A New Approach for Modeling Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Rotors Using Electrical Equivalent Circuit Analogy: Basis of Theoretical Formulations and Model Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Growing Interest for Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
1.2. The Necessity of a New Modeling Approach for Darrieus-Type Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
| Model | Main features | Advantages | Shortcomings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Momentum or blade element model |
|
|
|
| Vortex model |
|
|
|
| Cascade model |
|
|
|
| Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model |
|
|
|
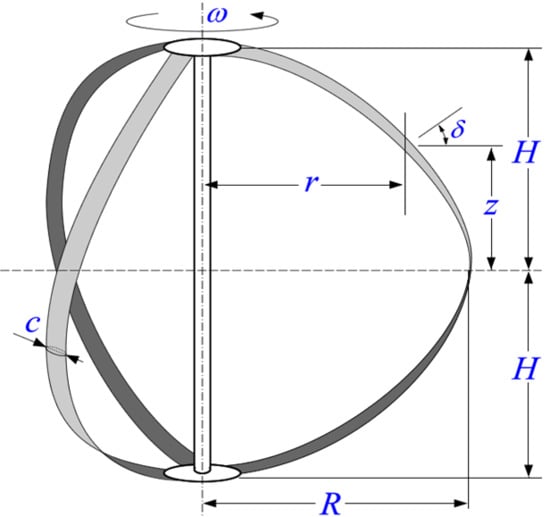
2. Theory: Working Principle of Darrieus-Type Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)


3. Method and Model Construction
3.1. The Mechanical-Electrical Analogy Approach
3.2. Wind Flow as an Electric Current Source





3.3. Single-Blade Electrical Equivalent Circuit (Normal, Tangential, Lift and Drag Coefficients)

3.3.1. Writing Normal, Tangential, Lift and Drag Coefficients as Complex Numbers

3.3.2. Normal, Tangential, Lift and Drag Impedances

- -
- is the aerodynamic resistance of the blade element;
- -
- is the equivalent aerodynamic coefficient of the blade;
- -
- is the cord surface of the blade.


3.3.3. Total Impedance and Equivalent Electrical Circuit of a Single Blade

4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Electrical Equivalent Model of a Single Blade

4.2. Simulations
| Parameter | Value/spécification |
|---|---|
| Number of blades | 1 |
| Aerofoil section | NACA0012 |
| Average blade Reynolds number | 40,000 |
| Aerofoil chord length | 9.14 cm |
| Rotor tip speed | 45.7 cm/s |
| Tip speed ratio | 5 |
| Chord-to-radius ratio | 0.15 |
4.2.1. Variations of Coefficients and Equivalent Electric Components with the Angle of Attack



4.2.2. Variations of Coefficients and Equivalent Electric Components with the Rotational Angle of the Blade




4.2.3. Cross Validation and Comparative Analysis


5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheurich, F.; Brown, R.E. Modelling the aerodynamics of vertical-axis wind turbines in unsteady wind conditions. Wind Energy 2013, 16, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howell, R.; Qin, N.; Edwards, J.; Durrani, N. Wind tunnel and numerical study of a small vertical axis wind turbine. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, S.; Bernhoff, H.; Leijon, M. Evaluation of different turbine concepts for wind power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.R.; Grandi, G.; Benini, E. Numerical analysis of the performance of the DU91-W2-250 airfoil for straight-bladed vertical-axis wind turbine application. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 6, 742–747. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Bussel, G.; Kuik, G.V. 2D CFD Simulation of Dynamic Stall on a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Verification and Validation with PIV Measurements. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007; pp. 1–11.
- Tjiu, W.; Marnoto, T.; Mat, S.; Ruslan, M.H.; Sopian, K. Darrieus vertical axis wind turbine for power generation I: Assessment of Darrieus VAWT configurations. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjiu, W.; Marnoto, T.; Mat, S.; Ruslan, M.H.; Sopian, K. Darrieus vertical axis wind turbine for power generation II: Challenges in HAWT and the opportunity of multi-megawatt Darrieus VAWT development. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, A.; Ferrara, G.; Ferrari, L. Design guidelines for H-Darrieus wind turbines: Optimization of the annual energy yield. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 89, 690–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, K.R. The Near Wake Structure of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Including the Development of a 3D Unsteady Free-Wake Panel Method for VAWTs. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carrigan, T.J.; Dennis, B.H.; Han, Z.X.; Wang, B.P. Aerodynamic shape optimization of a vertical-axis wind turbine using differential evolution. ISRN Renew. Energy 2011, 2012, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzafame, R.; Mauro, S.; Messina, M. 2D CFD modeling of H-Darrieus wind turbines using a transition turbulence model. Energy Procedia 2014, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakoua, P.; Wamkeue, R.; Tameghe, T.A.; Ekemb, G. A Review of Concepts and Methods for Wind Turbines Condition Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2013 World Congress on Computer and Information Technology (WCCIT), Sousse, Tunisia, 22–24 June 2013; pp. 1–9.
- Tchakoua, P.; Wamkeue, R.; Ouhrouche, M.; Slaoui-Hasnaoui, F.; Tameghe, T.; Ekemb, G. Wind turbine condition monitoring: State-of-the-art review, new trends, and future challenges. Energies 2014, 7, 2595–2630. [Google Scholar]
- Tchakoua, P.; Wamkeue, R.; Slaoui-Hasnaoui, F.; Tameghe, T.A.; Ekemb, G. New Trends and Future Challenges for Wind Turbines Condition Monitoring. In Proceeding of the 2013 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), Nha Trang, Vietnam, 25–28 November 2013; pp. 238–245.
- Chen, Y.; Lian, Y. Numerical investigation of vortex dynamics in an H-rotor vertical axis wind turbine. Eng. Appl. Comp. Fluid Mech. 2015, 9, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, K.; Ju, W. Darrieus vertical axis wind turbine: Basic research methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschivoiu, I. Double-multiple streamtube model for Darrieus in turbines. Wind Turbine Dyn. 1981, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.H. Performance investigation of H-rotor Darrieus turbine with new airfoil shapes. Energy 2012, 47, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, C.; Leclerc, C.; Paraschivoiu, I. Appropriate dynamic-stall models for performance predictions of VAWTs with NLF blades. Int. J. Rotat. Mach. 1998, 4, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyachuk, E.; Goude, A. Simulating dynamic stall effects for vertical Axis wind turbines applying a double multiple Streamtube model. Energies 2015, 8, 1353–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.M.; Gardiner, N.; Sutton, R.; Dyson, P.K. Hydrodynamic analysis models for the design of Darrieus-type vertical-axis marine current turbines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2011, 225, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.J. Numerical Simulation of a Cross Flow Marine Hydrokinetic Turbine. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Ting, D.S.K.; Fartaj, A. Aerodynamic models for Darrieus-type straight-bladed vertical axis wind turbines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1087–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beri, H.; Yao, Y. Double multiple Streamtube model and numerical analysis of vertical axis wind turbine. Energy Power Eng. 2011, 3, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Liang, Y.B.; Liu, X.H.; Jiao, Q.F.; Guo, J. Aerodynamic performance prediction of straight-bladed vertical axis wind turbine based on CFD. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, M.M.A.; Hayat, N.; Farooq, A.U.; Ali, Z.; Jamil, S.R.; Hussain, Z. Vertical axis wind turbine—A review of various configurations and design techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1926–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J. The Influence of Aerodynamic Stall on the Performance of Vertical Axis Wind Turbines. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alaimo, A.; Esposito, A.; Messineo, A.; Orlando, C.; Tumino, D. 3D CFD analysis of a vertical axis wind turbine. Energies 2015, 8, 3013–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkinderen, E.; Imam, B. A simplified dynamic model for mast design of H-Darrieus vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs). Eng. Struct. 2015, 100, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.M.; Akimoto, H.; Hara, Y. Comparative CFD analysis of vertical axis wind turbine in upright and tilted configuration. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmans, H.A.C. Equivalent circuit representation of electromechanical transducers: I. Lumped-parameter systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1996, 6, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W. An electromechanical representation of a piezoelectric crystal used as a transducer. Proc. Inst. Radio Eng. 1935, 23, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Tilmans, H.A.C. Equivalent circuit representation of electromechanical transducers: II. Distributed-parameter systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1997, 7, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakati, S.M. Modeling and Controller Design of a Wind Energy Conversion System Including a Matrix Converter. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Ko, H. Modeling and control of PMSG-based variable-speed wind turbine. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowy, B.S.; Salameh, Z.M. Dynamic response of a stand-alone wind energy conversion system with battery energy storage to a wind gust. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 1997, 12, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarue, P.; Bouscayrol, A.; Tounzi, A.; Guillaud, X.; Lancigu, G. Modelling, control and simulation of an overall wind energy conversion system. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slootweg, J.G.; de Haan, S.W.H.; Polinder, H.; Kling, W.L. General model for representing variable speed wind turbines in power system dynamics simulations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyent-Ferré, A.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Sumper, A.; Sala, M.; Mata, M. Modeling and control of the doubly fed induction generator wind turbine. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2010, 18, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolik, S.M. Modelling and Analysis of Variable Speed Wind Turbines with Induction Generator during Grid Fault. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Danmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Perdana, A. Dynamic Models of Wind Turbines; Chalmers University of Technology: Göteborg, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich, F.; Fletcher, T.M.; Brown, R.E. Simulating the aerodynamic performance and wake dynamics of a vertical-axis wind turbine. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paraschivoiu, I. Wind Turbine Design: With Emphasis on Darrieus Concept; Polytechnic International Press: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Claessens, M. The Design and Testing of Airfoils for Application in Small Vertical Axis Wind Turbines. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ajedegba, J.O.; Naterer, G.; Rosen, M.; Tsang, E. Effects of Blade Configurations on Flow Distribution and Power Output of a Zephyr Vertical Axis Wind Turbine. In Proceedings of the 3rd IASME/WSEAS International Conference on Energy & Environment, Stevens Point, WI, USA, 23 February 2008; pp. 480–486.
- Camporeale, S.M.; Magi, V. Streamtube model for analysis of vertical axis variable pitch turbine for marine currents energy conversion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2000, 41, 1811–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurich, F. Modelling the Aerodynamics of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chandramouli, S.; Premsai, T.; Prithviraj, P.; Mugundhan, V.; Velamati, R.K. Numerical analysis of effect of pitch angle on a small scale vertical axis wind turbine. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2014, 4, 929–935. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.W. Modeling Engineering Systems: PC-Based Techniques and Design Tools; LLH Technology Publishing: Eagle Rock, VA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, N.; Breedveld, P. The physical basis of analogies in network models of physical system dynamics. Simul. Ser. 1999, 31, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Firestone, F.A. A new analogy between mechanical and electrical systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1933, 4, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, H.F. Dynamical Analogies; D. Van Nostrand Company, Inc.: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Firestone, F.A. The mobility method of computing the vibration of linear mechanical and acoustical systems: Mechanical-electrical analogies. J. Appl. Phys. 1938, 9, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, J.A.; Alvarez-Caldas, C.; San, J.L. Analysis of Dynamic Systems Using Bond. Graph. Method through SIMULINK; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, R.H. Mechatronics: An Introduction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gilder, J.W.; Schmidt, R.R. Airflow Uniformity through Perforated Tiles in a Raised-Floor Data Center. In Proceedings of the ASME 2005 Pacific Rim Technical Conference and Exhibition on Integration and Packaging of MEMS, NEMS, and Electronic Systems collocated with the ASME 2005 Heat Transfer Summer Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–22 July 2005; pp. 493–501.
- Pugh, L.G.C.E. The influence of wind resistance in running and walking and the mechanical efficiency of work against horizontal or vertical forces. J. Physiol. 1971, 213, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, F.; Schmid, G.B. Analogy between mechanics and electricity. Eur. J. Phys. 1985, 6, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley, R.M. A resistance approach to analysis of natural ventilation airflow networks. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1997, 67, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Deglaire, P. Analytical Aerodynamic Simulation Tools for Vertical Axis Wind Turbines. Ph.D. Thesis, Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis, Uppsala, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goude, A. Fluid Mechanics of Vertical Axis Turbines: Simulations and Model Development. Ph.D. Thesis, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dyachuk, E.; Goude, A.; Bernhoff, H. Dynamic stall modeling for the conditions of vertical Axis wind turbines. AIAA J. 2014, 52, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.E.; Walker, S.N.; Lissaman, P.B.S. Aerodynamics of the Darrieus rotor. J. Aircr. 1976, 13, 1023–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goude, A.; Lundin, S.; Leijon, M. A Parameter Study of the Influence of Struts on the Performance of a Vertical-Axis Marine Current Turbine. In Proceedings of the 8th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC09), Uppsala, Sweden, 7–10 September 2009; pp. 477–483.
- Wekesa, D.W.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Danao, A.M. Influence of operating conditions on unsteady wind performance of vertical axis wind turbines operating within a fluctuating free-stream: A numerical study. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 135, 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Shires, A. Development and evaluation of an aerodynamic model for a novel vertical axis wind turbine concept. Energies 2013, 6, 2501–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antheaume, S.; Maître, T.; Achard, J. Hydraulic Darrieus turbines efficiency for free fluid flow conditions versus power farms conditions. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2186–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butbul, J.; MacPhee, D.; Beyene, A. The impact of inertial forces on morphing wind turbine blade in vertical axis configuration. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 91, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamati, F. Étude Numérique d’une Éolienne Hybride Asynchrone. Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnique Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, N.C.; Melìcio, R.; Matias, J.C.O.; Catalao, J.P.S. Self-Start Performance Evaluation in Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbines: Methodology and Computational Tool Applied to Symmetrical Airfoils. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ’11), Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 13–15 April 2011.
- Patel, M.V.; Chaudhari, M.H. Performance Prediction of H-Type Darrieus Turbine by Single Stream Tube Model for Hydro Dynamic Application. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, I.H.; Von Doenhoff, A.E. Theory of Wing Sections, Including a Summary of Airfoil Data; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.; Nahon, M. Dynamics modeling and performance evaluation of an autonomous underwater vehicle. Ocean Eng. 2004, 31, 1835–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, X.; Denny, A.G.; Fan, M.; Wu, J. Post-stall flow control on an airfoil by local unsteady forcing. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 371, 21–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.R.; Fedrigo, A.; Benini, E. Effect of dynamic stall, finite aspect ratio and streamtube expansion on VAWT performance prediction using the BE-M model. Int. J. Eng. Phys. Sci. 2012, 6, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Tala, H.; Patel, H.; Sapra, R.R.; Gharte, J.R. Simulations of small scale straight blade Darrieus wind turbine using latest CAE techniques to get optimum power output. Int. J. Adv. Found. Res. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, H.L.; Mutmansky, J.M.; Ramani, R.V.; Wang, Y. Mine Ventilation and Air Conditioning; John Wiley & Sons: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley, R. Indoor wind speed coefficients for estimating summer comfort. Int. J. Vent. 2006, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, M.J. Ventilation network analysis. In Subsurface Ventilation and Environmental Engineering; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 209–240. [Google Scholar]
- Acuña, E.I.; Lowndes, I.S. A review of primary mine ventilation system optimization. Interfaces 2014, 44, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, J.C.; Burrows, F.M. The dispersal effectiveness of the achene—Pappus units of selected Compositae in steady winds with convection. New Phytol. 1973, 72, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, H.M.; de Groot, G.; Savelberg, H.H.; Vervoorn, K.; Hollander, A.P.; van Ingen Schenau, G.J. Active drag related to velocity in male and female swimmers. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, L.G. The relation of oxygen intake and speed in competition cycling and comparative observations on the bicycle ergometer. J. Physiol. 1974, 241, 795–808. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.C.; Milliken, D.L.; Cobb, J.E.; McFadden, K.L.; Coggan, A.R. Validation of a mathematical model for road cycling power. J. Appl. Biomech. 1998, 14, 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyoto, H.; Tosha, K. Effect of Peened Surface Characteristics on Flow Resistance. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Shot Peening, Tokyo, Japan, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 535–540.
- Crawford, C. Advanced Engineering Models for Wind Turbines with Application to the Design of a Coning Rotor Concept. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi-Amin, M.; Ghadiri, B.; Abdalla, M.M.; Haddadpour, H.; de Breuker, R. Continuous-time state-space unsteady aerodynamic modeling based on boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2012, 36, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldahl, R.E.; Klimas, P.C. Aerodynamic Characteristics of Seven Symmetrical Airfoil Sections through 180-Degree Angle of attack for Use in Aerodynamic Analysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbines; Technical Report for Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Critzos, C.C.; Heyson, H.H.; Boswinkle, R.W. Aerodynamic Characteristics of NACA 0012 Airfoil Section at Angles of Attack from 0 Degree to 180 Degree; Technical Report for National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Langley Aeronautical Lab: Langley Field, VA, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Miley, S.J. A Catalog of Low Reynolds Number Airfoil Data for Wind Turbine Applications; Technical Rockwell International Corp: Golden, CO, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Timmer, W.A. Aerodynamic Characteristics of Wind Turbine Blade Airfoils at High Angles-of-Attack. In Proceedings of the 3rd EWEA Conference-Torque 2010: The Science of making Torque from Wind, Heraklion, Greece, 28–30 June 2010.
- Rathi, D. Performance Prediction and Dynamic Model Analysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Blades with Aerodynamically Varied Blade Pitch. Master’s Thesis, NC State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tchakoua, P.; Wamkeue, R.; Ouhrouche, M.; Tameghe, T.A.; Ekemb, G. A New Approach for Modeling Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Rotors Using Electrical Equivalent Circuit Analogy: Basis of Theoretical Formulations and Model Development. Energies 2015, 8, 10684-10717. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81010684
Tchakoua P, Wamkeue R, Ouhrouche M, Tameghe TA, Ekemb G. A New Approach for Modeling Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Rotors Using Electrical Equivalent Circuit Analogy: Basis of Theoretical Formulations and Model Development. Energies. 2015; 8(10):10684-10717. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81010684
Chicago/Turabian StyleTchakoua, Pierre, René Wamkeue, Mohand Ouhrouche, Tommy Andy Tameghe, and Gabriel Ekemb. 2015. "A New Approach for Modeling Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Rotors Using Electrical Equivalent Circuit Analogy: Basis of Theoretical Formulations and Model Development" Energies 8, no. 10: 10684-10717. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81010684
APA StyleTchakoua, P., Wamkeue, R., Ouhrouche, M., Tameghe, T. A., & Ekemb, G. (2015). A New Approach for Modeling Darrieus-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Rotors Using Electrical Equivalent Circuit Analogy: Basis of Theoretical Formulations and Model Development. Energies, 8(10), 10684-10717. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81010684