Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bats and Its Planetary Health Impact for Surveillance of Zoonotic Spillover Events: A Scoping Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Bacterial pathogens;
- Bat specimens such as feces, skin swab, oral, and rectal swab/cloacal swabs, etc.;
- Drug sensitivity testing done in a laboratory setting with/without Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) and/or other standard organizations cutoffs for drug susceptibility testing;
- Reports of resistance genes and plasmids in isolated bacterial samples.
- Review articles;
- Studies on bacteria isolated from bats without antimicrobial susceptibility, gene, or plasmid detection test results;
- Studies that did not specify bacterial antimicrobial susceptibility isolated from bats.
3. Results
3.1. Evidence of Antibiotic Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens in Bats
3.1.1. Escherichia coli (E. coli)
3.1.2. Enterobacter spp.
3.1.3. Salmonella spp.
3.1.4. Klebsiella spp.
3.1.5. ESBL-Producing and Colistin Resistant Enterobacterales
3.1.6. Other Gram-Negative Bacteria and Genes Responsible for Drug Resistance in Bats
3.2. Evidence of Antibiotic Resistant Gram-Positive Bacterial Pathogens in Bats
3.2.1. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus spp.
3.2.2. Other Gram-Positive Organisms
3.2.3. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
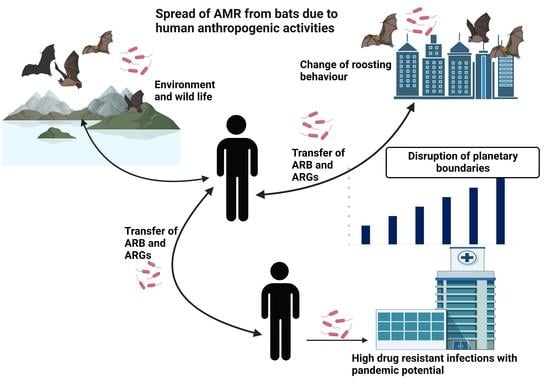
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, M.; Schulze, K.; Cassini, A.; Plachouras, D.; Mossialos, E. A governance framework for development and assessment of national action plans on antimicrobial resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e371–e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Thompson, R.A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Illegal wildlife trade: A gateway to zoonotic infectious diseases. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furness, L.E.; Campbell, A.; Zhang, L.; Gaze, W.H.; McDonald, R.A. Wild small mammals as sentinels for the environmental transmission of antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharout-Sait, A.; Touati, A.; Ahmim, M.; Brasme, L.; Guillard, T.; Agsous, A.; de Champs, C. Occurrence of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Bat Guano. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.T.; Fernandes, J.; Carvalho, J.; Cunha, M.V.; Caetano, T.; Mendo, S.; Serrano, E.; Fonseca, C. Wild boar as a reservoir of antimicrobial resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, H.D.; Vasco, K.A.; Zhang, L. A Review of Antimicrobial Resistance in Poultry Farming within Low-Resource Settings. Animals 2020, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Imtiaz, M.A.; Sayeed, M.A.; Shaikat, A.H.; Hassan, M.M. Antimicrobial resistance pattern in domestic animal-wildlife—Environmental niche via the food chain to humans with a Bangladesh perspective; a systematic review. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, J.; Noreddin, A.; El Zowalaty, M.E. Systematic Review of Important Bacterial Zoonoses in Africa in the Last Decade in Light of the ‘One Health’ Concept. Pathogens 2019, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Pitino, R. Carbapenemase-producing bacteria in food-producing animals, wildlife and environment: A challenge for human health. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2019, 8, 7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejska, M.; Papagiannitsis, C.C. Plasmid-mediated resistance is going wild. Plasmid 2018, 99, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; López, F.; Molina-López, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamase and emergence of OXA-48 producing Enterobacterales in wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, K.H.; Khor, W.C.; Quek, J.Y.; Low, Z.X.; Arivalan, S.; Humaidi, M.; Chua, C.; Seow, K.L.G.; Guo, S.; Tay, M.Y.F.; et al. Occurrence and Antimicrobial Resistance Traits of Escherichia coli from Wild Birds and Rodents in Singapore. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomard-Rabenirina, S.; Reynaud, Y.; Pot, M.; Albina, E.; Couvin, D.; Ducat, C.; Gruel, G.; Ferdinand, S.; Legreneur, P.; Le Hello, S.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife in Guadeloupe (French West Indies): Distribution of a Single blaCTX–M–1/IncI1/ST3 Plasmid Among Humans and Wild Animals. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Usui, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Izumi, K.; Ikeda, T.; Andoh, M. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolates obtained from wild mammals between 2013 and 2017 in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogden, N.H.; AbdelMalik, P.; Pulliam, J. Emerging infectious diseases: Prediction and detection. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2017, 43, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumla, A.; Hui, D.S.C. Emerging and Reemerging Infectious Diseases: Global Overview. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2019, 33, xiii–xix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Dhama, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, R.; Natesan, S.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Vora, K.S.; Latheef, S.K.; Karthik, K.; et al. Nipah virus: Epidemiology, pathology, immunobiology and advances in diagnosis, vaccine designing and control strategies—A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2019, 39, 26–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonsen, L.; Viboud, C. A comprehensive look at the COVID-19 pandemic death toll. Elife 2021, 10, e71974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Ebola Response Team; Aylward, B.; Barboza, P.; Bawo, L.; Bertherat, E.; Bilivogui, P.; Blake, I.; Brennan, R.; Briand, S.; Chakauya, J.M.; et al. Ebola virus disease in West Africa—The first 9 months of the epidemic and forward projections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1481–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langford, B.J.; Daneman, N.; Diong, C.; Marchand-Austin, A.; Adomako, K.; Saedi, A.; Schwartz, K.L.; Johnstone, J.; MacFadden, D.R.; Matukas, L.M.; et al. Antibiotic susceptibility reporting and association with antibiotic prescribing: A cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelfrene, E.; Botgros, R.; Cavaleri, M. Antimicrobial multidrug resistance in the era of COVID-19: A forgotten plight? Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuder Johnson, C.; Hitchens, P.L.; Smiley Evans, T.; Goldstein, T.; Thomas, K.; Clements, A.; Joly, D.O.; Wolfe, N.D.; Daszak, P.; Karesh, W.B.; et al. Spillover and pandemic properties of zoonotic viruses with high host plasticity. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leroy, E.M.; Epelboin, A.; Mondonge, V.; Pourrut, X.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J.; Formenty, P. Human Ebola outbreak resulting from direct exposure to fruit bats in Luebo, Democratic Republic of Congo, 2007. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, S.P.; Gurley, E.S.; Hossain, M.J. Transmission of human infection with Nipah virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohd, H.A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Memish, Z.A. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) origin and animal reservoir. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prompetchara, E.; Ketloy, C.; Palaga, T. Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: Lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allocati, N.; Petrucci, A.G.; Giovanni, P.D.; Masulli, M.; Ilio, C.D.; Laurenzi, V.D. Bat-man disease transmission: Zoonotic pathogens from wildlife reservoirs to human populations. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Zięba, P.; Gnat, S.; Trościańczyk, A.; Osińska, M.; Łagowski, D.; Kosior-Korzecka, U.; Puzio, I. Bats as a reservoir of resistant Escherichia coli: A methodical view. Can we fully estimate the scale of resistance in the reservoirs of free-living animals? Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 128, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cláudio, V.C.; Gonzalez, I.; Barbosa, G.; Rocha, V.; Moratelli, R.; Rassy, F. Bacteria richness and antibiotic-resistance in bats from a protected area in the Atlantic Forest of Southeastern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mbehang Nguema, P.P.; Onanga, R.; Ndong Atome, G.R.; Obague Mbeang, J.C.; Mabika Mabika, A.; Yaro, M.; Lounnas, M.; Dumont, Y.; Zohra, Z.F.; Godreuil, S.; et al. Characterization of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteria from Fruit Bats in an Unprotected Area of Makokou, Gabon. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frick, W.F.; Kingston, T.; Flanders, J. A review of the major threats and challenges to global bat conservation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1469, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanalgo, K.C.; Oliveira, H.F.; Hughes, A.C. Mapping global conservation priorities and habitat vulnerabilities for cave-dwelling bats in a changing world. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Ivens, S.; Ammerman, L.K.; Fenton, M.B.; Littlefair, J.E.; Ratcliffe, J.M.; Clare, E.L. Molecular diet analysis finds an insectivorous desert bat community dominated by resource sharing despite diverse echolocation and foraging strategies. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3117–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurek, K.; Gewartowska, O.; Tołkacz, K.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Mysłajek, R.W. Home range size, habitat selection and roost use by the whiskered bat (Myotis mystacinus) in human-dominated montane landscapes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berková, H.; Pokorný, M.; Zukal, J. Selection of buildings as maternity roosts by greater mouse-eared bats (Myotis myotis). J. Mammal. 2014, 95, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borzęcka, J.; Piecuch, A.; Kokurewicz, T.; Lavoie, K.H.; Ogórek, R. Greater mouse-eared bats (Myotis myotis) hibernating in the Nietoperek bat Reserve (Poland) as a vector of airborne culturable fungi. Biology 2021, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossa, G.; Kramer-Schadt, S.; Peel, A.J.; Scharf, A.K.; Voigt, C.C. The movement ecology of the straw-colored fruit bat, Eidolon helvum, in sub-Saharan Africa assessed by stable isotope ratios. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.D.; Santos, C.D.; Rainho, A.; Abedi-Lartey, M.; Fahr, J.; Wikelski, M.; Dechmann, D.K. Assessing roost disturbance of straw-coloured fruit bats (Eidolon helvum) through tri-axial acceleration. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igbokwe, C.O.; Bello, U.M.; Mbajiorgu, F.E. Anatomical and surface ultrastructural investigation of the tongue in the straw-coloured fruit bat (Eidolon helvum, Kerr 1972). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2021, 50, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, A.; Kinjo, K.; Izawa, M. Ranging patterns and habitat use of a solitary flying fox (Pteropus dasymallus) on Okinawa-jima Island, Japan. Acta Chiropterol. 2012, 14, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, D.J.; Restif, O.; Eby, P.; Plowright, R.K. Optimal foraging in seasonal environments: Implications for residency of Australian flying foxes in food-subsidized urban landscapes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Vuurst, P.; Díaz, M.M.; Pedro, R.-S.; Allendes, J.L.; Brown, N.; Gutiérrez, J.D.; Zarza, H.; de Oliveira, S.V.; Cárdenas-Canales, E.; Barquez, R.M. A database of common vampire bat reports. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.S.; do Canto Olegário, J.; Weber, M.N.; da Silva, M.S.; Canova, R.; Sauthier, J.T.; Baumbach, L.F.; Witt, A.A.; Varela, A.P.M.; Mayer, F.Q. Detection of coronavirus in vampire bats (Desmodus rotundus) in southern Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Kaplan, J.O.; Fuller, D.Q.; Vavrus, S.; Klein Goldewijk, K.; Verburg, P.H. Used planet: A global history. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7978–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sens-Junior, H.; Trindade, W.A.; Oliveira, A.F.; Zaniolo, M.M.; Serenini, G.F.; Araujo-Ceranto, J.B.; Gonçalves, D.D.; Germano, R.M. Bacterial resistance in bats from the Phyllostomidae family and its relationship with unique health. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Priority Pathogens List for R&D of New Antibiotics. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Benavides, J.A.; Shiva, C.; Virhuez, M.; Tello, C.; Appelgren, A.; Vendrell, J.; Solassol, J.; Godreuil, S.; Streicker, D.G. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in common vampire bats Desmodus rotundus and livestock in Peru. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDougall, F.K.; Wyres, K.L.; Judd, L.M.; Boardman, W.S.J.; Holt, K.E.; Power, M.L. Novel strains of Klebsiella africana and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Australian fruit bats (Pteropus poliocephalus). Res. Microbiol. 2021, 172, 103879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, S.; Kennelly-Merrit, S.; Tidemann, C.; Rawlinson, P.; Harvey, K.; Thornton, I. Antibiotic-resistance patterns of enteric bacteria of wild mammals on the Krakatau Islands and West Java, Indonesia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1988, 322, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apun, K.; CHONG, Y.L.; Abdullah, M.; Micky, V. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Escherichia coli isolates from food animals and wildlife animals in Sarawak, East Malaysia. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2008, 3, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, T.; Chibana, M.; Taira, C.; Nakayama, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Takase, K.; Nakamura, I.; Miyamoto, A.; Kawamoto, Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility in enterobacteriaceae recovered from Okinawa least horseshoe bat rhinolophus pumilus. Wildl. Biol. 2014, 20, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluduro, A.O. Antibiotic-resistant commensal Escherichia coli in faecal droplets from bats and poultry in Nigeria. Vet. Ital. 2012, 48, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, K.; Fahr, J.; Weber, N.; Lu, A.; Semmler, T.; Weiss, S.; Mombouli, J.-V.; Wieler, L.H. Highly diverse and antimicrobial susceptible Escherichia coli display a na ï ve bacterial population in fruit bats from the Republic of Congo. PLoS ONE 2017, 2, e0178146. [Google Scholar]
- Ngozi, A.; Agabus, N.; Eucharia, O.; Onyinyechi, U.-I.; Abraham, E.; Chika, E.; Ifeanyichukwu, I. A three-year study on the prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Escherichia coli isolated from cloacal swabs of wild and domestic birds in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. EC Microbiol. 2018, 14, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Hassell, J.M.; Ward, M.J.; Muloi, D.; Bettridge, J.M.; Robinson, T.P.; Kariuki, S.; Ogendo, A.; Kiiru, J.; Imboma, T.; Kang’ethe, E.K.; et al. Clinically relevant antimicrobial resistance at the wildlife–livestock–human interface in Nairobi: An epidemiological study. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e259–e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oladiran, F.; Ayodele Oluwayemisi, O.; Abike, O.; Olufunke, A.; Modupe, O. Molecular Characterization of Resistance and Virulence Genes in Escherichia coli Isolated from Bats (Eidolon helvum) Faeces in Osun State, Nigeria. J. Adv. Microbiol. 2022, 22, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Obodoechi, L.O.; Carvalho, I.; Chenouf, N.S.; Martínez-Álvarez, S.; Sadi, M.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F.; Torres, C. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from frugivorous (Eidolon helvum) and insectivorous (Nycteris hispida) bats in Southeast Nigeria, with detection of CTX-M-15 producing isolates. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcês, A.; Correia, S.; Amorim, F.; Pereira, J.E.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. First report on extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli from European free-tailed bats (Tadarida teniotis) in Portugal: A one-health approach of a hidden contamination problem. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 370, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skok, S.; Kogovšek, B.; Tomazin, R.; Šturm, S.; Avguštin, J.A.; Mulec, J. Antimicrobial resistant Escherichia coli from karst waters, surfaces and bat guano in Slovenian caves. J. Acta Carsol. 2020, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbáčová, K.; Maliničová, L.; Kisková, J.; Maslišová, V.; Uhrin, M.; Pristaš, P. The Faecal Microbiome of Building-Dwelling Insectivorous Bats (Myotis myotis and Rhinolophus hipposideros) also Contains Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Representatives. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcês, A.; Correia, S.; Silva, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Amorim, F.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Detection of antimicrobial resistance in faecal Escherichia coli from European free-tailed bats (Tadarida teniotis) in Portugal. J. Acta Chiropterol. 2019, 21, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Stewart-Johnson, A.; Thompson, N.N. Isolation of enteric pathogens from bats in Trinidad. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benavides, J.A.; Godreuil, S.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Mahamat, O.O.; Falcon, N.; Oravcova, K.; Streicker, D.G.; Shiva, C. Long-term maintenance of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli carried by vampire bats and shared with livestock in Peru. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.; Rocha, M.; Valera, A.; Eguiarte, L.E. Genetic structure of natural populations of Escherichia coli in wild hosts on different continents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3373–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDougall, F.K.; Boardman, W.S.J.; Power, M.L. Characterization of beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli from Australian fruit bats indicates anthropogenic origins. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Mikolon, A.; Mikoleit, M.; Ahmed, D.; Khan, S.U.; Sharker, M.A.; Hossain, M.J.; Islam, A.; Epstein, J.H.; Zeidner, N.; et al. Isolation of Salmonella Virchow from a fruit bat (Pteropus giganteus). EcoHealth 2013, 10, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, F.; Power, M. Occurrence of Salmonella enterica in grey-headed flying foxes from New South Wales. Aust. Vet. J. 2021, 99, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalá, L.; Alonso, C.A.; Simón, C.; González-Esteban, C.; Orós, J.; Rezusta, A.; Ortega, C.; Torres, C. Wild Birds, Frequent Carriers of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Escherichia coli of CTX-M and SHV-12 Types. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeta, P.; Radhouani, H.; Pinto, L.; Martinho, A.; Rego, V.; Rodrigues, R.; Gonçalves, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Estepa, V.; Torres, C.; et al. Wild boars as reservoirs of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli of different phylogenetic groups. J. Basic Microbiol. 2009, 49, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, Z.H.; Kabir, M.H.; Ali, S.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Imran, K.M.; Nafiz, T.N.; Islam, M.S.; Hussain, A.; Hakim, S.A.I.; Worth, M.; et al. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Drinking Water Samples From a Forcibly Displaced, Densely Populated Community Setting in Bangladesh. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigverdi, R.; Jabalameli, L.; Jabalameli, F.; Emaneini, M. Prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: First systematic review and meta-analysis from Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, S.; Ain, N.U.; Liaqat, H.; Hussain, S.; Rasheed, F.; Riaz, S. Distribution of bla CTX-M, bla TEM, bla SHV and bla OXA genes in Extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Clinical isolates: A three-year multi-center study from Lahore, Pakistan. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Prevalence and transmission of mobilized colistin resistance (mcr) gene in bacteria common to animals and humans. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbediwi, M.; Li, Y.; Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Li, X.; Xie, S.; Rajkovic, A.; Feng, Y.; Fang, W.; Rankin, S.C.; et al. Global Burden of Colistin-Resistant Bacteria: Mobilized Colistin Resistance Genes Study (1980–2018). Microorganisms 2019, 7, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuralayanapalya, S.P.; Patil, S.S.; Hamsapriya, S.; Shinduja, R.; Roy, P.; Amachawadi, R.G. Prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing bacteria from animal origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis report from India. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Lanong, S.; Syiem, D.; De Mandal, S.; Kayang, H.; Kumar, N.S.; Kiran, G.S. Culture-dependent and metagenomic analysis of lesser horseshoe bats’ gut microbiome revealing unique bacterial diversity and signatures of potential human pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Zięba, P.; Gnat, S.; Osińska, M.; Łagowski, D.; Kosior-Korzecka, U.; Puzio, I.; Król, J. Analysis of the occurrence and molecular characteristics of drug-resistant strains of Enterococcus faecalis isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of insectivorous bat species in Poland: A possible essential impact on the spread of drug resistance? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doernberg, S.B.; Lodise, T.P.; Thaden, J.T.; Munita, J.M.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Arias, C.A.; Boucher, H.W.; Corey, G.R.; Lowy, F.D.; Murray, B.; et al. Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections: Research Priorities, Accomplishments, and Future Directions of the Antibacterial Resistance Leadership Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vandžurová, A.; Bačkor, P.; Javorský, P.; Pristaš, P. Staphylococcus nepalensis in the guano of bats (Mammalia). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatimehin, A.; Shittu, A.O.; Onwugamba, F.C.; Mellmann, A.; Becker, K.; Schaumburg, F. Staphylococcus aureus Complex in the Straw-Colored Fruit Bat (Eidolon helvum) in Nigeria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akobi, B.; Aboderin, O.; Sasaki, T.; Shittu, A. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from faecal samples of the Straw-Coloured Fruit Bat (Eidolon helvum) in Obafemi Awolowo University (OAU), Nigeria. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Jong, C.E.; Jonsson, N.; Field, H.; Smith, C.; Crichton, E.G.; Phillips, N.; Johnston, S.D. Collection, seminal characteristics and chilled storage of spermatozoa from three species of free-range flying fox (Pteropus spp.). Theriogenology 2005, 64, 1072–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, K.; Roberts, L.; Young, V.; Barbon, A.; Frosini, S.M.; Lloyd, D.H.; Loeffler, A. Diversity of staphylococcal species cultured from captive livingstone’s fruit bats (Pteropus livingstonii) and their environment. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2019, 50, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.A.; Torres, C.; López, A.R.; Rodríguez, C.O.; Espinosa, J.O.; Valencia, C.S. Staphylococcus spp. from Wild Mammals in Aragón (Spain): Antibiotic Resistance Status. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.A.; Torres, C.; López, A.R.; Rodríguez, C.O.; Valencia, C.S. Antimicrobial resistance of species isolated from wild mammals in Aragón, Spain. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, R.; Abbott, Y.; Leonard, F.C.; Markey, B.K.; Quinn, P.J.; Pollock, P.J.; Fanning, S.; Rossney, A.S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from animals and veterinary personnel in Ireland. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 109, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.; Wieler, L.H.; Friedrich, A.W.; Hanssen, A.M.; Kohn, B.; Brunnberg, L.; Lübke-Becker, A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from small and exotic animals at a university hospital during routine microbiological examinations. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 127, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsohaby, I.; Samy, A.; Elmoslemany, A.; Alorabi, M.; Alkafafy, M.; Aldoweriej, A.; Al-Marri, T.; Elbehiry, A.; Fayez, M. Migratory Wild Birds as a Potential Disseminator of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria around Al-Asfar Lake, Eastern Saudi Arabia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhimiukor, O.O.; Odih, E.E.; Donado-Godoy, P.; Okeke, I.N. A bottom-up view of antimicrobial resistance transmission in developing countries. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovine Rde, O.; Dejuste, C.; Miranda, F.; Filoni, C.; Bueno, M.G.; de Carvalho, V.M. Isolation of Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. from free-ranging wild animals. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benklaouz, M.B.; Aggad, H.; Benameur, Q. Resistance to multiple first-line antibiotics among Escherichia coli from poultry in Western Algeria. Vet. World 2020, 13, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Executive Summary: The Selection and Use of Essential Medicines 2019: Report of the 22nd WHO Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines: WHO Headquarters, Geneva, 1–5 April 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zanardi, G.; Iemmi, T.; Spadini, C.; Taddei, S.; Cavirani, S.; Cabassi, C.S. Wild Micromammals as Bioindicators of Antibiotic Resistance in Ecopathology in Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistome: The nexus of chemical and genetic diversity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Z.B.; Zeng, Z.L.; Yang, X.W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.H. The role of wildlife (wild birds) in the global transmission of antimicrobial resistance genes. Zool. Res. 2017, 38, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachiri, T.; Lalaoui, R.; Bakour, S.; Allouache, M.; Belkebla, N.; Rolain, J.M.; Touati, A. First Report of the Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-1 in Escherichia coli ST405 Isolated from Wildlife in Bejaia, Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstrom, C.A.; Ramey, A.M.; Woksepp, H.; Bonnedahl, J. Repeated Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli in Gulls Inhabiting Alaska. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00758-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, S.; Ewers, C.; Wieler, L.H. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Producing E. coli in Wildlife, yet Another Form of Environmental Pollution? Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashbolt, N.J.; Amézquita, A.; Backhaus, T.; Borriello, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Collignon, P.; Coors, A.; Finley, R.; Gaze, W.H.; Heberer, T. Human health risk assessment (HHRA) for environmental development and transfer of antibiotic resistance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDougall, F.; Boardman, W.; Gillings, M.; Power, M. Bats as reservoirs of antibiotic resistance determinants: A survey of class 1 integrons in Grey-headed Flying Foxes (Pteropus poliocephalus). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 70, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Ramachandran, A.; Perron, G.G. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: From Microbial Ecology to Public Policy. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laborda, P.; Sanz-García, F.; Ochoa-Sánchez, L.E.; Gil-Gil, T.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Martínez, J.L. Wildlife and Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 873989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.C.; Shaw, H.; Rhodes, V.; Hart, A. Review of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment and Its Relevance to Environmental Regulators. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leivers, S.J.; Meierhofer, M.B.; Pierce, B.L.; Evans, J.W.; Morrison, M.L. External temperature and distance from nearest entrance influence microclimates of cave and culvert-roosting tri-colored bats (Perimyotis subflavus). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 14042–14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voigt, C.C.; Phelps, K.L.; Aguirre, L.F.; Corrie Schoeman, M.; Vanitharani, J.; Zubaid, A. Bats and Buildings: The Conservation of Synanthropic Bats. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World; Voigt, C.C., Kingston, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 427–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devnath, P.; Karah, N.; Graham, J.P.; Rose, E.S.; Asaduzzaman, M. Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bats and Its Planetary Health Impact for Surveillance of Zoonotic Spillover Events: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010243
Devnath P, Karah N, Graham JP, Rose ES, Asaduzzaman M. Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bats and Its Planetary Health Impact for Surveillance of Zoonotic Spillover Events: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(1):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010243
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevnath, Popy, Nabil Karah, Jay P. Graham, Elizabeth S. Rose, and Muhammad Asaduzzaman. 2023. "Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bats and Its Planetary Health Impact for Surveillance of Zoonotic Spillover Events: A Scoping Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 1: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010243
APA StyleDevnath, P., Karah, N., Graham, J. P., Rose, E. S., & Asaduzzaman, M. (2023). Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bats and Its Planetary Health Impact for Surveillance of Zoonotic Spillover Events: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(1), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010243