Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Impairment in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Air Pollutant Variables
2.3. Cognitive Impairment
2.4. Other Variables
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Study Population
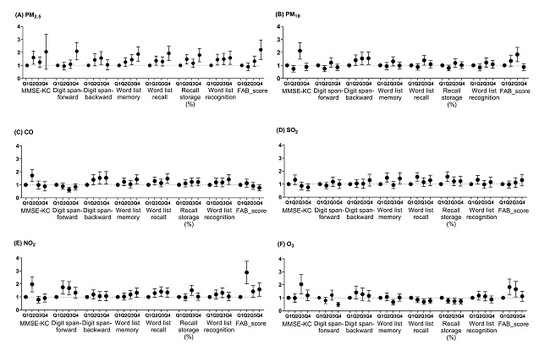
3.2. Cognitive Scales according to the Increases in Air Pollutants
3.2.1. Linear Mixed Model
3.2.2. Multiple logistic model
3.3. Cognitive Impairment Due to the Increase of PM2.5 and Participants’ Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilian, J.; Kitazawa, M. The emerging risk of exposure to air pollution on cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease—Evidence from epidemiological and animal studies. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, B.; Newby, D.; Lee, D.; Lyall, D.M.; Nevado-Holgado, A.J.; Evans, J.J.; Pell, J.P.; Lovestone, S.; Cavanagh, J. Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses of outdoor air pollution exposure and cognitive function in UK Biobank. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.; Guo, X.; Cheung, F.M.H.; Yung, K.K.L. The association between PM2.5 exposure and neurological disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 655, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Yu, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Qin, H. The prevalence and progression of mild cognitive impairment among clinic and community populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2017, 29, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, B.J.; Fratiglioni, L.; Viitanen, M.; Winblad, B.; Backman, L. The course of cognitive impairment in preclinical Alzheimer disease: Three- and 6-year follow-up of a population-based sample. Arch. Neurol. 2000, 57, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flicker, C.; Ferris, S.H.; Reisberg, B. Mild cognitive impairment in the elderly: Predictors of dementia. Neurology 1991, 41, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, E.; Szoeke, C.E.I.; Vollset, S.E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Aichour, M.T.E.; Akinyemi, R.O.; Alahdab, F.; Asgedom, S.W.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougere, B.; Delrieu, J.; Del Campo, N.; Soriano, G.; Sourdet, S.; Vellas, B. Cognitive Frailty: Mechanisms, Tools to Measure, Prevention and Controversy. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 33, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Solfrizzi, V.; Sardone, R.; Dibello, V.; Di Lena, L.; D’Urso, F.; Stallone, R.; Petruzzi, M.; Giannelli, G.; et al. Different Cognitive Frailty Models and Health- and Cognitive-related Outcomes in Older Age: From Epidemiology to Prevention. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2018, 62, 993–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, C.R.; Lin, Y.T.; Hwang, B.F. Ozone, particulate matter, and newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2015, 44, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurth, R.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Tucker, K.L.; Griffith, J.; Manjourides, J.; Suh, H. Fine Particle Sources and Cognitive Function in an Older Puerto Rican Cohort in Greater Boston. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiotakis, K.; Vlachogianni, T. Airborne Particulate Matter and Human Health: Toxicological Assessment and Importance of Size and Composition of Particles for Oxidative Damage and Carcinogenic Mechanisms AU - VALAVANIDIS, ATHANASIOS. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 2008, 26, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kwong, J.C.; Copes, R.; Tu, K.; Villeneuve, P.J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Hystad, P.; Martin, R.V.; Murray, B.J.; Jessiman, B.; et al. Living near major roads and the incidence of dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis: A population-based cohort study. Lancet 2017, 389, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kwong, J.C.; Copes, R.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Tu, K.; Brook, J.R.; Goldberg, M.S.; Martin, R.V.; Murray, B.J.; et al. Exposure to ambient air pollution and the incidence of dementia: A population-based cohort study. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culqui, D.R.; Linares, C.; Ortiz, C.; Carmona, R.; Diaz, J. Association between environmental factors and emergency hospital admissions due to Alzheimer’s disease in Madrid. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 592, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailshire, J.A.; Crimmins, E.M. Fine particulate matter air pollution and cognitive function among older US adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.E.; Park, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.H.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S.B.; Yu, S.D.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H. Comparison of Short-Term Associations between PM2.5 Components and Mortality across Six Major Cities in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Lung Association. State of the Air 2016. Available online: http://www.lung.org/assets/documents/healthy-air/stateof-the-air/sota-201 (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Broday, D.M.; The Citi-Sense Project Collaborators. Wireless Distributed Environmental Sensor Networks for Air Pollution Measurement-The Promise and the Current Reality. Sensors 2017, 17, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.U.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Jhoo, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, S.H.; Woo, J.I. Development of the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Packet (CERAD-K): Clinical and neuropsychological assessment batteries. J. Gerontol. B-Psychol. 2002, 57, P47–P53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Jhoo, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, J.C.; Woo, S.I.; Ha, J.; Woo, J.I. A normative study of the CERAD neuropsychological assessment battery in the Korean elderly. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2004, 10, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.H.; Huh, Y.; Choe, J.Y.; Jeong, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, J.J.; Jhoo, J.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Woo, J.I.; et al. Korean version of frontal assessment battery: Psychometric properties and normative data. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2010, 29, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Jhoo, J.H.; Youn, J.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Woo, S.I.; Woo, J.I. A normative study of the mini-mental state examination in the Korean elderly. J. Korean Neuropsychiatr. Assoc. 2002, 41, 508–525. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, W.; Kowal, P.; Chatterji, S.; Wang, L. Social-Economic Status and Cognitive Performance among Chinese Aged 50 Years and Older. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.C.; Choi, M.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.C.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, U.H.; Baek, J.H.; Gim, S.Y.; Choi, Y.C.; Lee, B.Y.; et al. Differences in and correlations between cognitive abilities and brain volumes in healthy control, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer disease groups. Clin. Anat. 2016, 29, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado-Pomares, M.; Carmen Terol-Cantero, M.; Sanchez-Perez, A.; Peral-Gomez, P.; Valera-Gran, D.; Navarrete-Munoz, E.M. The frontal assessment battery in clinical practice: A systematic review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 33, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, H.S.; Costa, A.S.; Castro, S.L.; Lima, C.F.; Vicente, S.G. Assessing Executive Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Critical Review of Brief Neuropsychological Tools. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Won, C.W.; Choi, H.R.; Kim, B.S.; Park, M.S. Physical frailty predicts medical expenses in community-dwelling, elderly patients: Three-year prospective findings from living profiles of older people surveys in Korea. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2015, 6, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hoore, W.; Sicotte, C.; Tilquin, C. Risk adjustment in outcome assessment: The Charlson comorbidity index. Methods Inf. Med. 1993, 32, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollutants and mental health status: A nationwide population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Rodriguez, A.; Fernandez-Nino, J.A.; Manrique-Espinoza, B.; Moreno-Banda, G.L.; Sosa-Ortiz, A.L.; Qian, Z.M.; Lin, H. Exposure to ambient PM2.5 concentrations and cognitive function among older Mexican adults. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Air Purifier Sales Shoot Up as Fine Dust Worries Shoppers. Available online: http://koreajoongangdaily.joins.com/news/article/article.aspx?aid=3059575 (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Power, M.C.; Adar, S.D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Weuve, J. Exposure to air pollution as a potential contributor to cognitive function, cognitive decline, brain imaging, and dementia: A systematic review of epidemiologic research. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Reed, W.; Maronpot, R.R.; Henriquez-Roldán, C.; Delgado-Chavez, R.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, A.; Dragustinovis, I.; Franco-Lira, M.; Aragón-Flores, M.; Solt, A.C.; et al. Brain Inflammation and Alzheimer’s-Like Pathology in Individuals Exposed to Severe Air Pollution. Toxicol. Pathol. 2004, 32, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, F.L.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Becher, B. Immune attack: The role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciottolo, M.; Wang, X.; Driscoll, I.; Woodward, N.; Saffari, A.; Reyes, J.; Serre, M.L.; Vizuete, W.; Sioutas, C.; Morgan, T.E.; et al. Particulate air pollutants, APOE alleles and their contributions to cognitive impairment in older women and to amyloidogenesis in experimental models. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryou, H.g.; Heo, J.; Kim, S.-Y. Source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 air pollution, and possible impacts of study characteristics in South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, N.M.; Henderson, V.W.; Hodis, H.N.; St John, J.A.; Lurmann, F.; Chen, J.-C.; Mack, W.J. Components of air pollution and cognitive function in middle-aged and older adults in Los Angeles. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Mean ± SD or N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, (min/max), years | 76.0 ± 3.9 (70.0/84.0) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 1377 (47.5) |
| Female | 1519 (52.5) |
| Smoking | |
| Current | 1104 (38.1) |
| Never/former | 1792 (61.9) |
| Alcohol intake | |
| Never/Less than one time per week | 520 (18.0) |
| More than one time per week | 2376 (82.0) |
| Physical activity, kcal/week | |
| Active | 2580 (89.1) |
| Inactive | 316 (10.9) |
| Education, years | |
| <9 | 1396 (48.2) |
| ≥9 | 1500 (51.8) |
| Marital status | |
| Married/with partner | 1950 (67.3) |
| Divorced/widowed/unmarried | 946 (32.7) |
| Household income, won/monthly | |
| <1,000,000 | 1370 (47.3) |
| ≥1,000,000 | 1526 (52.7) |
| Length of current residence, year | |
| 1~5 | 643 (22.2) |
| >5 | 2253 (77.8) |
| Residence | |
| Urban | 2013 (69.9) |
| Rural | 883 (30.1) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.5 ± 3.1 |
| K-ADL (min/max) | 7.1 ± 0.4 (7/14) |
| K-IADL (min/max) | 0.3 ± 0.8 (0/9) |
| Carlson comorbidity index (range: 0–7) | 0.48 ± 0.79 |
| MMSE-KC (range: 8–30) | 25.6 ± 3.3 |
| Digit span-forward (range: 0–9) | 5.8 ± 1.5 |
| Digit span-backward (range: 0–8) | 3.3 ± 1.1 |
| Word list memory (range: 0–29) | 16.7 ± 4.3 |
| Word list recall (range: 0–10) | 5.5 ± 2.1 |
| Recall storage (%) | 77.4 ± 24.2 |
| Word list recognition, (range: 0–10) | 8.6 ± 1.9 |
| Frontal assessment battery test (range: 0–18) | 13.4 ± 3.0 |
| 1-SD | MMSE-KC | Digit Forward Span | Digit Backward Span | Word List Memory | Word List Recall | Recall Storage | Word List Recognition | FAB_Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 1.5 μg/m3 | −0.010 (−0.019,−0.001)2 | −0.022 (−0.040,−0.005)2 | −0.039 (−0.057,−0.020)2 | −0.024 (−0.036,−0.011)2 | −0.036 (−0.054,−0.018)2 | −0.024 (−0.038,−0.010)2 | −0.016 (−0.029,−0.003)2 | −0.037 (−0.048,−0.025)2 |
| PM10 | 4.6 μg/m3 | −0.035 (−0.050,−0.020)2 | −0.029 (−0.057,−0.001)2 | 0.022 (−0.008,0.053) | 0.049 (0.015,0.083)2 | −0.011 (−0.033,0.011) | −0.014 (−0.031,0.003) | 0.001 (−0.015,0.016) | −0.002 (−0.021,0.017) |
| CO | 0.08 ppm | 0.044 (0.032,0.056)2 | 0.052 (0.029,0.075)2 | −0.022 (00.046,0.003) | −0.035 (−0.063,−0.007)2 | −0.018 (−0.034,−0.003)2 | −0.005 (−0.017,0.007) | −0.007 (−0.018,0.004) | −0.006 (−0.019,0.007) |
| SO2 | 0.9 ppb | 0.007 (−0.005,0.020) | 0.058 (0.035,0.082)2 | −0.032 (−0.058,−0.007)2 | −0.010 (−0.039,0.019) | −0.038 (−0.060,−0.017)2 | −0.022 (−0.039,−0.006)2 | −0.011 (−0.026,0.004) | 0.007 (−0.005,0.020) |
| NO2 | 7.7 ppb | 0.012 (0.001,0.025)2 | −0.026 (−0.050,−0.003)2 | 0.015 (−0.009,0.040) | 0.034 (0.006,0.063)2 | −0.019 (−0.035,−0.003)2 | −0.007 (−0.042,0.015) | −0.003 (−0.015,0.008) | −0.019 (−0.034,−0.005)2 |
| O3 | 4.3 ppb | 0.045 (0.027,0.062)2 | 0.062 (0.029,0.094)2 | −0.029 (−0.064,0.006) | 0.009 (−0.031,0.048) | 0.034 (0.018,0.049) 2 | 0.013 (0.001,0.025)2 | 0.010 (−0.001,0.021) | 0.011 (0.002,0.019)2 |
| Age | 1 year | −0.006 (−0.008,−0.005)2 | −0.009 (−0.012,−0.006)2 | −0.009 (−0.012, −0.006)2 | −0.020 (−0.024,−0.017)2 | −0.026 (−0.030,−0.022)2 | −0.012 (−0.016,−0.009)2 | −0.010 (−0.013,−0.007)2 | −0.009 (−0.011,−0.007)2 |
| Education | 1 year | −0.011 (−0.010,−0.012)2 | −0.018 (−0.016,−0.020)2 | −0.024 (−0.021,−0.026)2 | −0.016 (−0.014,−0.019)2 | −0.017 (−0.013,−0.021)2 | −0.005 (−0.002,−0.008)2 | −0.006 (−0.003,−0.009)2 | −0.023 (−0.021,−0.025)2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Han, S.-H.; Choi, J. Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Impairment in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193767
Shin J, Han S-H, Choi J. Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Impairment in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(19):3767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193767
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jinyoung, Seol-Heui Han, and Jaekyung Choi. 2019. "Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Impairment in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 19: 3767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193767
APA StyleShin, J., Han, S. -H., & Choi, J. (2019). Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Impairment in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(19), 3767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193767