Sequential Extraction Resulted in Similar Fractionation of Ionic Zn, Nano- and Microparticles of ZnO in Acidic and Alkaline Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selected Soils
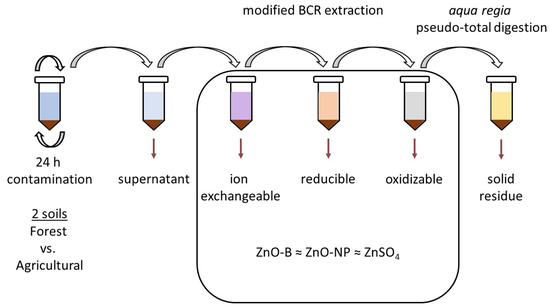
2.2. Amendment of Selected Soils and BCR Extraction
2.3. Analysis of Zn Content in Solids and Liquids
3. Results
3.1. Amendment of the Soils
3.2. Fractionation of Sorbed Zn in the Soils
3.3. Comparison between Amended and Unamended Soils
4. Discussion
4.1. Amendment of the Soils
4.2. Fractionation of Zn Retained in the Soils
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Violante, A.; Cozzolino, V.; Perelomov, L.; Caporale, A.G.; Pigna, M. Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 268–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourg, A.C.M. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and groundwater and implications for their natural and provoked mobility. In Heavy Metals; Förstner, U., Salomons, W., Mader, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 19–31. ISBN 978-3-642-79316-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, S.; Gondikas, A.; Neubauer, E.; Hofmann, T.; von der Kammer, F. Spot the difference: Engineered and natural nanoparticles in the environment—Release, behavior, and fate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12398–12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theng, B.K.G.; Yuan, G. Nanoparticles in the soil environment. Elements 2008, 4, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; Donner, E.; Tavakkoli, E.; Turney, T.W.; Naidu, R.; Miller, B.W.; Scheckel, K.G. Fate of zinc oxide nanoparticles during anaerobic digestion of wastewater and post-treatment processing of sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9089–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Levard, C.; Judy, J.D.; Unrine, J.M.; Durenkamp, M.; Martin, B.; Jefferson, B.; Lowry, G.V. Fate of zinc oxide and silver nanoparticles in a pilot wastewater treatment plant and in processed biosolids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y. Changes in the profiles of yield, yield component, oil content, and citral content in Litsea cubeba (Lour.) persoon following foliar fertilization with zinc and boron. Forests 2019, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Lal, R. Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenčík, M.; Ernst, D.; Komár, M.; Urík, M.; Šebesta, M.; Dobročka, E.; Černý, I.; Illa, R.; Kanike, R.; Qian, Y. Effect of foliar spray application of zinc oxide nanoparticles on quantitative, nutritional, and physiological parameters of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) under field conditions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Velo, I.A.; Barrios, A.C.; Zuverza-Mena, N.; Hernandez-Viezcas, J.A.; Chang, C.H.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Comparison of the effects of commercial coated and uncoated ZnO nanomaterials and Zn compounds in kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolenčík, M.; Ernst, D.; Urík, M.; Ďurišová, Ľ.; Bujdoš, M.; Šebesta, M.; Dobročka, E.; Kšiňan, S.; Illa, R.; Qian, Y.; et al. Foliar application of low concentrations of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles to the common sunflower under field conditions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.M.; Behal, A.; Sushkova, S.N.; Mandzhieva, S.; Singh, R.; Gorovtsov, A.; Tsitsuashvili, V.S.; Purvis, W.O.; Ghazaryan, K.A.; et al. Effects of zinc-oxide nanoparticles on soil, plants, animals and soil organisms: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 9, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, P.L.; Ortiz, M.D.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Chronic toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles, non-nano ZnO and ZnCl2 to Folsomia candida (Collembola) in relation to bioavailability in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Czech, B.; Kończak, M.; Bogusz, A.; Siatecka, A.; Godlewska, P.; Wiesner, M. Impact of ZnO and ZnS nanoparticles in sewage sludge-amended soil on bacteria, plant and invertebrates. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Szteke, B. Trace Elements in Abiotic and Biotic Environments; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2015; p. 427. [Google Scholar]
- Šebesta, M.; Nemček, L.; Urík, M.; Kolenčík, M.; Bujdoš, M.; Vávra, I.; Dobročka, E.; Matúš, P. Partitioning and stability of ionic, nano- and microsized zinc in natural soil suspensions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebesta, M.; Kolenčík, M.; Urík, M.; Bujdoš, M.; Vávra, I.; Dobročka, E.; Smilek, J.; Kalina, M.; Diviš, P.; Pavúk, M.; et al. Increased colloidal stability and decreased solubility—Sol-gel synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles with humic acids. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3024–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebesta, M.; Kolenčík, M.; Matúš, P.; Kořenková, L. Transport and distribution of engineered nanoparticles in soils and sediments. Chem. List. 2017, 111, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- García-Gómez, C.; Obrador, A.; González, D.; Babín, M.; Fernández, M.D. Comparative effect of ZnO NPs, ZnO bulk and ZnSO4 in the antioxidant defences of two plant species growing in two agricultural soils under greenhouse conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Mukherjee, A.; Rico, C.M.; José-Yacamán, M.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Comparative phytotoxicity of ZnO NPs, bulk ZnO, and ionic zinc onto the alfalfa plants symbiotically associated with Sinorhizobium meliloti in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 515–516, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, C.; Babin, M.; Obrador, A.; Álvarez, J.M.; Fernández, M.D. Integrating ecotoxicity and chemical approaches to compare the effects of ZnO nanoparticles, ZnO bulk, and ZnCl2 on plants and microorganisms in a natural soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16803–16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Yang, J.; Peng, Q.; Liang, X.; Mao, H. Comparison study of zinc nanoparticles and zinc sulphate on wheat growth: From toxicity and zinc biofortification. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žemberyová, M.; Zwaik, A.; Farkašovská, I. Sequential extraction for the speciation of some heavy metals in soils. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1998, 229, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Závadská, M.; Žemberyová, M.; Farkašovská, I. Speciation of mercury in soil samples using sequential extraction. Chem. List. 1999, 93, 391–393. [Google Scholar]
- Hagarová, I.; Žemberyová, M.; Bajčan, D. Sequential and single step extraction procedures used for fractionation of selenium in soil samples. Chem. Pap. 2005, 59, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Šebesta, M.; Matúš, P. Separation, determination, and characterization of inorganic engineered nanoparticles in complex environmental samples. Chem. List. 2018, 112, 583–589. [Google Scholar]
- Duborská, E.; Bujdoš, M.; Urík, M.; Matúš, P. Iodine fractionation in agricultural and forest soils using extraction methods. CATENA 2020, 195, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahuquillo, A.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Rubio, R.; Rauret, G.; Thomas, R.P.; Davidson, C.M.; Ure, A.M. Use of a certified reference material for extractable trace metals to assess sources of uncertainty in the BCR three-stage sequential extraction procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 382, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. BCR®-701: A review of 10-years of sequential extraction analyses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 680, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraballo, M.A.; Serna, A.; Macías, F.; Pérez-López, R.; Ruiz-Cánovas, C.; Richter, P.; Becerra-Herrera, M. Uncertainty in the measurement of toxic metals mobility in mining/mineral wastes by standardized BCR®SEP. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žemberyová, M.; Jankovič, R.; Hagarová, I.; Kuss, H.-M. Electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric determination of vanadium in extracts of soil and sewage sludge certified reference materials after fractionation by means of the Communities Bureau of Reference modified sequential extraction procedure. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žemberyová, M.; Hagarová, I.; Zimová, J.; Barteková, J.; Kuss, H.-M. Determination of molybdenum in extracts of soil and sewage sludge CRMs after fractionation by means of BCR modified sequential extraction procedure. Talanta 2010, 82, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žemberyová, M.; Barteková, J.; Hagarová, I. The utilization of modified BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure for the fractionation of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in soil reference materials of different origins. Talanta 2006, 70, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; He, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hu, Q.; Hu, B.; Tang, Y. Evaluation of the BCR sequential extraction scheme for trace metal fractionation of alkaline municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Soils and Sediments. An Account of the Improvement and Harmonization of Extraction Techniques Undertaken Under the Auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Lück, D.; Yli-Halla, M.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P. The Certification of the Extractable Contents (Mass Fractions) of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in Freshwater Sediment Following a Sequential Extraction BCR-701 Procedure; BCR Information European Commission: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pueyo, M.; Rauret, G.; Lück, D.; Yli-Halla, M.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P.; López-Sánchez, J.F. Certification of the extractable contents of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a freshwater sediment following a collaboratively tested and optimised three-step sequential extraction procedure. J. Environ. Monit. 2001, 3, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Societas Pedologica Slovaca. Morphogenetic Soil Classification System of Slovakia, Basal Reference Taxonomy, 2nd ed.; Soil Science and Conservation Research Institute: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2014; ISBN 978-80-8163-005-7. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group. WRB World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McKeague, J.A.; Day, J.H. Dithionite-and oxalate-extractable Fe and Al as aids in differentiating various classes of soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1966, 46, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, K.; Kobza, J.; Matúšková, Ľ.; Brečková, V.; Makovníková, J.; Barančíková, G.; Búrik, V.; Litavec, T.; Houšková, B.; Chromaničová, A. Záväzné Metódy Rozborov Pôd; VÚPOP: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description, 4th ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006; ISBN 92-5-105521-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kononova, M.M.; Belčikova, N.P. Uskorennyje metody opredelenija sostava gumusa minerálnych počv. Počvovedenije 1962, 10, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kappen, H. Die Bodenazidität; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1929; ISBN 978-3-642-89928-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerstva Pôdohospodárstva Slovenskej Republiky. Vyhláška Ministerstva Pôdohospodárstva Slovenskej Republiky z 23. Augusta 2004; Vyhláška č. 508/2004 Z. z; Ministerstva Pôdohospodárstva Slovenskej Republiky: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Čurlík, J.; Šefčík, P. Geochemický Atlas Slovenskej Republiky, Časť V: Pôdy [Online]; Štátny Geologický Ústav Dionýza Štúra: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2012; Available online: http://apl.geology.sk/atlaspody (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Cornelis, G.; Hund-Rinke, K.; Kuhlbusch, T.; van den Brink, N.; Nickel, C. Fate and bioavailability of engineered nanoparticles in soils: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2720–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikowska, D.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Bułkowska, K.; Klik, B. Feasibility of using humic substances from compost to remove heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) from contaminated soil aged for different periods of time. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Banfield, J.F. Particle size and pH effects on nanoparticle dissolution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 14876–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, F.M.; Aziz, H.A.; Stoll, S. Aggregation and disaggregation of ZnO nanoparticles: Influence of pH and adsorption of Suwannee River humic acid. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, S.-W.W.; Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Grassian, V.H. Aggregation and dissolution of 4 nm ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous environments: Influence of pH, ionic strength, size, and adsorption of humic acid. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, I.; Yaron, B.; Berkowitz, B. Abiotic soil changes induced by engineered nanomaterials: A critical review. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 181, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Yan, Y.; Huang, R.; Abdala, D.B.; Liu, F.; Tang, Y.; Tan, W.; Feng, X. Formation of Zn-Al layered double hydroxides (LDH) during the interaction of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) with γ-Al2O3. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.H.; Su, C. Transport and retention of zinc oxide nanoparticles in porous media: Effects of natural organic matter versus natural organic ligands at circumneutral pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, Y.F.; Schneidewind, U.; Bradford, S.A.; Šimůnek, J.; Klumpp, E.; Azzam, R. Transport and retention of engineered silver nanoparticles in carbonate-rich sediments in the presence and absence of soil organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, C.-H.; Elimelech, M. The “Shadow effect” in colloid transport and deposition dynamics in granular porous media: measurements and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3681–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peijnenburg, W.; Praetorius, A.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.; Cornelis, G. Fate assessment of engineered nanoparticles in solids dominated media—Current insights and the way forward. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.C.; Li, K.L.; Zhou, L.X.; Selvam, A. The sorption of Cd and Zn by different soils in the presence of dissolved organic matter from sludge. Geoderma 2007, 137, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, H.M.; Elbana, T.A.; Zhao, K.; Xu, J.; Fergusson, E.L. Miscible displacement of zinc in soil columns: Linear and nonlinear modeling. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, D.; Hwang, G.; Lee, B.; Eom, I.; Kim, P.J.; Tong, M.; Kim, H. Aggregation and dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by different methods: Influence of ionic strength and humic acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 451, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Shijirbaatar, A.; Fang, J.; Owens, G.; Lin, D.; Zhang, K. Distinguishable transport behavior of zinc oxide nanoparticles in silica sand and soil columns. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ranst, E.; Qafoku, N.P.; Noble, A.; Xu, R. Variable charge soils: Mineralogy and chemistry. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 2432–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4200-9368-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bacon, J.R.; Davidson, C.M. Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction? Analyst 2008, 133, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Soil Samples | alkSoil | acidSoil | Soil Samples | alkSoil | acidSoil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil code [40] | CH-cc | CM-st.dy | pHH2O | 7.98 | 4.10 |
| Location | Senec | Stara Tura | pHKCl | 7.45 | 3.40 |
| Land use | Crop | Forest | CaCO3 (%) | 3.3 | 0.4 |
| Texture | loam | loamy sand | Tot Al (mg·kg−1) e | 51,800 | 44,600 |
| Sand (%) | 34.3 | 79.2 | Tot Fe (mg·kg−1) e | 25,700 | 16,200 |
| Silt (%) | 45.8 | 16.4 | Tot Mn (mg·kg−1) e | 604 | 318 |
| Clay (%) | 19.9 | 4.5 | Tot Zn (mg·kg−1) e | 82.4 | 142 |
| TOC (%) a | 2.82 | 4.73 | Ox Al (mg·kg−1) f | 920 | 1560 |
| HS (%) b | 1.12 | 2.48 | Ox Fe (mg·kg−1) f | 1270 | 2970 |
| HA (%) c | 0.53 | 0.79 | Ox Mn (mg·kg−1) f | 390 | 320 |
| FA (%) d | 0.59 | 1.69 | CEC (mmol·kg−1) g | 484 | 291 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šebesta, M.; Urík, M.; Kolenčík, M.; Bujdoš, M.; Matúš, P. Sequential Extraction Resulted in Similar Fractionation of Ionic Zn, Nano- and Microparticles of ZnO in Acidic and Alkaline Soil. Forests 2020, 11, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101077
Šebesta M, Urík M, Kolenčík M, Bujdoš M, Matúš P. Sequential Extraction Resulted in Similar Fractionation of Ionic Zn, Nano- and Microparticles of ZnO in Acidic and Alkaline Soil. Forests. 2020; 11(10):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101077
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠebesta, Martin, Martin Urík, Marek Kolenčík, Marek Bujdoš, and Peter Matúš. 2020. "Sequential Extraction Resulted in Similar Fractionation of Ionic Zn, Nano- and Microparticles of ZnO in Acidic and Alkaline Soil" Forests 11, no. 10: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101077
APA StyleŠebesta, M., Urík, M., Kolenčík, M., Bujdoš, M., & Matúš, P. (2020). Sequential Extraction Resulted in Similar Fractionation of Ionic Zn, Nano- and Microparticles of ZnO in Acidic and Alkaline Soil. Forests, 11(10), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11101077