Efficiency of the Air-Pollution Control System of a Lead-Acid-Battery Recycling Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
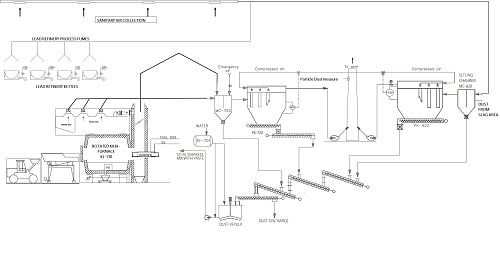
Air-Pollution Control-System Description
3. Results/Discussion
3.1. Air-Pollution Control-System Efficiency in Particle Removal
3.2. Particles in the Atmosphere
3.3. Heavy Metals Associated with the Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.Y.; Li, A.J.; Finlow, D.E. The lead and lead-acid battery industries during 2002 and 2007 in China. J. Power Sources 2009, 191, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesfeld, P.; Pokhrel, A.K. Review: Lead Exposure in Battery Manufacturing and Recycling in Developing Countries and Among Children in Nearby Communities. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2011, 8, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzu, G.; Sobanska, S.; Sarret, G.; Sauvain, J.J.; Pradère, P.; Dumat, C. Characterization of lead-recycling facility emissions at various workplaces: Major insights for sanitary risks assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Agyeiwaa, A.; Zuo, T. Residents’ behavior, awareness, and willingness to pay for recycling scrap lead-acid battery in Beijing. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, S.; Unguresan, M.L.; Bolundut, L.; Rada, M.; Vermesan, H.; Pica, M.; Culea, E. Structural and electrochemical investigations of the electrodes obtained by recycling of lead acid batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 780, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. A new process of lead recovery from waste lead-acid batteries by electrolysis of alkaline lead oxide solution. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 19, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhan, M.-X.; Lin, X.-Q.; Li, Y.-Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.-D.; Yan, J.-H.; Buekens, A. Emission and distribution of PCDD/Fs and CBzs from two co-processing RDF cement plants in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11845–11854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.; Gálvez, A.; Conesa, J.A.; de Correa, C.M. Characterization of fly ash from a hazardous waste incinerator in Medellin, Colombia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Takaoka, M.; Shiota, K.; Oshita, K.; Kitajima, Y. Chloride Chemical Form in Various Types of Fly Ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3932–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, T.G.; Ksandopulo, S.J.; Bushumov, S.A.; Burlaka, S.D.; Say, Y.V. Quantitative Chemical Analysis of Slag Ash of Novocherkassk State District Power Plant. Orient. J. Chem. 2017, 33, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Zhan, J.; Zheng, M.; Li, L.; Jin, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M. Concentrations and patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls at different process stages of cement kilns co-processing waste incinerator fly ash. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Su, G.; Lv, P.; Xiao, K. Estimation and characterization of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs, PCNs, HxCBz and PeCBz emissions from magnesium metallurgy facilities in China. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, M. Characterization and quantification of unintentional POP emissions from primary and secondary copper metallurgical processes in China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 15, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xueli, N.; Henggen, S.; Yinghui, W.; Liuke, Z.; Xingcheng, L.; Min, F. Investigation of the pyrolysis behaviour of hybrid filter media for needle-punched nonwoven bag filters. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 113, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quina, M.J.; Bordado, J.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Treatment and use of air pollution control residues from MSW incineration: An overview. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2097–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Songa, G.-J.; Kima, K.-H.; Seoa, Y.-C.; Kimb, S.-C. Characteristics of ashes from different locations at the MSW incinerator equipped with various air pollution control devices. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.; Cang, D. Study on the Respirable Particulate Matter Generated from the Petroleum Coke and Coal Mixed-fired CFB Boiler. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Digital Manufacturing and Automation, Changsha, China, 18–20 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Vicente, E.D.; Alves, C.; Querol, X.; Amato, F.; Tarelho, L.A.C. Characteristics of ash and particle emissions during bubbling fluidised bed combustion of three types of residual forest biomass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10018–10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobanska, S.; Ricq, N.; Laboudigue, A.; Guillermo, R.; Bremard, C.; Laureyns, J.; Merlin, J.C.; Wignacourt, J.P. Microchemical Investigations of Dust Emitted by a Lead Smelter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, T.M.; Svee, W.; Vincent, J.H.; Stanisich, N. Chemical Speciation of Lead Dust Associated with Primary Lead Smelting. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettler, V.; Johan, Z.; Baronnet, A.; Jankovsky, F.; Gilles, C.; Michaljevich, M.; Sebek, O.; Strand, L.; Bezdicka, P. Mineralogy of Air-Pollution-Control Residues from a Secondary Lead Smelter: Environmental Implication. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9309–9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Chang, D.Q.; Xie, Y.; Mao, N.; Sun, X. Research on fine particles capture of baghouse filter media. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevers, N.D. Air Pollution Control Engineering; Waveland Press: Long Crove, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rapsomanikis, S.; Kastrinakis, E. Ai Pollution Control; Tziolas Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.-H.; Ilgen, G.; Matzner, E. Fluxes and budgets of Cd, Zn, Cu, Cr and Ni in a remote forested catchment in Germany. Biogeochemistry 2011, 103, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Lawlor, A.; Hooper, H.L.; Wadsworth, R.; Svendsen, C.; Thomas, L.D.K.; Ellis, J.K.; Bundy, J.G.; Keun, H.C.; Jarup, L. Outdoor and indoor cadmium distributions near an abandoned smelting works and their relations to human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3425–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.K.; Friedland, A.J. Lead Migration in Forest Soils: Response to Changing Atmospheric Inputs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetke, L.M.; Chow-Johnson, H.S.; Chow, C.K. Copper: Toxicological relevance and mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanova, M.; Hristovski, S.; Musai, M.; Boškovska, V.; Rebok, K.; Dinevska-Ќovkarovska, S.; Melovski, L. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Some Organs in Barbel and Chub from Crn Drim River in the Republic of Macedonia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, S.; Kahraman, A.E.; Ulusoy, S. Potential Health Risks of Heavy Metals to the Turkish and Greek Populations via Consumption of Spiny Dogfish and Thornback Ray from the Sea of Marmara. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 19, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merian, E.; Anke, M.; Ihnat, M.; StoeppJer, M. Elements and Their Compounds in the Environment; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, M.K.; Arain, A.L.; Shao, J.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.; Lozoff, B.; Meeker, J.D. Distribution and predictors of 20 toxic and essential metals in the umbilical cord blood of Chinese newborns. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.-M.; Wang, Q.-S.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.-G.; Zhu, R.-L.; Wang, S.; Tang, C.-H. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaminder, J.; Bindler, R.; Emteryd, O.; Renberg, I. Uptake and recycling of lead by boreal forest plants: Quantitative estimates from a site in northern Sweden. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2485–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaminder, J.; Bindler, R.; Emteryd, O.; Appleby, P.; Grip, H. Estimating the mean residence time of lead in the organic horizon of boreal forest soils using 210-lead, stable lead and a soil chronosequence. Biogeochemistry 2006, 78, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Du, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Distributions and pools of lead (Pb) in a terrestrial forest ecosystem with highly elevated atmospheric Pb deposition and ecological risks to insects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.D.K.; Hodgson, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Jarup, L. Early Kidney Damage in a Population Exposed to Cadmium and Other Heavy Metals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordberg, G.F. Historical perspectives on cadmium toxicology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2009, 238, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanphear, B.P.; Rauch, S.; Auinger, P.; Allen, R.W.; Hornung, R.W. Low-level lead exposure and mortality in US adults: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Public Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng-Gyasi, E.; Armijos, R.X.; Weigel, M.M.; Filippelli, G.M.; Sayegh, M.A. Cardiovascular-Related Outcomes in U.S. Adults Exposed to Lead. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, F.; Sallsten, G.; Christensson, A.; Petkovic, M.; Hedblad, B.; Forsgard, N.; Melander, O.; Nilsson, P.M.; Yan Borne, G.E.; Barregard, L. Blood Lead Levels and Decreased Kidney Function in a Population-Based Cohort. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-L.; Lin-Tan, D.-T.; Hsu, K.-H.; Yu, C.-C. Environmental Lead Exposure and Progression of Chronic Renal Diseases in Patients without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng-Gyasi, E.; Armijos, R.X.; Weigel, M.M.; Filippelli, G.; Sayegh, M.A. Hepatobiliary-Related Outcomes in US Adults Exposed to Lead. Environments 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, S.; Bağcı, C.; Ozaslan, M.; Bozkurt, A.; Cengiz, B.; Çakmak, E.A.; Kocabaş, R.; Karadağ, E.; Tarakçıoğlu, M. Occupational lead exposure effect on liver functions and biochemical parameters. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2008, 95, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bag House Filters | PK720 (Bag House Furnace) | PK820 (Sanitary Bag House) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | Input | Output | |||||
| Elements | Average (gr/Kg) | STDEV | Average (gr/Kg) | STDEV | Average (gr/Kg) | STDEV | Average (gr/Kg) | STDEV |
| Ag | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.05 | ||||
| Al | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.55 | 0.22 | 0.95 | 0.09 |
| Bi | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Ca | N.D. | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 4.68 | 0.23 | |
| Co | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Cr | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.06 | ||||
| Cu | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 8.44 | 2.03 | 1.23 | 0.24 |
| Fe | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 6.46 | 0.36 | 2.28 | 1.08 |
| Ga | 0.68 | 0.16 | 0.87 | 0.11 | 1.58 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.09 |
| K | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.60 | 0.11 | N.D. | N.D. | ||
| Mg | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Mn | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Na | 16.90 | 0.37 | 22.55 | 0.82 | 17.29 | 0.73 | 3.29 | 0.58 |
| Ni | N.D. | N.D. | 0.62 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.02 | ||
| Pb | 3.80 | 0.42 | 4.74 | 0.15 | 9.03 | 0.13 | 3.53 | 0.17 |
| Sr | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Tl | 10.43 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Zn | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ||||
| Elements | Gravity Settlers | Bag Houses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC720 (ppm) | MC820(ppm) | PK720 (ppm) | PK820 (ppm) | |
| Al | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Ca | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Fe | 990 | 820 | 1580 | 1670 |
| Mg | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| P | 90 | 6680 | 120 | 7340 |
| K | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Si | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Na | 25950 | 17410 | 28470 | 16880 |
| S | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Ti | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| AS | 48 | 333 | 172 | 325 |
| Cd | 2501 | 120 | 1791 | 116 |
| Cr | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cu | 75 | 395 | 167 | 455 |
| Pb | 19774 | 2032 | 21096 | 21965 |
| Mn | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| V | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Zn | 172 | 262 | 597 | 222 |
| Ba | 229 | 169 | 271 | 302 |
| Ce | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Co | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Ga | 116 | 89 | 105 | 87 |
| La | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Mo | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| Nd | 63 | 50 | 58 | 48 |
| Ni | 14 | 62 | 34 | 75 |
| Rb | 20 | 34 | 27 | 35 |
| Sc | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Sr | 42 | 45 | N.D. | 48 |
| Th | 54 | 45 | 51 | 45 |
| U | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Sb | 820 | 3671 | 1889 | 3962 |
| Hg | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Br | 421 | N.D. | 240 | N.D. |
| Cs | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Bi | 26 | N.D. | 25 | 21 |
| Sm | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| W | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Zr | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cl | 836 | 641 | 1142 | 447 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelektsoglou, K.; Karali, D.; Stavridis, A.; Loupa, G. Efficiency of the Air-Pollution Control System of a Lead-Acid-Battery Recycling Industry. Energies 2018, 11, 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123465
Kelektsoglou K, Karali D, Stavridis A, Loupa G. Efficiency of the Air-Pollution Control System of a Lead-Acid-Battery Recycling Industry. Energies. 2018; 11(12):3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123465
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelektsoglou, Kyriaki, Dimitra Karali, Alexandros Stavridis, and Glykeria Loupa. 2018. "Efficiency of the Air-Pollution Control System of a Lead-Acid-Battery Recycling Industry" Energies 11, no. 12: 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123465
APA StyleKelektsoglou, K., Karali, D., Stavridis, A., & Loupa, G. (2018). Efficiency of the Air-Pollution Control System of a Lead-Acid-Battery Recycling Industry. Energies, 11(12), 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123465