Repurposing Itraconazole Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Improved Antitumor Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
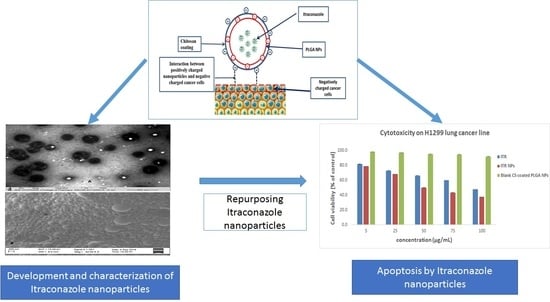
2.2. Development of Chitosan-Coated PLGA Nanoparticles
2.3. Particle Size, Polydispersity, and Zeta Potential Measurement
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Entrapment and Drug Loading Efficiency
2.7. In Vitro Release Study
3. Cell Culture
3.1. In Vitro Cell Viability Assay
3.2. Apoptosis Assay by Flow Cytometry
3.3. Effect of ITR and ITR NPs on Molecular Markers
3.4. Cell Cycle Status by Flow Cytometry
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Result and Discussions
4.1. Preparation and Characterization of Itraconazole Nanoparticles
4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.3. In Vitro Drug Release Study
4.4. Cytotoxic Effect/s of ITR and CS-ITR-PLGA NPs (ITR NPs)
4.5. Effect of ITR and ITR NPs on Cellular Apoptosis
4.6. Effect of ITR and ITR NPs on Cell Cycle Progression
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsoukalas, N.; Aravantinou-Fatorou, E.; Baxevanos, P.; Tolia, M.; Tsapakidis, K.; Galanopoulos, M.; Liontos, M.; Kyrgias, G. Advanced small cell lung cancer (SCLC): New challenges and new expectations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, C.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Pepe, V.; Silva, A.M.; Musumeci, T.; Puglisi, G.; Furneri, P.M.; Souto, E.B. Repurposing itraconazole to the benefit of skin cancer treatment: A combined azole-DDAB nanoencapsulation strategy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleire, L.; Førde, H.E.; Netland, I.A.; Leiss, L.; Skeie, B.S.; Enger, P.Ø. Drug repurposing in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 124, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, B.; Bai, B.; Huang, Y.; et al. Anti-proliferation of breast cancer cells with itraconazole: Hedgehog pathway inhibition induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death. Cancers Lett. 2017, 385, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Juergens, R.A.; Hann, C.L.; Ettinger, D.S.; Sebree, R.; Smith, R.; Aftab, B.T.; Huang, P.; Liu, J.O. Phase 2 study of pemetrexed and itraconazole as second-line therapy for metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Huang, Q.; Qiu, F.; Sui, M. Non-viral delivery systems for the application in p53 cancer gene therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 4118–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, V.; Mishra, G.P.; Mitra, A.K. Biodegradable polymers for ocular drug delivery. In Mitra AK: Advances in Ocular Drug Delivery; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2012; Volume 65, p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, K.; Si, J.; Sui, M.; Shen, Y. Charge-reversal polymers for biodelivery. In Bioinspired and Biomimetic Polymer Systems for Drug and Gene Delivery; Chemical Industry Press and Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; Volume 4, p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Nafee, N.; Taetz, S.; Schneider, M.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.M. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for DNA/RNA delivery: Effect of the formulation parameters on complexation and transfection of antisense oligonucleotides. Nanomedicine 2007, 1, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, A.; Sanchez, A.; Tobıo, M.; Calvo, P.; Alonso, M.J. Design of biodegradable particles for protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2002, 78, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, S.; Almalik, A.; Alshamsan, A. Optimizing indomethacin-loaded chitosan nanoparticle size, encapsulation, and release using Box–Behnken experimental design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhowyan, A.A.; Altamimi, M.A.; Kalam, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Badran, M.; Binkhathlan, Z.; Alkholief, M.; Alshamsan, A. Antifungal efficacy of Itraconazole loaded PLGA-nanoparticles stabilized by vitamin-E TPGS: In vitro and ex vivo studies. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 161, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.A.; Alshehri, S.; Alshamsan, A.; Haque, A.; Shakeel, F. Solid liquid equilibrium of an antifungal drug itraconazole in different neat solvents: Determination and correlation. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 234, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Ameeduzzafar, A.; Khanna, K.; Bhatnagar, A.; Ahmad, F.J.; Ali, A. Chitosan coated PLGA nanoparticles amplify the ocular hypotensive effect of forskolin: Statistical design, characterization and in vivo studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 116, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, B.; Parvathaneni, V.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Shukla, S.K.; Damon, J.K.; Sarode, A.; Kanabar, D.; Garcia, J.V.; Mitragotri, S.; Muth, A.; et al. Cyclodextrin modified erlotinib loaded PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic efficacy against non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.S.; Hu, L.L.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, A.W.; Liu, J. Resveratrol-loaded folic acid-grafted dextran stearate submicron particles exhibits enhanced antitumor efficacy in non-small cell lung cancers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Hu, J.J.; Fu, R.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.N.; Deng, Q.; Luo, Q.S.; et al. Flavonoids inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis and autophagy through downregulation of PI3Kγ mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K/ULK signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, N.; Schneider, M.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.M. Relevance of the colloidal stability of chitosan/PLGA nanoparticles on their cytotoxicity profile. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.A.; Khalil, N.M.; Tominaga, T.T.; Lechanteur, A.; Sarmento, B.; Mainardes, R.M. Mucoadhesive chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for oral delivery of ferulic acid. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Kong, L. Chitosan-modified PLGA nanoparticles with versatile surface for improved drug delivery. Aaps Pharmscitech 2013, 14, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parveen, S.; Sahoo, S.K. Long circulating chitosan/PEG blended PLGA nanoparticle for tumor drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoncheva, K.; Vandervoort, J.; Ludwig, A. Influence of chitosan layer on the properties of surface modified poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2009, 30, 213–21623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, J.; Sultana, Y.; Aqil, M. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles of bevacizumab as novel drug delivery to target retina: Optimization, characterization, and in vitro toxicity evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, G.K.; Pathan, S.A.; Akhter, S.; Ahmad, N.; Jain, N.; Talegaonkar, S.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmad, F.J. Mechanistic study of hydrolytic erosion and drug release behaviour of PLGA nanoparticles: Influence of chitosan. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2360–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Shah, B.A.; Kotadia, N.K.; Li, J.; Gu, H.; Wu, Z. The development and mechanism studies of cationic chitosan-modified biodegradable PLGA nanoparticles for efficient siRNA drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahuguna, A.; Khan, I.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kang, S.C. MTT assay to evaluate the cytotoxic potential of a drug. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, T.; Xi, J.; Liu, S.; Ren, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H. Protosappanin B promotes apoptosis and causes G1 cell cycle arrest in human bladder cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jing, L.; Wang, Q.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, X.; Diao, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X. Bax-PGAM5L-Drp1 complex is required for intrinsic apoptosis execution. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.H.; Han, S.I.; Lee, S.Y.; Youk, H.S.; Moon, J.Y.; Duong, H.Q.; Park, M.J.; Joo, Y.M.; Park, H.G.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Protein kinase C-ERK1/2 signal pathway switches glucose depletion-induced necrosis to apoptosis by regulating superoxide dismutases and suppressing reactive oxygen species production in A549 lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.; Wang, R.; Gandhi, V. Targeting the apoptosis pathway in hematologic malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 1980–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. The Bcl2 family: Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Xie, J.; Xu, N.; Huang, L.; Xu, A.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Liu, C.; et al. Glaucocalyxin A induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.R.; Llambi, F. Cell death signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a006080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.-L.; Qi, X.-M.; Qi, C.-T.; Yu, Q. Inhibitory activities of Lignum Sappan extractives on growth and growth-related signaling of tumor cells. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Shieh, D.E.; Chen, C.C.; Yeh, C.S.; Dong, H.P. Linalool Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Leukemia Cells and Cervical Cancer Cells through CDKIs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28169–28179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Formulations | Average PS (nm) ± SD | Average PDI ± SD | Average ZP (mV) ± SD | Average EE (%) ± SD | Average DL (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA NPs | 189.3 ± 3.4 | 0.086 ± 0.06 | −4.04 ± 1.21 | NA | NA |
| ITR-PLGA NPs | 184.53 ± 4.43 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 0.90 ± 0.55 | 79.68 ± 7.30 | 15.93 ± 1.46 |
| CS-ITR-PLGA-NPs | 275.9 ± 6.09 | 0.24 ± 0.074 | 21.13 ± 3.42 | 80.18 ± 8.12 | 16.03 ± 1.62 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhakamy, N.A.; Md, S. Repurposing Itraconazole Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Improved Antitumor Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120685
Alhakamy NA, Md S. Repurposing Itraconazole Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Improved Antitumor Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(12):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120685
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhakamy, Nabil A., and Shadab Md. 2019. "Repurposing Itraconazole Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Improved Antitumor Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 12: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120685
APA StyleAlhakamy, N. A., & Md, S. (2019). Repurposing Itraconazole Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Improved Antitumor Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Pharmaceutics, 11(12), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120685