The Role of Mangroves in the Retention of Heavy Metal (Chromium): A Simulation Study in the Thi Vai River Catchment, Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Integrated Numerical Model
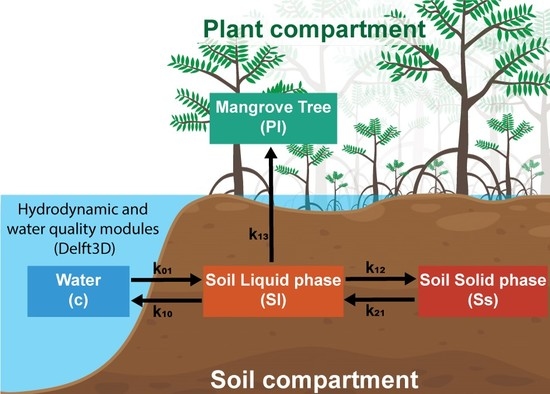
2.1. Compartment Model for Pollutant Transport in the Water–Soil–Plant Domain
2.2. Hydrodynamics and Water Quality Models Delft3D
3. Site Description
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Bathymetry Data
3.3. Hydrometric and Tide Data
3.4. Data of Chromium Concentrations in Water–Soil—Plant Domains
4. Model Setting and Scenarios
4.1. Calibration and Validation for the Model
4.2. Scenarios Description
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Results of Model Calibration and Validation
5.1.1. Calibration and Validation for the Hydrodynamic Model Delft3D
5.1.2. Parameters Estimation for the Compartment Model
5.2. Scenarios Simulation Results
5.2.1. Chromium Concentration in Water
5.2.2. Chromium Concentration in Soil
5.2.3. Chromium Concentration in Mangrove Trees
5.3. Model Applicability and Further Development
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosen, M.R. The Influence of Hydrology on Lacustrine Sediment Contaminant Records. In Environmental Contaminants: Using Natural Archives to Track Sources and Long-Term Trends of Pollution; Blais, J.M., Rosen, M.R., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, C.; Allenbach, M.; Lallier-Vergès, E. Relationships between heavy metals distribution and organic matter cycling in mangrove sediments (Conception Bay, New Caledonia). Geoderma 2011, 160, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Hu, B.; Bi, J.; Leng, Q.; Xiao, C.; Yang, Z. Heavy metals distribution and contamination in surface sediments of the coastal Shandong Peninsula (Yellow Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, G.R.; Koller, C.E.; Blomberg, S.P. Accumulation and partitioning of heavy metals in mangroves: A synthesis of field-based studies. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahalawattaarach, V.; Purushothaman, C.S.; Vennila, A. Metal phytoremediation potential of Rhizophora mucronata (Lam.). Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 38, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sodré, V.; Caetano, V.S.; Rocha, R.M.; Carmo, F.L.; Medici, L.O.; Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, A.S.; Reinert, F. Physiological aspects of mangrove (Laguncularia racemosa) grown in microcosms with oil-degrading bacteria and oil contaminated sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansel, B.; Lee, M.; Tansel, D.Z. Comparison of fate profiles of PAHs in soil, sediments and mangrove leaves after oil spills by QSAR and QSPR. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, X.; Guo, F. Paradigms of mangroves in treatment of anthropogenic wastewater pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K. Phytoremediation and Nanoremediation: Emerging Techniques for Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage Water. Def. Life Sci. J. 2018, 3, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.D.; Berti, W.R.; Huang, J.W. Phytoremediation of contaminated soils. Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. Heavy metals in plants and phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenger, P.; McConchie, D. Heavy metals in mangroves: Methodology, monitoring and management. Envis For. Bull. 2004, 4, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Wen-jiao, Z.; Xiao-yong, C.; Peng, L. Accumulation and biological cycling of heavy metal elements in Rhizophora stylosa mangroves in Yingluo Bay, China. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 159, 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Fengzhong, Z.; Liyu, H.; Wenjiao, Z. A primary study on adsorption of certain heavy metals on the litter leaf detritus of some mangrove species. J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1998, 37, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- MacFarlane, G.R.; Pulkownik, A.; Burchett, M.D. Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.)Vierh: Biological indication potential. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, G.R.; Burchett, M.D. Toxicity, growth and accumulation relationships of copper, lead and zinc in the grey mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, B.Y.; Ong, M.C.; Jalal, K.C.A.; Shahbudin, S.; Nor, O.M. Accumulation of lead and copper in Rhizophora apiculata from Setiu mangrove forest, Terengganu, Malaysia. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nazli, M.F.; Hashim, N.R. Heavy Metal Concentrations in an Important Mangrove Species, Sonneratia caseolaris, in Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Asia 2010, 3, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-E.; Liu, J.-L.; Ouyang, Y.; Liao, B.-W.; Zhao, B.-L. Physiological responses of mangrove Sonneratia apetala Buch-Ham plant to wastewater nutrients and heavy metals. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2011, 13, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, O.; Nguyen, H.A.; Nguyen, K.L.; Nguyen, V.P.; Biester, H.; Schmidt, P. Phytoremediation by mangrove trees: Experimental studies and model development. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titah, H.S.; Pratikno, H. Chromium Accumulation by Avicennia alba Growing at Ecotourism Mangrove Forest in Surabaya, Indonesia. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Favas, P.J.C.; Jonathan, M.P.; Venkatachalam, P.; Raja, P.; Sarkar, S.K. Bioremoval of trace metals from rhizosediment by mangrove plants in Indian Sundarban Wetland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunthiyal, M. Engineering Plants for Phytoremediation. In Advances in Biotechnology; Ravi, I., Baunthiyal, M., Saxena, J., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Burken, J.G.; Schnoor, J.L. Phytoremediation: Plant Uptake of Atrazine and Role of Root Exudates. J. Environ. Eng. 1996, 122, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.T.; Sheng, G.; Manes, M. A Partition-Limited Model for the Plant Uptake of Organic Contaminants from Soil and Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashi, M. Modeling Phytoremediation of Soils. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxicand Radioact. Waste Manag. 2004, 8, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Richter, O. Multiscale Modeling of Pollutant Uptake by Mangroves. Int. J. Multiphys. 2016, 10, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.A.; Richter, O.; Huynh, D.H.; Nguyen, K.L.; Kolb, M.; Nguyen, V.P.; Bao, T.T. Accumulation of contaminants in mangrove species Rhizophora apiculate along Thi Vai River in the South of Vietnam. In EWATEC-COAST: Technologies for Environmental and Water Protection of Coastal Regions in Vietnam: Contributions to 4th International Conference for Environment and Natural Resources—ICENR 2014; Meon, G., Pätsch, M., Phuoc, N.V., Quan, N.H., Eds.; Cuvillier: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Boddeker, S.; Hoelzmann, P.; Thuyen, L.X.; Huy, H.D.; Nguyen, H.A.; Richter, O.; Schwalb, A. Ecological risk assessment of a coastal zone in Southern Vietnam: Spatial distribution and content of heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Thi Vai Estuary and Can Gio Mangrove Forest. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BaraBkiewicz, D.; Siepak, J. Chromium, Nickel and Cobalt in Environmental Samples and Existing Legal Norms. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K.; Rodrigues, P.P.; Mubiana, V.K.; Blust, R.; De Boeck, G. Linking environmental heavy metal concentrations and salinity gradients with metal accumulation and their effects: A case study in 3 mussel species of Vitória estuary and Espírito Santo bay, Southeast Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 523, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.J.; Ravenscroft, J.E. Determination of chromium(III) and total chromium in marine waters. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1996, 354, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprapti, N.H.; Sya’rani, L.; Anggoro, S. The chromium (Cr) content in water and in the tissue of mud crab (Scylla serrata Forskal.) in the brackishwater ponds around Babon River Estuary of Semarang coastal areas in Central Java, Indonesia. J. Coast. Dev. 2012, 16, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, H.; Ahmed, E.; Mohamed, A.; El-Bassuony, A. Chromium Removal from Tannery Wastewater Using Chemical and Biological Techniques Aiming Zero Discharge of Pollution. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/1018200/CHROMIUM_REMOVAL_FROM_TANNERY_WASTEWATER_USING_CHEMICAL_AND_BIOLOGICAL_TECHNIQUES_AIMING_ZERO_DISCHARGE_OF_POLLUTION?auto=download (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Javernick, L.; Hicks, D.M.; Measures, R.; Caruso, B.; Brasington, J. Numerical Modelling of Braided Rivers with Structure-from-Motion-Derived Terrain Models. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.D.; Brasington, J.; Hicks, M.; Measures, R.; Rennie, C.D.; Vericat, D. Hydraulic validation of two-dimensional simulations of braided river flow with spatially continuous aDcp data. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5183–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duy Vinh, V.; Nguyen Minh, H.; Khanh, D. Impacts of pollution discharges from Dinh Vu industrial zone on water quality in the Hai Phong coastal area. Vietnam J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2020, 20, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew Mark, S.; Thomas, V.; Sander, P.; Bart-Jan van der, S.; Johan, H.; Marius, S. Comparison between MIKE 21 fm, Delft3d and Delft3d FM flow models of Western Port bay, Australia. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.P. Validation, Calibration and Evaluation of Delft3DFLOW Model with Ferry Measurements; TUDelft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Boddeker, S.; Thuyên, L.X.; Hoelzmann, P.; Stigter, H.C.d.; Gaever, P.V.; Huy, H.Đ.; Schwalb, A. The hidden threat of heavy metal pollution in high sedimentation and highly dynamic environment: Assessment of metal accumulation rates in the Thi Vai Estuary, Southern Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, V.; Tenzer, R. A comparison of model estimates of ocean-tide loading displacements in New Zealand. J. Geod. Sci. 2011, 1, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, K.L.; Nguyen, H.A.; Richter, O.; Pham, M.T.; Nguyen, V.P. Ecophysiological responses of young mangrove species Rhizophora apiculata (Blume) to different chromium contaminated environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.I.; Alongi, D.M. Tropical Mangrove Ecosystems; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Arcement, G.J.; Schneider, V.R. Guide for Selecting Manning’s Roughness Coefficients for Natural Channels and Flood Plains; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1989.
- McIvor, A.; Spencer, T.; Möller, I.; Spalding, M. Storm Surge Reduction by Mangroves. Available online: http://www.mangrovealliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/storm-surge-reduction-by-mangroves-1.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2020).
- Parsapour-moghaddam, P.; Rennie, C.D.; Slaney, J. Hydrodynamic Simulation of an Irregularly Meandering Gravel-Bed River: Comparison of MIKE 21 FM and Delft3D Flow models. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 40, 02004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Haider, M.R.; Yunus, A. A study on hydrodynamic and morphological behavior of Padma river using Delft3d model. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), Khulna, Bangladesh, 12–14 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J.J. Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the evaluation of model performance in physical geography. In Spatial Statistics and Models; Gaile, G.L., Willmott, C.J., Eds.; Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 443–460. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.P.; Bäse, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElrone, A.; Choat, B.; Gambetta, G.; Brodersen, C. Water uptake and transport in vascular plants. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- MacFall, J.S.; Johnson, G.A.; Kramer, P.J. Observation of a water-depletion region surrounding loblolly pine roots by magnetic resonance imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, H.-H.; Kramer, P.J. Absorption of Water and 32P through Suberized and Unsuberized Roots of Loblolly Pine. Can. J. For. Res. 1975, 5, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Discharge Source | Cr Discharge (mg/s) | Discharge Period |
|---|---|---|
| A2 | 0.5 | Wastewater is being discharged at neap tide (at about 12:00–14:00 every day) |
| A1 | 1 | |
| Cai Mep | 1 | |
| Phu My | 0.2 | |
| Go Dau | 2 |
| Water Level | Dry Season | Rainy Season | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE | d | RMSE (m) | NSE | d | RMSE (m) | ||
| Calibration | Station 1 | 0.816 | 0.953 | 0.345 | 0.937 | 0.984 | 0.259 |
| Station 4 | 0.86 | 0.964 | 0.303 | 0.867 | 0.965 | 0.402 | |
| Validation | Station 2 | 0.695 | 0.897 | 0.998 | 0.962 | 0.99 | 0.208 |
| Station 3 | 0.865 | 0.965 | 0.309 | 0.946 | 0.986 | 0.252 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, A.; Le, B.V.Q.; Richter, O. The Role of Mangroves in the Retention of Heavy Metal (Chromium): A Simulation Study in the Thi Vai River Catchment, Vietnam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165823
Nguyen A, Le BVQ, Richter O. The Role of Mangroves in the Retention of Heavy Metal (Chromium): A Simulation Study in the Thi Vai River Catchment, Vietnam. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(16):5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165823
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Anh, Bao V.Q Le, and Otto Richter. 2020. "The Role of Mangroves in the Retention of Heavy Metal (Chromium): A Simulation Study in the Thi Vai River Catchment, Vietnam" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 16: 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165823
APA StyleNguyen, A., Le, B. V. Q., & Richter, O. (2020). The Role of Mangroves in the Retention of Heavy Metal (Chromium): A Simulation Study in the Thi Vai River Catchment, Vietnam. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(16), 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165823