Optimal Dispatching of Offshore Microgrid Considering Probability Prediction of Tidal Current Speed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Prediction Models and Basic Theories
2.1. Support Vector Quantile Regression Based Probablity Prediction Model for Tidal Current Speed
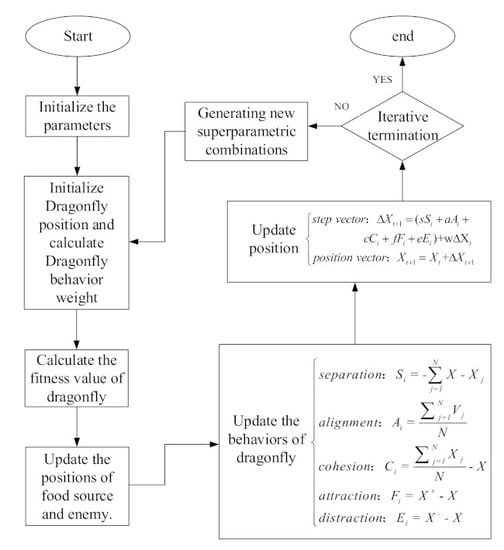
2.2. Probablistic Prediction Model of Tidal Current Speed Nased on Dragonfly Algorithm
3. Optimal Dispatching of the Offshore Microgrid with Tidal Current Power Generation
3.1. Objective Function
3.2. Constraint Conditions
4. Case Study
4.1. Analysis of Pradiction Results
4.2. Analysis of Optimal Dispatching Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Research on construction and development trend of micro-grid in China. Power Syst. Technol. 2016, 40, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, F.; Deng, L.; Xu, Q. Microgrid multi-source coordination optimal control based on multi-scenarios analysis. J. Eng. 2017, 13, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lam, W.-H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Hamill, G. Novel energy coefficient used to predict efflux velocity of tidal current turbine. Energy 2018, 158, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, S.P.; Vögler, A.; Goward-Brown, A.J.; Baston, S.; Lewis, M.J.; Gillibrand, P.A.; Waldman, S.; Woolf, D.K. The wave and tidal resource of Scotland. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, D.; Gundersen, Z. A novel flexible foil vertical axis turbine for rive ocean and tidal applications. Appl. Energy 2015, 151, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Duverger, E.; Penin, C.; Alexandre, P.; Thiery, F.; Gachon, D.; Talbert, T. Irradiance forecasting for microgrid energy management. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe), Torino, Italy, 26–29 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J. An online optimal dispatch schedule for CCHP microgrids based on model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2332–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, M.J.; Maswood, A.I.; Tseng, K.J. Long term prediction of tidal currents. IEEE Syst. J. 2011, 5, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Wang, B.; He, S.; Huang, D.; He, H.; Qi, H. Unmixing: A new direction from classical tidal harmonic analysis. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2015—MTS/IEEE Washington, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Polagye, B.L.; Epler, J.; Thomson, J. Limits to the predictability of tidal current energy. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 20–23 September 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Aït-Ahmed, N.; Zaïm, E.H.; Machmoum, M. Marine tidal current systems: State of the art. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Hangzhou, China, 28–31 May 2012; pp. 1431–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, H.H.H.; El-Hawary, M.E. A proposed ANN and FLSM hybrid model for tidal current magnitude and direction forecasting. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 39, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi-Fard, A. A hybrid accurate model for tidal current prediction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi-Fard, A.; Su, W. A combined prognostic model based on machine learning for tidal current prediction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3108–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, W.; Billinton, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, J. Modeling tidal current speed using a wakeby distribution. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 127, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Billinton, R.; Yu, J. Reliability evaluation of a tidal power generation system considering tidal current speeds. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 3179–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, W.; Billinton, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, J. Probabilistic modeling of tidal power generation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–30 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Jin, L.; Dai, Y. probabilistic power flow analysis of power systems incorporating tidal current generation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ren, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, W. Optimal sizing and arrangement of tidal current farm. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, W. A coordinated planning method for micrositing of tidal current turbines and collector system optimization in tidal current farms. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, Y.L.; Jiang, W. Wind-thermal dynamic economic emission dispatch with a hybrid multi-objective algorithm based on wind speed statistical analysis. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 3972–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchapda, G.Y.G.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Application of improved particle swarm optimization in economic dispatch of power system. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 9–10 December 2017; pp. 500–503. [Google Scholar]
- Pisei, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, W.P. Optimal power dispatch in multi-microgrid system using particle swarm optimization. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2017, 12, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, A.A.; Seifi, A.; Niknam, T. Multi-objective operation management of a renewable MG (micro-grid) with back-up micro-turbine/fuel cell/Battery hybrid power source. Energy 2011, 36, 6490–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Srinivas, P.; Divakar, M.S.M.; Venkatesh, G.S.N.M. Artificial bee colony optimization for multi objective economic load dispatch of a modern power system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT), Chennai, India, 3–5 March 2016; pp. 4097–4100. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Liu, M.; Li, Q.; Lu, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, C. Normalised normal constraint algorithm applied to multi-objective security-constrained optimal generation dispatch of large-scale power systems with wind farms and pumped-storage hydroelectric stations. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G. Regression quantiles. Econometrica 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R. Quantile Regression; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V.N. Statistical Learning Theory; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mirialili, S. Dragonfly algorithm: A new meta-heuristic optinization technigue for solving single-objective, discrete, and multiobiective problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| x, xi | Explanatory Variables |
|---|---|
| y, yi | Response variables |
| Qyi | Linear regression estimate |
| β(τ) | Regression coefficient vector |
| τ | Quantile |
| σ | Free parameter of the kernel parameter |
| C | Penalty parameter |
| Method | Evaluation Index | |
|---|---|---|
| MAPE% | RMSE% | |
| DA-SVQR | 2.8142 | 1.5069 |
| GA-SVQR | 7.2137 | 2.7217 |
| GA-SVR | 10.6869 | 3.0346 |
| Device | Parameter | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Energy storage system | Maximum charge and discharge power/kW | 50 |
| Charge and discharge efficiency/% | 85 | |
| Battery self-discharge ratio/% | 10 | |
| Battery rated capacity (KW*h) | 250 | |
| Operation and maintenance cost factor (RMB/KW) | 0.02748 | |
| Gas turbine | Rated power/KW | 200 |
| Climbing rate/(KW/min) | 3 | |
| Minimum operating power | 10 | |
| Operation and maintenance cost factor (RMB/KW) | 0.03640 | |
| Fuel price (RMB/m3) | 27.6 | |
| Emergency diesel engine | Upper limit of output power (KW) | 100 |
| Lower limit of output power (KW) | 0 | |
| Operation and maintenance cost factor (RMB/KW) | 0.0790 | |
| Fuel price (RMB/m3) | 38.4 | |
| Single start cost/RMB | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, A.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, H.; Feng, Y. Optimal Dispatching of Offshore Microgrid Considering Probability Prediction of Tidal Current Speed. Energies 2019, 12, 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173384
Zhang A, Sun Y, Yang W, Huang H, Feng Y. Optimal Dispatching of Offshore Microgrid Considering Probability Prediction of Tidal Current Speed. Energies. 2019; 12(17):3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173384
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Anan, Yangfan Sun, Wei Yang, Huang Huang, and Yating Feng. 2019. "Optimal Dispatching of Offshore Microgrid Considering Probability Prediction of Tidal Current Speed" Energies 12, no. 17: 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173384
APA StyleZhang, A., Sun, Y., Yang, W., Huang, H., & Feng, Y. (2019). Optimal Dispatching of Offshore Microgrid Considering Probability Prediction of Tidal Current Speed. Energies, 12(17), 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173384