Effect of Liming with Various Water Regimes on Both Immobilization of Cadmium and Improvement of Bacterial Communities in Contaminated Paddy: A Field Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Tested Soil and Amendment
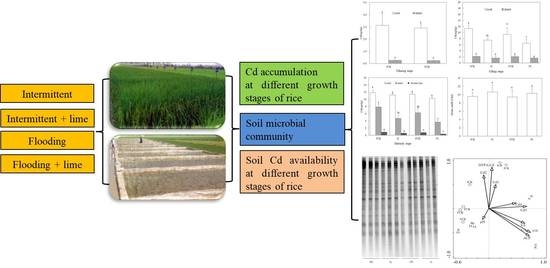
2.2. Experimental Setup in the Field
2.3. Sampling and Pretreatment
2.4. Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Community
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distribution of Cadmium in Various Parts of Rice
3.2. Soil pH and Availability of Cadmium
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Characteristics
3.4. Relationships among the Bacterial Community and Environmental Variables
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabarrón, M.; Faz, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A. Assessment of metals behaviour in industrial soil using sequential extraction, multivariable analysis and a geostatistical approach. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 172, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.L.; Sun, Z.H.; Hu, Y.N.; Zeng, X.Y.; Yu, Z.Q.; Cheng, H.F. Comparison of soil heavy metal pollution caused by e-waste recycling activities and traditional industrial operations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mominul, I.M.; Rezaul, K.M.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. Heavy metal and metalloid pollution of soil, water and foods in Bangladesh: A Critical Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2825. [Google Scholar]
- Cheraghi, M.; Lorestani, B.; Merrikhpour, H.; Rouniasi, N. Heavy metal risk assessment for potatoes grown in overused phosphate-fertilized soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.G. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.L.; Ma, X.W.; Ai, S.W.; Zhu, S.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in a sewage irrigation region, northwest China. J. Soil Sediment. 2016, 16, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmann, J.; Losak, T.; Pachner, M.; Watanabe, D.; Musilova, L.; Hlusek, J. Soybean cadmium concentration: Validation of a QTL affecting seed cadmium accumulation for improved food safety. Euphytica 2015, 203, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Wei, W.; Li, M.; Huang, R.; Yang, F.; Duan, Y. Heavy metal contamination in rice-producing soils of Hunan Province, China and potential health risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15584–15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.; Datta, S.P.; Golui, D.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Meena, M.C. Long-term impact of sewage irrigation on soil properties and assessing risk in relation to transfer of metals to human food chain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14269–14283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C. Current health risk assessment practice for dietary cadmium: Data from different countries. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, N.; Mu, G.; Shinwari, K.; Shen, Z.; Zheng, L. Screening for Cd-safe cultivars of Chinese cabbage and a preliminary study on the mechanisms of cd accumulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Liao, Q.; He, X.Q. Characterization of Cd translocation and accumulation in 19 maize cultivars grown on Cd-contaminated soil: Implication of maize cultivar selection for minimal risk to human health and for phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5410–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, M.E.; Chen, W.P.; Li, Y.L.; Peng, C. Cadmium accumulation risk in vegetables and rice in southern china: Insights from solid-solution partitioning and plant uptake factor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5463–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wen, X.H.; Cai, Y.X.; Cai, K.Z. Silicon-mediated enhancement of heavy metal tolerance in rice at different growth stages. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Guo, Z.H.; Peng, C.; Xiao, X.Y.; Feng, W.L.; Huang, B.; Ran, H.Z. Immobilization of cadmium and improvement of bacterial community in contaminated soil following a continuous amendment with lime mixed with fertilizers: A four-season field experiment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Shams, M.S.; Khalifa, M.R.; El-Dali, M.A.; Rinklebe, J. Various soil amendments and environmental wastes affect the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of potentially toxic elements in a sewage effluent irrigated sandy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Deng, Y.; Han, C. Lime and phosphate amendment can significantly reduce uptake of Cd and Pb by field-grown rice. Sustainability. 2017, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, T.; Kawasaki, A.; Baba, K.; Mori, S.; Matsumoto, S. Effects of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation and dimethylarsinic acid concentrations in Japanese rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9361–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.J.; Li, Z.; Yuan, C.; Ouyang, Y.N.; Zhou, L.Q.; Huang, J.X.; Huang, Y.J.; Luo, Y.M.; Christie, P.; Wu, L.H. Effect of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation by rice (Oryza sativa L.) with different metal accumulation capacities. J. Soil Sediment. 2013, 13, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Abbas, T.; Adrees, M.; Ziaurrehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Nawazd, R. Residual effects of biochar on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Cd stress with different water conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 206, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.F.; Wei, Z.B.; Penn, C.J.; Xu, T.F.; Wu, Q.T. Effect of soil washing and liming on bioavailability of heavy metals in acid contaminated soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Yang, Z.H.; Wu, B.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, R.P.; Liao, Y.P. Removal of Cd and Pb in calcareous soils by using Na2EDTA recycling washing. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 64–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatkar, A.K.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Talebi, A.F.; Moheimani, N.R.; Mchenry, M.P. Potential use of algae for heavy metal bioremediation, a critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.X.; Liao, B.; Yang, Z.H.; Chai, L.Y.; Li, J.T. Revegetation of extremely acid mine soils based on aided phytostabilization: A case study from southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyamine, A.; Moussa, M.; Ismael, M.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, C. Earthworms, rice straw, and plant interactions change the organic connections in soil and promote the decontamination of cadmium in soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments–A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadis, V.; Levizou, E.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Sebastian, A.; Baum, C.; Prasad, M.N.; Wenzel, W.W.; Rinklebe, J. Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: Phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation—A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.W.; Dunham, S.J.; Dennis, P.G.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P. Field evaluation of in situ remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil using lime and red-mud. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, L.A.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Mahar, A.; Li, R.; Kumar, A.M.; Ali, S.T.; Kumbhar, F.; Wang, P.; Shen, F. Potential use of lime combined with additives on (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of heavy metals from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Ippolito, J.A.; Ducey, T.F.; Watts, D.W.; Spokas, K.A.; Trippe, K.M.; Sigua, G.; Johnson, M. Remediation of an acidic mine spoil: Miscanthus biochar and lime amendment affects metal availability, plant growth, and soil enzyme activity. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Q.; Xiao, X.Y.; Guo, Z.H.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhu, H.W.; Peng, C.; Liang, Y.Q. Release of cadmium in contaminated paddy soil amended with NPK fertilizer and lime under water management. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W. Manganese, zinc, and pH affect cadmium accumulation in rice grain under field conditions in southern China. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Xie, T.H.; Liang, Q.F.; Liu, M.J.; Zhao, M.L.; Wang, M.K.; Wang, G. Effectiveness of lime and peat applications on cadmium availability in a paddy soil under various moisture regimes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7757–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.N.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.C.; Zeng, P. Phytostabilisation potential of giant reed for metals contaminated soil modified with complex organic fertiliser and fly ash: A field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, K.; Zhou, J.; Van Nostrand, J.; Mench, M.; Bes, C.; Giagnoni, L.; Renella, G. Functional activity and functional gene diversity of a Cu-contaminated soil remediated by aided phytostabilization using compost, dolomitic limestone and a mixed tree stand. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garau, G.; Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Deiana, P.; Melis, P. Influence of red mud, zeolite and lime on heavy metal immobilization, culturable heterotrophic microbial populations and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil. Geoderma 2007, 142, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.B.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.M.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.F.; Li, Y. Reliability and stability of immobilization remediation of Cd polluted soils using sepiolite under pot and field trials. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. The Analysis Method of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; Chinese Agricultural Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.; Koo, N.; Hyun, S.; Hwang, A. Evaluation of the effectiveness of various amendments on trace metals stabilization by chemical and biological methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China. Environmental Protection Industry Standard of China (HJ/T166-2004); State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments: An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the commission of the European Communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.R.; White, P.M.; Pierzynski, G.M. Changes in microbial properties after manure, lime, and bentonite application to a heavy metal-contaminated mine waste. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Liang, G.Q.; Sun, J.W.; He, P.; Tang, S.H.; Yang, S.H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.B. The alleviation of acid soil stress in rice by inorganic or organic ameliorants is associated with changes in soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2015, 51, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, L.; Becerril, J.M.; Barrutia, O.; González-Oreja, J.A.; Garbisu, C. Interactions between plant and rhizosphere microbial communities in a metalliferous soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, M.; Liao, B.H.; Liu, L.; Yang, W.T.; Wu, Y.M.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liang, D.L.; Liu, J.J.; Lei, L.M.; Yu, D.S. Transformation of heavy metal fractions on soil urease and nitrate reductase activities in copper and selenium co-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, R.P. Methods of Soil Enzymology; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.B.; Sun, G.H.; Xu, Y.M.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.F.; Lin, D.S. Assessment of sepiolite for immobilization of cadmium-contaminated soils. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Wang, M.W.; Zhu, H.W.; Guo, Z.H.; Han, X.Q.; Zeng, P. Response of soil microbial activities and microbial community structure to vanadium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y. Immobilization remediation of Cd-polluted soil with different water condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Qian, M.; Cai, G.L.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q.S. Uptake and translocation of Cd in different rice cultivars and the relation with Cd accumulation in rice grain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.B.; Huang, D.Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.L.; He, H.B.; Zhu, H.H.; Xu, C. A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Chai, R.; Tu, R.; Gao, H. Amendment damages the function of continuous flooding in decreasing Cd and Pb uptake by rice in acid paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sébastien, S.; William, H.; Herbert, E.A. Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: Dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Bradl, H.B. Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2004, 277, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashem, M.A.; Singh, B.R. Metal availability in contaminated soils: I. Effects of flooding and organic matter on changes in Eh, pH and solubility of Cd, Ni and Zn. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 61, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Duraisamy, V. Role of inorganic and organic soil amendments on immobilisation and phytoavailability of heavy metals: A review involving specific case studies. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, B.; Evans, L.; Lambert, R. Effects of cement or lime on Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn mobility in field-contaminated and aged soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199–200, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.F.; Han, J.; Xu, Y.M.; Sun, Y.M.; Wang, L.; Tan, X. In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite. Geoderma 2014, 235, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlatchka, R.; Cambier, P. Influence of reducing conditions on solubility of trace metals in contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 118, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Makino, T.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Kim, P.J.; Ishikawa, S.; Murakami, M.; Naidu, R.; Kirkham, M.B. Chapter Four–Cadmium contamination and its risk management in rice ecosystems. Adv. Agron. 2013, 119, 183–273. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbroekhoven, K.; Roy, S.V.; Gielen, C.; Maesen, M.; Ryngaert, A.; Diels, L.; Seuntjens, P. Microbial processes as key drivers for metal (im)mobilization along a redox gradient in the saturated zone. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roy, S.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; Dejonghe, W.; Diels, L. Immobilization of heavy metals in the saturated zone by sorption and in situ bioprecipitation processes. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 83, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, M. Effect of moisture regime on the redistribution of heavy metals in paddy soil. J. Environ. Sci. China 2011, 23, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, Z.; Nie, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y. Effect of moisture condition on the immobilization of Cd in red paddy soil using passivators. Environ. Technol. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, B.F.T.; Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J. Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Xu, C.; Duan, D.; Peng, C.; Zhu, S.; Shi, J. The variations in the soil enzyme activity, protein expression, microbial biomass, and community structure of soil contaminated by heavy metals. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 803150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Mcgrouther, K.; Huang, H.; Lu, K.; Guo, X.; He, L.; Lin, X.; Che, L.; Ye, Z.; Wang, H. Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ceccanti, B.; Cervelli, S.; Sequi, P. Stability and kinetic properties of humus-urease complexes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1978, 10, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Jiang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, L.M.; Luo, F. Effects of mining wastewater discharges on heavy metal pollution and soil enzyme activity of the paddy soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 147, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekenler, M.; Tabatabai, M.A. Effects of trace elements on β-glucosaminidase activity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1829–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renella, G.; Egamberdiyeva, D.; Landi, L.; Mench, M.; Nannipieri, P. Microbial activity and hydrolase activities during decomposition of root exudates released by an artificial root surface in Cd-contaminated soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazzaro, A.; Schulin, R.; Widmer, F.; Frey, B. Changes in lead availability affect bacterial community structure but not basal respiration in a microcosm study with forest soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 371, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaisen, M.H.; Ramsing, N.B. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) approaches to study the diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2002, 50, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.B.; Fan, Y.C.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, X.T.; Hu, Y.B.; Gao, L.M. Availability of soil Cu and Cd and microbial community structure as affected by applications of amendments. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 197–205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




| Treatment | Amendment/Management |
|---|---|
| Intermittent condition (ICK) | Without lime and maintained the depth of surface water at 3.0–5.0 cm until the full tillering stage followed by intermittent irrigation |
| Intermittent condition + lime (IL) | Liming 1500 kg/ha at the tillering stage of rice and same as the ICK for water management |
| Flooding condition (FCK) | Without lime and the plot was flooding during the crop growth season and maintained the depth of surface water at 3.0–5.0 cm |
| Flooding condition + lime (FL) | Liming 1500 kg/ha at the tillering stage of rice and same as the FCK for water management |
| Treatment | Rice Growth Stage | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tillering Stage (18 August) | Filling Stage (13 October) | Maturity Stage (10 November) | |
| ICK | Sampled | Sampled | Sampled |
| IL | N | Sampled | Sampled |
| FCK | Sampled | Sampled | Sampled |
| FL | N | Sampled | Sampled |
| Treatment | Tillering Stage | Filling Stage | Maturity Stage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Cd | pH | Cd | pH | Cd | |
| ICK | 5.65 ± 0.11a | 0.41 ± 0.06a | 5.73 ± 0.07c | 0.34 ± 0.019a | 5.75 ± 0.17c | 0.36 ± 0.044a |
| IL | – | – | 5.96 ± 0.19b | 0.27 ± 0.003b | 6.03 ± 0.15b | 0.28 ± 0.023bc |
| FCK | 5.63 ± 0.13a | 0.37 ± 0.05a | 5.81 ± 0.14bc | 0.27 ± 0.030b | 6.02 ± 0.30b | 0.31 ± 0.013ab |
| FL | – | – | 6.16 ± 0.16a | 0.25 ± 0.013b | 6.38 ± 0.22a | 0.25 ± 0.011c |
| Treatment | Band Number | Shannon Index | Urease (NH4-N mg/g) | Acid Phosphatase (µg/g) | Invertase (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICK | 26 ± 2bc | 3.12 ± 0.05b | 0.32 + 0.022c | 1.64 + 0.42b | 7.61 + 1.92ab |
| IL | 32 ± 4a | 3.37 ± 0.10a | 0.51 + 0.031a | 3.56 + 1.10a | 9.81 + 1.04a |
| FCK | 24 ± 1c | 3.09 ± 0.09b | 0.27 + 0.027d | 1.61 + 0.26b | 7.12 + 0.56b |
| FL | 27 ± 1b | 3.28 ± 0.05a | 0.39 + 0.020b | 2.28 + 0.43b | 8.6 + 1.19ab |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, L.; Guo, Z.; Liang, F.; Xiao, X.; Peng, C.; Zeng, P.; Feng, W.; Ran, H. Effect of Liming with Various Water Regimes on Both Immobilization of Cadmium and Improvement of Bacterial Communities in Contaminated Paddy: A Field Experiment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030498
Shi L, Guo Z, Liang F, Xiao X, Peng C, Zeng P, Feng W, Ran H. Effect of Liming with Various Water Regimes on Both Immobilization of Cadmium and Improvement of Bacterial Communities in Contaminated Paddy: A Field Experiment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(3):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030498
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Lei, Zhaohui Guo, Fang Liang, Xiyuan Xiao, Chi Peng, Peng Zeng, Wenli Feng, and Hongzhen Ran. 2019. "Effect of Liming with Various Water Regimes on Both Immobilization of Cadmium and Improvement of Bacterial Communities in Contaminated Paddy: A Field Experiment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 3: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030498
APA StyleShi, L., Guo, Z., Liang, F., Xiao, X., Peng, C., Zeng, P., Feng, W., & Ran, H. (2019). Effect of Liming with Various Water Regimes on Both Immobilization of Cadmium and Improvement of Bacterial Communities in Contaminated Paddy: A Field Experiment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030498