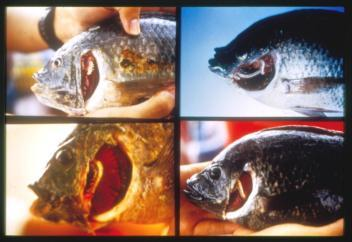
Morphological Deformities as Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Protocol
2.2. Water Quality Parameters
2.3. Morphological Examination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Collection Sites
3.2. Classification of Morphological Deformities and Their Rates of Occurrence
3.3. Seasonal Differences in Morphological Deformities
3.4. Comparison of Morphological Deformities among Stations
3.5. Relationship between Morphological Deformities and Water Quality
3.6. Morphological Deformities of Juvenile Fish in Kao-Ping River
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Sindermann, CJ. Pollution-associated diseases and abnormalities of fish and shellfish: a review. Fish. Bull 1979, 764, 717–749. [Google Scholar]
- Overstreet, RM. Aquatic pollution problems, Southeastern U.S. coasts: histopathological indicators. Aquat. Toxicol 1988, 11, 213–239. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, SM; Brown, AM; Goede, RW. A quantitative health assessment index for rapid evaluation of fish condition in the field. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc 1993, 122, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Blazer, VS; Facey, DE; Fournie, JW; Courtney, LA; Summers, JK. Macrophage Aggregates as indicators of environmental stress. In Modulators of Fish Immune Response; Stolen, JS, Fletcher, TC, Eds.; SOS Publications: Fair Haven, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 3, pp. 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Overstreet, RM. Parasitolgical data as monitors of environmental health. Parassitolgia 1997, 40, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, PL; Brown-Peterson, NJ; Hawkins, WE; Overstreet, RM; Krol, RM; Tsaio, SH; Zhu, Y. Morphological and histological abnormalities in tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) from two contaminated rivers in southern Taiwan. Environ. Sci 1998, 6, 129–152. [Google Scholar]
- Parente, TEM; De-Oliveira, ACAX; Silva, IB; Araujo, FG; Paumgartten, FJR. Induced alkoxyresorufin-O-dealkylases in tilapias (Oreochromis niloticus) from Guandu river, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Guilherme, S; Válega, M; Pereira, ME; Santos, MA; Pacheco, M. Erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities in wild and caged fish (Liza aurata) along an environmental mercury contamination gradient. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf 2008, 70, 411–421. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, PLRM; Sabhanayakam, S; Krishnakumar, N; Vadivelu, M. Morphological changes due to Lead exposure and the influence of DMSA on the gill tissues of the freshwater fish, Catla catla. Food Chem. Toxicol 2008, 46, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar]
- Frenzilli, G; Nigro, M; Lyons, BP. The Comet assay for the evaluation of genotoxic impact in aquatic environments. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res 2009, 681, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Thiyagarajah, A; Hartley, WR; Major, SE; Broxson, MW. Gill Histopathology of Two Species of Buffalo Fish From a Contaminated Swamp. Mar. Environ. Res 1996, 42, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank, KA. Histological alterations in fish from Sydney reefs: possible biomarkers for environmental effects. Biomarkers 2001, 6, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos, NG; Dias, AL; Silva-Souza, AT; Mantovani, MS. Evaluation of environmental waters using the comet assay in Tilapia rendalli. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2005, 19, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, CM; Liang, HM; Chen, BC; Singh, S; Tsai, JW; Chou, YH; Lin, WT. Dynamical coupling of PBPK/PD and AUC-based toxicity models for arsenic in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus from blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Environ. Pollut 2005, 135, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, K; Kannan, K; Tao, L; Takahashi, S; Tanabe, S. Skipjack tuna as a bioindicator of contamination by perfluorinated compounds in the oceans. Sci. Total Environ 2008, 403, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Linde-Arias, AR; Inácio, AF; Alburquerque, C; Freireand, MM; Moreira, JC. Biomarkers in an invasive fish species, Oreochromis niloticus, to assess the effects of pollution in a highly degraded Brazilian River. Sci. Total Environ 2008, 399, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, CK; Noorhaidah, A; Azlan, A; Nor Azwady, AA; Ismail, A; Ismail, AR; Siraj, SS; Tan, SG. Telescopium telescopium as potential biomonitors of Cu, Zn, and Pb for the tropical intertidal area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf 2009, 72, 496–506. [Google Scholar]
- Couillard, CM; Williams, PJ; Courtenay, SC; Rawn, GP. Histopathological evaluation of Atlantic tomcod (Microgadus tomcod) collected at estuarine sites receiving pulp and paper mill effluent. Aquat. Toxicol 1999, 44, 263–278. [Google Scholar]
- Reash, RJ; Berra, TM. Incidence of fin erosion and anomalous fishes in a polluted stream and a neaby clean stream. Water Air Soil Pollut 1989, 47, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, HW. Systemic Pathology of Fish; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lindesjoo, E; Thulin, J. A skeletal deformitay of northern pike (Esox lucius) related to pulp mill effluents. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci 1992, 49, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, C. Skeletal deformities and trace metal contents of European smelt, Osmerus eperlanus, in the Elbe Estuary. Meeresforsch 1990, 33, 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency of Taiwan (1995). Final Report on the Causes of Deformed Thornfishes (Terapon jarbua) Found in the Waters near the Second Nuclear Power Plant; Environmental Protection Agency: Taiwan, 1995. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Handwerker, TS; Douglas, T. Semioperculum: A nonheritable deformity in mozambique tilapia. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1994, 6, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, D; Almodóvar, A; Nicola, GG; Elvira, B. Fluctuating asymmetry, abnormalities and parasitism as indicators of environmental stress in cultured stocks of goldfish and carp. Aquaculture 2008, 279, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ribelin, WE; Migaki, G. The Pathology of Fishes; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1975; pp. 697–704. [Google Scholar]
- Thiyagarajah, A; Hartley, WR; Major, SE; Broxson, MW. Gill histopathology of two species of buffalo fish from a contaminated swamp. Mar. Environ. Res 1996, 42, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Pawert, M; Muller, E; Triebskorn, R. Ultrastructural changes in fish gills as biomarker to assess small stream pollution. Tissue Cell 1998, 30, 617–626. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, CR; Everett, S. Incidences of gross morphological disorders in barbell (Barbus barbus) in three rivers in southern England. J. Fish Biol 1993, 43, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Shackell, NL; Doyle, RW. Scale morphology as an index of developmental stability and stress resistance of tilapia. Can. J. Fish. Aquat Sci 1991, 48, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, HC. Systematic Detection Method to Find the Hazardous Materiaes which Existed in Water and may Cause Aquatic Animal Death; EPA (Taiwan)Environmental Protection Agency: Taiwan, 1994. EPA-83-E3K1-09-01 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, RH; Overstreet, RM. Mesenchymal tumors of some estuarine fishes of the northern Gulf of Mexico. I. Subcutaneous tumors, probably fibrosarcomas, in the striped mullet. Mugil cephalus. Bull. Mar. Sci 1976, 26, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chervinski, J; Dor, DN. Environmental Physiology of Tilapia. In The Biology and Culture of Tilapia, Proceedings of the International Conference on the Biology and Culture of Tilapias; Pullin, RSV, Lowe-McConnell, RH, Eds.; Manila, the Philippines; Sept. 2–5, 1982; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Popma, TJ; Lovshin, LL. Worldwide prospects for commercial production of Tilapia. In Research and Development Series No. 41; Fisheries and Allied Aquaculture, Auburn University: Auburn, AL, USA, 1996; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Administration. Pollution Control Plan of Tongkong River Drainage Basin Summary Report; Environmental Protection Administration: Taiwan, 1993. EPA-82-G105-09-14. p. 151. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Administration. Pollution Control Plan of Kaoping River Drainage Basin Summary Report; Environmental Protection Administration: Taiwan, 1993; p. 179. EPA-82-G105-09-14. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hung, JJ; Shy, CP. Speciation of dissolved Selenium in the Kaoping and Erhjen Rivers and Estuaries, southwestern Taiwan. Estuaries 1995, 18, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, YC; Soong, DK; Lee, MK. PCDD/DFs and coplanar PCBs in sediment and fish samples from the Er-Jen River in Taiwan. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar]
- Ueng, YF; Liu, TY; Ueng, TH. Induction of cytochrome P450 IAI and monooxygenase activity in tilapia by sediment extract. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 1995, 54, 60–67. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fong, LS; Chen, IS; Han, CC. An illustration of fish species existed in river of Kaoshiung County, Taiwan; Kaohsiung County Government: Taiwan, 1996; p. 215. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hung, JJ; Lu, CC; Huh, CA; Liu, JT. Geochemical controls on distributions and speciation of As and Hg in sediments along the Gaoping (Kaoping) Estuary–Canyon system off southwestern Taiwan. J. Mar. Syst 2008, 76, 479–495. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, SK; Chang, NB; Yang, L; Chen, HW; Hsu, HY. Assessing pollution prevention program by QUAL2E simulation analysis for the Kao-Ping River Basin, Taiwan. J. Environ. Manage 2001, 61, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, CF; Huang, SY; Wong, TH; Wong, GS. Cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase activity studies in Taiwan polluted rivers—cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase activity investigations in Era-Jiin river. Ann R NIEA Taiwa ROC 1993, 1, 93–102. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hung, JJ; Hsu, CL. Present state and historical changes of trace metal pollution in Kaoping coastal sediments, southwestern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut Bull 2004, 49, 986–998. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwan Province Government. Annual Water Quality Analyzed Results of Taiwan Rivers of 1993–1996; Taiwan Province Environmental Protection Agency: Taiwan; pp. 1994–1997. (In Chinese).
- Tsao-Jiin Memorial Foundation. The Investigation and Toxicity Identification Evaluation of Irrigation Water in Wan-Lai canal and Er-Ren Stream System of Kaohsiung Irrigation Association; Kaohsiung Irrigation Association: Taiwan, 1996. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Environmental Protection of National Pingtung University of Science and Technology. 1995; Kao-Ping & Tongkong River Water Quality & Hydrology Examination Plan for EPA of Pingtung Co.; National Pingtung University of Science and Technology: Taiwan, 1995. (In Chinese).
- Environmental Protection Administration. Environmental water quality information; Environmental Protection Administration: Taiwan, 2009. Available online: http://wqshow.epa.gov.tw/wqeng/Frame.aspx. (accessed 10 August 2009).
- Water Resources Bureau (1995–1997). Hydrological Year book of Taiwan 1994 & 1995, 1996; Ministry of Economic Affairs: Taiwan, 1994–1997. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Environmental Protection of National Pingtung University of Science and Technology. Kao-Ping & Tongkong River Water Quality & Hydrology Examination Plan for EPA of Pingtung Co.; National Pingtung University of Science and Technology: Taiwan, 1995. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Koumoundouros, G; Oran, G; Divanach, P; Stefanakis, S; Kentouri, M. The opercular complex deformity in intensive gilthead sea bream (sparus aurata L.) larviculture. Moment of apparition and description. Aquaculture 1997, 156, 165–177. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, RR; Rohif, FJ. Biometry, 3rd, ed; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- SPSS. SYSTAT 80 for Windows. SPSS Inc: Chicago, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Simons Li Consulting Co. Pollution Control Plan of Era-Jiin River, Drainage Basin; Simons Li Consulting Co: Taiwan, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tai-Jia Engineering Consultancy Co., Ltd Taiwan. Research and Planning for Improving the Water Quality of Dapeng Bay National Scenic Area; Tourism Bureau of Ministry of Traffic: Taiwan, 1999. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liao, SW; Lai, WL; Chen, JJ; Sheu, JY; Chin, CY. Discriminant analysis to recognize source of pollution of sediment properties from neighboring rivers in Tapeng Lagoon. J Coast Oce Eng 2007, 7, 85–100, (In Chinese with English abstract).. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, FH. An investigation on the present status of dioxin and planar polychlorinated biphenyls concentration in bottom mud of Era-Jiin and Kao-Ping River and the pollution background. Ann R NIEA Taiwa ROC 2002, 9, 89–110. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, PL. Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan. Final Report; National Science Council: Taiwan, 2000. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huggett, RJ; Kimerle, RA; Mehrie, PM, Jr; Bergman, HL. Biomarkers. In Biochemical, Physiological, and Histological Markers of Anthropogenic Stress; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]






| Table 1-1. Physical Characteristics of the Four Rivers. | ||||||
| Characteristic | Kao-Ping River | Tong Kong River | Era-Jiin River | Lin Bien River | ||
| River length (km) | 170.9 | 46.90 | 65.18 | 42.19 | ||
| Drainage area (km2) | 3,256.8 | 472.20 | 350.4 | 344 | ||
| Annual sediment discharge (MT/km2) | 10,934 | 1,292 | 37,424 | 5,349 | ||
| Mean annual runoff (106 M3) | 8,455.35 | 1,117.62 | 498.88 | 863.84 | ||
| Slope | 1:43 | 1:41 | 1:142 | 1:15 | ||
| Average annual Rainfall (mm) | 3,046.1 | 2,499.8 | 1,909.9 | 3,330.7 | ||
| Table 1-2. Physical Characteristics and Salinity of Collection Stations. | ||||||
| Characteristic | KP | Tong Kong River | Era-Jiin River | LB | ||
| TKS | TKM | EJ1 | EJ2 | |||
| River width (m) | 300 | 150–200 | 600–700 | 200 | 150 | 300–350 |
| Bottom type | Sand & stone | Sand & mud | Sand | Mud & sand | Mud | Sand & stone |
| Average depth (m) | 1.5 | 2.5 | 2.0–3.3 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 0.5–1.5 |
| Salinity | Tidal freshwater | Tidal freshwater | Mesohaline | Mesohaline | Tidal freshwater | Tidal freshwater |
| Discharge (m3/s) | 7.2–1,000a | 2.7–48.1b | 9.0–66.7b | 17.95 | ||
| Source | Tongkong River1 | Kao-Ping River2 | Era-Jiin River3 | Lin Bien River4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal Husbandry | Swine, chicken, duck, and fish farming—72% | Swine, chicken, duck, and fish farming—58% | Swine, duck, chicken, and fish farming—51% | Swine, duck, and chicken farming—70% Fish farm waste--22% |
| Industry | Industrial district (Food processing, fabric, metal industry, etc.)—11% | Leather industry heavy metal reclamation, food processing—31% | Heavy metal refinery, electrical processing, acid washing—38% | Few gravel factories—2% |
| Domestic | Sewage and garbage—12% | Sewage and garbage—8% | Sewage and garbage 10% | Sewage and garbage—6% |
| Seepage, Non-point source | 5% | 3.3% | <1% | <1% |
| Era-jiin River | Kao-ping River | Tong-Kong River | Lin-Bien River | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EJ-1 | EJ-2 | KP | TKS | TKM | LB | ||
| Suspended Solids (mg/L) | 8.0–65* | 8.5–120* | 13–312* | 5.5–83* | 6.0–121* | 18–5,700* | |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.64–34* | 0.77–44* | 0.16–6.1* | 0.85–16* | 0.11–14* | 0.04–0.74* | |
| DO (mg/L) | 0–11* | 0–10.7* | 0–8.7* | 0–5.5* | 0–14* | 0.69–9.2* | |
| BOD (mg/L) | 2.6–47* | 3.3–68* | 0.4–12* | 3.0–23* | 1.7–33* | 0.1–6.9* | |
| Coliform (MPN/100ML) | 240,000*a | 5,000–93,000* | 30,000–1,600,000* | 24,000–500,000* | 240–240,000* | ||
| Heavy metals | Cd (mg/L) | <0.005–<0.01 | <0.005–<0.05 | <0.005–<0.01 | <0.001–<0.01 | <0.005–<0.01 | <0.005–<0.01 |
| Cr (mg/L) | <0.001–0.19* | <0.001–0.29* | <0.01–0.11* | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01–0.08* | |
| Cu (mg/L) | 0.04–0.19* | 0.01–0.22* | <0.01–0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01–0.02 | <0.01–0.11* | |
| Pb (mg/L) | 0.001–0.04 | 0.01–0.111* | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01–0.13* | |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.07–0.81* | 0.6–1.0* | 0.02–0.10 | 0.02–0.06 | <0.01–0.08 | 0.02–2.2* | |
| Hg (μg/L) | 15.94*b | <0.011–3*c | <0.001–4.0*c | <0.001–0.9d | |||
| Deformity | TKS | TKM | KP | EJ1 | EJ2 | LB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Split fins | 46.0 | 37.5 | 52.0 | 87.5 | 62.5 | 50.0 | |
| Scale disorientation | 13.0 | 12.5 | 18.0 | 6.2 | 25.0 | 0 | |
| Mouth hyperplasia | 2.0 | 0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Muscle atrophy | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Opercular deformity | 8.0 | 12.5 | 14.0 | 12.5 | 0 | 3.0 | |
| Gill deformity | 2.0 | 25.0 | 2.0 | 31.2 | 16.7 | 3.0 | |
| Eye deformity | Exopthalmia | 3.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Concave eye | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Small eye | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Blindness | 1.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lens deformity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Opaque cornea | 5.8 | 12.5 | 4.5 | 6.2 | 0 | 3.0 | |
| Skeleton deformity | 6.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.0 | |
| Lower lip extension | 2.0 | 12.5 | 0 | 31.3 | 16.7 | 0 | |
| Tumor or bump | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.2 | 0 | |
| Jaw deformity | 13.0 | 0 | 7 | 37.5 | 16.7 | 6 | |
| Head or jaw bent to side | 0 | 0 | 7.0 | 0 | 0 | 3.0 | |
| Mouth protrusion | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fin deformity | 10.0 | 0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 6.0 | |
| Miscellaneous | 2.0* | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total number of fish | 52 | 8 | 44 | 16 | 24 | 32 | |
| Deformity | TKS | TKM | KP | EJ1 | EJ2 | LB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale disorientation | 12.5 | 20.4 | 9.6 | 6.2 | 25.0 | 0 | |
| Gill deformity | 2.6 | 7.4 | 2.4 | 31.2 | 16.7 | 3.0 | |
| Eye deformity | Exopthalmia | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Concave eye | 0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Small eye | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Blindness | 0.5 | 3.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lens deformity | 0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Opaque cornea | 10.0 | 10.0 | 26.0 | 6.2 | 0 | 3.0 | |
| Skeletal deformity | 28.5 | 46.3 | 37.1 | 50.0 | 16.7 | 21.8 | |
| Soft tissue deformity | 12.9 | 13.0 | 3.0 | 31.3 | 20.8 | 0 | |
| Split fins | 27.1 | 13.9 | 42.5 | 87.5 | 62.5 | 50.0 | |
| Total number of fish | 192 | 108 | 167 | 16 | 24 | 32 | |
| Deformity | Tongkong River (TKS) | Tongkong River (TKM) | Kao-Ping River (KP) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/94 | S/95 | A/95 | S/96 | A/94 | S/95 | A/95 | A/94 | S/95 | A/95 | S/96 | ||
| Split fins | 46.0 | 4.0 | 53.0 | 35.3 | 37.5 | 1.0 | 37.0 | 52.0 | 20.0 | 62.0 | 40.0 | |
| Scale disorientation | 13.0 | 13.0 | 9.0 | 11.8 | 12.5 | 16.0 | 33.0 | 18.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | |
| Mouth hyperplasia | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Muscle atrophy | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | 7.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.3 | |
| Opercular deformity | 8.0 | 2.0 | 9.0 | 5.9 | 12.5 | 0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 0 | 2.0 | 6.6 | |
| Gill deformity | 2.0 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 25.0 | 0 | 23.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 0 | 6.6 | |
| Eye | Exopthalmia | 3.8 | 0 | 3.1 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | 11.9 | 0 |
| Concave eye | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 0 | |
| Small eye | 0 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Blindness | 1.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lens deformity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Opaque cornea | 5.8 | 4.4 | 31.3 | 17.6 | 12.5 | 8.6 | 20.0 | 4.5 | 37.3 | 54.8 | 0 | |
| Skeletal deformity | 6.0 | 0 | 0 | 5.9 | 0 | 3.0 | 7.0 | 0 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 0 | |
| Lower lip extension | 2.0 | 14.0 | 22.0 | 0 | 12.5 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 0 | 0 | 7.0 | 0 | |
| Tumor or bump | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Jaw deformity | 13.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 0 | 0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 13.3 | |
| Head or jaw bent | 0 | 4.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.0 | 23.0 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 0 | 3.3 | |
| Mouth protrusion | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 5.9 | 0 | 1.0 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fin deformity | 10.0 | 11.0 | 9.0 | 5.9 | 0 | 14.0 | 33.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 29.0 | 30.0 | |
| Miscellaneous | 2.01 | 1.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.01 | 0 | 2.01 16.02 | 0 | 3.31 | |
| Total number of fish | 52 | 91 | 32 | 17 | 8 | 70 | 30 | 44 | 51 | 42 | 30 | |
| Station and Season | % Frayed Fins | N | Gadj | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TKS, Rainy
TKS, Dry | 48.8
9.1 | 84
108 | 19.41 | <0.001 |
| TKM, Rainy
TKM, Dry | 36.8
1.4 | 38
70 | 12.28 | <0.001 |
| KP, Rainy
KR, Dry | 57.0
27.2 | 86
81 | 7.66 | <0.01 |
| Deformity | Juvenile | Adult | Gadj | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 83 | 123 | – | – |
| Scale Disorientation | 0 | 7 | 3.97 | >0.05 |
| Opercular Deformity | 2 | 2 | 0.055 | >0.005 |
| Head or Vertebrae Deformity | 10 | 3 | 1.72 | >0.05 |
| Frayed Fins | 21 | 39 | 4.04 | <0.05 |
| Fin Deformity | 18 | 6 | 3.82 | >0.05 |
| Fin Elongation | 0 | 14 | 8.99 | <0.05 |
| Soft Tissue Deformity | 0 | 4 | 2.36 | >0.05 |
| Spp. Item | Pseudorasbora parva | Cyprinus carpio | Rhinogobius maculafasciatus | Tilapia spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 March, 1 April 1997 | 1 April 1997 | 13 March 1997 | 13 March, 1 April 1997 | |
| Split fins | 6.1 | 12.5 | 10 | 14.5 |
| Scale disorientation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mouth hyperplasia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Muscle atrophy | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Opercular deformity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.61 |
| Gill deformity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Eye deformity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.61 |
| Skeleton deformity | 8.2* | 0 | 10 | 12.9 |
| Lower lip extension | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tumor or bump | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Jaw deformity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Head or lower jaw bent to side | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.61 |
| Mouth protrusion | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.61 |
| Fin deformity | 0 | 19 | 30 | 16.1 |
| Miscellaneous | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.61 |
| Total number collected | 49 | 16 | 10 | 62 |
| River | Station | Historically | 1994 | 1995 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Era-Jiin | Ah Lian (2) | 9.22 CMS | 13.79 CMS | 5.34 |
| Kao-Ping | Lee Ling | 184.51 CMS | 270.71 CMS | 109.52 |
| Tong-Kong | Chao Chou | 16.41 CMS | 18.80 CMS | 8.69 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, P.L.; Hawkins, W.E.; Overstreet, R.M.; Brown-Peterson, N.J. Morphological Deformities as Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2307-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082307
Sun PL, Hawkins WE, Overstreet RM, Brown-Peterson NJ. Morphological Deformities as Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2009; 6(8):2307-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Peter Lin, William E. Hawkins, Robin M. Overstreet, and Nancy J. Brown-Peterson. 2009. "Morphological Deformities as Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 6, no. 8: 2307-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082307
APA StyleSun, P. L., Hawkins, W. E., Overstreet, R. M., & Brown-Peterson, N. J. (2009). Morphological Deformities as Biomarkers in Fish from Contaminated Rivers in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 6(8), 2307-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082307