Optimization of Continuous Solid-State Distillation Process for Cost-Effective Bioethanol Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Raw Material
2.1.2. Particle Size Distribution of Material
2.1.3. Solid-State Fermentation
2.1.4. Measurement of Specific Heat Capacity and Thermal Conductivity
2.2. Experiment Methods
2.2.1. Experiment Apparatus
2.2.2. Experiment Procedure
2.2.3. Experiment Arrangement
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Moisture Content Analysis
2.3.2. Ethanol Concentration Analysis
2.3.3. Other Chemical Components Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experiments Results
3.1.1. Particle Size Distribution
3.1.2. Specific Heat Capacity and Thermal Conductivity
3.1.3. Chemical Components in FSSB and Distillate
3.1.4. Distillation Experiments Results
3.2. Solid-State Distillation Process
3.2.1. Mass Transfer Model
3.2.2. Ethanol Yielding Point
3.2.3. Ethanol Extracting Kinetics Analysis
3.3. Optimization of Solid-State Distillation Process
3.3.1. Total Distillation Time
3.3.2. Process Optimization
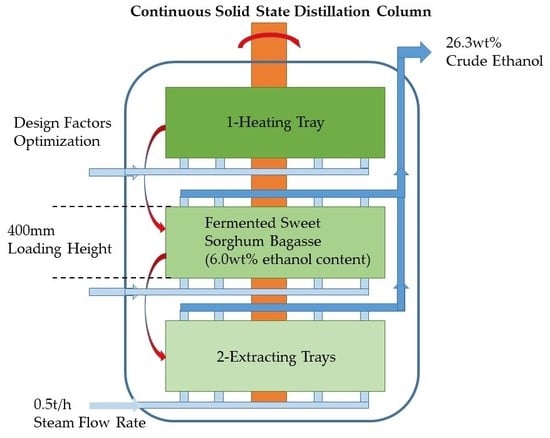
3.4. Continuous Solid-State Distillation
3.5. Economics Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.K. Biofuels (alcohols and biodiesel) applications as fuels for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabed, H.; Sahu, J.N.; Suely, A.; Boyce, A.N.; Faruq, G. Bioethanol production from renewable sources: Current perspectives and technological progress. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2017, 71, 475–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Z.; Chan-Halbrendt, C. Ethanol production in (the) People’s Republic of China: Potential and technologies. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, S162–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, J. The Role of Sorghum in Renewables and Biofuels. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1931, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Calvino, M.; Messing, J. Sweet sorghum as a model system for bioenergy crops. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Li, M.; Liu, H.H.; Ren, L.T.; Xie, G.H. Technical Feasibility and Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum for Bioethanol Production in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.C.; Yang, X.L.; Xie, G.H. Establishing sustainable sweet sorghum-based cropping systems for forage and bioenergy feedstock in North China Plain. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 227, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hao, M.M.; Fu, J.Y.; Liu, K.; Yan, X.X. Potential bioethanol production from sweet sorghum on marginal land in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.Y.; Cai, W.J.; Wang, C.; Huang, G.R.; Ding, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, H.R.; Ji, D.Y. Assessment of the potential and distribution of an energy crop at 1-km resolution from 2010 to 2100 in China—The case of sweet sorghum. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, G. Comprehensive Repair of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil Involves Planting Sweet Sorghum in Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil to Absorb Heavy Metal, Harvesting, Chopping, Fermenting, Distilling off Ethanol in Resultant Product, and Drying. China Patent CN104324933-A, 4 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Almodares, A.; Hadi, M.R. Production of bioethanol from sweet sorghum: A review. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 4, 772–780. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Chawhuaymak, J.; Riley, M.R.; Zimmt, W.; Ogden, K.L. Efficient extraction method to collect sugar from sweet sorghum. J. Biol. Eng. 2013, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.Z.; Li, G.M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.X.; Han, B.; Hou, W.H.; Wang, J.B.; Li, T.C. A demonstration study of ethanol production from sweet sorghum stems with advanced solid state fermentation technology. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chang, S.; Zhao, G. The mass transfer of sugar in sweet sorghum stalks for solid-state fermentation process. Fuel 2015, 144, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Feng, J. Enhancing mixing of cohesive particles by baffles in a rotary drum. Particuology 2016, 25, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, E.; Zhang, L.; Li, T. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum stalks by advanced solid state fermentation (ASSF) technology. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 966–973. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Feng, J.X.; Zhou, Z.X.; Li, S.Z. A Simulation Method Focused on Electric-Heating Distillation of Ethanol in Solid-State Fermented Crushed Straw Material. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Applied Mathematics, Modelling and Statistics Application, Istanbul, Turkey, 3–7 July 2017; Harish, B.S., Rojas, A.L., Weller, K., Eds.; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2017; Volume 141, pp. 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Xu, Q.; Song, J.T.; Ye, J.S. Thin-layer Steam Distillation of Fermented Grains: Effects of Steam Flow Rate and Temperature. Int. J. Food Eng. 2012, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, W.; Shen, C.; Yi, B. Optimization of the distillation process of Chinese liquor by comprehensive experimental investigation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.F.; Wu, C.D.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.Q. Changes in Volatile Compounds of Chinese Luzhou-Flavor Liquor during the Fermentation and Distillation Process. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C2373–C2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zu, X.; Zhang, L.; Qi, L.; Xu, W. Extraction of bioethanol from fermented sweet sorghum bagasse by batch distillation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G. Continuous Solid-State Separation Device and Process for Producing Fuel Ethanol. U.S. Patent US10239806, 26 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Du, R.; Yan, J.B.; Feng, Q.Z.; Li, P.P.; Zhang, L.; Chang, S.; Li, S.Z. A Novel Wild-Type Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain TSH1 in Scaling-Up of Solid-State Fermentation of Ethanol from Sweet Sorghum Stalks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, D.L. Rapid extraction and analysis of nonstructure carbohydrates in plant-tissues. Crop Sci. 1993, 33, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowski, L.; Wojcieszak, D.; Olek, W.; Przybyl, J. Thermal properties of fractions of corn stover. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phutela, U.G.; Kaur, J. Process Optimization for Ethanol Production from Sweet Sorghum Juice Using Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain NRRL Y-2034 by Response Surface Methodology. Sugar Tech 2014, 16, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Standards. Chinese National Standards for Food Safety: Edible Alcohol; China standard press: Beijing, China, 2016; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ohe, S. Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data, 1st ed.; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1989; pp. 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.M. Study on Life Cycle Assessment of Bioethanol production and vinasse treatment from Sweet Sorghum Stalks. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, June 2016. [Google Scholar]










| Temperature (K) | Mean Specific Heat Capacity (kJ/kg·K) | Thermal Conductivity w/(m·K) |
|---|---|---|
| 293 | 3.306 | 0.272 |
| 313 | 3.318 | 0.304 |
| 333 | 3.332 | 0.325 |
| 353 | 3.360 | 0.337 |
| 373 | 3.389 | 0.345 |
| No. | H mm | V m3/h | Ec %(w/w) | tH min | tE min | Rc %(w/w) | k1 min−1 | HL mm | EY %(v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 250 | 7.2 | 6.1 | 12.5 | 30.9 | 95.8 | 0.102 | 100 | 67.4 |
| 2 | 250 | 10.4 | 6.1 | 9.6 | 22.3 | 96.7 | 0.152 | 75 | 66.8 |
| 3 | 250 | 13.6 | 5.9 | 8.9 | 11.4 | 95.7 | 0.276 | 60 | 61.6 |
| 4 | 250 | 16.8 | 6.0 | 7.7 | 8.9 | 95.7 | 0.341 | 60 | 57.4 |
| 5 | 400 | 7.2 | 6.0 | 17.2 | 34.4 | 96.6 | 0.098 | 135 | 75.4 |
| 6 | 400 | 10.4 | 5.9 | 13.3 | 19.3 | 97.1 | 0.183 | 100 | 67.3 |
| 7 | 400 | 13.6 | 6.2 | 11.2 | 13.6 | 96.8 | 0.253 | 80 | 65.4 |
| 8 | 400 | 16.8 | 6.0 | 10.5 | 9.7 | 97.3 | 0.372 | 80 | 63.0 |
| 9 | 550 | 7.2 | 6.1 | 20.6 | 48.0 | 97.6 | 0.079 | 150 | 77.9 |
| 10 | 550 | 10.4 | 6.0 | 16.1 | 28.8 | 95.7 | 0.109 | 120 | 74.8 |
| 11 | 550 | 13.6 | 5.9 | 12.8 | 15.8 | 96.8 | 0.219 | 100 | 66.7 |
| 12 | 550 | 16.8 | 6.2 | 11.4 | 11.6 | 96.2 | 0.282 | 90 | 62.8 |
| 13 | 700 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 24.7 | 76.8 | 95.8 | 0.041 | 180 | 78.4 |
| 14 | 700 | 10.4 | 6.2 | 19.0 | 46.8 | 97.3 | 0.077 | 140 | 77.1 |
| 15 | 700 | 13.6 | 6.0 | 16.0 | 23.7 | 96.9 | 0.147 | 120 | 76.2 |
| 16 | 700 | 16.8 | 6.2 | 14.4 | 15.9 | 96.0 | 0.202 | 100 | 76.5 |
| Item | Unit | Price/CNY 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel ethanol 2 | t | 6270 |
| Sweet sorghum 2 | t | 324.8 |
| Yeast and Culture medium 2 | per ton FSSB | 11.5 |
| Steam (p4) | t | 190 |
| Vinasse (p3) | t | 320.7 |
| Charges from 25 wt% to absolute ethanol 2,3 | t | 4010 |
| Process | Material | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input (ton) | Output (ton) | ||||
| Solid-state process | Smash | Sweet sorghum | 4.23 | Bagasse | 4.23 |
| Seed culture | Water | 0.62 | seed liquid | 0.67 | |
| - | Barley malt | 0.04 | - | - | |
| - | Yeast and Enzymes | 0.01 | - | - | |
| Fermentation | Bagasse | 4.23 | FSSB | 4.62 | |
| - | Seed liquid | 0.67 | Carbon dioxide | 0.28 | |
| Distillation | FSSB | 4.62 | Crude ethanol | 1 | |
| - | Vapor | 1.23 | Vinasse | 4.85 | |
| Liquid-state process | Squeeze | Sweet sorghum | 4.54 | Juice | 4.03 |
| - | Water | 1.75 | Vinasse | 1.91 | |
| - | Lime | 0.01 | Wastewater | 0.36 | |
| Seed culture | Water and Nutrient salt | 0.05 | Seed liquid | 0.06 | |
| Yeast and Enzymes | 0.01 | - | - | ||
| Fermentation | Juice | 4.03 | Fermented liquid | 3.87 | |
| Seed liquid | 0.06 | Carbon dioxide | 0.22 | ||
| Distillation | Fermented liquid | 3.87 | Crude ethanol | 1 | |
| - | - | - | Wastewater | 2.87 | |
| Process | Energy Input (kWh) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-state process | Smash | Electricity | 26.71 |
| Seed culture | Electricity | 5.67 | |
| - | Steam | 17.6 | |
| Fermentation | Electricity | 20.7 | |
| Distillation | Electricity | 15.84 | |
| - | Steam | 771.42 | |
| - | Total | 857.94 | |
| Liquid-state process | Squeeze | Electricity | 54.64 |
| - | Steam | 386.34 | |
| Seed culture | Electricity | 3.79 | |
| - | Steam | 6.18 | |
| Fermentation | Electricity | 35.38 | |
| Distillation | Steam | 420.05 | |
| - | Total | 906.38 | |
| Item | Amount | Unit Price/CNY | Cost/CNY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Sweet sorghum | 16 tons | 324.8 | −5196.8 |
| - | Seed culture Storage 1 | - | - | −184 −164.8 |
| Utility | Electricity | 261+81 kWh 2 | 0.8 | −272.8 |
| - | Steam | 2.89+2.4 tons 2,3 | 190 | −1005.1 |
| - | Water | 3 tons | 5 | −15 |
| Operation | Labor and Management | - | - | −646.3 |
| - | Depreciation and Amortization 4 | - | - | −1515 |
| - | Maintenance 5 | - | - | −697 |
| Income | Cattle feed | 18.3 tons | 320.7 | 5868.8 |
| - | Fuel ethanol | 1 ton | 6270 | 6270 |
| Profit | - | - | - | 2442 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Li, S. Optimization of Continuous Solid-State Distillation Process for Cost-Effective Bioethanol Production. Energies 2020, 13, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040854
Li H, Li S. Optimization of Continuous Solid-State Distillation Process for Cost-Effective Bioethanol Production. Energies. 2020; 13(4):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040854
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongshen, and Shizhong Li. 2020. "Optimization of Continuous Solid-State Distillation Process for Cost-Effective Bioethanol Production" Energies 13, no. 4: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040854
APA StyleLi, H., & Li, S. (2020). Optimization of Continuous Solid-State Distillation Process for Cost-Effective Bioethanol Production. Energies, 13(4), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040854