Psychological Climacteric Symptoms and Attitudes toward Menopause among Emirati Women
Abstract
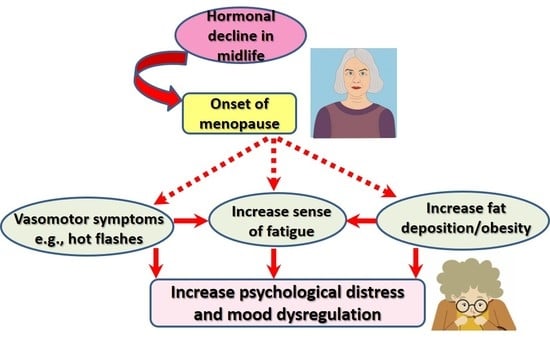
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants, and Procedure
2.2. Study Instruments
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT2A | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| ATMS | Attitudes toward menopause scale |
| BDI | Beck depression inventory |
| ERs | Estrogen receptors |
| HRT | Hormonal replacement therapy |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MENQOL | Menopause-Specific Quality of Life |
| UAE | United Arab Emirates |
References
- Santoro, N.; Epperson, C.N.; Mathews, S.B. Menopausal Symptoms and Their Management. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 44, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smail, L.; Jassim, G.A.; Al-Shboul, Q.M.; Hattawi, A.S. Emirati women’s attitudes towards menopause: Implications for health care policy. Post Reprod. Health 2019, 25, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunugi, H.; Ali, A.M. Royal Jelly and Its Components Promote Healthy Aging and Longevity: From Animal Models to Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smail, L.; Jassim, G.; Shakil, A. Menopause-Specific Quality of Life among Emirati Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilbur, J.; Shaver, J.; Kogan, J.; Buntin, M.; Wang, E. Menopausal Transition Symptoms in Midlife Women Living with Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue. Health Care Women Int. 2006, 27, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaletto, K.B.; Elahi, F.M.; Staffaroni, A.M.; Walters, S.; Contreras, W.R.; Wolf, A.; Dubal, D.; Miller, B.; Yaffe, K.; Kramer, J.H. Cognitive aging is not created equally: Differentiating unique cognitive phenotypes in “normal” adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 77, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, M.Y.; Fares, J.; Baydoun, H.; Fares, Y. Sport and exercise medicine research activity in the Arab world: A 15-year bibliometric analysis. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2017, 3, e000292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Population Review. Arab Countries 2020. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/arab-countries/ (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- El Hajj, A.; Wardy, N.; Haidar, S.; Bourgi, D.; Haddad, M.E.; Chammas, D.E.; El Osta, N.; Rabbaa Khabbaz, L.; Papazian, T. Menopausal symptoms, physical activity level and quality of life of women living in the Mediterranean region. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gharaibeh, M.; Al-Obeisat, S.; Hattab, J. Severity of menopausal symptoms of Jordanian women. Climacteric 2010, 13, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gava, G.; Orsili, I.; Alvisi, S.; Mancini, I.; Seracchioli, R.; Meriggiola, M.C. Cognition, Mood and Sleep in Menopausal Transition: The Role of Menopause Hormone Therapy. Medicina 2019, 55, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maki, P.M.; Henderson, V.W. Cognition and the menopause transition. Menopause 2016, 23, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, A.; Tabrez, E.S.; Muhammad, A.; Peela, J.R. The Mechanisms of Dietary Phytoestrogen as a Potential Treatment and Prevention Agent against Alzheimer’s Disease. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2018, 28, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, A.; Matsushita, H.; Ieno, D.; Matsuda, Y.; Horii, Y.; Ishii, A.; Takahashi, T.; Kanazawa, H.; Wakatsuki, A.; Suzuki, T. Improvement of neurological disorders in postmenopausal model rats by administration of royal jelly. Climacteric 2016, 19, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, M.J.; Grimshaw, V.; Wynalda, K.M.; Mohajeri, M.H.; Butt, C.M. Long-Term Administration of Queen Bee Acid (QBA) to Rodents Reduces Anxiety-Like Behavior, Promotes Neuronal Health and Improves Body Composition. Nutrients 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llaneza, P.; García-Portilla, M.P.; Llaneza-Suárez, D.; Armott, B.n.; Pérez-López, F.R. Depressive disorders and the menopause transition. Maturitas 2012, 71, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.N. Taking a fresh look at mood, hormones, and menopause. Menopause 2020, 27, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, A.K.; Sohel, N.; Gilsing, A.; Mayhew, A.J.; Griffith, L.E.; Raina, P. Depression, hormone therapy, and the menopausal transition among women aged 45 to 64 years using Canadian Longitudinal Study on aging baseline data. Menopause 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, N. Attitudes towards menopause and depression, body image of women during menopause. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, J.A. Depression, anxiety, and “the incredible shrinking vagina”. Menopause 2020, 27, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Hendawy, A.O. So, Antidepressant Drugs have Serious Adverse Effects, but what are the Alternatives? Nov. Approaches Drug Des. Dev. 2018, 4, 555636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Converso, D.; Viotti, S.; Sottimano, I.; Loera, B.; Molinengo, G.; Guidetti, G. The relationship between menopausal symptoms and burnout. A cross-sectional study among nurses. BMC Womens Health 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, F.; Freeman, M.P.; Petrillo, L.; Barsky, M.; Galvan, T.; Kim, S.; Cohen, L.; Joffe, H. Armodafinil for fatigue associated with menopause: An open-label trial. Menopause 2016, 23, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.-H.; Tsao, L.-I.; Lin, M.-H. Suffering Exhausted Life Like Burning at Both Ends of a Candle -Women with Menopausal Fatigue. Int. J. Stud. Nurs. 2020, 5, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncker, W.D.; Dantzer, R.; Ormstad, H.; Kuppuswamy, A. Mechanisms of poststroke fatigue. J. Neurol Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, D.; Martin, C.R. The interface between chronic fatigue syndrome and depression: A psychobiological and neurophysiological conundrum. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2017, 47, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elavsky, S.; Gold, C.H. Depressed mood but not fatigue mediate the relationship between physical activity and perceived stress in middle-aged women. Maturitas 2009, 64, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mofid, B.; Rezaeizadeh, H.; Termos, A.; Rakhsha, A.; Mafi, A.R.; Taheripanah, T.; Ardakani, M.M.; Taghavi, S.M.E.; Moravveji, S.A.; Kashi, A.S.Y. Effect of Processed Honey and Royal Jelly on Cancer-Related Fatigue: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Electron. Phys. 2016, 8, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, J.; Simpson, I.; Collins, A.; Wang, X. Mind control of menopause. Womens Health Issues 2003, 13, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenabi, E.; Shobeiri, F.; Hazavehei, S.M.M.; Roshanaei, G. Assessment of Questionnaire Measuring Quality of Life in Menopausal Women: A Systematic Review. Oman Med. J. 2015, 30, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, A.A.; Hayhoe, R.P.G.; Cameron, D. The relationships between sarcopenic skeletal muscle loss during ageing and macronutrient metabolism, obesity and onset of diabetes. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, K. Sarcopenia. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2019, 169, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, M.J.; Verdile, G.; Kirubakaran, S.; Münch, G. Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease, and Prevention with Antioxidants and Phenolic Compounds—What Are the Most Promising Candidates? In Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of Diabetes, Genetics, Hormones, and Lifestyle; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Derry, H.M.; Fagundes, C.P. Inflammation: Depression fans the flames and feasts on the heat. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.M.; Mancano, G.; Kashofer, K.; Fröhlich, E.E.; Matak, A.; Mayerhofer, R.; Reichmann, F.; Olivares, M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. High-fat diet induces depression-like behaviour in mice associated with changes in microbiome, neuropeptide Y, and brain metabolome. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barth Olofsson, A.S.; Collins, A. Psychosocial factors, attitude to menopause and symptoms in Swedish perimenopausal women. Climacteric 2000, 3, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Ji, T.; Hou, D.; Wu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, B. Spouses’ perceptions of and attitudes toward female menopause: A mixed-methods systematic review. Climacteric 2020, 23, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.M.; Verjee, M.A.; Bener, A.; Gerber, L.M. The hopeless age? A qualitative exploration of the experience of menopause in Arab women in Qatar. Climacteric 2013, 16, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, S.; Henderson, V.W.; Siseles, N.; Tan, D.; Villaseca, P. Age of menopause and impact of climacteric symptoms by geographical region. Climacteric 2010, 13, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, D.E.E.; Bener, A.; Ezimokhai, M.; Hassan, M.Y.; Micallef, R. The age and symptomatology of natural menopause among United Arab Emirates women. Maturitas 1998, 29, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilditch, J.R.; Lewis, J.; Peter, A.; van Maris, B.; Ross, A.; Franssen, E.; Guyatt, G.H.; Norton, P.G.; Dunn, E. A menopause-specific quality of life questionnaire: Development and psychometric properties. Maturitas 2008, 61, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazibara, T.; Kovacevic, N.; Nurkovic, S.; Kurtagic, I.; Radovanovic, S.; Rancic, B.; Terzic, M.; Dotlic, J. Menopause-specific Quality of Life Questionnaire: Factor and Rasch analytic approach. Climacteric 2019, 22, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Ahmed, A.; Sharaf, A.; Kawakami, N.; Abdeldayem, S.M.; Green, J. The Arabic Version of The Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21: Cumulative scaling and discriminant-validation testing. Asian J. Psychiatry 2017, 30, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Green, J. Differential Item Functioning of the Arabic Version of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21). JOJ Nurse Health Care 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Green, J. Factor structure of the depression anxiety stress Scale-21 (DASS-21): Unidimensionality of the Arabic version among Egyptian drug users. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 2019, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpe, S.E. How to analyze Likert and other rating scale data. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2015, 7, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedraui, P.; Pérez-López, F.R.; Morales, B.; Hidalgo, L. Depressive symptoms in climacteric women are related to menopausal symptom intensity and partner factors. Climacteric 2009, 12, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.; Judd, F.K.; Hickey, M. Anxiety during the menopausal transition: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 139, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Ando, S.; Imai, T. The association of cognitive fatigue with menopause, depressive symptoms, and quality of life in ambulatory breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer 2016, 23, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.; Lee, J.J.; Bei, B. Postpartum fatigue and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord 2019, 246, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, N.A.; Singh, B.; Romo-Nava, F.; Joseph, B.; Veldic, M.; Cuellar-Barboza, A.; Cabello Arreola, A.; Vande Voort, J.L.; Croarkin, P.; Moore, K.M.; et al. Efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive modafinil/armodafinil in bipolar depression: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Bipolar Disord. 2020, 22, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, H.; Ikeda, T.; Kajita, K.; Fujioka, K.; Mori, I.; Okada, H.; Uno, Y.; Ishizuka, T. Effect of royal jelly ingestion for six months on healthy volunteers. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosicki, G.J.; Fielding, R.A.; Lustgarten, M.S. Gut Microbiota Contribute to Age-Related Changes in Skeletal Muscle Size, Composition, and Function: Biological Basis for a Gut-Muscle Axis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleau, C.; Karelis, A.D.; St-Pierre, D.H.; Lamontagne, L. Crosstalk between intestinal microbiota, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle as an early event in systemic low-grade inflammation and the development of obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Bee honey protects astrocytes against oxidative stress: A preliminary in vitro investigation. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2019, 39, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, N.; Deschenes, S.S.; Burns, R.J.; Danna, S.M.; Franco, O.H.; Ikram, M.A.; Kivimaki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Tiemeier, H. Cardiometabolic dysregulation and cognitive decline: Potential role of depressive symptoms. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 212, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moazzami, K.; Lima, B.B.; Sullivan, S.; Shah, A.; Bremner, J.D.; Vaccarino, V. Independent and joint association of obesity and metabolic syndrome with depression and inflammation. Health Psychol. 2019, 38, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, C.; Catania, C.; Remus-Borel, J.; Ladeveze, E.; Leste-Lasserre, T.; Mazier, W.; Binder, E.; Gonzales, D.; Clark, S.; Guzman-Quevedo, O.; et al. mTORC1 pathway disruption abrogates the effects of the ciliary neurotrophic factor on energy balance and hypothalamic neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzanowska, J.; Wawer, A.; Joniec-Maciejak, I.; Piechal, A.; Blecharz-Klin, K.; Graikou, K.; Chinou, I.; Widy-Tyszkiewicz, E. Long-term administration of Greek Royal Jelly decreases GABA concentration in the striatum and hypothalamus of naturally aged Wistar male rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 675, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfarpour, M.; Kaviani, M.; Abdolahian, S.; Bonakchi, H.; Najmabadi Khadijeh, M.; Naghavi, M.; Khadivzadeh, T. The relationship between women’s attitude towards menopause and menopausal symptoms among postmenopausal women. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 31, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, B.; Forshaw, M.; Hunter, M.S. The impact of attitudes towards the menopause on women’s symptom experience: A systematic review. Maturitas 2010, 65, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrami, H.A.; Alsibai, J.; Clark, C.C.T.; Faris, M.e.A.-I.E. A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of the impact of diurnal intermittent fasting during Ramadan on body weight in healthy subjects aged 16 years and above. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Symptoms | With Experience NO (%) | Without Experience NO (%) | Degree of Being Bothered by Symptoms Median (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Being dissatisfied with my personal life | 16 (26.7%) | 44 (73.3%) | 1 (2) |
| Feeling anxious or nervous | 35 (58.3%) | 25 (41.7%) | 3 (5) |
| Experiencing poor memory | 33 (55.0%) | 27 (45.0%) | 3 (4) |
| Accomplishing less than I used to | 25 (41.7%) | 35 (58.3%) | 1 (3) |
| Feeling depressed, down or blue | 30 (50.0%) | 30 (50.0%) | 2 (4) |
| Being impatient with other people | 28 (46.7%) | 32 (53.3%) | 1 (4) |
| Feelings of wanting to be alone | 21 (35.0%) | 39 (65.0%) | 1 (3) |
| Feeling tired or worn out | 39 (65.0%) | 21 (35.0%) | 4 (5) |
| Difficulty sleeping | 37 (61.7%) | 23 (38.3%) | 4 (5) |
| Decrease in stamina | 29 (48.3%) | 31 (51.7%) | 1 (4) |
| Feeling a lack of energy | 39 (65.0%) | 21 (35.0%) | 4 (5) |
| Fatigue▲ | Minimum = 2 | Minimum = 16 | 7.5 (9) |
| Anxiety▲ | Minimum = 2 | Minimum = 16 | 5.5 (8) |
| Depression▲ | Minimum = 4 | Minimum = 11 | 7 (11) |
| Psychological distress▲ | Minimum= 9 | Maximum= 69 | 21.5 (23) |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Anxiety | -- | |||||||||
| 2. Depression | 0.793 ** | -- | ||||||||
| 3. Psychological distress | 0.893 ** | 0.861 ** | -- | |||||||
| 4. Memory problems | 0.537 ** | 0.517 ** | 0.654 ** | -- | ||||||
| 5. Difficulty sleeping | 0.214 | 0.242 | 0.457 ** | 0.177 | -- | |||||
| 6. Fatigue | 0.593 ** | 0.491 ** | 0.664 ** | 0.510 ** | 0.361 ** | -- | ||||
| 7. Vasomotor symptoms | 0.540 ** | 0.486 ** | 0.607 ** | 0.370 ** | 0.449 ** | 0.540 ** | -- | |||
| 8. Sexual symptoms | 0.426 ** | 0.427 ** | 0.443 ** | 0.087 | 0.260 * | 0.475 ** | 0.435 ** | -- | ||
| 9. Total MENQOL | 0.823 ** | 0.738 ** | 0.898 ** | 0.582 ** | 0.411 ** | 0.826 ** | 0.681 ** | 0.628 ** | -- | |
| 10. ATMS | −0.374 ** | −0.309 * | −0.390 ** | −0.268 * | −0.191 | −0.304 * | −0.358 ** | −0.201 | −0.334 ** | -- |
| 11. Weight gain▲ | 0.427 ** | 0.437 ** | 0.476 ** | 0.372 ** | 0.121 | 0.372 ** | 0.225 | 0.368 ** | 0.499 ** | −0.350 ** |
| Outcome Variables | χ2 | P | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | R2 | SE | P | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | 5.932 | 0.204 | 0.976 | 0.941 | 0.090 | 0.476 | 0.088 | 0.009 | 0.298 to 0.591 |
| Depression | 4.203 | 0.379 | 0.997 | 0.993 | 0.029 | 0.445 | 0.090 | 0.013 | 0.258 to 0.557 |
| Psychological distress | 6.180 | 0.186 | 0.977 | 0.942 | 0.096 | 0.566 | 0.080 | 0.008 | 0.406 to 0.671 |
| Memory problems | 4.731 | 0.316 | 0.988 | 0.970 | 0.056 | 0.291 | 0.102 | 0.013 | 0.115 to 0.425 |
| Items | Agreement (%) | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A woman should see a doctor at menopause | 46 (76.7%) | 1.95 ± 0.84 |
| 2 | Menopause is one of the biggest changes that happens in a woman’s life | 46 (76.7%) | 1.98 ± 0.82 |
| 3 | A woman is concerned about how her husband will feel about her after menopause | 35 (58.3%) | 2.14 ± 0.85 |
| 4 | Menopause is an unpleasant experience | 37 (61.7%) | 2.19 ± 0.82 |
| 5 | After the change of life, a woman feels freer to do things for herself | 37 (61.7%) | 2.80 ± 0.71 |
| 6 | Women generally feel better after menopause | 29 (48.3%) | 2.52 ± 0.71 |
| 7 | Women are generally calmer and happier after the change of life | 28 (46.7%) | 2.50 ± 0.71 |
| 8 | A woman has a broader outlook on life after the change | 28 (46.7%) | 2.61 ± 0.74 |
| 9 | Menopause is a disturbing thing that women naturally dread | 36 (60%) | 2.21 ± 0.81 |
| 10 | Women should expect some trouble during menopause | 43 (71.7%) | 2.19 ± 0.71 |
| 11 | A woman’s body may change in menopause, but otherwise, she doesn’t change much | 35 (58.3%) | 2.61 ± 0.83 |
| 12 | It is no wonder women feel down in the dumps at the time of menopause | 31 (51.7%) | 2.39 ± 0.79 |
| 13 | Life is more interesting for a woman after menopause | 24 (40%) | 2.47 ± 0.80 |
| 14 | Changes inside the body that women cannot control cause all the trouble during menopause | 33 (55%) | 2.37 ± 0.72 |
| 15 | A woman gains more confidence in herself after the change of life | 23 (38.3%) | 2.39 ± 0.77 |
| 16 | Going through menopause really does not change a woman in any important way | 21 (35%) | 2.29 ± 0.77 |
| 17 | Women worry about losing their minds during menopause | 23 (38.3%) | 2.54 ± 0.85 |
| 18 | Women think of menopause as the beginning of the end | 24 (40%) | 2.55 ± 0.86 |
| 19 | The only difference between a woman who has been through menopause and one who has not is that one menstruates and the other doesn’t | 30 (50%) | 2.54± 0.89 |
| 20 | In truth, just about every woman is depressed about menopause | 40 (66.7%) | 2.24± 0.75 |
| 21 | Women often use the change of life as an excuse for getting attention | 14 (23.3%) | 2.74 ± 0.66 |
| 22 | After the change of life, women do not consider themselves real women | 14 (23.3%) | 2.75 ± 0.76 |
| 23 | It’s not surprising that most women become disagreeable during menopause | 15 (25%) | 2.78 ± 0.77 |
| 24 | After the change of life, a woman has a better relationship with her husband | 23 (38.3%) | 2.34 ± 0.79 |
| 25 | Many women think menopause is the best thing that ever happened to them | 26 (43.3%) | 2.50 ± 0.84 |
| 26 | After the change of life, a woman becomes more interested in community affairs than before | 40 (66.7%) | 2.71 ± 0.70 |
| 27 | Women who have trouble with menopause are usually those who have nothing to do with their time | 33 (55%) | 2.60 ± 0.72 |
| 28 | Women who have trouble with menopause are those who are expecting it | 26 (43.3%) | 2.36 ± 0.74 |
| 29 | Women often become self-centered at the time of menopause | 34 (56.7%) | 2.34 ± 0.78 |
| 30 | A woman in menopause is apt to do crazy things she herself does not understand | 18 (30%) | 2.79 ± 0.73 |
| 31 | Menopause is a mysterious thing that most women don’t understand | 25 (41.7%) | 2.54 ± 0.86 |
| 32 | After menopause, a woman is more interested in sex than she was before | 9 (15%) | 2.02 ± 0.60 |
| 33 | Unmarried women have a harder time than married women do at the time of menopause | 22 (36.7%) | 2.50 ± 0.84 |
| 34 | A good thing about menopause is that a woman can quit worrying about becoming pregnant | 38 (63.3%) | 2.75 ± 0.82 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.M.; Ahmed, A.H.; Smail, L. Psychological Climacteric Symptoms and Attitudes toward Menopause among Emirati Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145028
Ali AM, Ahmed AH, Smail L. Psychological Climacteric Symptoms and Attitudes toward Menopause among Emirati Women. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(14):5028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145028
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Amira Mohammed, Afaf Hassan Ahmed, and Linda Smail. 2020. "Psychological Climacteric Symptoms and Attitudes toward Menopause among Emirati Women" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 14: 5028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145028
APA StyleAli, A. M., Ahmed, A. H., & Smail, L. (2020). Psychological Climacteric Symptoms and Attitudes toward Menopause among Emirati Women. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 5028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17145028