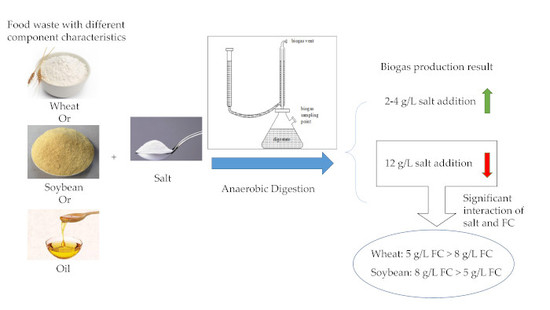
Effects of Salt on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste with Different Component Characteristics and Fermentation Concentrations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Substrate
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Analytical Methods and Calculation
2.4. Kinetic Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Promotion Effects of Salt on Biogas and Methane Yield
3.2. Promotion Effects of Salt on Biogas Production Rate
3.3. Interaction of FC and High Salt Addition on Inhibition Degree of Biogas Yield
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Unit | 2009 | 2013 | 2016 | 2018 | Parameter | Unit | 2009 | 2013 | 2016 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | mg∙kg−1 | <2.7 | <1.2 | 0.714 | 0.926 | Al | g∙kg−1 | 52.8 | 53.6 | 25.4 | 24.1 |
| Cr | mg∙kg−1 | 33.5 | 27 | 21.4 | 18.2 | Fe | g∙kg−1 | 8.84 | 9.58 | 8.21 | 4.33 |
| Cu | mg∙kg−1 | 375 | 327 | 348 | 379 | Ca | g∙kg−1 | 31.3 | 32.7 | 24.4 | 24.0 |
| Ni | mg∙kg−1 | 22.7 | 28.7 | 16.1 | 17.5 | K | g∙kg−1 | 6.47 | 6.56 | 5.15 | 3.50 |
| Pd | mg∙kg−1 | 33.1 | 27 | 18.4 | 13.6 | Mg | g∙kg−1 | 5.1 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| Zn | mg∙kg−1 | 1161 | 1070 | 867 | 865 | Mn | g∙kg−1 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Hg | mg∙kg−1 | 5.05 | 3.45 | 0.71 | 0.64 |
| Salt Addition (g∙L−1) | Conductivity | Salt Addition (g∙L−1) | Conductivity | Salt Addition (g∙L−1) | Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.13 | 4.5 | 0.82 | 8.5 | 1.46 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.9 | 9 | 1.53 |
| 1.5 | 0.3 | 5.5 | 0.97 | 9.5 | 1.6 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 6 | 1.06 | 10 | 1.72 |
| 2.5 | 0.48 | 6.5 | 1.16 | 10.5 | 1.73 |
| 3 | 0.56 | 7 | 1.26 | 11 | 1.8 |
| 3.5 | 0.66 | 7.5 | 1.35 | 11.5 | 1.88 |
| 4 | 0.74 | 8 | 1.44 | 12 | 1.95 |
| Salt Addition (g∙L−1) | Corresponding Sodium Addition (g∙L−1) | Sodium Concentration (g∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0.10 |
| 2 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| 4 | 1.56 | 1.66 |
| 6 | 2.34 | 2.44 |
| 9 | 3.51 | 3.61 |
| 12 | 4.68 | 4.78 |
References
- Gao, S.; Bao, J.; Liu, X.; Stenmarck, A. Life cycle assessment on food waste and its application in China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 108, 042037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçkun Kiran, E.; Trzcinski, A.P.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Bioconversion of food waste to energy: A review. Fuel 2014, 134, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, J.D.; Allen, E.; Murphy, J.D. Assessing the variability in biomethane production from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste in batch and continuous operation. Appl. Energy 2014, 128, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, G.; Chen, Y.; Bond, P.L.; Li, X. How Does Poly(hydroxyalkanoate) Affect Methane Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12253–12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Yu, X.; Zou, J.; Li, L. GB/T 5461-2016 Edible Salt; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China and Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Q. Potential impact of salinity on methane production from food waste anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, G.B.; Roth, L.A. Effect of sodium chloride on growth and methane production of methanogens. Can. J. Microbiol. 1977, 23, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelman, I.J.; Chin, K.K. Toxicity, Synergism, and Antagonism in Anaerobic Waste Treatment Processes. Adv. Chem. 1971, 105, 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Li, S.; Yuan, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Chufo, A.; Jaffar, M.; Li, X. Evaluating biomethane production from anaerobic mono- and co-digestion of food waste and floatable oil (FO) skimmed from food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Peng, Y. Enhanced volatile fatty acids production of waste activated sludge under salinity conditions: Performance and mechanisms. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.J.; Novak, J.T. The effect of cations on the settling and dewatering of activated sludges: Laboratory results. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomec, C.Y.; Kim, M.; Ahn, Y.; Speece, R.E. The role of pH in mesophilic anaerobic sludge solubilization. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2002, 37, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, H.; Baeyens, J.; Tan, T. Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste for biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; An, H.; Xie, T.; Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, G.; et al. Revealing the underlying mechanisms of how sodium chloride affects short-chain fatty acid production from the cofermentation of waste activated sludge and food waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4675–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Kim, S.H. Effects of chemical compositions and ensiling on the biogas productivity and degradation rates of agricultural and food processing by-products. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatek, M.; Lisowski, A.; Kasprzycka, A.; Lisowska, B. The dynamics of an anaerobic digestion of crop substrates with an unfavourable carbon to nitrogen ratio. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Lee, J.; Loh, K.-C.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y.W. Enhancement of biogas production in anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and waste activated sludge by biological co-pretreatment. Energy 2017, 137, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, P.L. Anaerobic Waste Treatment Fundamentals (parts 1–4). Chem. Microbiol. 1964, 95, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinzema, A.; van Lier, J.; Lettinga, G. Sodium inhibition of acetoclastic methanogens in granular sludge from a UASB reactor. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1988, 10, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; Banks, C.J.; Siegert, I.; Heaven, S.; Borja, R. Influence of inoculum to substrate ratio on the biochemical methane potential of maize in batch tests. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Bhattarai, S.; Kim, S.H.; Chen, L. Effect of feed to microbe ratios on anaerobic digestion of Chinese cabbage waste under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: Biogas potential and kinetic study. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gioannis, G.; Diaz, L.F.; Muntoni, A.; Pisanu, A. Two-phase anaerobic digestion within a solid waste/wastewater integrated management system. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Norli, I.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Yhaya, M.F. Impacts of trace element supplementation on the performance of anaerobic digestion process: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A.P.H. Others Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Weiland, P.; Rieger, C. Prozessstörungen frühzeitig erkennen. Biogas J. 2006, 9, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation, F.C.Q.A. Methods Book for the Analysis of Compost; Ger. Bundesgütegemeinschaft Kompost eV: Colonge, Germany, 1994; p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Anthonisen, A.C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S.; Srinath, E.G. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J. (Water Pollut. Control Fed.) 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar]
- VDI 4630. Fermentation of Organic Materials: Characterization of the SUBSTRATE, sampling, Collection of Material Data, Fermentation Tests; Verein Deutscher Ingenieure, Ed.; VDI-handbuch Energietechnik, Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lang, Q.; Fang, M.; Li, X.; Bah, H.; Dong, H.; Dong, R. Combined effect of crude fat content and initial substrate concentration on batch anaerobic digestion characteristics of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, G.; Zhang, L.; Jahng, D. Osmoprotectants enhance methane production from the anaerobic digestion of food waste containing a high content of salt. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 2010, 83, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlostathis, S.G.; Giraldo-Gomez, E. Kinetics of anaerobic treatment: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1991, 21, 411–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Chen, X.; Pan, J.; Kloss, R.; Wei, Y. Effect of ammonia and nitrate on biogas production from food waste via anaerobic digestion. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 116, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, R.; Rincón, B.; Raposo, F.; Alba, J.; Martín, A. Kinetics of mesophilic anaerobic digestion of the two-phase olive mill solid waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 15, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Milled Wheat | Skimmed Soybeans | Edible Sunflower Oil | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total solid (TS) (%) | 90 | 89 | 100 | 3 |
| Volatile solid (VS) (%TS) | 100 | 93 | 100 | 64 |
| pH | 5.5 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 7.9 |
| NH4+ (mg∙L−1) | ND | ND | ND | 979 |
| Salt (g∙kg−1) | <0.1 * | 2.1 | <0.1 * | 0.5 |
| C (%VS) | 45.0 | 45.4 | 83.8 | 28.0 |
| H (%VS) | 6.8 | 6.4 | 19.3 | 4.6 |
| N (%VS) | 1.9 | 7.7 | 0.0 | 3.9 |
| Protein (%VS) | 13.3 * | 71.4 * | 0.0 * | ND |
| Carbohydrate (%VS) | 84.8 * | 26 * | 0.0 * | ND |
| Fat (%VS) | 1.2 * | 2.6 * | 100.0 * | ND |
| FC (gVS∙L−1) | Salt Addition (g∙L−1) | Total SBP (mL∙g−1VS) | AD Efficiency (%) | Total SMP (mL∙g−1VS) | VS Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0 | 713 a, 601 b, 883 c | 89.7 a, 77.1 b, 63.5 c | 261 a, 277 b, 459 c | 66.5 a, 79.0 b, 74.2 c |
| 2 | 774 a, 624 b, 1003 c | 97.4 a, 80.0 b, 72.2 c | 315 a, 278 b, 535 c | 58.7 a, 81.7 b, 85.6 c | |
| 4 | 738 a, 599 b, 809 c | 92.9 a, 76.8 b, 58.2 c | 299 a, 267 b, 445 c | 57.6 a, 78.7 b, 67.6 c | |
| 6 | 745 a, 561 b, 866 c | 93.7 a, 72.0 b, 62.3 c | 268 a, 231 b, 449 c | 52.3 a, 72.6 b, 58.4 c | |
| 9 | 698 a, 495 b, 744 c | 87.9 a, 63.5 b, 53.5 c | 206 a, 207 b, 322 c | 61.2 a, 61.2 b, 50.8 c | |
| 12 | 644 a, 443 b, 623 c | 81.0 a, 56.8 b, 44.8 c | 173 a, 184 b, 310 c | 54.3 a, 56.4 b, 53.4 c | |
| 8 | 0 | 664 a, 568 b, 621 c | 83.5 a, 72.9 b, 44.7 c | 247 a, 256 b, 326 c | 72.0 a, 75.3 b, 35.4 c |
| 2 | 647 a, 613 b, 733 c | 81.5 a, 78.6 b, 52.7 c | 259 a, 301 b, 374 c | 70.0 a, 76.4 b, 35.9 c | |
| 4 | 759 a, 628 b, 653 c | 95.5 a, 80.6 b, 47.0 c | 269 a, 270 b, 308 c | 78.5 a, 70.6 b, 50.8 c | |
| 6 | 764 a, 620 b, 610 c | 96.2 a, 79.5 b, 43.9 c | 261 a, 275 b, 332 c | 72.5 a, 69.9 b, 46.1 c | |
| 9 | 697 a, 534 b, 643 c | 87.7 a, 68.5 b, 46.2 c | 225 a, 244 b, 341 c | 74.2 a, 61.4 b, 58.2 c | |
| 12 | 319 a, 509 b, 410 c | 40.1 a, 65.3 b, 29.5 c | 112 a, 231 b, 194 c | 72.8 a, 62.5 b, 27.6 c |
| FC (gVS∙L−1) | Salt Addition (g∙L−1) | Yp (mL∙g−1VS) | Rmax (mL∙g−1VS) | λ (d) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0 | 717.0 a, 592.8 b, 858.2 c | 100.7 a, 76.0 b, 49.1 c | 0.11 a, 0.58 b, 1.89 c | 0.98 a, 1.00 b, 0.99 c |
| 2 | 762.1 a, 613.4 b, 940.0 c | 110.9 a, 97.3 b, 50.8 c | 0.03 a, 0.48 b, 0.50 c | 0.99 a, 1.00 b, 0.97 c | |
| 4 | 727.0 a, 589.7 b, 761.3 c | 107.2 a, 96.2 b, 47.7 c | 0.10 a, 0.45 b, 0.36 c | 0.99 a, 1.00 b, 0.98 c | |
| 6 | 728.4 a, 558.5 b, 816.9 c | 100.9 a, 89.0 b, 52.2 c | 0.08 a, 0.35 b, 0.37 c | 0.99 a, 1.00 b, 0.98 c | |
| 9 | 687.6 a, 498.3 b, 715.5 c | 73.1 a, 54.6 b, 45.3 c | 0.00 a, 1.41 b, 0.43 c | 0.97 a, 1.00 b, 0.99 c | |
| 12 | 652.8 a, 630.5 b, 627.2 c | 55.6 a, 26.3 b, 39.8 c | 0.00 a, 2.93 b, 5.20 c | 0.98 a, 1.00 b, 1.00 c | |
| 8 | 0 | 659.8 a, 623.9 b, 599.5 c | 47.8 a, 41.4 b, 46.1 c | 0.00 a, 0.36 b, 0.91 c | 0.85 a, 0.99 b, 1.00 c |
| 2 | 653.3 a, 618.1 b, 696.7 c | 64.1 a, 62.6 b, 45.5 c | 0.00 a, 0.80 b, 0.43 c | 0.94 a, 1.00 b, 0.99 c | |
| 4 | 754.0 a, 630.0 b, 620.2 c | 90.3 a, 62.5 b, 45.7 c | 0.00 a, 0.76 b, 0.62 c | 0.91 a, 1.00 b, 1.00 c | |
| 6 | 749.4 a, 614.4 b, 584.3 c | 82.7 a, 62.0 b, 39.8 c | 0.00 a, 0.79 b, 0.65 c | 0.88 a, 1.00 b, 0.99 c | |
| 9 | 718.6 a, 578.0 b, 620.8 c | 60.8 a, 41.3 b, 46.8 c | 0.00 a, 0.84 b, 1.41 c | 0.81 a, 1.00 b, 1.00 c | |
| 12 | 406.9 a, 731.0 b, 414.5 c | 277.3 a, 29.5 b, 31.5 c | 0.00 a, 2.05 b, 7.84 c | 0.60 a, 0.99 b, 1.00 c |
| FC (gVS∙L−1) | Salt Addition (mg∙L−1) | pH | TAN (mg∙L−1) | TOA/TIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0 | 7.15 (0.05) a, 7.31 (0.01) b, 7.13 (0.15) c | 548.2 (83.6) a, 1002.8 (19.3) b, 508.1 (10.7) c | 0.08 (0.016) a,0.07 (0.003) b, 0.11 (0.041) c |
| 2 | 7.11 (0.01) a, 7.30 (0.02) b, 7.10 (0.04) c | 586.6 (125.8) a, 1077.3 (180.5) b, 628.0 (67.28) c | 0.10 (0.043) a,0.04 (0.015) b, 0.19 (0.000) c | |
| 4 | 7.10 (0.01) a, 7.12 (0.05) b, 7.10 (0.01) c | 586.3 (71.84) a, 1169.9 (145.3) b, 503.1 (53.33) c | 0.11 (0.005) a,0.05 (0.015) b, 0.14 (0.002) c | |
| 6 | 7.06 (0.03) a, 7.15 (0.04) b, 7.09 (0.00) c | 702.6 (67.3) a, 1080.4 (70.5) b, 503.1 (18.2) c | 0.08 (0.023) a,0.05 (0.025) b, 0.10 (0.022) c | |
| 9 | 7.10 (0.01) a, 7.07 (0.01) b, 7.13 (0.00) c | 564.7 (0.5) a, 849.5 (17.9) b, 508.0 (48.7) c | 0.08 (0.037) a,0.10 (0.006) b, 0.11 (0.013) c | |
| 12 | 7.08 (0.07) a, 7.00 (0.02) b, 7.15 (0.01) c | 694.5 (22.8) a, 959.7 (80.6) b, 502.9 (30.5) c | 0.13 (0.082) a,0.10 (0.019) b, 0.15 (0.069) c | |
| 8 | 0 | 7.01 (0.01) a, 7.08 (0.03) b, 7.06 (0.01) c | 685.2 (18.5) a, 1072.2 (124.7) b, 426.5 (54.7) c | 0.06 (0.003) a,0.10 (0.004) b, 0.09 (0.009) c |
| 2 | 7.06 (0.04) a, 7.00 (0.02) b, 7.10 (0.01) c | 670.6 (62.5) a, 1120.4 (48.2) b, 468.8 (30.5) c | 0.06 (0.001) a,0.12 (0.001) b, 0.04 (0.007) c | |
| 4 | 7.01 (0.00) a, 7.10 (0.00) b, 6.97 (0.04) c | 411.4 (53.1) a, 1134.2 (86.4) b, 579.2 (30.6) c | 0.10 (0.000) a,0.13 (0.006) b, 0.16 (0.006) c | |
| 6 | 6.98 (0.01) a, 7.04 (0.03) b, 6.85 (0.01) c | 575.2 (55.1) a, 1005.5 (99.0) b, 582.8 (12.1) c | 0.16 (0.052) a,0.10 (0.035) b, 0.16 (0.014) c | |
| 9 | 6.83 (0.01) a, 7.05 (0.01) b, 6.83 (0.01) c | 556.6 (42.7) a, 988.5 (37.3) b, 582.7 (12.0) c | 0.16 (0.044) a,0.08 (0.001) b, 0.19 (0.005) c | |
| 12 | 4.72 (0.05) a, 6.98 (0.02) b, 6.76 (0.04) c | 488.5 (63.6) a, 1076.2 (137.8) b, 492.4 (30.1) c | UD a, 0.12 (0.001) b, 0.24 (0.008) c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, T.; Maurer, C.; Kranert, M. Effects of Salt on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste with Different Component Characteristics and Fermentation Concentrations. Energies 2019, 12, 3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183571
Li X, Huang J, Liu Y, Huang T, Maurer C, Kranert M. Effects of Salt on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste with Different Component Characteristics and Fermentation Concentrations. Energies. 2019; 12(18):3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183571
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaofeng, Jingjing Huang, Yiyun Liu, Tao Huang, Claudia Maurer, and Martin Kranert. 2019. "Effects of Salt on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste with Different Component Characteristics and Fermentation Concentrations" Energies 12, no. 18: 3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183571
APA StyleLi, X., Huang, J., Liu, Y., Huang, T., Maurer, C., & Kranert, M. (2019). Effects of Salt on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste with Different Component Characteristics and Fermentation Concentrations. Energies, 12(18), 3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183571