Addressing Abrupt PV Disturbances, and Mitigating Net Load Profile’s Ramp and Peak Demands, Using Distributed Storage Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Power Variabilities of a PV Generator
2.1. Abrupt Disturbances in PV Generation
2.2. Daily Power Profile of PV
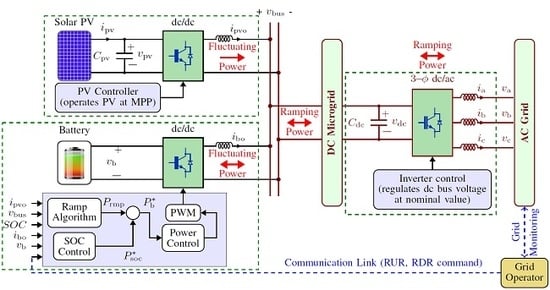
3. Proposed BES System and Control
3.1. Defining Operational Scenario of BES
3.2. BES Converter and Its Mathematical Modeling
3.3. BES Control Structure and Design
3.3.1. Power Control Loop
3.3.2. Reference Power Calculation
3.3.3. SOC Control Loop
3.4. Determining the BES Capacity
4. Numerical Designs, Results, and Comparisons
4.1. Abrupt Disturbances: Case Study 1
4.1.1. System and Control Parameters
4.1.2. Results and Discussion
4.2. Abrupt Disturbances: Case Study 2
4.3. Daily Power Profile of PV
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. Experimental Setup
4.4.2. Results
4.5. Comparisons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PV | Photovoltaic | BES | Battery Energy Storage |
| DER | Distributed Energy Resources | LQR | Linear quadratic regulator |
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking | PCC | Point of common coupling |
| PI | Proportional Integrator | pu | per unit |
| RDR | Ramp Down Rate | RUR | Ramp Up Rate |
| SG | Synchronous generator | SOC | State of Charge |
| ISO | Independent System Operator | ||
| Symbols and Variables | |||
| t | Time | k | Sampling instant |
| Change in time | Synchronous generator power | ||
| Voltage of synchronous generator | H | Inertia constant | |
| Resistance of transformer | Reactance of transformer | ||
| Transformer voltage ratio | Dc voltage at the PCC | ||
| L-L rms ac voltage at PCC | Filter inductance of dc/ac converter | ||
| Filter resistance of dc/ac converter | Capacitor on dc side of dc/ac converter | ||
| Voltage at PV-BES connection | Voltage of bus | ||
| Ramp up rate | Ramp down rate | ||
| Minimum ramp rate | PV power | ||
| Output power of PV converter | Change in PV power | ||
| Desired output power | Maximum change in PV power | ||
| Total output power of PV-BES system | Filter inductance of PV converter | ||
| Capacitor across PV terminals | Filter resistance of PV converter | ||
| PV control gain | PV current | ||
| Output current of PV converter | PV voltage | ||
| PV reference voltage | PV voltage at maximum PV power | ||
| PV current at maximum PV power | Open-circuit voltage of PV | ||
| Short-circuit current of PV | BES reference power | ||
| Reference power for SOC control of BES | Battery Power | ||
| Output power of BES converter | Battery current | ||
| Output current of BES converter | Duty cycle for BES converter | ||
| Control input of BES converter | Battery voltage | ||
| Nominal voltage of battery | State of charge of BES | ||
| Nominal SOC of BES | Change in SOC of BES | ||
| Maximum change in SOC | Filter inductance of BES converter | ||
| Filter resistance of BES converter | Q | Battery capacity | |
| Minimum battery capacity | BES power control gain | ||
| gain of SOC control | J | Cost function | |
| weighting factor in cost function | |||
References
- Al-Hallaj, S. More than enviro-friendly: Renewable energy is also good for the bottom line. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2004, 2, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Guerrero, J.M. Voltage Stabilization: A Critical Step Toward High Photovoltaic Penetration. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2019, 13, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Administration, U.E.I. Annual Energy Outlook 2019: With Projections to 2050. 2019. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/pdf/aeo2019.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- Kroposki, B.; Johnson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gevorgian, V.; Denholm, P.; Hodge, B.M.; Hannegan, B. Achieving a 100% renewable grid: Operating electric power systems with extremely high levels of variable renewable energy. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2017, 15, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwal, S.; Karimi-Ghartemani, M. On Transient Responses of a Class of PV Inverters. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qunais, T.; Sharma, R.; Karimi-Ghartemani, M.; Silwal, S.; Khajehoddin, S.A. Application of Battery Storage System to Improve Transient Responses in a Distribution Grid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, B.A.; Shah, S.; Norris, B.L.; Dise, J.H.; Yu, L.; Paradis, D.; Katiraei, F.; Seguin, R.; Costyk, D.; Woyak, J.; et al. NREL/SCE High Penetration PV Integration Project: FY13 Annual Report; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2014.
- Katiraei, F.; Aguero, J.R. Solar PV integration challenges. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2011, 9, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, P.G.; Hernández, J.C.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, F.J. Stability assessment for transmission systems with large utility-scale photovoltaic units. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamuri, J.N.; Das, K.; Altin, M.; Cutululis, N.A.; Hansen, A.D.; Tielens, P.; Van Hertem, D. Improved frequency control from wind power plants considering wind speed variation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Power Systems Computation Conference (PSCC), Genoa, Italy, 20–24 June 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gevorgian, V.; Booth, S. Review of PREPA Technical Requirements for Interconnecting Wind and Solar Generation; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2013.
- IEEE Std 1547-2018 Standard for Interconnection and Interoperability of Distributed Energy Resources with Associated Electric Power Systems Interfaces. 2018, pp. 1–138. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8332112 (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- Denholm, P.; O’Connell, M.; Brinkman, G.; Jorgenson, J. Overgeneration from Solar Energy in California. A Field Guide to the Duck Chart; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2015.
- Ghosh, S.; Rahman, S.; Pipattanasomporn, M. Distribution voltage regulation through active power curtailment with PV inverters and solar generation forecasts. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Guerrero, J.M. Smart Inverters for Utility and Industry Applications. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe 2015; International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremberg, Germany, 19–21 May 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bragard, M.; Soltau, N.; Thomas, S.; De Doncker, R.W. The balance of renewable sources and user demands in grids: Power electronics for modular battery energy storage systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleke, S.; Baran, M.E.; Bhattacharya, S.; Huang, A.Q. Rule-based control of battery energy storage for dispatching intermittent renewable sources. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2010, 1, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceja-Espinosa, C.; Espinosa-Juárez, E. Smoothing of photovoltaic power generation using batteries as energy storage. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE PES—Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference-Latin America (ISGT Latin America), Quito, Ecuador, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lujano-Rojas, J.M.; Dufo-López, R.; Bernal-Agustín, J.L.; Catalão, J.P. Optimizing daily operation of battery energy storage systems under real-time pricing schemes. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 8, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.; Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, F. Design criteria for the optimal sizing of a hybrid energy storage system in PV household-prosumers to maximize self-consumption and self-sufficiency. Energy 2019, 186, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gonzalez, M.; Hernandez, J.; Vera, D.; Jurado, F. Optimal sizing and power schedule in PV household-prosumers for improving PV self-consumption and providing frequency containment reserve. Energy 2020, 191, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Muttaqi, K.; Sutanto, D. A novel approach for ramp-rate control of solar PV using energy storage to mitigate output fluctuations caused by cloud passing. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 507–518. [Google Scholar]
- Sangwongwanich, A.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. A cost-effective power ramp-rate control strategy for single-phase two-stage grid-connected photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hui, D.; Lai, X. Battery energy storage station (BESS)-based smoothing control of photovoltaic (PV) and wind power generation fluctuations. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.C.; Bueno, P.G.; Sanchez-Sutil, F. Enhanced utility-scale photovoltaic units with frequency support functions and dynamic grid support for transmission systems. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Parkhideh, B. Control and Operating Range Analysis of AC-Stacked PV Inverter Architecture Integrated with Battery. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10032–10037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Islam, M.R.; Sutanto, D.; Muttaqi, K.M. Mitigation of Solar PV Intermittency Using Ramp-Rate Control of Energy Buffer Unit. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 34, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Hussain, I.; Singh, B.; Vyas, A.L. Implementation of a Grid-Integrated PV-Battery System for Residential and Electrical Vehicle Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6592–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, K. A Flexible Power Control for PV-Battery-Hybrid System Using Cascaded H-Bridge Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 7, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallabandi, V.; Akeyo, O.M.; Jewell, N.; Ionel, D.M. Incorporating Battery Energy Storage Systems Into Multi-MW Grid Connected PV Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, M.; Andreas, A. Lowry Range Solar Station: Arapahoe County, Colorado (Data). Available online: https://data.nrel.gov/submissions/30 (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- Lew, D.; Miller, N. Reaching new solar heights: integrating high penetrations of PV into the power system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California ISO. Renewables and Emission Reports. Available online: http://www.caiso.com/market/Pages/ReportsBulletins/RenewablesReporting.aspx (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- Karimi-Ghartemani, M.; Khajehoddin, S.A.; Jain, P.; Bakhshai, A. Linear quadratic output tracking and disturbance rejection. Int. J. Control 2011, 84, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, M.A.G.; Galotto, L.; Sampaio, L.P.; e Melo, G.d.A.; Canesin, C.A. Evaluation of the main MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Malesani, L. Current control techniques for three-phase voltage-source PWM converters: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1998, 45, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Timbus, A.V. Overview of Control and Grid Synchronization for Distributed Power Generation Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silwal, S.; Karimi-Ghartemani, M.; Sharma, R.; Karimi, H. Impact of Feed-forward and Decoupling Terms on Stability of Grid-Connected Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 2641–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwal, S.; Taghizadeh, S.; Karimi Ghartemani, M.; Hossain, J.; Davari, M. An Enhanced Control System for Single-Phase Inverters Interfaced with Weak and Distorted Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 12538–12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]























| Nominal Bus Voltage: 600 V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads: | |||
| Load 0: 1.5 kW | Load 1: 0.5 kW | Load 2: 1.5 kW | |
| Load 3: 2.0 kW | Load 4: 1.5 kW | Load 5: 5.0 kW | |
| Load 6: 4.4 kW | |||
| Lines: | |||
| Line | Length | Resistance | Inductance |
| Line1g | 0.75 km | 0.482 Ω | 0.198 mH |
| Line12 | 0.5 km | 0.321 Ω | 0.132 mH |
| Line23 | 0.3 km | 0.0.193 Ω | 0.079 mH |
| Line34 | 0.5 km | 0.321 Ω | 0.132 mH |
| Line45 | 0.5 km | 0.321 Ω | 0.132 mH |
| Line56 | 1 km | 0.642 Ω | 0.264 mH |
| PV system: | |||
| Rated power: 15 kW at 1000 W/m2, 1000 V | |||
| Synchronous Generator (SG): | ||
|---|---|---|
| Power (): 250 kVA, voltage (): 12.47 V | ||
| Inertia constant (H): 5.0 | ||
| Loads: | ||
| ac load 0: 0.05 pu, ac load 1: 0.846 pu | ||
| Ac Line: | ||
| 200 km, 32.2 Ω, 120.96 mH | ||
| Transformer: | ||
| Resistance (): 0.02 pu, Reactance (): 0.05 pu | ||
| Voltage ratio (VR): 207.8 V/12.47 kV | ||
| Three-phase dc/ac Converter: | ||
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
| Filter inductance | 10 mH | |
| Filter resistance | 10 mΩ | |
| Dc capacitor | 1200 μF | |
| Voltage on dc side | 600 V | |
| Voltage on ac side | 207.8 V | |
| PV System: |
|---|
| 15 kW @ 1000 and 1000 V |
| : 600 V |
| Converter: |
| , , : 10 mΩ |
| Controller: |
| Switching Frequency: 10 kHz |
| Control Gains: |
| : −316.22, : 3.07, : 31.62 |
| : 344.49, : 1.38, : −0.59 |
| BES System: |
|---|
| : 1000 V, RUR/RDR: 30%/minute ≈75 W/s |
| : 600 V, : 15 kW, : 30% |
| : 5040 As, Choose Q: 5400 As |
| Converter: :10 mH, :10 mH |
| Controller: |
| Switching Frequency: 10 kHz |
| Power Control: |
| With : 316.22, : 0.0001 |
| Poles: |
| Gains: : −17.78, : 0.0263 |
| SOC Control: |
| With : 316.22, |
| Poles −0.0015 ± j0.0011 |
| Gains: : 17.7828, : −15,757 |
| S.N | Ramp Setting | BES Size | Maximum Ramp in Net Load | Peak Net Load | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power | Energy | ||||
| 1 | No BES | - | - | 5300 | 22,580 |
| 2 | RUR: 1200 MW/h | 5000 MW | 19,411 MWh | 2767 MW/h | 18,747 MW |
| RDR: 1200 MW/h | |||||
| 3 | RUR: 1400 MW/h | 5571 MW | 15,201 MWh | 2660 MW/h | 21,535 MW |
| RDR: 1000 MW/h till 20:00 | |||||
| RDR: 3000 MW/h after 20:00 | |||||
| Modular Solar Array Simulator: |
|---|
| PV Curve I: : 20.0 V, : 0.3 A, : 23.0 V, : 0.5 A |
| PV Curve II: : 20.0 V, : 2.0 A, : 23.0 V, : 2.5 A |
| PV converter: : 1 mH, : 0.2587 , : 100μF |
| BES and converter: : 30.0 V, Local Load: 30 , : 1 mH, : 0.250 Ω |
| Dc bus: : 10.0 V, Local Load: 2 Ω |
| Controller: |
| Switching Frequency: 32 kHz |
| PV converter control gains |
| : −56.23, : 0.18, : 10.00, : 382.76, : 1.02, : −0.16 |
| BES controller settings |
| RUR & RDR: 1.0 W/s, Control Gains: = −5.6234, = 0.0189 (Power control) |
| References | Smoothing Method | Ramp Calculation Simplicity | Plug-and-Play Level | Model Details | SOC Control Design | Optimal Control Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | Ramp | Average | Poor | Fair | No | No |
| [22] | Ramp | Fair | Poor | Fair | No | No |
| [25] | P-f droop | Average | Fair | Average | No | No |
| [26] | Ramp | Fair | Poor | Average | No | No |
| [27] | Ramp, Constant power | Fair | Fair | Average | No | No |
| [28] | Constant power | Average | Fair | Average | No | No |
| [29] | Constant power | Average | Poor | Average | No | No |
| [30] | Moving average, P-f droop | Fair | Poor | Poor | No | No |
| Proposed method | Ramp | Good | Good | Good | Yes | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, R.; Karimi-Ghartemani, M. Addressing Abrupt PV Disturbances, and Mitigating Net Load Profile’s Ramp and Peak Demands, Using Distributed Storage Devices. Energies 2020, 13, 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051024
Sharma R, Karimi-Ghartemani M. Addressing Abrupt PV Disturbances, and Mitigating Net Load Profile’s Ramp and Peak Demands, Using Distributed Storage Devices. Energies. 2020; 13(5):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051024
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Roshan, and Masoud Karimi-Ghartemani. 2020. "Addressing Abrupt PV Disturbances, and Mitigating Net Load Profile’s Ramp and Peak Demands, Using Distributed Storage Devices" Energies 13, no. 5: 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051024
APA StyleSharma, R., & Karimi-Ghartemani, M. (2020). Addressing Abrupt PV Disturbances, and Mitigating Net Load Profile’s Ramp and Peak Demands, Using Distributed Storage Devices. Energies, 13(5), 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051024