Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
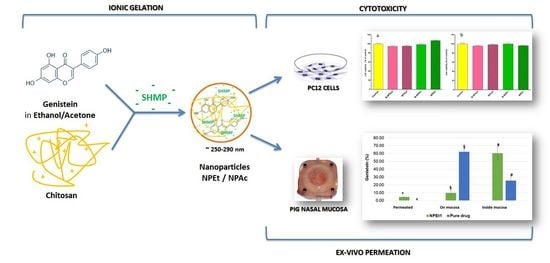
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Purification of Chitosan
2.3. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles
2.4. Analysis of Particle Size and Polydispersity
2.5. Stability Studies
2.6. Determination of the Entrapment Efficiency
2.7. HPLC Method
2.8. Evaluation of pH
2.9. Morphological Analysis
2.9.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.9.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.10. X-Ray Analysis
2.11. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies on Nasal Mucosa
2.12. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
2.12.1. Cell Culture
2.12.2. MTT Assay
2.12.3. Trypan Blue Assay
2.12.4. Apoptosis Assessment
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Particle Size and Polydispersity
3.2. Stability Studies
3.3. Determination of the Entrapment Efficiency
3.4. Evaluation of pH
3.5. Morphological Analysis
3.6. X-Ray Analysis
3.7. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies on Nasal Mucosa
3.8. In Vitro Cell Viability Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NDDs | Neurodegenerative diseases |
| GEN | Genistein |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PC12 cells | Rat pheochromocytoma-derived cell line |
| CS | Chitosan |
| SHMP | Sodium hexametaphosphate |
| DMEM/F12 | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethyl- thiazol-2-yl)-2, 5, diphenyl tetrazolium bromide |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| B-NPAc, NPAc1, and NPAc2 | Unloaded and loaded nanoparticles prepared by adding acetone as organic solvent |
| B-NPEt and NPEt1 | Unloaded and loaded nanoparticles prepared by adding ethanol as organic solvent |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| PCS | Photo correlation spectroscopy |
| DL | Drug loading |
| EE | Entrapment efficiency |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
References
- Fratiglioni, L.; Qiu, C. Prevention of common neurodegenerative disorders in the elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor, S.; Puentes, F.; Baker, D.; Van Der Valk, P. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2010, 129, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.E.; Rhie, S.J.; Yoon, S. The role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 24, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.C.; Lockwood, A.H.; Sonawane, B.R. Neurodegenerative diseases: An overview of environmental risk factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, S.; Haque, E.; Mir, S.S. Neurodegenerative diseases: Multifactorial conformational diseases and their therapeutic interventions. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 563481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnham, K.J.; Masters, C.L.; Bush, A.I. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanan, R.; Oikawa, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Ohnishi, S.; Ma, N.; Pinlaor, S.; Yongvanit, P.; Kawanishi, S.; Murata, M. Oxidative stress and its significant roles in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanty, N.; Dichter, M.A. Antioxidant therapy in neurologic disease. Arch. Neurol. 2000, 57, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poprac, P.; Jomova, K.; Simunkova, M.; Kollar, V.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganai, A.A.; Farooqi, H. Bioactivity of genistein: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 76, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.Q.; Kuhn, G.; Wegner, J.; Chen, J. Isoflavones, substances with multi-biological and clinical properties. Eur. J. Nutr. 2001, 40, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B. Natural antioxidants protect neurons in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Ko, J.W.; Jeon, S.; Kwon, Y.H. Protective Effect of Genistein against Neuronal Degeneration in ApoE−/− Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2016, 8, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrás, C.; Gambini, J.; Gómez-Cabrera, M.C.; Sastre, J.; Pallardó, F.V.; Mann, G.E.; Viña, J. Genistein, a soy isoflavone, up-regulates expression of antioxidant genes: Involvement of estrogen receptors, ERK1/2, and NFκB. FASEB J. 2006, 20, E1476–E1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnuolo, C.; Russo, G.L.; Orhan, I.E.; Habtemariam, S.; Daglia, M.; Sureda, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Devi, K.P.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; et al. Genistein and cancer: Current status, challenges, and future directions. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikand, G.; Kris-Etherton, P.; Boulos, N.M. Impact of functional foods on prevention of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.N.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, C.F. Efficacy of phytoestrogens for menopausal symptoms: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Climacteric 2015, 18, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odle, B.; Dennison, N.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Broderick, T.L.; Plochocki, J.H. Genistein treatment improves fracture resistance in obese diabetic mice. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Lan, T.; Liao, W.; Zhao, M.; Yang, H. Genistein Inhibits Aβ 25–35–Induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells via PKC Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2787–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, X.; Hou, C.; Ma, W.; Yu, H.; Xiao, R. Genistein antagonizes inflammatory damage induced by β-amyloid peptide in microglia through TLR4 and NF-κB. Nutrition 2014, 30, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Shanmuganathan, B.; Manayi, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M. Molecular and therapeutic targets of genistein in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7028–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xu, N.; Ji, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. Eudragit nanoparticles containing genistein: Formulation, development, and bioavailability assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C.; Mei, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Fabrication of genistein-loaded biodegradable TPGS-b-PCL nanoparticles for improved therapeutic effects in cervical cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2461–2473. [Google Scholar]
- Neves Carvalho, A.; Firuzi, O.; Joao Gama, M.; van Horssen, J.; Saso, L. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in neurological diseases: Is there still hope? Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, A.; Stolnik, S.; Illum, L. Nose-to-brain delivery: Investigation of the transport of nanoparticles with different surface characteristics and sizes in excised porcine olfactory epithelium. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeshi, C.V.; Belgamwar, V.S. Direct nose to brain drug delivery via integrated nerve pathways bypassing the blood–brain barrier: An excellent platform for brain targeting. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourganis, V.; Kammona, O.; Alexopoulos, A.; Kiparissides, C. Recent Advances in Carrier Mediated Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Pharmaceutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Posadino, A.M.; Pintus, G.; Sarmento, B.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nose-to-brain delivery of BACE1 siRNA loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, A.; Stolnik, S.; Illum, L. Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, T.; Pellitteri, R.; Spatuzza, M.; Puglisi, G. Nose-to-brain delivery: Evaluation of polymeric nanoparticles on olfactory ensheathing cells uptake. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Saraf, S.; Antimisiaris, S.G.; Chougule, M.B.; Shoyele, S.A.; Alexander, A. Nose-to-brain drug delivery: An update on clinical challenges and progress towards approval of anti-Alzheimer drugs. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langasco, R.; Fancello, S.; Rassu, G.; Cossu, M.; Cavalli, R.; Galleri, G.; Giunchedi, P.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E. Increasing protective activity of Genistein by loading into transfersomes: A new potential adjuvant in the oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative diseases? Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illum, L. Nanoparticulate systems for nasal delivery of drugs: A real improvement over simple systems? J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Haukvik, T.; Lanni, C.; Racchi, M.; Giunchedi, P. Mucoadhesive microspheres for nasal administration of cyclodextrins. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Md, S.; Khan, R.A.; Mustafa, G.; Chuttani, K.; Baboota, S.; Sahni, J.K.; Ali, J. Bromocriptine loaded chitosan nanoparticles intended for direct nose to brain delivery: Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and scintigraphy study in mice model. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vllasaliu, D.; Exposito-Harris, R.; Heras, A.; Casettari, L.; Garnett, M.; Illum, L.; Stolnik, S. Tight junction modulation by chitosan nanoparticles: Comparison with chitosan solution. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Cossu, M.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P.; Dalpiaz, A. Particulate formulations based on chitosan for nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpiaz, A.; Fogagnolo, M.; Ferraro, L.; Capuzzo, A.; Pavan, B.; Rassu, G.; Salis, A.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nasal chitosan microparticles target a zidovudine prodrug to brain HIV sanctuaries. Antiviral Res. 2015, 123, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Cossu, M.; Brundu, A.; Cerri, G.; Marchetti, N.; Ferraro, L.; Regan, R.F.; Giunchedi, P.; Dalpiaz, A. Solid microparticles based on chitosan or methyl-β-cyclodextrin: A first formulative approach to increase the nose-to-brain transport of deferoxamine mesylate. J. Control. Release 2015, 201, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bshara, H.; Osman, R.; Mansour, S.; El-Shamy, A.E.H.A. Chitosan and cyclodextrin in intranasal microemulsion for improved brain buspirone hydrochloride pharmacokinetics in rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, B.A. In situ-based gels for nose to brain delivery for the treatment of neurological diseases. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandapani, G.; Prasad, S.; Sudha, P.N.; Sukumaran, A. Size optimization and in vitro biocompatibility studies of chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parab, H.J.; Huang, J.H.; Lai, T.C.; Jan, Y.H.; Liu, R.S.; Wang, J.L.; Hsiao, M.; Chen, C.H.; Hwu, Y.K.; Tsai, D.P.; et al. Biocompatible transferrin-conjugated sodium hexametaphosphate-stabilized gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity and cellular uptake. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 395706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasti, A.; Zaki, N.M.; de Leonardis, P.; Ungphaiboon, S.; Sansongsak, P.; Rimoli, M.G.; Tirelli, N. Chitosan/TPP and chitosan/TPP-hyaluronic acid nanoparticles: Systematic optimisation of the preparative process and preliminary biological evaluation. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1918–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, P.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Vila-Jato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Novel hydrophilic chitosan-polyethylene oxide nanoparticles as protein carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Nieddu, M.; Bosi, P.; Trevisi, P.; Colombo, M.; Priori, D.; Manconi, P.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E.; Boatto, G. Encapsulation and modified-release of thymol from oral microparticles as adjuvant or substitute to current medications. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zampieri, A.L.T.C.; Ferreira, F.S.; Resende, É.C.; Gaeti, M.P.N.; Diniz, D.G.A.; Taveira, S.F.; Lima, E.M. Biodegradable polymeric nanocapsules based on poly (DL-lactide) for genistein topical delivery: Obtention, characterization and skin permeation studies. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, F.; Hanieh, P.N.; Chan, L.K.N.; Angeloni, L.; Passeri, D.; Rossi, M.; Wang, J.T.; Imbriano, A.; Carafa, M.; Marianecci, C. Chitosan Glutamate-Coated Niosomes: A Proposal for Nose-to-Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavini, E.; Spada, G.; Rassu, G.; Cerri, G.; Brundu, A.; Cossu, M.; Sorrenti, M.; Giunchedi, P. Development of solid nanoparticles based on hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin aimed for the colonic transmucosal delivery of diclofenac sodium. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Cossu, M.; Langasco, R.; Carta, A.; Cavalli, R.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Propolis as lipid bioactive nano-carrier for topical nasal drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, J.; Liu, F.; Majeed, H.; Qi, J.; Yokoyama, W.; Zhong, F. Physicochemical and morphological properties of size-controlled chitosan–tripolyphosphate nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 465, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Laouini, A.; Fessi, H.; Charcosset, C. Preparation of chitosan–TPP nanoparticles using microengineered membranes–Effect of parameters and encapsulation of tacrine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z. Preparation and biological activity studies of resveratrol loaded ionically cross-linked chitosan-TPP nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonassen, H.; Kjøniksen, A.L.; Hiorth, M. Stability of chitosan nanoparticles cross-linked with tripolyphosphate. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3747–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, L.; Pal, M.K.; Ray, R.S. Synergism of co-delivered nanosized antioxidants displayed enhanced anticancer efficacy in human colon cancer cell lines. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, K.R.; Gambhire, M.N.; Shaikh, I.M.; Kadam, V.J.; Pisal, S.S. Nasal drug delivery system-factors affecting and applications. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2007, 2, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.M.; Misra, M.; Shishoo, C.J.; Padh, H. Nose to brain microemulsion-based drug delivery system of rivastigmine: Formulation and ex-vivo characterization. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casettari, L.; Illum, L. Chitosan in nasal delivery systems for therapeutic drugs. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazancová, P.; Némethová, V.; Trel’ová, D.; Kleščíková, L.; Lacík, I.; Rázga, F. Dissociation of chitosan/tripolyphosphate complexes into separate components upon pH elevation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Formulation | CS:SHMP Mass Ratio | Particle Size (nm ±SD) | PDI (±SD) | Visual Observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2:1 | #ç§* 694.3 ± 124.1 | *ç#° 0.625 ± 0.12 | Aggregation |
| B | 2.5:1 | #ç§* 523.2 ± 65.7 | §#° 0.563 ± 0.08 | Opalescence with aggregates |
| C | 3:1 | #ç§* 385.6 ± 65.7 | *ç# 0.476 ± 0.02 | Opalescence |
| D | 4:1 | #ç§* 267.6 ± 23.7 | *§ç#° 0.330 ± 0.01 | Opalescence |
| E | 5:1 | ç§* 252.2 ± 12.4 | *§#° 0.421 ± 0.05 | Clear |
| Formulation | Organic Solvent | GEN (mg) | Particle Size (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-NPAc | Acetone | - | *# 232.8 ± 4.3 | 0.213 ± 0.02 |
| B-NPEt | Ethanol | - | * 286.3 ± 11.2 | 0.417 ± 0.56 |
| NPAc1 | Acetone | 1 | ç§# 252.4 ± 5.8 | 0.244 ± 0.03 |
| NPAc2 | Acetone | 2 | ç§# 267.5 ± 9.5 | 0.229 ± 0.05 |
| NPEt1 | Ethanol | 0.5 | § 296.7 ± 12.3 | 0.412 ± 0.62 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rassu, G.; Porcu, E.P.; Fancello, S.; Obinu, A.; Senes, N.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010008
Rassu G, Porcu EP, Fancello S, Obinu A, Senes N, Galleri G, Migheli R, Gavini E, Giunchedi P. Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleRassu, Giovanna, Elena Piera Porcu, Silvia Fancello, Antonella Obinu, Nina Senes, Grazia Galleri, Rossana Migheli, Elisabetta Gavini, and Paolo Giunchedi. 2019. "Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010008
APA StyleRassu, G., Porcu, E. P., Fancello, S., Obinu, A., Senes, N., Galleri, G., Migheli, R., Gavini, E., & Giunchedi, P. (2019). Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics, 11(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010008