Residential Radon and Histological Types of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case‒Control Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
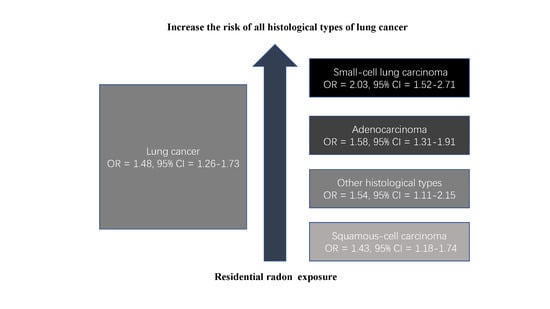
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Overall Pooled Analysis
3.4. Histology Subgroup Analyses
3.5. Other Subgroup Analyses
3.6. Dose‒Response Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Globocan. Globocan 2018-Home. 2018. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/15-Lung-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2019).
- Nicholson, A.G.; Matsuno, Y.; Chan, J.K.C. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart; IARC: Lyon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to the 2015 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus, and heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nasim, F.; Sabath, B.F.; Eapen, G.A. Lung Cancer. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, E.B.; Jalal, S.I. Small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2016, 170, 301–322. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, L.A.; Rudin, C.M. Small cell lung cancer: Where do we go from here? Cancer 2015, 121, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, R.; Page, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Read, W.; Tierney, R.; Vlahiotis, A.; Spitznagel, E.L.; Piccirillo, J. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: Analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4539–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelee, H.; Kelly, K.; Edelman, M.J. 50 Years of progress in the systemic therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Proceedings of American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book; American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2014; p. 177. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. UNSCEAR 2006 Report. Annex A: Epidemiological Studies of Radiation and Cancer; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 13–322. [Google Scholar]
- Tchorz-Trzeciakiewicz, D.; Kłos, M. Factors affecting atmospheric radon concentration, human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; García-Paniagua, J.; Guillén, J.; Montalbán, B. Influence of architectural style on indoor radon concentration in a radon prone area: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Kang, D.R.; Park, S.H.; Yoon, D.K.; Lee, C.M. Indoor radon concentration in Korea residential environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12678–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawel, D.; Puskin, J. The US Environmental Protection Agency’s assessment of risks from indoor radon. Health Phys. 2004, 87, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- López-Abente, G.; Núñez, O.; Fernández-Navarro, P.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Martín-Méndez, I.; Bel-Lan, A.; Locutura, J.; Quindós, L.; Sainz, C.; Ruano-Ravina, A. Residential radon and cancer mortality in Galicia, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzillo, C.; Pugliese, M.; Loffredo, F.; Quarto, M. Indoor radon exposure and lung cancer risk: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Transl. Cancer Res. 2017, 6, S934–S943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Sun, J.; Dong, J.Y.; Tian, H.L.; Xue, L.; Qin, L.Q.; Tong, J. Residential radon and lung cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis of case-control studies. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. BMJ Clin. Res. Ed. 2005, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krewski, D.; Lubin, J.H.; Zielinski, J.M.; Alavanja, M.; Catalan, V.S.; Field, R.W.; Klotz, J.B.; Létourneau, E.G.; Lynch, C.F.; Lyon, J.I. Residential radon and risk of lung cancer: A combined analysis of 7 North American case-control studies. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, J.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Boice, J.D., Jr.; Xu, Z.Y.; Blot, W.J.; De Wang, L.; Kleinerman, R.A. Risk of lung cancer and residential radon in China: Pooled results of two studies. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyński, L.; Fornalski, K.W.; Reszczyńska, J. Meta-analysis of thirty-two case–control and two ecological radon studies of lung cancer. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 59, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martinez, A.; Torres-Duran, M.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Ruano-Ravina, A. Residential radon and small cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Lett. 2018, 426, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.A.; Clarke, M.; Rovers, M.; Riley, R.D.; Simmonds, M.; Stewart, G.; Tierney, J.F. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data: The PRISMA-IPD statement. JAMA 2015, 313, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta- analyses. 2011. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_%20epidemiolo-Tc/oxford.htm (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg, J.B.; Klotz, J.B.; Wilcox, H.B.; Nicholls, G.P.; Gil-del-Real, M.T.; Stemhagen, A.; Mason, T.J. Case-control study of residential radon and lung cancer among New Jersey women. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 6520–6524. [Google Scholar]
- Biberman, R.; Lusky, A.; Schlesinger, T.; Margaloit, M.; Neeman, E.; Modan, B. Increased risk for small cell lung cancer following residential exposure to low-dose radon: A pilot study. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1993, 48, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, C.; Pershagen, G.; Klominek, J. Lung cancer in women and type of dwelling in relation to radon exposure. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blot, W.J.; Xu, Z.Y.; Boice, J.D.; Zhao, D.Z.; Stone, B.J.; Sun, J.; Jing, L.B.; Fraumeni, J.F. Indoor radon and lung cancer in China. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershagen, G.; Liang, Z.H.; Hrubec, Z.; Svensson, C.; Boice, J.J. Residential radon exposure and lung cancer in Swedish women. Health Phys. 1992, 63, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershagen, G.; Akerblom, G.; Axelson, O.; Clavensjo, B.; Damber, L.; Desai, G.; Enflo, A.; Lagarde, F.; Mellander, H.; Svartengren, M. Residential radon exposure and lung cancer in Sweden. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneau, E.G.; Krewski, D.; Choi, N.W.; Goddard, M.J.; McGregor, R.G.; Zielinski, J.M.; Du, J. Case-control study of residential radon and lung cancer in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 140, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavanja, M.C.; Brownson, R.C.; Lubin, J.H.; Berger, E.; Chang, J.; Boice, J.D., Jr. Residential radon exposure and lung cancer among nonsmoking women. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1994, 86, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvinen, A.; Mäkeläinen, I.; Hakama, M.; Castrén, O.; Pukkala, E.; Reisbacka, H.; Rytömaa, T. Indoor radon exposure and risk of lung cancer: A nested case-control study in Finland. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996, 88, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruosteenoja, E.; Mäkeläinen, I.; Rytömaa, T.; Hakulinen, T.; Hakama, M. Radon and lung cancer in Finland. Health Phys. 1996, 71, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.; Whitley, E.; Silcocks, P.; Thakrar, B.; Green, M.; Lomas, P.; Miles, J.; Reeves, G.; Fearn, T.; Doll, R. Risk of lung cancer associated with residential radon exposure in south-west England: A case-control study. Br. J Cancer 1998, 78, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alavanja, M.; Lubin, J.H.; Mahaffey, J.A.; Brownson, R.C. Residential radon exposure and risk of lung cancer in Missouri. Am. J. Public Health 1999, 89, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, R.W.; Steck, D.J.; Smith, B.J.; Brus, C.P.; Fisher, E.L.; Neuberger, J.S.; Platz, C.E.; Robinson, R.A.; Woolson, R.F.; Lynch, C.F. Residential radon gas exposure and lung cancer—The Iowa radon lung cancer study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreienbrock, L.; Kreuzer, M.; Gerken, M.; Dingerkus, G.; Wellmann, J.; Keller, G.; Erich Wichmann, H. Case-control study on lung cancer and residential radon in western Germany. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 153, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobue, T.; Lee, V.S.; Ye, W.; Tanooka, H.; Mifune, M.; Suyama, A.; Koga, T.; Morishima, H.; Kondo, S. Residential radon exposure and lung cancer risk in Misasa, Japan: A case-control study. J. Radiat. Res. 2000, 41, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagarde, F.; Axelsson, G.; Damber, L.; Mellander, H.; Nyberg, F.; Pershagen, G. Residential radon and lung cancer among never-smokers in Sweden. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, F.E.; Barbone, F.; Betta, A.; Bonomi, M.; Alessandrini, B.; Bovenzi, M. Residential radon and risk of lung cancer in an Italian alpine area. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 2001, 56, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Dios, J.M.; Barreiro, M.A.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Figueiras, A. Exposure to residential radon and lung cancer in Spain: A population-based case-control study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 156, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Lubin, J.H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Boice, J.D., Jr.; Cui, H.; Zhang, S.; Conrath, S.; Xia, Y.; Shang, B. Residential radon and lung cancer risk in a high-exposure area of Gansu Province, China. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreuzer, M.; Heinrich, J.; Wölke, G.; Rosario, A.S.; Gerken, M.; Wellmann, J.; Keller, G.; Kreienbrock, L.; Wichmann, H.E. Residential radon and risk of lung cancer in Eastern Germany. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baysson, H.; Tirmarche, M.; Tymen, G.; Gouva, S.; Caillaud, D.; Artus, J.C.; Vergnenegre, A.; Ducloy, F.; Laurier, D. Indoor radon and lung cancer in France. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochicchio, F.; Forastiere, F.; Farchi, S.; Quarto, M.; Axelson, O. Residential radon exposure, diet and lung cancer: A case-control study in a Mediterranean region. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, D.P.; Weinberg, C.R.; Shore, D.L.; Archer, V.E.; Bishop Stone, M.; Lyon, J.L.; Rothney-Kozlak, L.; Shepherd, M.; Stolwijk, J.A. Indoor radon and lung cancer risk in Connecticut and Utah. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, H.B.; Al-Zoughool, M.; Garner, M.J.; Jiang, H.; Klotz, J.B.; Krewski, D.; Nicholson, W.J.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Zielinski, J.M. Case-control study of radon and lung cancer in New Jersey. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 128, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.E.; Nelson, D.F.; Popkin, J.H.; Popkin, Z. Case-control study of lung cancer risk from residential radon exposure in Worcester County, Massachusetts. Health Phys. 2008, 94, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros-Dios, J.M.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Pérez-Ríos, M.; Castro-Bernárdez, M.; Abal-Arca, J.; Tojo-Castro, M. Residential radon exposure, histologic types, and lung cancer risk: A case–control study in Galicia, Spain. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2012, 21, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todea, D.; Cosma, C.; Dicu, T.; Roşca, L.; Dinu, A.C.; Rişteiu, M.; Iancu, D.; Papuc, I.; Rădulescu, D. Lung cancer risk induced by residential radon in cluj and alba counties, romania. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. EEMJ 2013, 12, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Durán, M.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Parente-Lamelas, I.; Leiro-Fernández, V.; Abal-Arca, J.; Montero-Martínez, C.; Pena-Álvarez, C.; González-Barcala, F.J.; Castro-Añón, O.; Golpe-Gómez, A. Lung cancer in never-smokers: A case–control study in a radon-prone area (Galicia, Spain). Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duran, M.T.; Ravina, A.R.; Lamelas, I.P.; Fernandez, V.L.; Arca, J.A.; Martinez, C.M.; ALvarez, C.P.; Barcala, J.G.; Añon, O.C.; Gomez, A.G. Residential radon exposure and risk of lung cancer in never smoking women. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 2734. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Durán, M.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Parente-Lamelas, I.; Leiro-Fernández, V.; Abal-Arca, J.; Montero-Martínez, C.; Pena-Álvarez, C.; Castro-Añón, O.; Golpe-Gómez, A.; Martínez, C.; et al. Residential radon and lung cancer characteristics in never smokers. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuder, S.A. Effect of cigarette smoking on major histological types of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2001, 31, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.S. Tobacco smoke carcinogens and lung cancer. In Chemical Carcinogenesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, W.; Morlier, J.; Monchaux, G. Interaction of smoking and radon in rats: A biologically based mechanistic model. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2005, 44, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. A Citizen’s Guide to Radon: The Guide to Protecting Yourself and Your Family from Radon. Washington, US Environmental Protection Agency, 2012. Available online: www.epa.gov/radon/pubs/citguide (accessed on 1 February 2020).



| Study | Study Location | Study Design | Sex | Age (Years) | Smoking Status | Cases/Controls (n) | Exposure Comparison (Bq/m3) | OR (95% CI) | Adjusted Covariates | Quality Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Svensson et al. (1989) a, b [31] | Sweden | PCC, HCC | F | All | mixed | 210/400 | <4500 vs. ≥6000 | 1.7(0.9–3.3) | age, smoking, and municipality of residency | 6 |
| Blot et al. (1990) a [32] | China | PCC | F | 30–69 | mixed | 308/356 | <70 vs. ≥296 | 0.7 (0.4–1.3) | age, education, smoking status, and an index of indoor air pollution | 8 |
| Pershagen et al. (1992) a [33] | Sweden | PCC, HCC | F | All | mixed | 210/209 | ≤75 vs. ≥151 | 1.7 (1.0–2.9) | age, smoking, and municipality of residency | 7 |
| Pershagen et al. (1994) a, b [34] | Sweden | PCC | M/F | 35–74 | mixed | 1360/2847 | ≤50 vs. >400 | 1.8 (1.1–2.9) | Age, sex, smoking, occupation, area of residence | 7 |
| Letourneau et al. (1994) a [35] | Canada | PCC | M/F | 35–80 | mixed | 738/738 | <25 vs. ≥200 | 1.18(0.95–1.46) | smoking and education | 7 |
| Alavanja et al. (1994) a [36] | USA | PCC | F | 30–84 | NS | 538/1138 | <30 vs. 91–566 | 1.2 (0.9–1.7) | Age and smoking | 8 |
| Auvinen et al. (1996) [37] | Finland | PCC | M/F | All | mixed | 517/517 | ≤49 vs. 400–1277 | 1.15 (0.69–1.93) | smoking | 7 |
| Ruosteenoja et al. (1996) a, b [38] | Finland | PCC | M | 0–64 | mixed | 164/331 | ≤95 vs. >186 | 1.5 (0.8–2.9) | age, smoking intensity, and quitting of smoking prior to 1979 | 8 |
| Darby et al. (1998) [39] | UK | HCC | M/F | <75 | mixed | 982/3185 | <25 vs. ≥400 | 1.79 (0.74–4.33) | age, sex, smoking, county of residence and social class | 7 |
| Alavanja et al. (1999) a [40] | USA | PCC | F | 30-84 | mixed | 247/299 | <37 vs. ≥148 | 0.71 (0.3–1.3) | Age, education, smoking, previous lung disease, and vegetable consumption | 8 |
| Field et al. (2000) a [41] | USA | PCC | F | 40–84 | mixed | 413/614 | ≤57 vs. >228 | 1.79 (0.99–3.26) | Age, smoking, and education | 8 |
| Kreienbrock et al. (2000) a, b [42] | Germany | PCC | M/F | ≤75 | mixed | 1449/2297 | <50 vs. >140 | 1.93 (0.99–3.77) | smoking and asbestos | 8 |
| Sobue et al. (2000) [43] | Japan | PCC | M/F | ≥40 | mixed | 28/36 | ≤24 vs. ≥100 | 0.25 (0.03–.33) | sex, year of birth, smoking status and occupational history | 7 |
| Lagarde et al. (2001) [44] | Sweden | PCC | M/F | ≥28 | NS | 258/487 | <50 vs. >140 | 1.55 (0.88–2.73) | Age, sex, passive smoking, area of current residence, and socioeconomic status | 8 |
| Pisa et al. (2001) b [45] | Italy | PCC | M/F | All | mixed | 138/291 | <40 vs. ≥200 | 1.0 (0.3-3.1) | Age, sex, and smoking | 7 |
| Barros-Dios et al. (2002) [46] | Spain | PCC | M/F | ≥35 | mixed | 163/241 | <36.9 vs. ≥148 | 2.96 (1.29–6.79) | Age, sex, and family history | 8 |
| Wang et al. (2002) b [47] | China | PCC | M/F | 30-75 | mixed | 768/1659 | <100 vs. ≥300 | 1.58 (1.1–2.3) | Age, sex, prefecture, smoking and socioeconomic factors | 8 |
| Kreuzer et al. (2003) a [48] | Germany | PCC | M/F | <76 | mixed | 1192/1640 | <50 vs. >140 | 1.30 (0.88–1.93) | Smoking, occupational asbestos | 8 |
| Baysson et al. (2004) b [49] | France | HCC | M/F | <75 | mixed | 486/984 | <50 vs. >400 | 1.11 (0.59–2.09) | Age, sex, region, smoking and occupational exposure to asbestos and carcinogens | 7 |
| Bochicchio et al. (2005) b [50] | Italy | HCC | M/F | 35–90 | mixed | 384/401 | <50 vs. >400 | 2.89 (0.45–18.6) | sex, age, sex X age, area of residence in Lazio, smoking and dietary variables | 7 |
| Sandler et al. (2006) [51] | USA | PCC | M/F | 40–79 | mixed | 1474/1811 | <18 vs. ≥53 | 1.00 (0.93–1.07) | Age, sex, and smoking | 7 |
| Wilcox et al. (2008) b [52] | USA | PCC | M/F | All | mixed | 561/740 | <25 vs. ≥150 | 0.76(0.36–1.61) | Age, sex, and smoking | 8 |
| Thompson et al. (2008) [53] | USA | HCC | M/F | >40 | mixed | 200/397 | <25 vs. ≥250 | 2.50 (0.47–13.46) | smoking, residency, job exposure, income, and education | 7 |
| Barros-Dios et al. (2012) a, b [54] | Spain | HCC | M/F | >30 | mixed | 308/484 | <50 vs. >147 | 2.21 (1.33–3.69) | age, sex, and tobacco consumption | 7 |
| Todea et al. (2013) [55] | Romania | PCC | M/F | All | mixed | 104/137 | <50 vs. >147 | 2.67 (1.14–6.27) | age and sex | 8 |
| Torres-Durán et al. (2014) b [56] | Spain | HCC | M/F | >30 | NS | 192/329 | <100 vs. ≥200 | 2.42 (1.45–4.06) | sex, age and environmental tobacco-smoke exposure | 7 |
| Duran et al. (2014) [57] | Spain | HCC | F | >30 | NS | 140/212 | ≤100 vs. ≥200 | 2.84 (1.58–5.09) | age and environmental tobacco exposure | 7 |
| Torres-Durán et al. (2015) a, b [58] | Spain | HCC | M/F | >30 | NS | 216/329 | <200 vs. ≥200 | 2.11(1.43–3.11) | age and gender | 7 |
| Study | No. of Studies | OR (95% CI) | Heterogeneity Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 (%) | p-Value | |||
| All studies | 28 | 1.48 (1.26–1.73) | 67.5 | 0.000 |
| Histological subtype | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 12 | 1.58 (1.31–1.91) | 30.9 | 0.144 |
| Small-cell carcinoma | 11 | 2.03 (1.52–2.71) | 0.0 | 0.445 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 10 | 1.43 (1.18–1.74) | 0.0 | 0.473 |
| Other histological types | 10 | 1.54 (1.11–2.15) | 34.8 | 0.129 |
| Study population | ||||
| Europe | 18 | 1.77 (1.54–2.03) | 0.0 | 0.473 |
| North America | 7 | 1.09 (0.94–1.27) | 34.0 | 0.168 |
| Asia | 3 | 0.93 (0.42–2.06) | 72.8 | 0.025 |
| Study design | ||||
| Population-based controls | 18 | 1.28 (1.09–1.50) | 56.5 | 0.002 |
| Hospital-based controls | 8 | 2.10 (1.69–2.60) | 0.0 | 0.595 |
| Hospital and population-based controls | 2 | 1.70 (1.13–2.57) | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| Smokers | 8 | 14.80 (6.27–34.90) | 80.0 | 0.000 |
| Nonsmokers | 12 | 1.38 (1.03–1.84) | 65.3 | 0.001 |
| Ex-smokers | 3 | 2.21 (0.85–5.76) | 52.9 | 0.120 |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 7 | 1.38 (0.98–1.94) | 63.7 | 0.011 |
| Male and female | 20 | 1.52 (1.26–1.84) | 69.5 | 0.000 |
| Duration of radon measurements (months) | ||||
| ≥12 | 16 | 1.19 (1.03–1.38) | 43.5 | 0.033 |
| <12 | 12 | 2.02 (1.70–2.40) | 0.0 | 0.699 |
| Study | Study Location | EOR per 100 Bq/m3 (95% CI) Radon Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Adenocarcinoma | Small-Cell Carcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Other Histological Types | ||
| Pershagen et al. (1994) | Sweden | 0.10 (0.01–0.22) | 0.17 (0.01–0.42) | - | - | - |
| Darby et al. (1998) | UK | 0.12 (−0.05–0.33) | 0.18 (−0.09–0.45) | 0.20 (0.02–0.38) | −0.05 (−0.23–0.13) | 0.03 (−0.19–0.25) |
| Kreienbrock et al. (2000) | Germany | 0.13 (−0.12–0.46) | - | 0.11 (−0.17–0.47) | - | - |
| Lagarde et al. (2001) | Sweden | 0.28 (−0.05–1.05) | - | - | - | - |
| Wang et al. (2002) | China | 0.19 (0.05–0.47) | - | - | - | - |
| Kreuzer et al. (2003) | Germany | 0.08 (−0.03–0.20) | −0.02 (−0.23–0.22) | 0.23 (0.02–0.47) | 0.05 (−0.14–0.27) | - |
| Bochicchio et al. (2005) | Italy | 0.14 (−0.11–0.46) | 0.36 (−0.1–1.05) | 0.22 (−0.21–0.89) | 0.19 (−0.12–0.60) | −0.46 (−0.76–0.18) |
| Sandler et al. (2006) | USA | 0.13 (−0.23–0.50) | 0.20 (−0.19–0.59) | 0.17 (−0.35–0.69) | −0.18 (−0.39–0.37) | 0.21 (−0.35–0.78) |
| Wilcox et al. (2008) | USA | 0.05 (−0.14–0.56) | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, W.; Shi, T. Residential Radon and Histological Types of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case‒Control Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041457
Li C, Wang C, Yu J, Fan Y, Liu D, Zhou W, Shi T. Residential Radon and Histological Types of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case‒Control Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(4):1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041457
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Cong, Chunhong Wang, Jun Yu, Yongsheng Fan, Duanya Liu, Wenshan Zhou, and Tingming Shi. 2020. "Residential Radon and Histological Types of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case‒Control Studies" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 4: 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041457
APA StyleLi, C., Wang, C., Yu, J., Fan, Y., Liu, D., Zhou, W., & Shi, T. (2020). Residential Radon and Histological Types of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case‒Control Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(4), 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041457