Individual Rubber Tree Segmentation Based on Ground-Based LiDAR Data and Faster R-CNN of Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
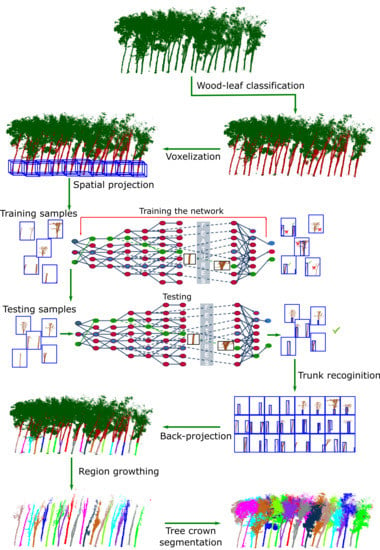
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Laser Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Faster R-CNN
2.4.1. The Pre-Training CNN Model
2.4.2. Training Process of the RPN Network
2.4.3. The Training of the Fast R-CNN Detection Network
2.4.4. The Loss Function of the Training Process
2.4.5. The Testing Process for Using Faster R-CNN to Recognise Trunks
3. Results
3.1. Testing the Faster R-CNN Model
3.2. Realising Individual Tree Segmentation
4. Discussion
4.1. The Advantages of Our Approach
4.2. Potential Improvement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, G.; Li, Y.; Lesueur, D.; Wu, Z.; Xie, G. Seasonal changes impact soil bacterial communities in a rubber plantation on Hainan Island, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Xie, G. Estimation of rubber stand age in typhoon and chilling injury afflicted area with Landsat TM data: A case study in Hainan Island, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 274, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.-T.; Shi, Z.; Li, M.-F.; Luo, W.; Cha, Z.-Z. A robust method to estimate foliar phosphorus of rubber trees with hyperspectral reflectance. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 126, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Pan, Z.; Li, P. A 3D Point Cloud Filtering Method for Leaves Based on Manifold Distance and Normal Estimation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; Cao, L.; An, F.; Chen, B.; Xue, L.; Li, W.; Pincebourde, S.; Smith, M.J.; Eichhorn, M.P. Simulation of multi-platform LiDAR for assessing total leaf area in tree crowns. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyyppä, J.; Kelle, O.; Lehikoinen, M.; Inkinen, M. A segmentation-based method to retrieve stem volume estimates from 3-D tree height models produced by laser scanners. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Q.; Jakubowski, M.K.; Kelly, M. A new method for segmenting individual trees from the lidar point cloud. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wei, C.; Xu, W. Adaptive Mean Shift-Based Identification of Individual Trees Using Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.E.; Kwak, D.A.; Park, T.; Lee, W.K.; Yoo, S. Estimating Crown Variables of Individual Trees Using Airborne and Terrestrial Laser Scanners. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2346–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, Y.; Quackenbush, L.J. A review of methods for automatic individual tree-crown detection and delineation from passive remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4725–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, L.; Cook, B.; Hurtt, G.; Dubayah, R. An efficient, multi-layered crown delineation algorithm for mapping individual tree structure across multiple ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Mallet, C.; Brédif, M. Detection, segmentation and localization of individual trees from MMS point cloud data. In Proceedings of the Geobia 2016: Synergies & Solutions Conference, Enschede, The Netherlands, 14–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mongus, D.; Žalik, B. An efficient approach to 3D single tree-crown delineation in LiDAR data. Isprs J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, J.; Maltamo, M.; Hyyppä, J.; Yu, X. Adaptive methods for individual tree detection on airborne laser based canopy height model. Int. Arch. Photogram. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2004, 36, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Thomson, G.; Lo, C.S.; Yang, M.S.J.P.E.; Sensing, R. A Multi-level Morphological Active Contour Algorithm for Delineating Tree Crowns in Mountainous Forest. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Hu, B.; Noland, T.; Li, J. An individual tree crown delineation method based on multi-scale segmentation of imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 70, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, W.; Flanagan, J. A bottom-up approach to segment individual deciduous trees using leaf-off lidar point cloud data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, K.; Holmgren, J.; Olsson, H. Tree Stem and Height Measurements using Terrestrial Laser Scanning and the RANSAC Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4323–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindberg, E.; Olofsson, K.; Olsson, H. Estimation of stem attributes using a combination of terrestrial and airborne laser scanning. Eur. J. For. Res. 2012, 131, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Cheng, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, M. Segmentation of Individual Trees From TLS and MLS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Yue, W.; Shu, S.; Tan, W.; Hu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, H. A Voxel-Based Method for Automated Identification and Morphological Parameters Estimation of Individual Street Trees from Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 584–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, T.; Jiang, K.; Hou, H.; An, F.; Chen, B.; Jiang, A.; Li, W.; Xue, L. Rubber Tree Crown Segmentation and Property Retrieval using Ground-Based Mobile LiDAR after Natural Disturbances. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppä, J.; Jaakkola, A.; Yu, X. Three-level frame and RD-schematic algorithm for automatic detection of individual trees from MLS point clouds. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 33, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, H.X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Fu, L. Piecewise Linear Regression Based on Plane Clustering. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29845–29855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, B. Plane-Gaussian artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2011, 21, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Sui, Z. Intelligent fault detection of high voltage line based on the Faster R-CNN. Measurement 2019, 138, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, M.P.; Atkinson, J.A.; Townsend, A.J.; Wilson, M.H.; Griffiths, M.; Jackson, A.S.; Bulat, A.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Wells, D.M.; Murchie, E.H.; et al. Deep machine learning provides state-of-the-art performance in image-based plant phenotyping. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Oda, T.; Ikeda, M.; Barolli, L. A Vegetable Category Recognition System Using Deep Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th International Conference on Innovative Mobile and Internet Services in Ubiquitous Computing (IMIS), Fukuoka, Japan, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, J.; Gui, G.; Hao, X.; Gao, W.; Wang, M. Deep Learning Based Improved Classification System for Designing Tomato Harvesting Robot. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 67940–67950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Su, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, F.; Hu, T.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Deep Learning: Individual Maize Segmentation From Terrestrial Lidar Data Using Faster R-CNN and Regional Growth Algorithms. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Hughes, D.P.; Salathe, M. Using Deep Learning for Image-Based Plant Disease Detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierzchała, M.; Giguère, P.; Astrup, R. Mapping forests using an unmanned ground vehicle with 3D LiDAR and graph-SLAM. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.; Xie, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, G. An Easy-to-Use Airborne LiDAR Data Filtering Method Based on Cloth Simulation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; An, F.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Cao, L.; Xue, L. A Novel Approach for Retrieving Tree Leaf Area from Ground-Based LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Song, Z.; Zeng, W. A model for fine-grained vehicle classification based on deep learning. Neurocomputing 2017, 257, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Wang, D. A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.; Kai, L.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, A.-V.; Truong-Hong, L.; Laefer, D.F.; Bertolotto, M. Octree-based region growing for point cloud segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A Probabilistic Interpretation of Precision, Recall and F-Score, with Implication for Evaluation. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Zheng, X. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Cao, L.; Xue, L.; Chen, B.; An, F.; Yun, T. Extraction of Leaf Biophysical Attributes Based on a Computer Graphic-based Algorithm Using Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Individual tree crown delineation using localized contour tree method and airborne LiDAR data in coniferous forests. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, D.; Wimmer, M. Efficient tree modeling from airborne LiDAR point clouds. Comput. Graph. 2017, 67, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Yang, B.; Dong, Z.; Shaker, A. A new method for 3D individual tree extraction using multispectral airborne LiDAR point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiya, A.M.; Nidamanuri, R.R.; Krishnan, R. Individual tree detection from airborne laser scanning data based on supervoxels and local convexity. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-H.; Ehsani, R.; Toudeshki, A.; Zou, X.-J.; Wang, H.-J. Detection of citrus fruit and tree trunks in natural environments using a multi-elliptical boundary model. Comput. Ind. 2018, 99, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Feng, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, P. Applicability of personal laser scanning in forestry inventory. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Chen, B.; Xue, L.; Chen, F. Quantitative Inversion for Wind Injury Assessment of Rubber Trees by Using Mobile Laser Scanning. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 3452–3463. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Ye, Q.; Fan, X. Infinite norm large margin classifier. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2018, 10, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Cheng, M.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, J. Tree Classification in Complex Forest Point Clouds Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Meng, W.; Xi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Lu, L.; Zhang, X. 3D Point Cloud Analysis and Classification in Large-Scale Scene Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 55649–55658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Deep Neural Network With Spatial Pooling (DNNSP) for 3-D Point Cloud Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4594–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, J.; An, W. Learning Multi-View Representation With LSTM for 3-D Shape Recognition and Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wei, T.; Peng, C.; Du, P. A Fast Face Recognition System Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 8–9 December 2018; pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kwak, S.; Ko, B.C. Fast Pedestrian Detection in Surveillance Video Based on Soft Target Training of Shallow Random Forest. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12415–12426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Device | Technical Parameters | Technical Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Velodyne HDL-32E | Scanner weight | <2 kg |
| Operating temperature | −10 °C to +60 °C | |
| Field of view | Horizontal: 0° to 360° | |
| Vertical: −30.67° to +10.67° | ||
| Scanning accuracy | <2 cm | |
| Points per second | Up to 700,000 | |
| Laser wavelength | 905 nm | |
| Scanning frequency | 10 Hz |
| Rubber Tree Plot 1 (PR107) | Rubber Tree Plot 2 (CATAS7-20-59) | Rubber Tree Plot 3 (CATAS8-7-9) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of scanned points/number of trees | 5,387,676/180 | 7,097,159/256 | 8,820,133/276 | |
| Average tree height (m) | 15.97 | 17.11 | 16.05 | |
| Training sites | Number of scanned points/trees number | 3,711,510/124 | 4,879,297/176 | 6,039,974/189 |
| Length/width/height of voxels (m) | 8/3/5.62 | 8/3/8.40 | 8/3/9.35 | |
| Number of generated deep images | 233 | 268 | 301 | |
| Testing sites | Number of scanned points/trees number | 1,676,166/56 | 2,217,862/80 | 2,780,159/87 |
| Number of generated deep images | 90 | 126 | 143 | |
| Number of Trees/Images | Number of Segmented Trees | TP | FP | FN | r1 | P2 | F3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest plot 1 (PR 107) | 56/90 | 56 | 56 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Forest plot 2 (CATAS 7-20-59) | 80/126 | 78 | 78 | 1 | 2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Forest plot 3 (CATAS 8-7-9) | 87/143 | 85 | 85 | 1 | 2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Overall | 223/359 | 219 | 219 | 3 | 4 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Training Sites | Testing Sites | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Trees/Images | Number of Trees/Images | Number of Detected Trees | TP | FP | FN | r1 | P2 | F3 | |
| a: The images contains only one complete tree trunk | 237/474 | 114/228 | 114 | 114 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| b: The images contains two complete tree trunks | 62/60 | 22/22 | 21 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.97 |
| c: Multiple trunks with branches appear in a voxel | 69/94 | 39/48 | 39 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| d: The information of the trunk is occluded by leaves or branches | 36/56 | 14/18 | 14 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| e: The information of the trunks belonging to multiple trees overlap in one voxel | 31/31 | 14/14 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 2 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.92 |
| f: The trunk of a tree appears in two adjacent voxels. | 54/87 | 20/29 | 19 | 19 | 3 | 1 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.90 |
| Overall | 489/802 | 223/359 | 219 | 219 | 3 | 4 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; An, F.; Chen, B.; Xue, L.; Yun, T. Individual Rubber Tree Segmentation Based on Ground-Based LiDAR Data and Faster R-CNN of Deep Learning. Forests 2019, 10, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10090793
Wang J, Chen X, Cao L, An F, Chen B, Xue L, Yun T. Individual Rubber Tree Segmentation Based on Ground-Based LiDAR Data and Faster R-CNN of Deep Learning. Forests. 2019; 10(9):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10090793
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiamin, Xinxin Chen, Lin Cao, Feng An, Bangqian Chen, Lianfeng Xue, and Ting Yun. 2019. "Individual Rubber Tree Segmentation Based on Ground-Based LiDAR Data and Faster R-CNN of Deep Learning" Forests 10, no. 9: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10090793
APA StyleWang, J., Chen, X., Cao, L., An, F., Chen, B., Xue, L., & Yun, T. (2019). Individual Rubber Tree Segmentation Based on Ground-Based LiDAR Data and Faster R-CNN of Deep Learning. Forests, 10(9), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10090793