Characterization of Phosphorus in a Toposequence of Subtropical Perhumid Forest Soils Facing a Subalpine Lake
Abstract
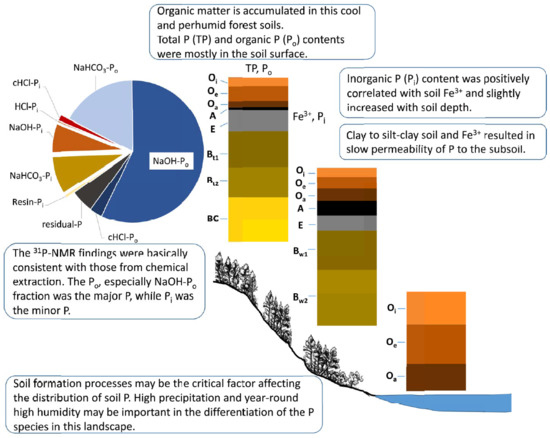
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. General Soil Chemical Properties
2.4. Sequential Fractionation of P
2.5. 31P-NMR Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Physiochemical Properties and Chemical Extractable P
4.2. Chemical Extraction of Soil P
4.3. Spectra of 31P-NMR Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutsch, M.; Lasch-Born, P.; Kollas, C.; Suckow, F.; Reyer, C.P.O. Balancing trade-offs between ecosystem services in Germany’s forests under climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 045012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzeghello, D.; Francioso, O.; Concheri, G.; Muscolo, A.; Nardi, S. Land use affects the soil C sequestration in alpine environment, NE Italy. Forests 2017, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.; Sun, S.Q.; Luo, J.; Bing, H.J.; Sun, H.Y. Phosphorus biogeochemical cycle research in mountainous ecosystems. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassagne, N.; Remaury, M.; Gauquelin, T.; Fabre, A. Forms and profile distribution of soil phosphorus in alpine Inceptisols and Spodosols (Pyrenees, France). Geoderma 2000, 95, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Dentener, F.J.; Capone, D.G.; Boyer, E.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Asner, G.P.; Cleveland, C.C.; Green, P.A.; Holland, E.A.; et al. Nitrogen cycles: Past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 2004, 70, 153–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Jenny, H. On a state factor model of ecosystems. BioScience 1997, 47, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Porder, S.; Houlton, B.Z.; Chadwick, O.A. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.W.; Syers, J.K. The fate of phosphorus during pedogenesis. Geoderma 1976, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.I.; Mooney, H.; Chapin, M.; Matson, P. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Egli, M.; Filip, D.; Mavris, C.; Fischer, B.; Götze, J.; Raimondi, S.; Seibert, J. Rapid transformation of inorganic to organic and plant-available phosphorous in soils of a glacier forefield. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achat, D.L.; Bakker, M.R.; Zeller, B.; Pellerin, S.; Bienaimé, S.; Morel, C. Long-term organic phosphorus mineralization in Spodosols under forests and its relation to carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.S.B.; Schaefer, C.E.R.; Sampaio, E.V.S.B. Soil phosphorus fractions from toposequences of semi-arid Latosols and Luvisols in northeastern Brazil. Geoderma 2004, 119, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; García, F.O.; Picone, L.I.; Rubio, G. Phosphorus budget and soil extractable dynamics in field crop rotations in Mollisols. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamuner, E.C.; Picone, L.I.; Echeverria, H.E. Organic and inorganic phosphorus in Mollisol soil under different tillage practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 99, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-J.; Sun, L.-F.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.-L.; Qiao, J.-J. Conversion of spent mushroom substrate to biofertilizer using a stress-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing Pichia farinose fl7. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, I.M.; Van der Meer, P.; Oenema, O.; Janssen, B.H.; Kuyper, T.W. Analysis of phosphorus by 31pnmr in Oxisols under agroforestry and conventional coffee systems in Brazil. Geoderma 2003, 112, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.T.; Tang, C.; Armstrong, R.D. Transformations and availability of phosphorus in three contrasting soil types from native and farming systems: A study using fractionation and isotopic labeling techniques. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 10, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achat, D.L.; Augusto, L.; Bakker, M.R.; Gallet-Budynek, A.; Morel, C. Microbial processes controlling P availability in forest Spodosols as affected by soil depth and soil properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Pitman, A.J.; Dai, Y.J. Limitations of nitrogen and phosphorous on the terrestrial carbon uptake in the 20th century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L22701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberson, A.; Fardeau, J.C.; Besson, J.M.; Sticher, H. Soil phosphorus dynamics in cropping systems managed according to conventional and biological agricultural methods. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1993, 16, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, R.L.; Jordan, C.F.; Guedes, R.M.; Batmanian, G.J.; Han, X.G. Assessment of a phosphorus fractionation method for soils: Problems for further investigation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1991, 34, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttenberg, K.C. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 1460–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Moir, J.O. Characterisation of available P by sequential extraction. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Lewis Publisher: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Condron, L.M.; Frossard, E.; Tiessen, H.; Newmans, R.H.; Stewart, J.W.B. Chemical nature of organic phosphorus in cultivated and uncultivated soils under different environmental conditions. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 41, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizewski, F.; Liu, Y.-T.; Morris, A.; Hesterberg, D. Spectroscopic approaches for phosphorus speciation in soils and other environmental systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, C.M. Applications of nmr to soil organic matter analysis: History and prospects. Soil Sci. 1996, 161, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feudis, M.; Cardelli, V.; Massaccesi, L.; Bol, R.; Willbold, S.; Cocco, S.; Corti, G.; Agnelli, A. Effect of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) rhizosphere on phosphorous availability in soils at different altitudes (central Italy). Geoderma 2016, 276, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolette, A.L.; Smernik, R.J.; McLaren, T.I. The composition of organic phosphorus in soils of the Snowy Mountains region of south-eastern Australia. Soil Res. 2017, 55, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhou, G.; Han, T.; Li, Y. Increasing phosphorus limitation along three successional forests in southern China. Plant Soil 2012, 364, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Bai, J.; Gao, H.; Huang, L.; Deng, W. Spatial distribution of phosphorus in marsh soils of a typical land/inland water ecotone along a hydrological gradient. Catena 2012, 98, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.S. An Introduction to the Geology of Taiwan: Explanatory Text of the Geologic Map of Taiwan, 2nd ed.; Central Geological Survey: Taipei, Taiwan, 1988.
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12 ed.; Agricultural Handbook No 436; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Chiu, C.-Y.; Lai, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-M.; Chiang, H.-C. Distribution of the radionuclide 137Cs in the soils of a wet mountainous forest in Taiwan. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1999, 50, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. Soluble salts. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Kenney, D.R., Eds.; Agronomy Monograph: Kincaid, DC, USA, 1982; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, O.P.; Jackson, M.L. Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. In Clays and Clay Minerals; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- McKeague, J.A.; Day, J.H. Dithionite- and oxalate-extractable Fe and Al as aids in differentiating various classes of soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1966, 46, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Sci. S. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.D.; Allen, H.L.; Li, J.; Markewitz, D.; Raikes, J. Bioavailability of slowly cycling soil phosphorus: Major restructuring of soil P fractions over four decades in an aggrading forest. Oecologia 2006, 150, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheinheimer, D.S.; Anghinoni, I.; Flores, A.F. Organic and inorganic phosphorus as characterized by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance in subtropical soils under management systems. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 1853–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajtha, K.; Driscoll, C.; Jarrell, W.; Elliott, E. Soil phosphorous: Characterization and total element analysis. In Standard Soil Methods for Long-Term Ecological Research; Roberston, G., Coleman, D., Bledsoe, C., Sollins, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.S.; Johnston, C.T.; Reddy, K.R. Combined chemical and 31P-NMR spectroscopic analysis of phosphorus in wetland organic soils. Soil Sci. 1998, 163, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.H.; Tate, K.R. Soil phosphorus characterisation by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1980, 11, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.M. Review of solution NMR of humic substances. In NMR of Humic Substances and Coal; Wershaw, R.L., Mikita, M.A., Eds.; Lewis Publisher: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1987; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.O.H.; David, M.B.; Vance, G.F.; Krzyszowska, A.J. Characterization of phosphorus in a spruce-fir Spodosol by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-S.; Chiu, C.-Y. Effect of topography on the composition of soil organic substances in a perhumid sub-tropical montane forest ecosystem in taiwan. Geoderma 2000, 96, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Fernandez, I.J.; Hiradate, S.; Sherman, J.F. Effects of soil acidification and forest type on water soluble soil organic matter properties. Geoderma 2007, 140, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietzel, J.; Dümig, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Klysubun, W. Synchrotron-based P k-edge XANES spectroscopy reveals rapid changes of phosphorus speciation in the topsoil of two glacier foreland chronosequences. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 108, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candler, R.; Zech, W.; Alt, H.G. A comparison of water soluble organic substances in acid soils under beech and spruce in NE-Bavaria. Z. Pflanz. Bodenk. 1989, 152, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien, S.H.; Baillie, I.; Hu, C.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Iizuka, Y.; Chiu, C.-Y. Forms and distribution of phosphorus in a placic podzolic toposequence in a subtropical subalpine forest, Taiwan. Catena 2016, 140, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien, S.H.; Hseu, Z.Y.; Iizuka, Y.; Chen, T.H.; Chiu, C.Y. Geochemical characterization of placic horizons in subtropical montane forest soils, northeastern Taiwan. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.-Y.; Chen, Z.-S.; Wu, Z.-D. Characterization of placic horizons in two subalpine forest Inceptisols. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.P.; Chen, Z.S. Characteristics and genesis of Inceptisols with placic horizons in the subalpine forest soils of Taiwan. Geoderma 2005, 125, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollins, P.; Robertson, G.P.; Uehara, G. Nutrient mobility in variable- and permanent-charge soils. Biogeochemistry 1988, 6, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-Y.; Pai, C.-W.; Yang, K.-L. Characterization of phosphorus in sub-alpine forest and adjacent grassland soils by chemical extraction and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spark, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.-W.; Kratz, T.K.; Hanson, P.C.; Kimura, N.; Liu, W.-C.; Lin, F.-P.; Chou, H.-M.; Wu, J.-T.; Chiu, C.-Y. Metabolic changes and the resistance and resilience of a subtropical heterotrophic lake to typhoon disturbance. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeck, N.E. Phosphorus. Soil Sci. 1973, 115, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeck, N.E. Phosphorus dynamics in soils and landscapes. Geoderma 1985, 36, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbenin, J.O.; Tiessen, H. Phosphorus forms in particle-size fractions of a toposequence from northeast Brazil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichting, A.; Leinweber, P.; Meissner, R.; Altermann, M. Sequentially extracted phosphorus fractions in peat-derived soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.R.; Miller, B.W.; Rubilar, R.; Stape, J.L.; Albaugh, T.J. Phosphorus nutrition of forest plantations: The role of inorganic and organic phosphorus. In Soil Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 317–338. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.L.; Mahieu, N.; Condron, L.M. Quantification of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in alkaline soil extracts by solution 31P NMR spectroscopy and spectral deconvolution. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Mahieu, N.; Condron, L.M.; Chen, C.R. Quantification and bioavailability of scyllo-inositol hexakisphosphate in pasture soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, J.; Tiessen, H.; Condron, L.M. Dynamics of organic phosphorus in soils under natural and agricultural ecosystems. In Humic Substances in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 429–466. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, T.I.; Smernik, R.J.; Guppy, C.N.; Bell, M.J.; Tighe, M.K. The organic P composition of Vertisols as determined by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, J.; Djodjic, F.; Börjesson, G.; Mattsson, L. Identification and quantification of organic phosphorus forms in soils from fertility experiments. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Cheesman, A.W.; Godage, H.Y.; Riley, A.M.; Potter, B.V.L. Determination of neo- and D-chiro-inositol hexakisphosphate in soils by solution 31P NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4994–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.G.; Vestergren, J.; Gröbner, G.; Persson, P.; Schleucher, J.; Giesler, R. Soil organic phosphorus transformations in a boreal forest chronosequence. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Newman, S.; Cheesman, A.W.; Reddy, K.R. Sample pretreatment and phosphorus speciation in wetland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade-Menun, B.J. Characterizing phosphorus in environmental and agricultural samples by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Talanta 2005, 66, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade-Menun, B.J.; Berch, S.M.; Preston, C.M.; Lavkulich, L.M. Phosphorus forms and related soil chemistry of podzolic soils on northern Vancouver Island. I. A comparison of two forest types. Can. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 1714–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, M.I.; Guggenberger, G.; Zech, W.; Alt, H.G. Organic phosphorus species in humic acids of mountain soils along a toposequence in the northern Caucasus. Z. Pflanz. Bodenk. 1996, 159, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, J.C.; Zech, W. Phosphorus status of a soil catena under liberian evergreen rain forest: Results of 31P NMR spectroscopy and phosphorus adsorption experiments. Z. Pflanz. Bodenk. 1993, 156, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, W.; Alt, H.G.; Haumaier, L.; Blasek, R. Characterization of phosphorus fractions in mountain soils of the Bavarian Alps by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Z. Pflanz. Bodenk. 1987, 150, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltner, A.; Haumaier, L.; Zech, W. Transformations of phosphorus during incubation of beech leaf litter in the presence of oxides. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1998, 49, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorn, L.; Frossard, E.; Newman, R.H. Use of 31P NMR in the study of soils and the environment. In Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Environmental Chemistry; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 247–271. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, K.R.; Newman, R.H. Phosphorus fractions of a climosequence of soils in New Zealand tussock grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Baath, E. Contrasting soil ph effects on fungal and bacterial growth suggest functional redundancy in carbon mineralization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, M.I.; Haumaier, L.; Zech, W.; Marfenina, O.E.; Lysak, L.V. Can 31P NMR spectroscopy be used to indicate the origins of soil organic phosphates? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade-Menun, B.J.; Preston, C.M. A comparison of soil extraction procedures for 31P NMR spectroscopy. Soil Sci. 1996, 161, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, R.; Amelung, W.; Haumaier, L. Phosphorus-31–nuclear magnetic–resonance spectroscopy to trace organic dung phosphorus in a temperate grassland soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Oades, J.M. Comparative organic geochemistries of soils and marine sediments. Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 319–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinweber, P.; Haumaier, L.; Zech, W. Sequential extractions and 31P-NMR spectroscopy of phosphorus forms in animal manures, whole soils and particle-size separates from a densely populated livestock area in northwest Germany. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1997, 25, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Site | Horizon | Depth | pH | CEC | Base Saturation | TOC | Total N | Total P | Pi | Po | Feo | Fed | Alo | Ald |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (cmol(+) kg−1) | (%) | (g kg−1) | (g kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | (g kg−1) | (g kg−1) | (g kg−1) | (g kg−1) | |||
| Summit | Oi | +10~+7 | 3.7 | 73.1 | 1.2 | 352.4 | 8.88 | 945.8 | 125.5 | 571.6 | 0.5 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 1.8 |
| Oe | +7~+2 | 3.5 | 124.9 | 3.3 | 492.5 | 17.49 | 1040.2 | 147.2 | 621.4 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 2.2 | |
| Oa | +2~0 | 3.5 | 146.9 | 2.3 | 492.4 | 22.1 | 606.7 | 178.6 | 535.8 | 1.2 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 2.5 | |
| A | 0~1 | 3.5 | 60.1 | 1.8 | 207.3 | 11.9 | 667.8 | 171.7 | 305.2 | 1.5 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 1.6 | |
| E | 1~8 | 3.8 | 19.5 | 4.6 | 38.0 | 1.9 | 308.1 | 89.3 | 226.1 | 1.0 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |
| Bt1 | 8~20 | 4.1 | 19.6 | 4.1 | 10.0 | 0.95 | 194.2 | 116.0 | 131.9 | 17.2 | 38.5 | 2.3 | 7.7 | |
| Bt2 | 20~30 | 4.2 | 12.4 | 6.5 | 11.9 | 1.07 | 269.0 | 162.2 | 132.8 | 25.8 | 41.3 | 1.8 | 7.8 | |
| BC | 30~45 | 4.3 | 12.7 | 3.9 | 9.0 | 1.06 | 245.8 | 129.3 | 102.6 | 23.9 | 34.9 | 1.6 | 7.5 | |
| Footslope | Oi | +11~+8 | 3.8 | 98.9 | 10.6 | 541.7 | 12.8 | 905.0 | 122.3 | 714.5 | 0.4 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| Oe | +8~+4 | 3.5 | 120.3 | 5.3 | 511.8 | 19.1 | 701.6 | 120.8 | 653.2 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 1.2 | |
| Oa | +4~0 | 3.3 | 102.9 | 5.0 | 476.7 | 22.9 | 402.5 | 193.6 | 545.5 | 0.4 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 1.9 | |
| A | 0~5 | 3.5 | 65.3 | 2.6 | 237.6 | 12.9 | 305.9 | 213.4 | 318.9 | 14.9 | 18.3 | 2.5 | 4.0 | |
| E | 5~10 | 4 | 11.5 | 7.8 | 7.0 | 0.7 | 171.7 | 139.7 | 78.7 | 1.3 | 5.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | |
| Bw1 | 10~23 | 4.1 | 16.6 | 2.4 | 10.0 | 1.1 | 283.8 | 239.7 | 82.0 | 18.1 | 35.9 | 1.6 | 4.5 | |
| Bw2 | 23~42 | 4.5 | 17.6 | 4.5 | 19.9 | 1.5 | 928.3 | 258.9 | 125.1 | 18.3 | 47.0 | 2.2 | 7.9 | |
| Lakeshore | Oi | +33~+22 | 3.5 | 36.3 | 5.7 | 363.1 | 12.7 | 934.1 | 103.0 | 561.8 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| Oe | +22~+9 | 3.4 | 18.7 | 8 | 186.7 | 8.7 | 563.4 | 107.9 | 431.7 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 0.6 | 0.8 | |
| Oa | +9~0 | 3.5 | 17.7 | 7.3 | 176.9 | 7.4 | 945.8 | 124.6 | 417.3 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| Site | Inorganic P in Extracts | Summed Inorganic P (Pi) | Organic P in Extracts | Summed Organic P (Po) | Residual-P | Summed P | Total P | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaOH-Pi | HCl-Pi | cHCl-Pi | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Po | cHCl-Po | ||||||
| Summit | 4.8 ab | 61.2 a | 46.4 b | 2.3 | 9.4 | 124.1 ab | 124.4 b | 415.6 a | 20.6 b | 560.6 ab | 38.0 | 722.7 ab | 757.0 ab |
| Footslope | 2.4 b | 35.3 b | 83.3 a | 4.4 | 4.7 | 130.1 a | 272.7 a | 335.3 ab | 31.6 a | 639.6 a | 29.4 | 799.0 a | 828.3 a |
| Lakeshore | 7.3 a | 25.4 b | 36.4 b | 5.9 | 9.9 | 84.8 b | 177.5 b | 306.5 b | 27.6 ab | 511.5 b | 34.9 | 631.2 b | 668.2 b |
| Soil | Pi | Po | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical § | NMR | Chemical § | NMR | |
| % | ||||
| Summit | 17.2 ± 2.8 | 17.5 ± 1.2 | 77.5 ± 2.9 | 82.5 ± 3.7 |
| Footslope | 16.3 ± 2.1 | 17.3 ± 1.4 | 80.0 ± 2.4 | 82.7 ± 2.7 |
| Lakeshore | 16.9 ± 1.4 | 11.6 ± 1.7 | 81.1 ± 1.5 | 88.4 ± 5.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiau, Y.-J.; Pai, C.-W.; Tsai, J.-W.; Liu, W.-C.; Yam, R.S.W.; Chang, S.-C.; Tang, S.-L.; Chiu, C.-Y. Characterization of Phosphorus in a Toposequence of Subtropical Perhumid Forest Soils Facing a Subalpine Lake. Forests 2018, 9, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060294
Shiau Y-J, Pai C-W, Tsai J-W, Liu W-C, Yam RSW, Chang S-C, Tang S-L, Chiu C-Y. Characterization of Phosphorus in a Toposequence of Subtropical Perhumid Forest Soils Facing a Subalpine Lake. Forests. 2018; 9(6):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060294
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiau, Yo-Jin, Chung-Wen Pai, Jeng-Wei Tsai, Wen-Cheng Liu, Rita S. W. Yam, Shih-Chieh Chang, Sen-Lin Tang, and Chih-Yu Chiu. 2018. "Characterization of Phosphorus in a Toposequence of Subtropical Perhumid Forest Soils Facing a Subalpine Lake" Forests 9, no. 6: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060294
APA StyleShiau, Y. -J., Pai, C. -W., Tsai, J. -W., Liu, W. -C., Yam, R. S. W., Chang, S. -C., Tang, S. -L., & Chiu, C. -Y. (2018). Characterization of Phosphorus in a Toposequence of Subtropical Perhumid Forest Soils Facing a Subalpine Lake. Forests, 9(6), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060294