Powering-up Wireless Sensor Nodes Utilizing Rechargeable Batteries and an Electromagnetic Vibration Energy Harvesting System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MicaZ System Architecture and Energy Consumption Features
2.1. Hardware and Software
2.2. Energy Consumption Model and Components
| Radio unit (mA) | MCU (mA) | Acceleration sensor | Light emitting diodes (LEDs) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX: 0 dBm | 17.2 | Active Idle Standby | 7.8 3.4 0.024 | ~0.5 mA | 2.2 mA each |
| TX: −1 dBm | 16.2 | ||||
| TX: −3 dBm | 15.5 | ||||
| TX: −5 dBm | 13.8 | ||||
| TX: −7 dBm | 12.5 | ||||
| TX: −10 dBm | 11 | ||||
| TX: −15 dBm | 10 | ||||
| TX: −25 dBm | 8.5 | ||||
| RX | 19 | ||||
2.3. MicaZ Operation Scenario

| Event | Current draw | Duration | Energy consumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCU check | 0.8 mA | 300 × 760 µs | 474 µJ |
| Reading acceleration sensor (10×) | 3.7 mA | 670 ms | 6.4 mJ |
| Radio power up | ~60 mA | 590 µs | 92 µJ |
| MCU activation | 7.8 mA | 760 µs | 15.41 µJ |
| Packet send from MCU to radio | 23.8 mA | 840 µs | 51.97 µJ |
| Listen channel | 22 mA | 7.16 ms | 410 µJ |
| Radio calibration and packet transmission | 13.2 mA | 960 µs | 32.94 µJ |
| Standby time | 24 µA | 59.091 s | 3.687 mJ |
| Total | – | 60 s | 11.162 mJ (186.04 µW) |
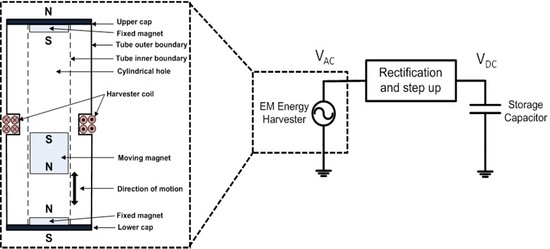
3. Electromagnetic Energy Harvester
3.1. Energy Harvester Implementation





3.2. Charging Characteristics of NiMH Rechargeable Battery




4. Energy Harvesting Wireless Sensor Node








| Task: Read acceleration (10×), average, transmit data execution time | Average current on the batteries | Battery lifetime increment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without energy harvester | With energy harvester (7.4 Hz and 0.4 g) | ||
| 1 s | 255 µA | 195 µA | 30% |
| 20 s | 99.7 µA | 38.1 µA | 161% |
| 1 min | 72 µA | 6.3 µA | 1042% |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelenbe, E.; Lent, R. Power-aware ad hoc cognitive packet networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2004, 2, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekbiyik, N.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. Energy efficient wireless unicast routing alternatives for machine-to-machine networks. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2011, 34, 1587–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Gunduz, D. Optimum power level for communications with interference. In Proceedings of the 24th Tyrrhenian International Workshop on Digital Communications-Green ICT (TIWDC), Genoa, Italy, 23–25 September 2013.
- Gelenbe, E.; Lent, R.; Douratsos, M. Choosing a local or remote cloud. In Proceedings of the Second IEEE Symposium on Network Cloud Computingand Applications NCCA2012, London, UK, 3–5 December 2012.
- Bacinoglu, B.T.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. Finite-horizon online transmission scheduling on an energy harvesting communication link with a discrete set of rates. J. Commun. Netw. 2014, 16, 300–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba-Herfeh, M.; UysalBiyikoglu, E. Optimization of feedback in a MISO downlink with energy harvesting users. In Proceedings of the European Wireless 2014, Barcelona, Spain, 14–16 May 2014.
- Gelenbe, E.; Gesbert, D.; Gunduz, D.; Kulah, H.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. Energy harvesting communication networks: Optimization and demonstration (the E-CROPS Project). In Proceedings of the 24th Tyrrhenian International Workshop on Digital Communications-Green ICT (TIWDC), Genoa, Italy, 23–25 September 2013.
- Guo, W.; Member, S.; Healy, W.M.; Zhou, M. Battery discharge characteristics of wireless sensors in building applications. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Beijing, China, 11–14 April 2012; pp. 133–138.
- Rao, R.; Vrudhula, S.; Rakhmatov, D. Battery Modeling for energy aware system design. Computer 2003, 36, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Morfopoulou, C. A framework for energy-aware routing in packet networks. Comput. J. 2011, 54, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alippi, C.; Galperti, C. An adaptive system for optimal solar energy harvesting in wireless sensor network nodes. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 55, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, M.; Morito, T. Solar biscuit: A battery-less wireless sensor network system for environmental monitoring applications. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Networked Sensing Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–28 June 2005.
- Barnett, R.E.; Liu, J.; Lazar, S. A RF to DC voltage conversion model for multi-stage rectifiers in UHF RFID transponders. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorcioni, S.; Larcher, L. An integrated rf energy harvester for UHF wireless powering applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Wireless Power Transfer (WPT), Perugia, Italy, 15–16 May 2013; pp. 92–95.
- Roundy, S.; Wright, P.K. A piezoelectric vibration based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, S.; Wright, P.K.; Rabaey, J. A study of low level vibrations as a power source for wireless sensor nodes. Comput. Commun. 2003, 26, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruse, Y.; Matsubara, N.; Mabuchi, K.; Izumi, M.; Suzuki, S. Electrostatic micro power generation from low-frequency vibration such as human motion. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galchev, T.; Aktakka, E.E.; Kim, H.; Najafi, K. A piezoelectric frequency-increased power generator for scavenging low-frequency ambient vibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE 23rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Hong Kong, China, 24–28 January 2010; pp. 1203–1206.
- Rahimi, A.; Zorlu, O.; Muhtaroglu, A.; Kulah, H. Fully self-powered electromagnetic energy harvesting system with highly efficient dual rail output. Sens. J. IEEE 2012, 12, 2287–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Seyedi, A.; Sikdar, B. An analytical approach to the design of energy harvesting wireless sensor nodes. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 4010–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooti, H.; Dang, N.; Mishra, D.; Bozorgzadeh, E. Energy budget management for energy harvesting embedded systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications (RTCSA), Seoul, Korea, 19–22 August 2012.
- Ramachandran, K.; Sikdar, B. A population based approach to model the lifetime and energy distribution in battery constrained wireless sensor networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2010, 28, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weddell, A.; Grabham, N.; Harris, N.; White, N. Optimal energy management policies for energy harvesting sensor nodes. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2008, 9, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Dondi, D.; Scorcioni, S.; Bertacchini, A.; Larcher, L.; Pavan, P. An autonomous wireless sensor network device powered by a RF energy harvesting system. In Proceedings of the IECON-38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 2557–2562.
- Jang, J.H.; Berdy, D.B.; Lee, J.; Peroulis, D.; Jung, B. A wireless condition monitoring system powered by a Sub-100 µW vibration energy harvester. IEEE Trans. Ciruits Syst. 2013, 60, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Namboothiri, P.G.; Sivalingam, K.M. Capacity analysis of multi-hop wireless sensor networks using multiple transmission channels: A case study using IEEE 802.15.4 based networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 35th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Denver, CO, USA, 10–14 October 2010; pp. 168–171.
- Crossbow. MTS/MDA Sensor Board Users Manual. Available online: http://www.xbow.com (accessed on 10 March 2014).
- Tinyos.net. TinyOS. Available online: http://www.tinyos.net (accessed on 10 March 2014).
- Baghaee, S.; Gurbuz, S.Z.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. Application and modeling of a magnetic WSN for target localization. In Proceedings of the UKSim 15th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation, Cambridge, UK, 10–12 April 2013; pp. 687–692.
- Crossbow. MPR/MIB User’s Manual. Available online: http://www.xbow.com (accessed on 10 March 2014).
- Uluşan, H.; Gharehbaghi, K.; Zorlu, Ö.; Muhtaroğlu, A.; Külah, H. A fully-integrated and battery-free interface electronics for low voltage electromagnetic energy harvesters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Zorlu, Ö.; Muhtaroğlu, A.; Külah, H. A compact electromagnetic vibration harvesting system with high performance interface electronics. Eurosensors XXV Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaee, S.; Ulusan, H.; Chamanian, S.; Zorlu, O.; Kulah, H.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. Towards a vibration energy harvesting wsn demonstration testbed. In Proceedings of the 24th Tyrrhenian International Workshop on Digital Communications-Green ICT (TIWDC), Genoa, Italy, 23–25 September 2013; pp. 1–6.
- NXP. PMEG2005EL PMEG2005AEL datasheet. Available online: http://www.nxp.com (accessed on 30 January 2014).
- Energizer.com. Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH). 7323, 1–16. Available online: http://www.energizer.com (accessed on 30 January 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chamanian, S.; Baghaee, S.; Ulusan, H.; Zorlu, Ö.; Külah, H.; Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. Powering-up Wireless Sensor Nodes Utilizing Rechargeable Batteries and an Electromagnetic Vibration Energy Harvesting System. Energies 2014, 7, 6323-6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en7106323
Chamanian S, Baghaee S, Ulusan H, Zorlu Ö, Külah H, Uysal-Biyikoglu E. Powering-up Wireless Sensor Nodes Utilizing Rechargeable Batteries and an Electromagnetic Vibration Energy Harvesting System. Energies. 2014; 7(10):6323-6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en7106323
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamanian, Salar, Sajjad Baghaee, Hasan Ulusan, Özge Zorlu, Haluk Külah, and Elif Uysal-Biyikoglu. 2014. "Powering-up Wireless Sensor Nodes Utilizing Rechargeable Batteries and an Electromagnetic Vibration Energy Harvesting System" Energies 7, no. 10: 6323-6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en7106323
APA StyleChamanian, S., Baghaee, S., Ulusan, H., Zorlu, Ö., Külah, H., & Uysal-Biyikoglu, E. (2014). Powering-up Wireless Sensor Nodes Utilizing Rechargeable Batteries and an Electromagnetic Vibration Energy Harvesting System. Energies, 7(10), 6323-6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/en7106323