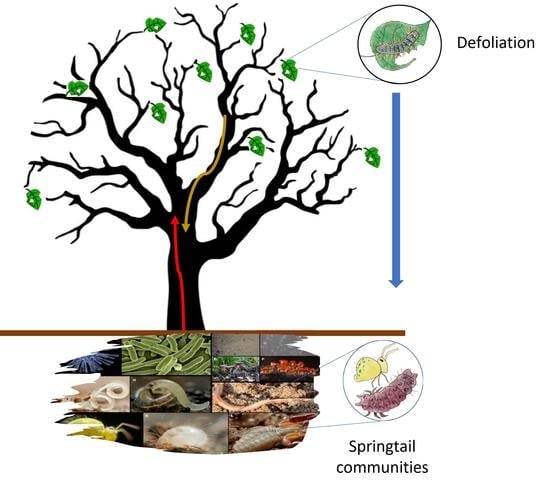
Soil Springtail Communities Are Resilient to Forest Tent Caterpillar Defoliation in Quebec Mixed Hardwood Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Extraction and Identification of Springtails
2.3. Soil Microorganisms
2.4. Soil Parameters
2.5. Canopy Openness
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Species Composition Response to Defoliation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bale, J.S.; Masters, G.J.; Hodkinson, I.D.; Awmack, C.; Bezemer, T.M.; Brown, V.K.; Butterfield, J.; Buse, A.; Coulson, J.C.; Farrar, J.; et al. Herbivory in Global Climate Change Research: Direct Effects of Rising Temperature on Insect Herbivores. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uelmen, J.A.; Lindroth, R.L.; Tobin, P.C.; Reich, P.B.; Schwartzberg, E.G.; Raffa, K.F. Effects of Winter Temperatures, Spring Degree-Day Accumulation, and Insect Population Source on Phenological Synchrony between Forest Tent Caterpillar and Host Trees. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 362, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pureswaran, D.S.; Roques, A.; Battisti, A. Forest Insects and Climate Change. Curr. For. Rep. 2018, 4, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battisti, A. Forests and Climate Change—Lessons from Insects. iForest Biogeosciences For. 2008, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinet, C.; Roques, A. Direct Impacts of Recent Climate Warming on Insect Populations. Integr. Zool. 2010, 5, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowalter, T.D. Biology and Management of the Forest Tent Caterpillar (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae). J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooke, B.J.; Sturtevant, B.R.; Robert, L.-E. The Forest Tent Caterpillar in Minnesota: Detectability, Impact, and Cycling Dynamics. Forests 2022, 13, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, B.J.; Lorenzetti, F. The Dynamics of Forest Tent Caterpillar Outbreaks in Québec, Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 226, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.W.; Frank, D.A.; Hinchey, P.M.; Murray, T.R. Defoliation Induces Root Exudation and Triggers Positive Rhizospheric Feedbacks in a Temperate Grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, A.T.; Hart, S.C.; Whitman, T.G.; Cobb, N.S.; Koch, G.W. Insect Infestations Linked to Shifts in Microclimate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, B.C.; Crossley, D.A., Jr.; Hunter, M.D. Response of Soil Invertebrates to Forest Canopy Inputs along a Productivity Gradient. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsfield, T.D.; Bentz, B.J.; Faccoli, M.; Jactel, H.; Brockerhoff, E.G. Forest Health in a Changing World: Effects of Globalization and Climate Change on Forest Insect and Pathogen Impacts. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2016, 89, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotton-Gagnon, A.; Simard, M.; De Grandpré, L.; Kneeshaw, D. Salvage Logging during Spruce Budworm Outbreaks Increases Defoliation of Black Spruce Regeneration. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 430, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, M.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; Kosunen, M.; Kantola, T.; Holopainen, M. Defoliation-Induced Growth Reduction of Pinus sylvestris L. after a Prolonged Outbreak of Diprion pini L.—A Case Study from Eastern Finland. Forests 2022, 13, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulinier, J.; Lorenzetti, F.; Bergeron, Y. Effects of a Forest Tent Caterpillar Outbreak on the Dynamics of Mixedwood Boreal Forests of Eastern Canada. Écoscience 2013, 20, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zou, C.B.; Wang, Z.-L. Aboveground Biomass Invariance Masks Significant Belowground Productivity Changes in Response to Salinization and Nitrogen Loading in Reed Marshes. Wetlands 2017, 37, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.; Montoro Girona, M.; Morin, H. Vulnerability of Conifer Regeneration to Spruce Budworm Outbreaks in the Eastern Canadian Boreal Forest. Forests 2019, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavoie, J.; Montoro Girona, M.; Grosbois, G.; Morin, H. Does the Type of Silvicultural Practice Influence Spruce Budworm Defoliation of Seedlings? Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silfver, T.; Paaso, U.; Rasehorn, M.; Rousi, M.; Mikola, J. Genotype × Herbivore Effect on Leaf Litter Decomposition in Betula Pendula Saplings: Ecological and Evolutionary Consequences and the Role of Secondary Metabolites. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büchel, K.; Fenning, T.; Gershenzon, J.; Hilker, M.; Meiners, T. Elm Defence against Herbivores and Pathogens: Morphological, Chemical and Molecular Regulation Aspects. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 961–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, L.; Fierravanti, A.; Rossi, S.; Delzon, S.; De Grandpré, L.; Kneeshaw, D.D.; Deslauriers, A. The Paradox of Defoliation: Declining Tree Water Status with Increasing Soil Water Content. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 290, 108025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Sanou, I.; Münkemüller, T.; Zinger, L.; Schimann, H.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Gielly, L.; Foulquier, A.; Hedde, M.; Ohlmann, M.; Roy, M.; et al. Cascading Effects of Moth Outbreaks on Subarctic Soil Food Webs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.D. Insect Population Dynamics Meets Ecosystem Ecology: Effects of Herbivory on Soil Nutrient Dynamics. Agric. For. Entomol. 2001, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Wardle, D.A. Herbivore-Mediated Linkages Between Aboveground and Belowground Communities. Ecology 2003, 84, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, D.B.; Asner, G.P.; Martin, R.E.; Espejo, J.E.S.; Huasco, W.H.; Amézquita, F.F.F.; Carranza-Jimenez, L.; Cabrera, D.F.G.; Baca, L.D.; Sinca, F.; et al. Herbivory Makes Major Contributions to Ecosystem Carbon and Nutrient Cycling in Tropical Forests. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Lanoue, A.; Strecker, T.; Scheu, S.; Steinauer, K.; Thakur, M.P.; Mommer, L. Root Biomass and Exudates Link Plant Diversity with Soil Bacterial and Fungal Biomass. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maaroufi, N.I.; Palmqvist, K.; Bach, L.H.; Bokhorst, S.; Liess, A.; Gundale, M.J.; Kardol, P.; Nordin, A.; Meunier, C.L. Nutrient Optimization of Tree Growth Alters Structure and Function of Boreal Soil Food Webs. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 428, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, T.C.; Sadowsky, J.; Dunleavy, H.; Subke, J.-A.; Frey, S.D.; Wookey, P.A. Slowed Biogeochemical Cycling in Sub-Arctic Birch Forest Linked to Reduced Mycorrhizal Growth and Community Change after a Defoliation Event. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, J.Å.; Rousk, J.; Metcalfe, D.B. Below-Ground Responses to Insect Herbivory in Ecosystems with Woody Plant Canopies: A Meta-Analysis. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandén, H.; Mayer, M.; Stark, S.; Sandén, T.; Nilsson, L.O.; Jepsen, J.U.; Wäli, P.R.; Rewald, B. Moth Outbreaks Reduce Decomposition in Subarctic Forest Soils. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- L-M-Arnold, A.; Grüning, M.; Simon, J.; Reinhardt, A.-B.; Lamersdorf, N.; Thies, C. Forest Defoliator Pests Alter Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, S.K.; Whitham, T.G.; Powell, M. Herbivory Differentially Alters Plant Litter Dynamics of Evergreen and Deciduous Trees. Oikos 2006, 114, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.K.; Hart, S.C.; Cobb, N.S.; Whitham, T.G.; Koch, G.W. Insect Herbivory Increases Litter Quality and Decomposition: An Extension of the Acceleration Hypothesis. Ecology 2003, 84, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, D.A.; Williamson, W.M.; Yeates, G.W.; Bonner, K.I. Trickle-down Effects of Aboveground Trophic Cascades on the Soil Food Web. Oikos 2005, 111, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukonen, M.; Ruotsalainen, A.L.; Wäli, P.R.; Männistö, M.K.; Setälä, H.; Saravesi, K.; Huusko, K.; Markkola, A. Moth Herbivory Enhances Resource Turnover in Subarctic Mountain Birch Forests? Ecology 2013, 94, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenfalk, L.A.; Bengtsson, J.; Berggren, Å.; Zwiggelaar, K.; Spijkman, E.; Huyer-Brugman, F.; Berg, M.P. Spatially Structured Environmental Filtering of Collembolan Traits in Late Successional Salt Marsh Vegetation. Oecologia 2015, 179, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potapov, A.; Bellini, B.; Chown, S.; Deharveng, L.; Janssens, F.; Kováč, Ľ.; Kuznetsova, N.; Ponge, J.-F.; Potapov, M.; Querner, P.; et al. Towards a Global Synthesis of Collembola Knowledge—Challenges and Potential Solutions. Soil Org. 2020, 92, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, A.M.; Beaulieu, F.; Birkhofer, K.; Bluhm, S.L.; Degtyarev, M.I.; Devetter, M.; Goncharov, A.A.; Gongalsky, K.B.; Klarner, B.; Korobushkin, D.I.; et al. Feeding Habits and Multifunctional Classification of Soil-Associated Consumers from Protists to Vertebrates. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1057–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, A.M.; Guerra, C.A.; van den Hoogen, J.; Babenko, A.; Bellini, B.C.; Berg, M.P.; Chown, S.L.; Deharveng, L.; Kováč, Ľ.; Kuznetsova, N.A.; et al. Globally Invariant Metabolism but Density-Diversity Mismatch in Springtails. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, L.; Venier, L.; Hazlett, P.; Fleming, R.; Morris, D.; Handa, I.T. Forest Floor Mesofauna Communities Respond to a Gradient of Biomass Removal and Soil Disturbance in a Boreal Jack Pine (Pinus Banksiana) Stand of Northeastern Ontario (Canada). For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 407, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond-Léonard, L.J.; Gravel, D.; Reich, P.B.; Handa, I.T. Springtail Community Structure Is Influenced by Functional Traits but Not Biogeographic Origin of Leaf Litter in Soils of Novel Forest Ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławski, M.; Sławska, M. Soil Faunal Communities in Mass Outbreak Areas of the Great Web-Spinning Sawfly Acantholyda Posticalis (Mats.) Are Impoverished Compared to Pest-Free Scots Pine Forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 529, 120681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiunov, A.V.; Scheu, S. Arbuscular Mycorrhiza and Collembola Interact in Affecting Community Composition of Saprotrophic Microfungi. Oecologia 2005, 142, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erktan, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Carminati, A.; Jousset, A.; Scheu, S. Protists and Collembolans Alter Microbial Community Composition, C Dynamics and Soil Aggregation in Simplified Consumer–Prey Systems. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 4961–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, A.M.; Pollierer, M.M.; Salmon, S.; Šustr, V.; Chen, T.-W. Multidimensional Trophic Niche Approach: Gut Content, Digestive Enzymes, Fatty Acids and Stable Isotopes in Collembola. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, S.; Kaneko, N. Collembolans Feeding on Soil Affect Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization by Their Influence on Microbial and Nematode Activities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 44, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, T.; Ruess, L.; Filser, J. Collembola Gut Passage Shapes Microbial Communities in Faecal Pellets but Not Viability of Dietary Algal Cells. Chemoecology 2014, 24, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.; Bönn, M.; Feldhahn, L.; Kurth, F.; Grams, T.E.E.; Herrmann, S.; Tarkka, M.; Buscot, F.; Scheu, S. Collembola Interact with Mycorrhizal Fungi in Modifying Oak Morphology, C and N Incorporation and Transcriptomics. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potapov, A.M.; Goncharov, A.A.; Tsurikov, S.M.; Tully, T.; Tiunov, A.V. Assimilation of Plant-Derived Freshly Fixed Carbon by Soil Collembolans: Not Only via Roots? Pedobiologia 2016, 59, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinka, M.; Jones, T.H.; Hartley, S.E. The Indirect Effect of Above-Ground Herbivory on Collembola Populations Is Not Mediated by Changes in Soil Water Content. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 36, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinka, M.; Jones, T.H.; Hartley, S.E. Collembola Respond to Aphid Herbivory but Not to Honeydew Addition. Ecol. Entomol. 2009, 34, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despland, E.; Lessard, J.-P. Social Predation by Ants as a Mortality Source for an Arboreal Gregarious Forest Pest. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, K.L.; Wise, D.H. Spider Predation on Forest-Floor Collembola and Evidence for Indirect Effects on Decomposition. Pedobiologia 2000, 44, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonja, M.; Aupic-Samain, A.; Forey, E.; Chauvat, M. Increasing Temperature and Decreasing Specific Leaf Area Amplify Centipede Predation Impact on Collembola. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 89, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.A.; Gancos, T.; Frost, C.J. Slow-Cycle Effects of Foliar Herbivory Alter the Nitrogen Acquisition and Population Size of Collembola. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bowman, W.D.; Kaufmann, R.; Schmidt, S.K. A Temporal Approach to Linking Aboveground and Belowground Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, B. The Lake Duparquet Research and Teaching Forest: Building a Foundation for Ecosystem Management. For. Chron. 1999, 75, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneeshaw, D.D.; Harvey, B.D.; Reyes, G.P.; Caron, M.-N.; Barlow, S. Spruce Budworm, Windthrow and Partial Cutting: Do Different Partial Disturbances Produce Different Forest Structures? For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.D.; Leduc, A.; Gauthier, S.; Bergeron, Y. Stand-Landscape Integration in Natural Disturbance-Based Management of the Southern Boreal Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 155, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitaille, A.; Saucier, J.-P. Paysages Régionaux du Québec Méridional; Les Publications du Québec: Montréal, QC, Canada, 1998; p. 213. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère de la Faune, des Forêts et des Parc (MFFP). Aires Infestées Par La Livrée Des Forêts Au Québec En 2017; Gouvernement du Québec, Direction de la Protection des Forêts: Québec, QC, Canada, 2017; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère de la Faune, des Forêts et des Parc (MFFP). Aires Infestées Par La Livrée Des Forêts Au Québec En 2018; Gouvernement du Québec, Direction de la Protection des Forêts: Québec, QC, Canada, 2018; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkin, S.P. Biology of the Springtails (Insecta: Collembola); Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fjellberg, A. Collembola of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Part I: Poduromorpha; Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica; 35; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 1998; ISBN 9789004112414. [Google Scholar]
- Fjellberg, A. Collembola of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Part II: Entomobryomorpha and Symphypleona; Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 9004157700. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, K.; Bellinger, P. The Collembola of North America, North of the Rio Grande, 2nd ed.; Grinnell College: Grinnell, IA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sigovini, M.; Keppel, E.; Tagliapietra, D. Open Nomenclature in the Biodiversity Era. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansereau-Macias, É.; Despland, E.; Handa, I.T. Decreased Soil Microbial Biomass and Changed Microbial Community Composition Following a Defoliation Event by the Forest Tent Caterpillar. Forests 2023, 14, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.D.; Chapman, S.J.; Cameron, C.M.; Davidson, M.S.; Potts, J.M. A Rapid Microtiter Plate Method to Measure Carbon Dioxide Evolved from Carbon Substrate Amendments so as to Determine the Physiological Profiles of Soil Microbial Communities by Using Whole Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yash, P.K. Handbook on Reference Methods for Soil Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, G.P.; Mitchell, J.D.; Andersen, C.B.; Haney, D.C.; Liao, M.-K.; Sargent, K.A. Urban Influences on Stream Chemistry and Biology in the Big Brushy Creek Watershed, South Carolina. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 182, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.; Ainsworth, M. A Method of Linking Multivariate Community Structure to Environmental Variables. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 92, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P. Vegan: Community Ecology Package Version 2. 6-4. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P. Vegan: Community Ecology Package Version 2.5-3. 2018. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Caron, A.-S.; Gagnon Koudji, E.; Handa, I.T.; Girona, M.M.; Despland, E. Forest Tent Caterpillar Outbreaks Drive Change in Ant Community in Boreal Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, N.; Bengtsson, J. Population Responses of Oribatid Mites and Collembolans after Drought. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 28, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, N.; Bengtsson, J. Recovery of Forest Soil Fauna Diversity and Composition after Repeated Summer Droughts. Oikos 2006, 114, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, A. Collembola in Low Stumps at Clear-Cuts. Is Stump Harvesting a Threat? Scand. J. For. Res. 2012, 27, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Wardle, D.A.; Yeates, G.W. Linking Above-Ground and below-Ground Interactions: How Plant Responses to Foliar Herbivory Influence Soil Organisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.H. Vertical Distribution of Collembola in a Pinus Nigra Organic Soil. Pedobiologia 1993, 37, 336–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ponge, J.-F. Vertical Distribution of Collembola (Hexapoda) and Their Food Resources in Organic Horizons of Beech Forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulibaly, S.F.M.; Winck, B.R.; Akpa-Vinceslas, M.; Mignot, L.; Legras, M.; Forey, E.; Chauvat, M. Functional Assemblages of Collembola Determine Soil Microbial Communities and Associated Functions. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollierer, M.M.; Dyckmans, J.; Scheu, S.; Haubert, D. Carbon Flux through Fungi and Bacteria into the Forest Soil Animal Food Web as Indicated by Compound-Specific 13C Fatty Acid Analysis. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, L.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Pausch, J.; Scheu, S.; Pollierer, M.M. The Flux of Root-Derived Carbon via Fungi and Bacteria into Soil Microarthropods (Collembola) Differs Markedly between Cropping Systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond-Léonard, L.J.; Gravel, D.; Handa, I.T. A Novel Set of Traits to Describe Collembola Mouthparts: Taking a Bite out of the Broad Chewing Mandible Classification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombos, M. Collembola of Loess Grassland: Effects of Grazing and Landscape on Community Composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiniger, C.; Barot, S.; Ponge, J.-F.; Salmon, S.; Meriguet, J.; Carmignac, D.; Suillerot, M.; Dubs, F. Collembolan Preferences for Soil and Microclimate in Forest and Pasture Communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 86, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anslan, S.; Bahram, M.; Tedersoo, L. Seasonal and Annual Variation in Fungal Communities Associated with Epigeic Springtails (Collembola Spp.) in Boreal Forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollierer, M.M.; Scheu, S. Stable Isotopes of Amino Acids Indicate That Soil Decomposer Microarthropods Predominantly Feed on Saprotrophic Fungi. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerpina, R.; Boiteau, G.; Lynch, D.H. Collembola Diet Switching in the Presence of Maize Roots Varies with Species. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2017, 97, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, M.D.; Linnen, C.R.; Reynolds, B.C. Effects of Endemic Densities of Canopy Herbivores on Nutrient Dynamics along a Gradient in Elevation in the Southern Appalachians. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Grandpré, L.; Marchand, M.; Kneeshaw, D.D.; Paré, D.; Boucher, D.; Bourassa, S.; Gervais, D.; Simard, M.; Griffin, J.M.; Pureswaran, D.S. Defoliation-Induced Changes in Foliage Quality May Trigger Broad-Scale Insect Outbreaks. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Chang, L.; Wu, D. Euedaphic and Hemiedaphic Collembola Suffer Larger Damages than Epedaphic Species to Nitrogen Input. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santorufo, L.; Cortet, J.; Arena, C.; Goudon, R.; Rakoto, A.; Morel, J.-L.; Maisto, G. An Assessment of the Influence of the Urban Environment on Collembolan Communities in Soils Using Taxonomy- and Trait-Based Approaches. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 78, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yin, X.; Xu, H.; Tao, Y. Responses of Soil Collembolans to Vegetation Restoration in Temperate Coniferous and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forests. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 2333–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeszowski, K.; Zadrożny, P.; Nicia, P. The Effect of Soil Nutrient Gradients on Collembola Communities Inhabiting Typical Urban Green Spaces. Pedobiologia 2017, 64, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Scheu, S.; Bhusal, D.R.; Luo, R.; Qiang, W.; Wang, M.; Pang, X. Phosphorus Addition Increases the Total Abundance and Favors Microbivorous Collembola in Subalpine Plantation Forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, L.; Wei, S.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Peguero, G.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Huang, C. Phosphorus Addition Reverses the Negative Effect of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Arthropods during Litter Decomposition in a Subtropical Forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.-J.; Luo, R.-Y.; Pang, X.-Y. Response of soil Collembola to nitrogen and phosphorus deposition: A review. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2022, 33, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenzind, T.; Hempel, S.; Homeier, J.; Horn, S.; Velescu, A.; Wilcke, W.; Rillig, M.C. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions Impact Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Abundance and Molecular Diversity in a Tropical Montane Forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3646–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnon, M.; Paré, D.; Hébert, C. Relationships between Soil Chemistry, Microbial Biomass and the Collembolan Fauna of Southern Québec Sugar Maple Stands. Écoscience 2000, 7, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribb, B.W.; Stewart, A.; Huang, H.; Truss, R.; Noller, B.; Rasch, R.; Zalucki, M.P. Insect Mandibles—Comparative Mechanical Properties and Links with Metal Incorporation. Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperman, R.G.; Checkai, R.T.; Simini, M.; Phillips, C.T. Manganese Toxicity in Soil for Eisenia fetida, Enchytraeus crypticus (Oligochaeta), and Folsomia candida (Collembola). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shahar, Y. The Impact of Environmental Mn Exposure on Insect Biology. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aupic-Samain, A.; Baldy, V.; Delcourt, N.; Krogh, P.H.; Gauquelin, T.; Fernandez, C.; Santonja, M. Water Availability Rather than Temperature Control Soil Fauna Community Structure and Prey–Predator Interactions. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, K.I.; Sivakoff, F.S.; Wallin, K.F.; Wenzel, J.W.; Herms, D.A. Forest Disturbance and Arthropods: Small-Scale Canopy and Understory Disturbances Alter Movement of Mobile Arthropods. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, K.I.; Wallin, K.F.; Wenzel, J.W.; Herms, D.A. Forest Disturbance and Arthropods: Small-Scale Canopy Gaps Drive Invertebrate Community Structure and Composition. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Genera and Species or Morphospecies | Relative Abundance (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undefoliated 2018 | Outbreak 2018 | Undefoliated 2019 | Outbreak 2019 | |
| Anurophorus sp1 | 31.93 | - | 3.57 | 1.47 |
| Arrthopalites sp1 | 0.40 | 0.43 | - | - |
| Desoria sp1 | 0.40 | - | 0.32 | 5.15 |
| Desoria sp2 | 0.60 | 1.30 | - | - |
| Desoria sp3 | 2.01 | 11.74 | - | - |
| Desoria sp4 | - | 0.87 | - | - |
| Entomobrya sp1 | 0.60 | 0.87 | - | - |
| Entomobrya sp2 | - | 1.30 | - | - |
| Entomobrya sp3 | - | 3.04 | - | - |
| Folsomia candida Willen, 1902 | 0.20 | - | - | - |
| Folsomia nivalis Packard, 1873 | 6.63 | - | 6.82 | 3.68 |
| Folsomia similis Bagnall, 1939 | - | - | 0.32 | - |
| Friesea mirabilis Tullberg, 1871 | 1.00 | 3.48 | 2.27 | 5.88 |
| Friesea pentacantha Mills, 1934 | - | 0.43 | - | - |
| Heteromurus nitidus Templeton et Westwood, 1836 | - | 0.43 | 1.30 | - |
| Hypogastrura sp1 | - | 1.30 | - | 0.74 |
| Isotoma viridis Bourlet, 1839 | 0.40 | 0.43 | - | - |
| Isotomiella minor Schäffer, 1896 | 2.21 | - | 1.30 | - |
| Isotomorus palustri Müller, 1776 | - | - | 1.30 | - |
| Lepidocyrtus sp1 | 13.05 | 38.70 | 67.53 | 58.82 |
| Mesaphorura sp1 | 3.01 | 5.22 | 1.62 | 1.47 |
| Mesaphorura sp2 | 0.40 | - | - | - |
| Metisotoma grandiceps Reuter, 1891 | 1.00 | - | 0.65 | - |
| Neanura muscorum Templeton, 1836 | - | 6.09 | 1.30 | - |
| Morulodes serratus Folsom, 1916 | - | - | 1.30 | 11.03 |
| Orchesella sp1 | 0.60 | - | - | 0.74 |
| Paranura sp1 | - | - | - | 0.74 |
| Parisotoma ekmani Fjellberg, 1977 | 2.01 | 0.43 | 3.25 | 8.09 |
| Parisotoma notabilis Schäffer, 1896 | 0.20 | 11.30 | 3.57 | 1.47 |
| Pseudachorutes simplex Maynard, 1951 | 2.21 | - | - | - |
| Pseudachorutes sp1 | 1.00 | - | - | - |
| Sinela sp1 | 0.20 | - | 1.95 | - |
| Sminthurides lepus Mills, 1934 | 0.40 | 0.43 | - | - |
| Sminthurides occultus Mills, 1934 | 1.20 | 3.48 | - | - |
| Sminthurides pumilis Krausbauer, 1878 | - | 4.78 | - | - |
| Sminthurides quadrimaculatus Ryder, 1878 | 0.80 | - | - | - |
| Sminthurides sp1 | 0.20 | 1.74 | - | - |
| Plutomurus californicus Folsom, 1913 | 0.40 | - | - | - |
| Pogonognathellus celsus Christensen, 1965 | - | - | 0.32 | - |
| Tomocerus curtus Christensen, 1964 | 0.40 | - | - | - |
| Pogonognathellus elongatus Maynard, 1951 | - | - | 0.32 | - |
| Pogonognathellus flavescens Tullberg, 1871 | 2.81 | - | - | - |
| Tomocerina lamellifera Mills, 1934 | 0.20 | - | - | - |
| Xenylla christianseni Yosii, 1960 | 21.89 | - | - | - |
| Xenyllodes armatus Axelson, 1903 | 0.60 | - | - | - |
| Xenyllodes sp1 | 0.40 | - | - | - |
| Unknown species | 0.60 | 2.17 | 0.97 | 0.74 |
| Df | SS | R2 | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | 3 | 1.6115 | 0.16796 | 1.8841 | 0.005 *** |
| Year | 1 | 0.6342 | 0.0661 | 2.1233 | 0.021 * |
| Residual | 28 | 7.9831 | 0.83204 | ||
| Total | 31 | 9.5946 | 1 |
| Factors | Df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 1 | 2.4116 | 0.0160 ** |
| Nitrogen (N) | 1 | 1.1221 | 0.3510 |
| pH | 1 | 1.8049 | 0.0870 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 1 | 2.9531 | 0.0020 *** |
| Calcium (Ca) | 1 | 0.7862 | 0.6660 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 1 | 2.5395 | 0.0120 ** |
| Sodium (Na) | 1 | 1.4269 | 0.2280 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 1 | 3.8932 | 0.0020 *** |
| Canopy cover | 1 | 1.5824 | 0.1480 |
| Soil humidity | 1 | 0.7431 | 0.7010 |
| Predator | 1 | 1.3414 | 0.1910 |
| Microbial biomass | 1 | 1.3136 | 0.2390 |
| Residual | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gagnon Koudji, E.; Despland, E.; Caron, A.-S.; Handa, I.T. Soil Springtail Communities Are Resilient to Forest Tent Caterpillar Defoliation in Quebec Mixed Hardwood Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071302
Gagnon Koudji E, Despland E, Caron A-S, Handa IT. Soil Springtail Communities Are Resilient to Forest Tent Caterpillar Defoliation in Quebec Mixed Hardwood Forests. Forests. 2023; 14(7):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071302
Chicago/Turabian StyleGagnon Koudji, Essivi, Emma Despland, Anne-Sophie Caron, and I. Tanya Handa. 2023. "Soil Springtail Communities Are Resilient to Forest Tent Caterpillar Defoliation in Quebec Mixed Hardwood Forests" Forests 14, no. 7: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071302
APA StyleGagnon Koudji, E., Despland, E., Caron, A. -S., & Handa, I. T. (2023). Soil Springtail Communities Are Resilient to Forest Tent Caterpillar Defoliation in Quebec Mixed Hardwood Forests. Forests, 14(7), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071302