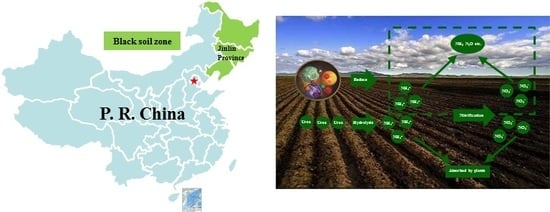
Evaluation of Controlled Release Urea on the Dynamics of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Its Nitrogen Release in Black Soils of Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Dynamics of Nitrate and Ammonium
3.1.1. Variation on the Ratio of Nitrate and Ammonium
3.1.2. Kinetics of Nitrate and Ammonium
3.2. Dynamics of Nitrogen Release from PCU and SCU
3.2.1. Characterization of Nitrogen Release
3.2.2. Kinetics Analysis
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of CRU on Nitrate and Ammonium
4.2. Characterization and Prediction of Nitrogen Release from CRU in Black Soils
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Burras, C.L.; Kravchenko, Y.S.; Duran, A.; Huffman, T.; Morras, H.; Studert, G.; Zhang, X.; Cruse, R.M.; Yuan, X. Overview of Mollisols in the world: Distribution, land use and management. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, Z.; You, Z.; Zhang, Y. Short-term gully retreat rates over rolling hill areas in black soil of Northeast China. Catena 2007, 71, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Xu, S.G.; Zhang, H.W. Soil loss and conservation in the black soil region of Northeast China: A retrospective study. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y. Calculation of county cultivated land productivity and its analysis of influential factors of grain main production area in Northeast China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 308–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B.; Guan, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, J.; Cao, F.; Li, L.; Li, J. Effect of 35 years inorganic fertilizer and manure amendment on structure of bacterial and archaeal communities in black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yu, W.-T.; Zhao, S.-H.; Zhang, L. Relationship between Water-Stable Aggregates and Nutrients in Black Soils after Reclamation. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akelah, A. Novel utilizations of conventional agrochemicals by controlled release formulations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1996, 4, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ghoshal, N.; Singh, K.P. Synchronizing nitrogen availability through application of organic inputs of varying resource quality in a tropical dryland agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 36, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.-D.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Fu, B.-J.; Han, X.-Z.; Zhang, L.; He, J.-Z. Effect of Long-Term Application of Chemical Fertilizers on Microbial Biomass and Functional Diversity of a Black Soil. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Bao, X.; Simon, G.P.; Petinakis, E.; Chen, L. Preparation and characterization of slow-release fertilizer encapsulated by starch-based superabsorbent polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papangkorn, J.; Isaraphan, C.; Phinhongthong, S.; Opaprakasit, M.; Opaprakasit, P. Controlled-release material for urea fertilizer from polylactic acid. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 55, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Liang, Y.; Ye, S.; He, Z. Superabsorbent hydrogels as carriers for the controlled-release of urea: Experiments and a mathematical model describing the release rate. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 102, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow-and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Efficiency in Agriculture; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shaviv, A. Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Adv. Agron. 2001, 71, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Naz, M.Y.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Ariwahjoedi, B.; Shaari, K.Z.K. Characterization of modified tapioca starch solutions and their sprays for high temperature coating applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 375206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, M.; Chi, G.; Huang, B. Fixation of labeled (15NH4)2 SO4 and its subsequent release in black soil of Northeast China over consecutive crop cultivation. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, A.M.; Mehta, M.H.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Soppimath, K.S. A review on controlled release of nitrogen fertilizers through polymeric membrane devices. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 1999, 38, 675–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Rind, D.; Streets, D.G. Effects of 2000–2050 changes in climate and emissions on global tropospheric ozone and the policy-relevant background surface ozone in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortoletto-Santos, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Polito, W.L. Controlled release of nitrogen-source fertilizers by natural-oil-based poly (urethane) coatings: The kinetic aspects of urea release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. Coupling effects of plastic film mulching and urea types on water use efficiency and grain yield of maize in the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 157, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, A.; Mikkelsen, R.L. Controlled-release fertilizers to increase efficiency of nutrient use and minimize environmental degradation—A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1993, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S. An introduction to the global nitrogen cycle. Soil Use Manag. 1990, 6, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestone, M.K.; Davidson, E.A. Microbiological basis of NO and N2O production and consumption in soil. Exch. Trace Gases Terr. Ecosyst. Atmos. 1989, 47, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.; Li, Q.; Liao, N.; Guo, H.; Min, W.; Ma, L.; Ye, J.; Hou, Z. Saline water irrigation stimulate N2O emission from a drip-irrigated cotton field. Acta Agric. Scand. 2016, 66, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angás, P.; Lampurlanés, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Tillage and N fertilization: Effects on N dynamics and barley yield under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Zhao, M.Q.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X. Accumulation and profile distribution of soil mineralized nitrogen in fallow season. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2008, 39, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.L. Nitrification in soil. Nitrogen Agric. Soils 1982, 22, 253–288. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.; Man, Z.B.; Basit, A.; Thanh, T.H. Review on materials & methods to produce controlled release coated urea fertilizer. J. Control. Release 2014, 181, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.L.; Rosen, C.J.; Moncrief, J.F. A comparison of techniques for determining nitrogen release from polymer-coated urea in the field. HortScience 2009, 44, 492–494. [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt, C.R.; Venterea, R.T.; Rosen, C.J.; McNearney, M.; Wilson, M.L.; Dolan, M.S. Polymer-coated urea maintains potato yields and reduces nitrous oxide emissions in a Minnesota loamy sand. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, D.D.; Liu, M.; Geng, Y.Q. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, yield, and quality of wheat. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, D.; Liu, M.; Geng, Y.; Chen, J. Controlled-release urea for rice production and its environmental implications. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, W.; Tian, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency and yield of wheat and corn. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. National Environmental Protection Standards of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 717-2014; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. National Environmental Protection Standards of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 634-2012; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. National Environmental Protection Standards of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 613-2011; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. National Environmental Protection Standards of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 802-2016; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Agricultural Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. NYT 1121.4-2006; Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Agricultural Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. NYT 1377-2007; Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Wilson, M.L.; Rosen, C.J.; Moncrief, J.F. Effects of polymer-coated urea on nitrate leaching and nitrogen uptake by potato. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 39, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Geng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Biobased polymer composites derived from corn stover and feather meals as double-coating materials for controlled-release and water-retention urea fertilizers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8166–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, B.; Venterea, R.T. Nitrite intensity explains N management effects on N2O emissions in maize. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, S.; Alva, A.K. Leaching of nitrogen forms from controlled-release nitrogen fertilizers. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 1997, 28, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunt, O.R. Modified sulphur coated granular urea for controlled nutrient release. Int. Soc. Soil Sci. Trans. 1968, 3, 337–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann, H.; Engels, T. Nitrogen Utilisation in Relation to N-Fertilisation; Fertiliser Society: Colchester, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.J.; Schepers, J.S.; Porter, L.K. Assessing and managing agricultural nitrogen losses to the environment. In Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liao, L.; Tan, J.; Shao, X. Ammonia volatilization in gemmiparous and early seedling stages from direct seeding rice fields with different nitrogen management strategies: A pots experiment. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Kuldipsingh, D.J. Effects of 4-amino 1, 2, 4-triazole, dicyandiamide and encapsulated calcium carbide on nitrification inhibition in a subtropical soil under upland and flooded conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 33, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.Y.; Sulaiman, S.A. Slow release coating remedy for nitrogen loss from conventional urea: A review. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, K.L.; Maddux, L.D.; Pierzynski, G.M.; Kissel, D.E.; Bock, B.R. Corn responses to ammonium-and nitrate-nitrogen fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, S.M.; Alderman, S.C.; Streeter, D.J. Italian ryegrass and nitrogen source fertilization in western Oregon in two contrasting climatic years. II. Plant nitrogen accumulation and soil nitrogen status. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, S.M.; Streeter, D.J. Nitrate and ammonium nutrition in ryegrass: Changes in growth and chemical composition under hydroponic conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 1994, 17, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, B.R. Increasing cereal yields with higher ammonium/nitrate ratios: Review of potentials and limitations. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 1986, 21, 723–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.L.; Kamprath, E.J.; Moll, R.H.; Jackson, W.A. Prolificacy in corn: Its effects on nitrate and ammonium uptake and utilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, F.; Jalali, M. Empirical and Mechanistic Evaluation of NH4+ Release Kinetic in Calcareous Soils. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi-Ghiri, M. Effects of zeolite and vermicompost applications on potassium release from calcareous soils. Soil Water Res. 2014, 9, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.H.; Geng, Y.Q. Improving the quality of polymer-coated urea with recycled plastic, proper additives, and large tablets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y. Structure and properties of controlled release fertilizers coated with thermosetting resin. Polym. Plast. Technol. 2013, 52, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, C.; Li, Y.; Mao, Z. Use of polyurea from urea for coating of urea granules. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, W.M.; Boersma, L. Release of urea by granules of sulfur-coated urea. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrell, W.M.; Boersma, L. Model for the release of urea by granules of sulfur-coated urea applied to soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1979, 43, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhou, J.; Shaviv, A. Release characteristics of nutrients from polymer-coated compound controlled release fertilizers. J. Polym. Environ. 2006, 14, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Liu, M.; Wu, L. Controlled release NPK compound fertilizer with the function of water retention. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.J.; Fan, X.L.; Yu, J.G.; Fang, L.I.U.; Zhang, Q. Study on the rapid method to predict longevity of controlled release fertilizer coated by water soluble resin. Agric. Sci. China 2008, 7, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiex, N. Determination of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium release rates of slow-and controlled-release fertilizers: Single-laboratory validation, first action 2015. 15. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.S.; Yuan, J.F.; Hu, R.G. Characteristics of nutrient release kinetics for organic polymer-coated fertilizers. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 733–735. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Ling, Y.; Dang, X.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. Solubility characteristics and slow-release mechanism of nitrogen from organic-inorganic compound coated urea. Int. J. Photoenergy 2015, 2015, 705471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Adhikari, T.; Coumar, M.V.; Rajendiran, S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Saha, J.K.; Biswas, A.K.; Rao, A.S. Pine oleoresin: A potential urease inhibitor and coating material for slow-release urea. Curr. Sci. India 2013, 104, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Nyborg, M.; Malhi, S.S.; McKenzie, R.H.; Solberg, E. Phosphorus release from coated monoammonium phosphate: Effect of coating thickness, temperature, elution medium, soil moisture and placement method. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2000, 80, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Baligar, V.C.; Martens, D.C.; Ritchey, K.D.; Elrashidi, M. Effect of byproduct, nitrogen fertilizer, and zeolite on phosphate rock dissolution and extractable phosphorus in acid soil. Plant Soil 1999, 208, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Fan, X.; Ni, X.; Li, L.; Zou, G.; Cao, B. Predicting Nitrogen Release from Parabolic-type Resin-coated Urea in Greenhouse Tomato and Cucumber Production. HortScience 2017, 52, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Types | Labeled Nitrogen Content (%) | Determined Nitrogen Content (%) | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| conventional urea (U) | 46.2 | 46.85 | Hanfeng Slow-Release Fertilizer Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China |
| sulfur coated urea (SCU) | 37 | 39.78 | Hanfeng Slow-Release Fertilizer Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China |
| polyurethane coated urea (PCU) | 43 | 46.04 | Audiocodes Technology Co., Ltd. Mianyang, China |
| Basic Indicators | Values | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Organic matter | 538.64 | g/kg |
| Water content | 176.47 | g/kg |
| pH | 7.34 | / |
| Conductivity (EC) | 178.2 | us/cm |
| Bulk density | 0.858 | g/cm3 |
| Porosity | 67.62 | % |
| Total nitrogen | 6427 | mg/kg |
| Treatment | Model | Equation | r | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | First-order kinetic | qt = 615.085 (1 − e−0.06t) | 0.952 | 46.36 |
| Simple Elovich | qt = − 33.493 + 220.584 ln(t) | 0.950 | 50.73 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = − 63.984 + 106.174 t0.5 | 0.926 | 59.58 | |
| PCU | First-order kinetic | qt = 332.770 (1 − e−0.039t) | 0.917 | 30.79 |
| Simple Elovich | qt = − 102.950 + 96.473 ln(t) | 0.897 | 31.32 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = − 38.947 + 48.720 t0.5 | 0.918 | 28.8 | |
| SCU | First-order kinetic | qt = 676.778 (1 − e−0.040t) | 0.939 | 54.47 |
| Simple Elovich | qt = − 235.365 + 205.318 ln(t) | 0.950 | 47.22 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = − 93.994 + 102.525 t0.5 | 0.926 | 57.53 |
| Treatment | Model | Equation | r | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | First-order kinetic | / | / | / |
| Simple Elovich | qt = 1234.959 − 239.999 ln(t) | 0.858 | 90.49 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = 1023.124 − 109.340 t0.5 | 0.709 | 99.33 | |
| PCU | First-order kinetic | qt = 413 (1 − e−0.302t) | 0.537 | 21.13 |
| Simple Elovich | qt = 267.512 + 46.085 ln(t) | 0.815 | 19.57 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = 294.295 + 24.128 t0.5 | 0.866 | 17.95 | |
| SCU | First-order kinetic | / | / | / |
| Simple Elovich | qt = 500.964 − 33.184 ln(t) | 0.932 | 8.798 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = 474.185 − 15.684 t0.5 | 0.893 | 10.5 |
| Controlled Release Urea | Model | Equation | r | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCU | First-order kinetic | qt = − 15.829 (1 − e0.018t) | 0.946 | 1.671 |
| Simple Elovich | qt = − 20.2 + 6.001 ln(t) | 0.854 | 2.683 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = − 5.98 + 3.146 t0.5 | 0.907 | 2.171 | |
| SCU | First-order kinetic | qt = 37.76 (1 − e−0.269t) | 0.634 | 3.272 |
| Simple Elovich | qt = 26.64 + 3.364 ln(t) | 0.584 | 3.434 | |
| Parabolic diffusion | qt = 29.65 + 1.524 t0.5 | 0.536 | 3.571 |
| Regression Equation | Collinearity | r | SE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | VIF | |||
| PCU = 0.03618N + 0.06146A − 23.1 | 0.454 | 2.203 | 0.973 | 1.449 |
| SCU = −0.004514N − 0.1409A + 95.06 | 0.232 | 4.310 | 0.731 | 3.537 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, X.; He, X.; Duan, H.; Han, L.; Huang, G. Evaluation of Controlled Release Urea on the Dynamics of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Its Nitrogen Release in Black Soils of Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010119
Tong X, He X, Duan H, Han L, Huang G. Evaluation of Controlled Release Urea on the Dynamics of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Its Nitrogen Release in Black Soils of Northeast China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010119
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Xin, Xueqin He, Hongwei Duan, Lujia Han, and Guangqun Huang. 2018. "Evaluation of Controlled Release Urea on the Dynamics of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Its Nitrogen Release in Black Soils of Northeast China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 1: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010119
APA StyleTong, X., He, X., Duan, H., Han, L., & Huang, G. (2018). Evaluation of Controlled Release Urea on the Dynamics of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Its Nitrogen Release in Black Soils of Northeast China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010119