Grinding Behaviour of Microwave-Irradiated Mining Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Microwave Treatment
2.3. Bond Ball Mill Grindability Test
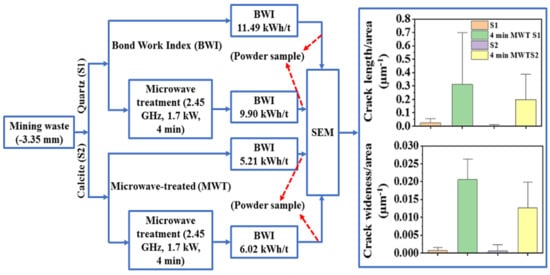
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. FESEM-EDX Characterization
3.2. Grindability
Bond Work Index
3.3. Mineralogy Analysis
3.3.1. FTIR Analysis
3.3.2. XRD Analysis
3.4. Morphology Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gokcen, H.S.; Cayirli, S.; Ucbas, Y.; Kayaci, K. The Effect of Grinding Aids on Dry Micro Fine Grinding of Feldspar. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 136, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, S.O.; Ahmed, H.A.M.; Ahmed, H.M.A. Methods of Ore Pretreatment for Comminution Energy Reduction. Minerals 2020, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisels, R.; Toifl, M.; Hartlieb, P.; Kuchar, F.; Antretter, T. Microwave Propagation and Absorption and Its Thermo-Mechanical Consequences in Heterogeneous Rocks. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 135, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvo, G.; Mudd, G.; Valero, A.; Valero, A. Decreasing Ore Grades in Global Metallic Mining: A Theoretical Issue or a Global Reality? Resources 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodall, W.R.; Scales, P.J.; Butcher, A.R. The use of QEMSCAN and Diagnostic Leaching in the Characterisation of Visible Gold in Complex Ores. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y. Characterisation and Beneficiation of Complex Ores for Sustainable Use of Mineral Resources: Refractory Gold Ore Beneficiation as an Example. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. Japan 2014, 20, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reemeyer, L. Ore sorting and Pre-Concentration-Potential to Boost Profit and Ease Risks. Available online: http://www.resourcefulpaths.com/blog/2016/12/6/ore-sorting-and-pre-concentration-potential-to-boost-profit-and-ease-risks (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Jankovic, A.; Valery, W.; Davis, E. Cement Grinding Optimisation. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makul, N.; Rattanadecho, P.; Agrawal, D.K. Applications of Microwave Energy in Cement and Concrete-A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.; Wang, C.; Nadolski, S. Energy-Efficient Comminution: Best Practices and Future Research Needs. In Energy Efficiency in the Minerals Industry Best Practices and Research Directions; Awuah-Offei, K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 197–211. ISBN 9783319541990. [Google Scholar]
- Fuerstenau, D.W. Grinding Aids. KONA Powder Part. J. 1995, 13, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, R.B.; Narasimhan, K.S.; Rao, T.C. Effect of Additives on Grinding of Magnetite Ore. Min. Met. Explor. 1991, 8, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, P. Effect of Magnetic Pulse Pretreatment on Grindability of a Magnetite Ore and Its Implication on Magnetic Separation. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 3108–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Zuo, W.; Manlapig, E. Characterisation of Pre-Weakening Effect on Ores by High Voltage Electrical Pulses Based on Single-Particle Tests. Miner. Eng. 2013, 50, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Shi, F.; Manlapig, E. Pre-Weakening of Mineral Ores by High Voltage Pulses. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, B.; Uddin, I.; Khan, S.; Ravi, V.; Selvraj, K.; Poddar, P.; Ahmad, A. Bio-Milling Technique for the Size Reduction of Chemically Synthesized BiMnO3 Nanoplates. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3910–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T.; Elmahdy, A.M.; Abdel-Khalek, N.A.; Gornostayev, S. Improvement of Phosphorus Removal from Iron Ore Using Combined Microwave Pretreatment and Ultrasonic Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaete-Garretón, L.F.; Vargas-Hermández, Y.P.; Velasquez-Lambert, C. Application of Ultrasound in Comminution. Ultrasonics 2000, 38, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshami, M.; Ahmadi, R. Effect of Thermal Treatment on Specific Rate of Breakage of Manganese Ore. J. Min. Environ. 2018, 9, 339–348. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, S.; Bilgen, S.; Ozbayoglu, G. Effect of Heat Treatment on Grindabilities of Celestite and Gypsum and Separation of Heated Mixture by Differential Grinding. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, A.J.; Mendonidis, P. Evaluating the Effect of Radio-Frequency Pre-Treatment on Granite Rock Samples for Comminution Purposes. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 120, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E. Comminution Behaviour of Microwave Heated Two Sulphide Copper Ores. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2010, 17, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Walkiewicz, J.W.; Clark, A.E.; McGill, S.L. Microwave-Assisted Grinding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobicki, E.R.; Boucher, D.; Forster, J.; Gillis, A.; Holcrof, G.; Fragomeni, D.E. Whiteman CANMICRO: Scaling up Microwave Technology for the Mining Industry. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Canadian Mineral Processors Operators Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 21–23 January 2020; pp. 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y. Technical Amenability Study of Laboratory-Scale Sensor Based Ore Sorting on a Missippi Valley Type Lead-Zinc Ore. Master’s Thesis, Mining Engineering, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bobicki, E.R.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Microwave Treatment of Ultramafic Nickel Ores: Heating Behavior, Mineralogy, and Comminution Effects. Minerals 2018, 8, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T.; Mattila, R. Thermally Assisted Liberation of High Phosphorus Oolitic Iron Ore: A Comparison between Microwave and Conventional Furnaces. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sahoo, B.K.; De, S.; Kar, D.D.; Chakraborty, S.; Meikap, B.C. Iron Ore Grindability Improvement by Microwave Pre-Treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T.; Abdel-Khalek, N.; El-Aref, M.; Elmanawi, A.E.-H.; Nasr, M.; Elmahdy, A. Microwave Assisted Liberation of High Phosphorus Oolitic Iron Ore. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2014, 2, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingman, S.W.; Vorster, W.; Rowson, N.A. The Influence of Mineralogy on Microwave Assisted Grinding. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, C.; Jordens, A.; Maloney, C.; Langlois, R.; Waters, K.E. Effect of Microwave Radiation on the Processing of Cu-Ni Sulphide Ore. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 94, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorster, W.; Rowson, N.A.; Kingman, S.W. The Effect of MICROWAVE Radiation Upon the Processing of Neves Corvo copper Ore. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2001, 63, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, A.R.; Jones, D.A.; Plint, S.; Kingman, S.W. Increasing the Grind Size for Effective Liberation and Flotation of a Porphyry Copper Ore by Microwave Treatment. Miner. Eng. 2016, 94, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kamath, B.P.; Ramarao, V.V.; Mohanty, D.B. Microwave Energy Aided Mineral Comminution. In Proceedings of the International Seminar on Mineral Processing Technology, Chennai, India, 8–10 March 2006; pp. 398–404. [Google Scholar]
- Glencore, C. XPS: A Key Team Member for the Crush It! Challenge. Available online: https://www.glencore.ca/en/Media-and-insights/Insights/XPS-A-Key-Team-Member-for-the-Crush-It-Challenge (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Mejeoumov, G.G. Improved Cement Quality and Grinding Efficiency by Means of Closed Mill Circuit Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Civil Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fall, M.; Yakovlev, V.; Sahi, C.; Baranova, I.; Bowers, J.; Esquenazi, G. Energy Efficient Microwave Hybrid Processing of Lime for Cement, Steel, and Glass Industries; Ceralink Inc.: Troy, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, B.B.; Panda, T.; Dash, S.; Mustakim, S.M. Phase Changes During Microwave Sintering of Flyash. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 4131–4136. [Google Scholar]
- Hartlieb, P.; Grafe, B. Experimental Study on Microwave Assisted Hard Rock Cutting of Granite. BHM 2017, 162, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Forssberg, E.; Svensson, M. Microwave Assisted COMMINUTION and Liberation of Minerals. In Mineral Processing on the Verge of the 21st Century; Özbayoğlu, G., Hoşten, Ç., Atalay, M.Ü., Hiҫyılmaz, C., Arol, A.İ., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; p. 753. ISBN 90 5809 172 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bilen, C. Microwave Assisted Limestone Grinding. Part. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Scanning Electron Microscopy: Principle and Applications in Nanomaterials Characterization. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Sharma, S.K., Verma, D.S., Khan, L.U., Kumar, S., Khan, S.B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 113–145. ISBN 97833199295452. [Google Scholar]
- Milinovic, J.; Dias, Á.A.; Janeiro, A.I.; Pereira, M.F.; Martins, S.; Petersen, S.; Barriga, F.J. XRD Identification of Ore Minerals during Cruises: Refinement of Extraction Procedure with Sodium Acetate Buffer. Minerals 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amana. Amana Commercial Microwave Oven Owner’s Manual; Amana: Benton Harbor, MI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Man, Y.T. Why is the Bond Ball Mill Grindability Test Done the Way It Is done? Eur. J. Miner. Process. Environ. Prot. 2002, 2, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bico, F.C. Bond Bico Ball Mill Manual; Bico Braun International: Burbank, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, F.C. Crushing and Grinding Calculations—Part I. Br. Chem. Eng. 1961, 6, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, A.R.; Buttress, A.J.; Jones, D.A.; Katrib, J.; Way, D.; Chenje, T.; Stoll, D.; Dodds, C.; Kingman, S.W. Towards Large Scale Microwave Treatment of Ores: Part 2-Metallurgical Testing. Miner. Eng. 2017, 111, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, J.B.; Tague, C.B. Conduct and Precision of Bond Grindability Testing. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkiewicz, J.W.; Kazonich, G.; McGill, S.L. Microwave Heating Characteristics of Minerals and Compounds. Miner. Metall. Process. 1988, 39, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lovás, M.; Znamenáčková, I.; Zubrik, A.; Kováčová, M.; Dolinská, S. The Application of Microwave Energy in Mineral Processing-A Review. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2011, 16, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, H.; Lu, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Infrared Emission Properties of a Kind of Natural Carbonate: Interpretation from Mineralogical Analysis. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2020, 47, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, R.T.; Blair, N.E.; Masterson, A.L. Carbonate Mineral Identification and Quantification in Sediment Matrices Using Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform Spectroscopy. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, M.B. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Determination of Shale Minerals in Reservoir Rocks. Niger. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 18, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saikia, B.J.; Parthasarathy, G.; Sarmah, N.C. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Estimation of Crystallinity in SiO2 Based Rocks. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Niaei, A.; Salari, D. Production of γ-Al2O3 from Kaolin. Open J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.Y.; Bradshaw, S.M. Bonded-Particle Modelling of Microwave-Induced Damage in Ore Particles. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Delle Piane, C.; Sarout, J. A New Computational Approach to Cracks Quantification from 2D Image Analysis: Application to Micro-Cracks Description in Rocks. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 66, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, J.; Bankole, S.A.; Zihms, S.; Lewis, H.; Couples, G.; Corbett, P.W.M. Quantifying Porosity Through Automated Image Collection and Batch Image Processing: Case study of three carbonates and an aragonite cemented sandstone. Geosciences 2017, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Mineral/ Ore | Country | Mass (kg) | Feed Size (mm) | MW Power (kW) | t (min) | Measured Property | (%) Impact on Measured Property | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetite | USA | 0.35 | −3.36 | 3.0 | 3.5 | RWI | +21.4 | [23] |
| Taconite | USA | 0.35 | −3.36 | 3.0 | 3.5 | RWI | +18.2 | [23] |
| Hematite | USA | 0.35 | −3.36 | 3.0 | 3.5 | RWI | +23.7 | [23] |
| Hematite | Egypt | 0.10 | - | 0.9 | 1.0 | −125 µm | +13.2 | [27] |
| Hematite | India | 0.50 | −19.05 +12.70 | 0.9 | 2.0 | −253 µm | +47.9 | [28] |
| Hematite | Egypt | 0.05 | −0.125 | 0.9 | 1.0 | −125 µm | +13.2 | [29] |
| Sulphide * | Portugal | 0.50 | −22.50 | 2.6 | 1.5 | RWI | +68.0 | [30] |
| Sulphide | Canada | 0.25 | 3.36 | 3.0 | 1.5 | RWI | +41.5 | [31] |
| Gold * | Guinea | 0.50 | 22.50 | 2.6 | 4.0 | RWI | +2.9 | [30] |
| Copper * | Portugal | 0.50 | - | 2.6 | 1.5 | RWI | +70.0 | [32] |
| Copper | Chile | 1.25 | −53.00 + 9.50 | 14.1 | - | RWI | +8.0 | [33] |
| Sphalerite * | India | 3.00 | −19.00 + 2.00 | 4.0 | 5.0 | RWI | +30.0 | [34] |
| Nickel | USA | 0.10 | −2.00 + 1.00 | 1.0 | 15.0 | RWI | +3.6 | [26] |
| Copper (1) | Turkey | 1.00 | −3.40 | 6.0 | 10.0 | BWI | −7.0 | [22] |
| Copper (2) | Turkey | 1.00 | −3.40 | 6.0 | 2.0 | BWI | +13.2 | [22] |
| Sample Status | Time (min) | Parameter | Run Number | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||
| Untreated (UT) | 0 (test 1) | No. Rev. | 100 | 229 | 231 | 216 | 199 | 190 | 191 | - |
| Gbp | 1.4836 | 1.4389 | 1.5198 | 1.6494 | 1.7349 | 1.7348 | 1.7352 | - | ||
| 0 (test 2) | No. Rev. | 100 | 200 | 227 | 214 | 199 | 197 | 190 | 191 | |
| Gbp | 1.5402 | 1.4623 | 1.5395 | 1.6496 | 1.6776 | 1.7363 | 1.7327 | 1.7320 | ||
| Microwave- treated (MWT) | 2 | No. Rev. | 100 | 288 | 234 | 209 | 192 | 185 | 185 | 185 |
| Gbp | 1.19 | 1.3885 | 1.5612 | 1.7052 | 1.7839 | 1.7884 | 1.7882 | 1.7868 | ||
| 4 | No. Rev. | 100 | 238 | 224 | 200 | 190 | 187 | 180 | 181 | |
| Gbp | 1.428 | 1.4743 | 1.6333 | 1.7359 | 1.7634 | 1.8335 | 1.8313 | 1.8307 | ||
| 6 | No. Rev. | 100 | 235 | 228 | 201 | 184 | 179 | 180 | - | |
| Gbp | 1.446 | 1.449 | 1.6287 | 1.7798 | 1.839 | 1.8388 | 1.8374 | - | ||
| Sample Status | Time (min) | Parameter | Run Number | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |||
| Untreated (UT) | 0 (test 1) | No. of Rev. | 100 | 95 | 87 | 88 | 75 | 61 | 63 |
| Gbp | 2.9121 | 3.2373 | 3.2378 | 3.7526 | 4.5372 | 4.5351 | 4.5357 | ||
| 0 (test2) | No. of Rev. | 100 | 95 | 86 | 85 | 73 | 62 | 63 | |
| Gbp | 2.9001 | 3.2786 | 3.3476 | 3.8405 | 4.5085 | 4.5169 | 4.5146 | ||
| Microwave- treated (MWT) | 2 | No. of Rev. | 100 | 78 | 71 | 71 | 74 | 71 | 71 |
| Gbp | 3.4421 | 3.9409 | 3.9946 | 3.8559 | 4.0159 | 4.0152 | 4.0128 | ||
| 4 | No. of Rev. | 100 | 83 | 75 | 75 | 74 | 73 | 73 | |
| Gbp | 3.2591 | 3.7616 | 3.7829 | 3.8377 | 3.9123 | 3.9114 | 3.9127 | ||
| 6 | No. of Rev. | 100 | 87 | 79 | 76 | 76 | 75 | 75 | |
| Gbp | 3.1391 | 3.5754 | 3.7211 | 3.7339 | 3.8161 | 3.8148 | 3.8155 | ||
| Sample | Test | P1 (μm) | Gbp (g/rev) | P80 (μm) | F80 (μm) | Wi (kWh/ton) | Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 106 | 1.7350 | 91.52 | 2444 | 11.49 | 0.087 |
| 2 | 106 | 1.7337 | 91.30 | 2444 | 11.48 | ||
| S2 | 1 | 106 | 4.5360 | 90.55 | 2365 | 5.21 | 0.384 |
| 2 | 106 | 4.5133 | 89.40 | 2365 | 5.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adewuyi, S.O.; Ahmed, H.A.M. Grinding Behaviour of Microwave-Irradiated Mining Waste. Energies 2021, 14, 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133991
Adewuyi SO, Ahmed HAM. Grinding Behaviour of Microwave-Irradiated Mining Waste. Energies. 2021; 14(13):3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133991
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdewuyi, Sefiu O., and Hussin A. M. Ahmed. 2021. "Grinding Behaviour of Microwave-Irradiated Mining Waste" Energies 14, no. 13: 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133991
APA StyleAdewuyi, S. O., & Ahmed, H. A. M. (2021). Grinding Behaviour of Microwave-Irradiated Mining Waste. Energies, 14(13), 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133991