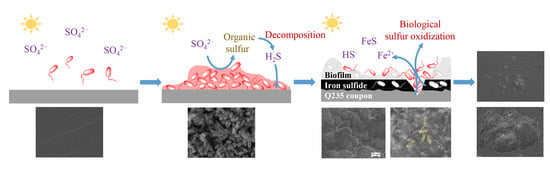
Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel by Ectothiorhodospira sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Identification and Cultivation
2.2. Metal Material Preparation and Immersion Corrosion Test
2.3. Morphological, Elemental Composition and Pit Depth Characteriazitions
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Strain Identification

3.2. Morphological, Elemental Composition and Pit Depth
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The presence of the strain PHS-Q promoted the formation of a protective film on the carbon steel surface. The protective film composed of the biofilm and corrosion product (mainly the iron sulfide) slowed the uniform corrosion rate to a certain extent.
- (2)
- The PHS-Q cells attached to and oxidised the iron sulfide, which made the protective film discompose and incur pitting.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Little, B.J.; Blackwood, D.J.; Hinks, J.; Lauro, F.M.; Marsili, E.; Okamoto, A.; Rice, S.A.; Wade, S.A.; Flemming, H.C. Microbially influenced corrosion—Any progress? Corros. Sci. 2020, 170, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, B.; Duan, J.; Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Yang, L.; Hou, B. Synergistic effect of carbon starvation and exogenous redox mediators on corrosion of X70 pipeline steel induced by Desulfovibrio singaporenus. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 788, 147573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Kijkla, P.; Mohamed, M.E.; Saleh, M.A.; Kumseranee, S.; Punpruk, S.; Gu, T. Aggressive corrosion of carbon steel by Desulfovibrio ferrophilus IS5 biofilm was further accelerated by riboflavin. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 142, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewayde, E.; Nehdi, M.; Allouche, E.; Nakhla, G. Effect of geopolymer cement on microstructure, compressive strength and sulphuric acid resistance of concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2006, 58, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Du, M.; Li, Z. Investigation of mixed species biofilm on corrosion of X65 steel in seawater environment. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 143, 107951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Lin, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Review on corrosion and corrosion scale formation upon unlined cast iron pipes in drinking water distribution systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 117, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jia, R.; Kumseranee, S.; Punpruk, S.; Gu, T. Comparison of 304 and 316 stainless steel microbiologically influenced corrosion by an anaerobic oilfield biofilm consortium. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 122, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guan, F.; Hou, B.; Duan, J. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of marine steels within the interaction between steel and biofilms: A brief view. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Bardiau, M.; Brennan, R.; Burgess, H.; Caplin, J.; Ray, S.; Urios, T. Accelerated low water corrosion: The microbial sulfur cycle in microcosm. npj Mater. Degrad. 2019, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, B.J.; Ray, R.I.; Pope, R.K. Relationship between corrosion and the biological sulfur cycle: A review. Corrosion 2000, 56, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, G.; Zheng, X.; Qian, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R. Formation, growth and corrosion effect of sulfur oxidizing bacteria biofilm on mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, S.H.; Boren, A.; Hernandez-Maldonado, J.; Stoneburner, B.; Saltikov, C.W.; Stolz, J.F.; Oremland, R.S. Arsenite as an electron donor for anoxygenic photosynthesis: Description of three strains of Ectothiorhodospira from Mono Lake, California and Big Soda Lake, Nevada. Life 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trüper, H.G.; Peck, H.D. Formation of adenylyl sulfate in phototrophic bacteria. Arch. Mikrobiol. 1970, 73, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yin, S.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J. Microbial-induced concrete corrosion under high-salt conditions: Microbial community composition and environmental multivariate association analysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 164, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Choi, H.; Sakong, H.; Youk, J.H. Sulfur-source dependent wet mechanochemical synthesis of pyrrhotite nanoparticles and evaluation of their sonocatalytic dye degradability. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 145, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mendili, Y.; Abdelouas, A.; El Hajj, H.; Bardeau, J.-F. Phase transitions of iron sulphides formed by steel microbial corrosion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 26343–26351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, D.L.; Venancio Silva, S.; De Oliveira, M.T.; Haroon, S. Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Raman. Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærvik, M.; Ramstedt, M.; Schwibbert, K.; Dietrich, P.M.; Unger, W.E.S. Comparative study of NAP-XPS and Cryo-XPS for the investigation of surface chemistry of the bacterial cell-envelope. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 666161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Deng, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D. Corrosion of Q235 carbon steel in seawater containing Mariprofundus ferrooxydans and Thalassospira sp. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, S.; Kima, S.Y.; Kima, S.H.; Kima, Y.D. Fe-oxide/Al2O3 for the enhanced activity of H2S decomposition under realistic conditions: Mechanistic studies by in-situ DRIFTS and XPS. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Yang, X.-Y.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy on microbial cell surfaces: A forgotten method for the characterization of microorganisms encapsulated with surface-engineered shells. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 666159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramana, V.V.; Sasikala, C.; Ramaprasad, E.V.V.; Ramana, C.V. Description of Ectothiorhodospira salini sp. nov. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 56, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Yang, C.; Saleh, M.A.; Alotaibi, M.D.; Mohamed, M.E.; Xu, D.; Gu, T. Conductive magnetite nanoparticles considerably accelerated carbon steel corrosion by electroactive Desulfovibrio vulgaris biofilm. Corros. Sci. 2022, 205, 110440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, G.; Jiang, C.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F. Accelerated biocorrosion of stainless steel in marine water via extracellular electron transfer encoding gene phzH of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Maldonado, J.; Stoneburner, B.; Boren, A.; Miller, L.; Rosen, M.; Oremland, R.S.; Saltikova, C.W. Genome sequence of the photoarsenotrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira sp. strain BSL-9, isolated from a hypersaline alkaline arsenic-rich extreme environment. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01139-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Tindall, B.J.; Grant, W.D. Ectothiorhodospira vacuolata sp. nov., a new phototrophic bacterium from soda lakes. Arch. Microbiol. 1981, 130, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Jia, R.; Jin, Y.; Song, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Direct microbial electron uptake as a mechanism for stainless steel corrosion in aerobic environments. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| βa (mV dec−1) | βc (mV dec−1) | Ecorr (V vs. SCE) | Icorr (10−7 A cm−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sterile | 154.28 | −66.80 | −0.72 | 17.20 |
| PHS-Q-inoculated | 130.52 | −89.53 | −0.85 | 4.46 |
| Time (d) | Qf (MΩ−1 sn cm−2) | nf | Rf (Ω cm2) | Qint (kΩ−1 sn cm−2) | nint | Rint (kΩ cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sterile | 0 | 1.52 | 0.87 | 7.57 | 0.57 | 0.81 | 1.27 |
| 1 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 2.78 | 0.29 | 0.85 | 2.60 | |
| 2 | 1.91 | 0.88 | 7.86 | 0.35 | 0.82 | 3.23 | |
| 4 | 2.24 | 0.85 | 9.64 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 4.00 | |
| 7 | 34.32 | 0.63 | 14.56 | 0.58 | 0.74 | 6.22 | |
| 14 | 7.02 | 0.70 | 51.16 | 1.29 | 0.72 | 33.50 | |
| Time (d) | Qb (MΩ−1 sn cm−2) | n1 | Rb (Ω cm2) | Qint (kΩ−1 sn cm−2) | n2 | Rint (kΩ cm2) | |
| PHS-Q-inoculated | 0 | 0.50 | 0.99 | 8.37 | 0.31 | 0.80 | 2.67 |
| 1 | 0.41 | 0.99 | 8.77 | 0.24 | 0.84 | 4.61 | |
| 2 | 0.39 | 0.99 | 8.69 | 0.22 | 0.87 | 10.45 | |
| 4 | 0.63 | 0.99 | 5.61 | 0.21 | 0.87 | 30.78 | |
| 7 | 0.48 | 0.99 | 7.14 | 0.21 | 0.87 | 41.74 | |
| 14 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 3.88 | 0.22 | 0.87 | 38.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J.; Peng, R.; Shi, Q.; Xie, X. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel by Ectothiorhodospira sp. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215416
Qi H, Wang Y, Feng J, Peng R, Shi Q, Xie X. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel by Ectothiorhodospira sp. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215416
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Hong, Yingsi Wang, Jin Feng, Ruqun Peng, Qingshan Shi, and Xiaobao Xie. 2022. "Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel by Ectothiorhodospira sp." International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215416
APA StyleQi, H., Wang, Y., Feng, J., Peng, R., Shi, Q., & Xie, X. (2022). Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel by Ectothiorhodospira sp. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215416