Feasibility of Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Marine Dredged Sediments by Active Capping with Enteromorpha Biochar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
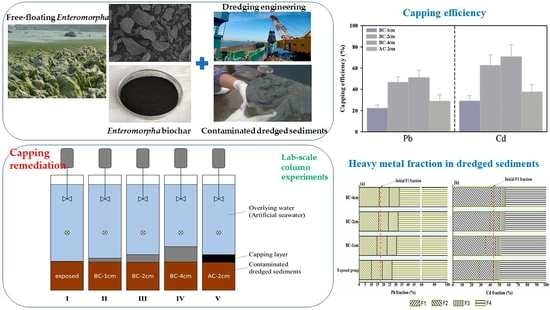
2.1. Preparation of Enteromorpha BC and Contaminated Dredged Sediments
2.2. Incubation Experiments
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Enteromorpha BC
3.2. Effect of Capping on the Release of Heavy Metals from Dredged Sediments
3.3. Heavy-Metal Fraction in Dredged Sediments under the Effect of Capping
3.4. Time-Scale and Release Kinetics for Capping Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben Salem, Z.; Capelli, N.; Laffray, X.; Elise, G.; Ayadi, H.; Aleya, L. Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water, sediment and roach tissues in a landfill draining system pond (Etueffont, France). Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, B.; Wang, D. Transport mechanisms of contaminants released from fine sediment in rivers. Acta Mech. Sin. 2015, 31, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, D.; Tam, N.F.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y. Enhancement of active thin-layer capping with natural zeolite to simultaneously inhibit nutrient and heavy metal release from sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 119, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Toriman, M.E.; Juahir, H.; Zain, S.M.; Habir, N.L.A.; Retnam, A.; Kamarudin, M.K.A.; Umar, R.; Azid, A. Spatial assessment and source identification of heavy metals pollution in surface water using several chemometric techniques. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achary, M.S.; Satpathy, K.; Panigrahi, S.; Mohanty, A.; Padhi, R.K.; Biswas, S.; Prabhu, R.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Panigrahy, R. Concentration of heavy metals in the food chain components of the nearshore coastal waters of Kalpakkam, southeast coast of India. Food Control 2017, 72, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Diao, Z.-H.; Xu, X.-R.; Xie, Q. Effects of dissolved oxygen, salinity, nitrogen and phosphorus on the release of heavy metals from coastal sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norén, A.; Fedje, K.K.; Strömvall, A.-M.; Rauch, S.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Integrated assessment of management strategies for metal-contaminated dredged sediments—What are the best approaches for ports, marinas and waterways? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 135510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Gao, S.; Fu, Z.; Tang, W.; Wu, Y.; Gong, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Efficacy of dredging engineering as a means to remove heavy metals from lake sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S. Electrokinetic Enhancement: Effect of Sample Stacking on Strengthening Heavy Metal Removal in Electrokinetic Remediation of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. J. Environ. Eng. 2019, 145, 4018148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrat, A.; Ezzat, K.; Muhammad, A.S. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xing, M.; Marhaba, T.; Zhang, W. In situ capping technology for controlling heavy metals release from contaminated sediment. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 168, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, A.S.; Paller, M.H.; Dixon, K.L. Evaluation of Active Cap Materials for Metal Retention in Sediments. Remediat. J. 2014, 24, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefsson, S.; Schaanning, M.; Samuelsson, G.S.; Gunnarsson, J.S.; Olofsson, I.; Eek, E.; Wiberg, K. Capping efficiency of various carbonaceous and mineral materials for in situ remediation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran contaminated marine sediments: Sediment-to-water fluxes and bioaccumulation in boxcosm tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Li, X.; Xiao, S.; Fan, W. Review of remediation technologies for sediments contaminated by heavy metals. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1701–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, J.; Wu, W.; Jia, F. Evaluation of in situ capping with clean soils to control phosphate release from sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Hibino, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Mito, Y.; Nakamoto, K.; Lee, I.-C. Field experiments on remediation of coastal sediments using granulated coal ash. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.-W.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. The feasibility of using bentonite, illite, and zeolite as capping materials to stabilize nutrients and interrupt their release from contaminated lake sediments. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, F.; Barjoveanu, G.; De Gisi, S.; Teodosiu, C.; Notarnicola, M. Sustainability assessment of reactive capping alternatives for the remediation of contaminated marine sediments. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H. Pb(II) sorption from aqueous solution by novel biochar loaded with nano-particles. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.B.; Tao, X.D.; Wang, H.; Li, W.K.; Ding, X.; Chu, H.Q. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizmur, T.; Fresno, T.; Akgül, G.; Frost, H.; Moreno-Jiménez, E. Biochar modification to enhance sorption of inorganics from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Deng, R.; Wan, J.; Zeng, G.; Xue, W.; Wen, X.; Xu, P. Remediation of lead-contaminated sediment by bio-char-supported nano-chlorapatite: Accompanied with the change of available phosphorus and organic matters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.O.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Gibson, B.D.; Landis, R.C.; Dyer, J.; Ma, J. Application of hardwood biochar as a reactive capping mat to stabilize mercury derived from contaminated floodplain soil and riverbank sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Bannon, D.I.; Wartelle, L.H. Retention of Heavy Metals by Carboxyl Functional Groups of Biochars in Small Arms Range Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, S.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Song, B.; Chen, Q. Application of biochar for the remediation of polluted sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monitor. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, W.; Harsh, J.B.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Fortuna, A.-M.; Dallmeyer, I.; Garcia-Perez, M. Influence of feedstock source and pyrolysis temperature on biochar bulk and surface properties. Biomass-Bioenergy 2016, 84, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, W.-J.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.-S.; Jiang, H.; Sheng, G.-P. Polyethylenimine modified biochar adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from the aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.M.; Panda, S.S.; Dhal, N.K. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for heavy metal removal: A review. Int. J. Res. Biosci. 2017, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, O.R.; Herbert, B.E.; Rhue, R.D.; Kuo, L.J. Metal interactions at the biocharwater interface: Energetics and structure-sorption relationships elucidated by flow adsorption microcalorimetry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5550–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Zeng, G.-M.; Yu, Z.G.; Cui, F.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Shen, L.-Q. Active capping technology: A new environmental remediation of contaminated sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4370–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Rahman, K.M.A.; El-Kamash, A.M.; El-Sourougy, M.R.; Abdel-Moniem, N.M. Thermodynamic modeling for the removal of Cs+, Sr2+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ions from aqueous waste solutions using zeolite A. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 268, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Hong, M.; Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Tan, Z. Contributions and mechanisms of components in modified biochar to adsorb cadmium in aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of cadmium and lead sorption by Phyllostachys pubescens biochar produced under a low-oxygen pyrolysis atmosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Chen, T.; Xu, W.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Yan, B. Application Research of Biochar for the Remediation of Soil Heavy Metals Contamination: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, K.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Abas, M.R.; Sobhanzadeh, E. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capangpangan, R.Y.; Pagapong, N.K.; Pineda, C.P.; Sanchez, P.B. Evaluation of potential ecological risk and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediment samples using different environmental quality indices—A case study in Agusan River, Caraga Philippines. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2016, 8, 2220–6663. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Ren, L.; Wang, D.; Cai, Z.; Xia, X.; Ding, A. Assessing the capacity of biochar to stabilize copper and lead in con-taminated sediments using chemical and extraction methods. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, X.; Gu, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; He, Y. Rice waste biochars produced at different pyrolysis temperatures for arsenic and cadmium abatement and detoxification in sediment. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Han, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Cheng, J. Adsorption of copper(II) and lead(II) from seawater using hydrothermal biochar derived from Enteromorpha. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplat, C.; Texier, H.; Barillier, D.; Lelievre, C. Heavy metals mobility in harbour contaminated sediments: The case of Port-en-Bessin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.E. Intraparticle diffusion process for lead(II) biosorption onto mansonia wood sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5868–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-J.; Liu, Y.-G.; Tan, X.; Zeng, G.-M.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Liu, S.-B.; Yin, Z.-H.; Jiang, L.-H.; Li, M.-F.; Wen, J. The effect of several activated biochars on Cd immobilization and microbial community composition during in-situ remediation of heavy metal contaminated sediment. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Capping Thickness | Capping Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | |
| 1 cm | 22.2 ± 3.0 | 29.1 ± 4.8 |
| 2 cm | 46.7 ± 5.1 | 62.5 ± 9.9 |
| 4 cm | 51.1 ± 6.9 | 70.8 ± 11.1 |
| Speciation | Pb | Cd | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed | BC-1 cm | BC-2 cm | BC-4 cm | Exposed | BC-1 cm | BC-2 cm | BC-4 cm | |
| F1 (%) | 10.0 | 14.6 | 16.0 | 16.4 | 28.0 | 35.0 | 40.0 | 41.3 |
| F2 (%) | 9.0 | 8.3 | 8.0 | 8.2 | 16.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 9.7 |
| F3 (%) | 8.0 | 7.8 | 8.0 | 8.2 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 5.6 | 5.4 |
| F4 (%) | 73.0 | 69.3 | 68 | 67.2 | 50.0 | 48.0 | 44.4 | 43.6 |
| Rmax (%) | t0 (d) | b | r2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Exposed group | 35 | 3 | 1.7 | 0.8991 |
| BC-1 cm | 30 | 4 | 2.4 | 0.9300 | |
| BC-2 cm | 21 | 6 | 2.7 | 0.9334 | |
| Cd | Exposed group | 37 | 2 | 1.5 | 0.9092 |
| BC-1 cm | 28 | 3 | 1.4 | 0.9387 | |
| BC-2 cm | 16 | 5 | 1.0 | 0.8563 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Han, J.; Chen, H. Feasibility of Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Marine Dredged Sediments by Active Capping with Enteromorpha Biochar. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19094944
Wang Z, Song S, Wang H, Yang W, Han J, Chen H. Feasibility of Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Marine Dredged Sediments by Active Capping with Enteromorpha Biochar. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(9):4944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19094944
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhaowei, Shuang Song, Huan Wang, Wenchao Yang, Jianbo Han, and Hong Chen. 2022. "Feasibility of Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Marine Dredged Sediments by Active Capping with Enteromorpha Biochar" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 9: 4944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19094944
APA StyleWang, Z., Song, S., Wang, H., Yang, W., Han, J., & Chen, H. (2022). Feasibility of Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Marine Dredged Sediments by Active Capping with Enteromorpha Biochar. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9), 4944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19094944