Determination of Tangeretin in Rat Plasma: Assessment of Its Clearance and Absolute Oral Bioavailability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.3. Preparation of Samples
2.4. Assay Validation
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Examination
2.6. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assay Validation
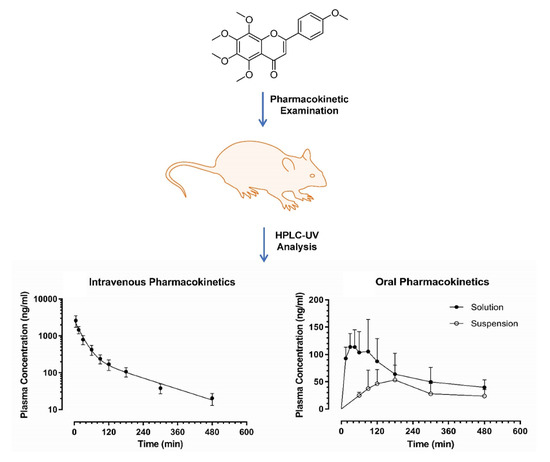
3.2. Application to a Pre-Clinical Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Lo, C.Y.; Ho, C.T. Hydroxylated polymethoxyflavones and methylated flavonoids in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) peel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4176–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, J.A.; Grohmann, K. Phenols in citrus peel byproducts. Concentrations of hydroxycinnamates and polymethoxylated flavones in citrus peel molasses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3268–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, R.; Shanthi, P.; Sachdanandam, P. Effect of tangeretin, a polymethoxylated flavone on glucose metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Hur, H.J.; Kwon, D.Y.; Hwang, J.T. Tangeretin stimulates glucose uptake via regulation of AMPK signaling pathways in C2C12 myotubes and improves glucose tolerance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 358, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Shimada, A.; Sato, T.; Ito, A.; Yamanouchi, T.; Kosano, H. Regulation of adipocytokine secretion and adipocyte hypertrophy by polymethoxyflavonoids, nobiletin and tangeretin. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Park, J.S.; Jang, S.E.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Mechanism of Tangeretin in Activated Microglia. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, H.A.; Mohamed, W.R.; Arab, H.H.; Arafa, E.S.A. Tangeretin Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury in Rats: Targeting MAPKs and Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; Jiao, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Kuang, H. Tangeretin exerts anti-neuroinflammatory effects via NF-kappaB modulation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglial cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.M.; Deng, Z.K. Tangeretin ameliorates renal failure via regulating oxidative stress, NF-kappaB-TNF-alpha/iNOS signalling and improves memory and cognitive deficits in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Inflammopharmacology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenlocher, Y.; Feilhauer, K.; Schaffer, M.; Bischoff, S.C.; Lorentz, A. Citrus peel polymethoxyflavones nobiletin and tangeretin suppress LPS- and IgE-mediated activation of human intestinal mast cells. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Yang, J. Tangeretin has anti-asthmatic effects via regulating PI3K and Notch signaling and modulating Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokine balance in neonatal asthmatic mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, S.H.; Woo, J.T.; Kim, D.H. Tangeretin Inhibits IL-12 Expression and NF-kappaB Activation in Dendritic Cells and Attenuates Colitis in Mice. Planta Medica 2017, 83, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, G.C.; Chung, H.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhuang, L.; Li, M.M.; Li, Y.L. Tangeretin from Citrus reticulate Inhibits Respiratory Syncytial Virus Replication and Associated Inflammation in Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9520–9527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Ali, M.S.; Moraes, L.A.; Sage, T.; Lewis, K.R.; Jones, C.I.; Gibbins, J.M. Tangeretin regulates platelet function through inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and cyclic nucleotide signaling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akachi, T.; Shiina, Y.; Ohishi, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kawagishi, H.; Morita, T.; Mori, M.; Sugiyama, K. Hepatoprotective effects of flavonoids from shekwasha (Citrus depressa) against d-galactosamine-induced liver injury in rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2010, 56, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Vermeer, M.A.; Bos, W.; van Buren, L.; Schuurbiers, E.; Miret-Catalan, S.; Trautwein, E.A. Molecular structures of citrus flavonoids determine their effects on lipid metabolism in HepG2 cells by primarily suppressing apoB secretion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4496–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.H.; Chen, W.J.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Ho, C.T.; Lin, J.K. Tangeretin induces cell-cycle G1 arrest through inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases 2 and 4 activities as well as elevating Cdk inhibitors p21 and p27 in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyasamy, K.; Baskaran, K.; Ilakkia, A.; Vanitha, K.; Selvaraj, S.; Sakthisekaran, D. Antitumor efficacy of tangeretin by targeting the oxidative stress mediated on 7,12-dimethylbenz(a) anthracene-induced proliferative breast cancer in Sprague-Dawley rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 75, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.Q.; Feng, S.L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C.X.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y. Role of tangeretin as a potential bioavailability enhancer for silybin: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacological studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.L.; Yuan, Z.W.; Yao, X.J.; Ma, W.Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xie, Y. Tangeretin, a citrus pentamethoxyflavone, antagonizes ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance by inhibiting its transport function. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 110, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowska, O.; Wisniewski, J.; Sroda-Pomianek, K.; Bielawska-Pohl, A.; Paprocka, M.; Dus, D.; Duarte, N.; Ferreira, M.J.; Michalak, K. Multidrug resistance reversal and apoptosis induction in human colon cancer cells by some flavonoids present in citrus plants. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, B. Tangeretin enhances radiosensitivity and inhibits the radiation-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, K.; Yu, Y.; Lee, J.; Jeong, W.S.; Ho, C.T.; Jun, M. Polymethoxyflavones: Novel beta-Secretase (BACE1) Inhibitors from Citrus Peels. Nutrients 2017, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braidy, N.; Behzad, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Ahmed, T.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Nabavi, S.F. Neuroprotective Effects of Citrus Fruit-Derived Flavonoids, Nobiletin and Tangeretin in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Q.; Cao, Y.L.; Hao, F.; Yan, Z.R.; Wang, M.L.; Liu, X.W. Tangeretin alters neuronal apoptosis and ameliorates the severity of seizures in experimental epilepsy-induced rats by modulating apoptotic protein expressions, regulating matrix metalloproteinases, and activating the PI3K/Akt cell survival pathway. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Wu, X.H.; Yu, H.G.; Teng, L.S. Tangeretin inhibits neurodegeneration and attenuates inflammatory responses and behavioural deficits in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced Parkinson’s disease dementia in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datla, K.P.; Christidou, M.; Widmer, W.W.; Rooprai, H.K.; Dexter, D.T. Tissue distribution and neuroprotective effects of citrus flavonoid tangeretin in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 3871–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, J.A.; Cesar, T.B.; Jackson, E.; Mertens-Talcott, S. Pharmacokinetic study of nobiletin and tangeretin in rat serum by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Xia, C.; Lin, Z.; Rogers, M.A.; Huang, Q. Viscoelastic emulsion improved the bioaccessibility and oral bioavailability of crystalline compound: A mechanistic study using in vitro and in vivo models. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T. Methoxylated flavones, a superior cancer chemopreventive flavonoid subclass? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2007, 17, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yeo, S.C.; Chuang, X.F.; Lin, H.S. Determination of pinostilbene in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm Biomed. Anal. 2016, 120, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yeo, S.C.; Elhennawy, M.G.; Xiang, X.; Lin, H.S. Determination of naturally occurring resveratrol analog trans-4,4′-dihydroxystilbene in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5793–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.C.; Sviripa, V.M.; Huang, M.; Kril, L.; Watt, D.S.; Liu, C.; Lin, H.S. Analysis of trans-2,6-difluoro-4′-(N,N-dimethylamino)stilbene (DFS) in biological samples by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Metabolite identification and pharmacokinetics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7319–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.Y.; Cardullo, N.; Yeo, S.C.; Spatafora, C.; Tringali, C.; Ong, P.S.; Lin, H.S. Quantification of the resveratrol analogs trans-2,3-dimethoxy-stilbene and trans-3,4-dimethoxystilbene in rat plasma: Application to pre-clinical pharmacokinetic studies. Molecules 2014, 19, 9577–9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yeo, S.C.M.; Elhennawy, M.; Lin, H.S. Oxyresveratrol: A bioavailable dietary polyphenol. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S.; Ho, P.C. Preclinical pharmacokinetic evaluation of resveratrol trimethyl ether in sprague-dawley rats: The impacts of aqueous solubility, dose escalation, food and repeated dosing on oral bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 4491–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.C.; Ho, P.C.; Lin, H.S. Pharmacokinetics of pterostilbene in Sprague-Dawley rats: The impacts of aqueous solubility, fasting, dose escalation, and dosing route on bioavailability. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhennawy, M.G.; Lin, H.S. Quantification of apigenin trimethyl ether in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a pre-clinical pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 142, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, S.; Loi, C.M.; Brodfuehrer, J.; El-Kattan, A. Impact of physiological, physicochemical and biopharmaceutical factors in absorption and metabolism mechanisms on the drug oral bioavailability of rats and humans. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2007, 3, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, O.H.; Stewart, B.H. Physicochemical and drug-delivery considerations for oral drug bioavailability. Drug Discov. Today 1996, 1, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintieri, L.; Palatini, P.; Nassi, A.; Ruzza, P.; Floreani, M. Flavonoids diosmetin and luteolin inhibit midazolam metabolism by human liver microsomes and recombinant CYP 3A4 and CYP3A5 enzymes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1426–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/68077#section=Top (assessed on 5 November 2017).



| Intraday Assay | Nominal Concentrations (ng/mL) | ||
| 45.0 | 450 | 1200 | |
| Measured concentrations (ng/mL) | 47.1 ± 1.0 | 434.8 ± 6.9 | 1149 ± 6 |
| Accuracy (%) | 104.6 ± 2.2 | 96.6 ± 1.5 | 95.7 ± 0.5 |
| RSD (%) | 2.1 | 1.6 | 0.6 |
| Absolute Recovery (%) | 89.2 ± 3.5 | 105.1 ± 2.3 | 99.5 ± 0.86 |
| Inter-day Assay | Nominal Concentrations (ng/mL) | ||
| 45.0 | 450 | 1200 | |
| Measured concentrations (ng/mL) | 44.3 ± 1.3 | 440 ± 9.8 | 1183 ± 30 |
| Accuracy (%) | 98.5 ± 2.9 | 97.7 ± 2.1 | 98.8 ± 2.4 |
| RSD (%) | 3.0 | 2.3 | 2.5 |
| Storage Conditions | Remaining (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | |||
| 45.0 | 450 | 1200 | |
| Plasma samples stored for 24 h at 4 °C | 101.7 ± 4.5 | 103.2 ± 4.6 | 94.9 ± 1.9 |
| Post-preparative samples stored for 24 h at 25 °C | 89.4 ± 4.0 | 113.1 ± 3.0 | 87.0 ± 2.1 |
| Plasma samples after three freeze-thaw cycles | 90.6 ± 7.1 | 95.2 ± 6.9 | 93.8 ± 0.3 |
| Plasma samples stored for 14 days at −80 °C | 93.4 ± 4.1 | 110.4 ± 2.6 | 98.5 ± 1.0 |
| Stock solution stored for 7 days at 25 °C | 111.5 ± 5.5 | ||
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | Intravenous | Oral | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | Solution (n = 5) | Suspension (n = 6) | Solution (n = 5) |
| Dose (mg·kg−1) | 10 | 50 | 50 |
| A (µg·mL−1) | 2.22 ± 0.48 | - | - |
| B (ng·mL−1) | 254 ± 128 | - | - |
| α (10−2 × min−1) | 4.06 ± 1.21 | - | - |
| β (10−3 × min−1) | 5.47 ± 1.63 | - | - |
| Vc (L·kg−1) | 4.20 ± 0.82 | - | - |
| AUC0→last (104 × min·ng·mL−1) | 10.5 ± 2.5 | 1.61 ± 0.34 | 3.17 ± 1.65 |
| Cl (mL·min−1·kg−1) | 94.1 ± 20.2 | - | - |
| t1/2 λz (min) | 166 ± 42 | - | - |
| MRT0→last (min) | 73.3 ± 10.3 | 260 ± 102 | 187 ± 73 |
| MAT (min) | - | 187 ± 102 | 114 ± 73 |
| Cmax (ng·mL−1) | 2470 ± 557 | 65.3 ± 20.1 | 135 ± 46 ** |
| tmax (min) | - | 90–120 | 30–90 ** |
| Mean F (%) | - | < 3.05 | 6.02 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elhennawy, M.G.; Lin, H.-S. Determination of Tangeretin in Rat Plasma: Assessment of Its Clearance and Absolute Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010003
Elhennawy MG, Lin H-S. Determination of Tangeretin in Rat Plasma: Assessment of Its Clearance and Absolute Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleElhennawy, Mai Gamal, and Hai-Shu Lin. 2018. "Determination of Tangeretin in Rat Plasma: Assessment of Its Clearance and Absolute Oral Bioavailability" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010003
APA StyleElhennawy, M. G., & Lin, H. -S. (2018). Determination of Tangeretin in Rat Plasma: Assessment of Its Clearance and Absolute Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics, 10(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010003