cd | 5.94 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 34.29% | 65.71% |
| Pb | 2.2 | 0.00% | 32.35% | 64.71% | 2.94% |
| Li | 1.31 | 5.71% | 94.29% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sr | 1.3 | 5.71% | 94.29% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Ba | 1.24 | 5.88% | 94.12% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Mo | 2.35 | 0.00% | 48.57% | 48.57% | 2.86% |
| Element | Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Pb | 0.93 | −0.01 | −0.06 | 0.00 |
| Zn | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Cd | 0.91 | 0.05 | −0.16 | 0.17 |
| Cu | 0.78 | 0.08 | 0.17 | −0.13 |
| Mo | 0.58 | −0.03 | 0.08 | 0.56 |
| Co | 0.14 | 0.95 | −0.17 | 0.08 |
| V | −0.20 | 0.84 | 0.16 | −0.17 |
| Ni | 0.34 | 0.76 | −0.36 | 0.25 |
| Li | 0.22 | 0.51 | −0.68 | −0.23 |
| Sr | −0.06 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.10 |
| Ba | 0.48 | −0.09 | 0.78 | −0.07 |
| Cr | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.86 |
| Eigenvalue | 3.94 | 2.48 | 2.13 | 1.28 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 32.80 | 20.69 | 17.74 | 10.65 |
| Accumulating contribution rate (%) | 32.80 | 53.48 | 71.22 | 81.88 |
| V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | Mo | HI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQing | Max | 6.08 × 10−3 | 2.11 × 10−2 | 2.56 × 10−4 | 8.15 × 10−4 | 7.16 × 10−4 | 3.17 × 10−4 | 3.99 × 10−4 | 8.12 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−4 | 3.80 × 10−2 |
| Min | 3.22 × 10−3 | 7.26 × 10−3 | 1.63 × 10−4 | 3.23 × 10−4 | 2.12 × 10−4 | 7.75 × 10−5 | 7.29 × 10−5 | 2.93 × 10−3 | 4.89 × 10−5 | 1.38 × 10−2 | |
| Mean | 4.62 × 10−3 | 1.08 × 10−2 | 2.18 × 10−4 | 5.38 × 10−4 | 4.15 × 10−4 | 1.80 × 10−4 | 1.88 × 10−4 | 4.21 × 10−3 | 9.92 × 10−5 | 2.12 × 10−2 | |
| HQinh | Max | 6.71 × 10−7 | 2.45 × 10−4 | 9.89 × 10−5 | 8.73 × 10−8 | 7.86 × 10−8 | 3.50 × 10−8 | 4.40 × 10−8 | 8.91 × 10−7 | 2.14 × 10−8 | 3.45 × 10−4 |
| Min | 3.56 × 10−7 | 8.40 × 10−5 | 6.31 × 10−5 | 3.46 × 10−8 | 2.32 × 10−8 | 8.55 × 10−9 | 8.04 × 10−9 | 2.62 × 10−7 | 5.45 × 10−9 | 1.48 × 10−4 | |
| Mean | 5.10 × 10−7 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 8.41 × 10−5 | 5.76 × 10−8 | 4.55 × 10−8 | 1.99 × 10−8 | 2.07 × 10−8 | 4.62 × 10−7 | 1.11 × 10−8 | 2.10 × 10−4 | |
| HQder | Max | 6.93 × 10−3 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 3.65 × 10−6 | 3.44 × 10−5 | 2.72 × 10−5 | 1.81 × 10−5 | 4.55 × 10−4 | 6.17 × 10−4 | 5.76 × 10−6 | 2.01 × 10−2 |
| Min | 3.68 × 10−3 | 4.14 × 10−3 | 2.33 × 10−6 | 1.36 × 10−5 | 8.04 × 10−6 | 4.42 × 10−6 | 8.31 × 10−5 | 1.82 × 10−4 | 1.47 × 10−6 | 8.11 × 10−3 | |
| Mean | 5.27 × 10−3 | 6.14 × 10−3 | 3.10 × 10−6 | 2.27 × 10−5 | 1.58 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−5 | 2.14 × 10−4 | 3.20 × 10−4 | 2.98 × 10−6 | 1.20 × 10−2 | |
| HIt | Max | 1.30 × 10−2 | 3.34 × 10−2 | 3.59 × 10−4 | 8.49 × 10−4 | 7.43 × 10−4 | 3.35× 10−4 | 8.54 × 10−4 | 8.74 × 10−3 | 1.98 × 10−4 | 5.85 × 10−2 |
| Min | 6.9 × 10−3 | 1.15 × 10−2 | 2.29 × 10−4 | 3.37 × 10−4 | 2.20 × 10−4 | 8.19 × 10−5 | 1.56 × 10−4 | 2.57 × 10−3 | 5.04 × 10−5 | 2.20 × 10−2 | |
| Mean | 9.9 × 10−3 | 1.70 × 10−2 | 3.05 × 10−4 | 5.61 × 10−4 | 4.30 × 10−4 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 4.03 × 10−4 | 4.54 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−4 | 3.34 × 10−2 | |
| risk | Max | 2.5 × 10−8 | 4.7 × 10−10 | 1.3 × 10−10 | 2.4 × 10−11 | ||||||
| Min | 8.7 × 10−9 | 3 × 10−10 | 5.1 × 10−11 | 4.3 × 10−12 | |||||||
| Mean | 1.3 × 10−8 | 4 × 10−10 | 8.5 × 10−11 | 1.1 × 10−11 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Lv, M. Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070727
Sun C, Zhao W, Zhang Q, Yu X, Zheng X, Zhao J, Lv M. Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(7):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070727
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chunyuan, Wenji Zhao, Qianzhong Zhang, Xue Yu, Xiaoxia Zheng, Jiayin Zhao, and Ming Lv. 2016. "Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 7: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070727
APA StyleSun, C., Zhao, W., Zhang, Q., Yu, X., Zheng, X., Zhao, J., & Lv, M. (2016). Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(7), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070727