Formulation Strategies to Improve Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil
Abstract
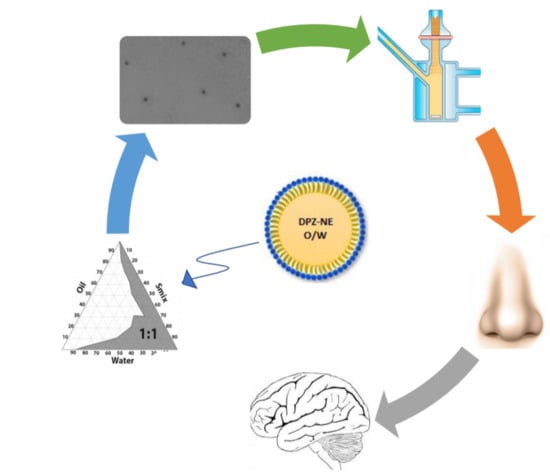
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. Solubility Study
2.4. Construction of Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
2.5. Preparation of DPZ-NE and DPZ-PNE
2.6. Characterization of DPZ-NE and DPZ-PNE
2.7. Stability Studies
2.8. In Vitro Release Study
2.9. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies
2.10. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.11. Histological Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Solubility Studies
3.2. Pseudo-Ternary Diagrams and Formulation of DPZ-NE and DPZ-PNE
3.3. Characterization of DPZ-NE and DPZ-PNE
3.4. Stability Studies
3.5. In Vitro Release Study
3.6. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies
3.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.8. Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.B.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, H.; Nemeş, B. New Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Gerontol. 2017, 11, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.; Grabowski, P.; Rehman, I. Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: Is there a role for folate? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 174, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arrigo, J. Alzheimer’s Disease, Brain Injury, and CNS Nanotherapy in Humans: Sonoporation Augmenting Drug Targeting. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nisha, C.M.; Silakari, C.; Sharma, I.; Anusha, K.; Gupta, N.; Nair, P.; Tripathi, T.; Kumar, A. Current and novel therapeutic molecules and targets in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.A.; Sabbagh, M.N. Donepezil: Potential neuroprotective and disease-modifying effects. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; He, S.; Chen, Y.; Feng, F.; Qu, W.; Sun, H. Donepezil-based multi-functional cholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Marinelli, L.; Di Stefano, A. Transdermal donepezil on the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2012, 8, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Antimisiaris, S.G.; Chougule, M.B.; Shoyele, S.A.; Alexander, A. Nose-to-brain drug delivery: An update on clinical challenges and progress towards approval of anti-Alzheimer drugs. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, J.; Lupo, N.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Advanced formulations for intranasal delivery of biologics. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, C.; Rijo, P.; Reis, C.P. Nanotechnological strategies for nerve growth factor delivery: Therapeutic implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Pharm. Res. 2017, 120, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, T.P.; Greenlee, M.H.W.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Hsu, W.H. Mechanism of intranasal drug delivery directly to the brain. Life Sci. 2018, 195, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.R.; Liu, M.; Khan, M.W.; Zhai, G. Progress in brain targeting drug delivery system by nasal route. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 364–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappelle, W.F.; Siersema, P.D.; Bogte, A.; Vleggaar, F.P. Challenges in oral drug delivery in patients with esophageal dysphagia. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Md, S.; Bhattmisra, S.K.; Zeeshan, F.; Shahzad, N.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Srikanth Meka, V.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Nano-carrier enabled drug delivery systems for nose to brain targeting for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, Y.K.; Piazza, J.E.; Bhandari, J.; Daya, R.P.; Akilan, K.; Simpson, M.J.; Hoare, T.; Mishra, R.K. Intranasal delivery of antipsychotic drugs. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 184, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderibigbe, B.A. In Situ-Based Gels for Nose to Brain Delivery for the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre, C.; Cena, V. The Delivery Challenge in Neurodegenerative Disorders: The Nanoparticles Role in Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics and Diagnostics. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallarate, M.; Chirio, D.; Bussano, R.; Peira, E.; Battaglia, L.; Baratta, F.; Trotta, M. Development of O/W nanoemulsions for ophthalmic administration of timolol. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.M.; El-Salamouni, N.S.; El-Refaie, W.M.; Hazzah, H.A.; Ali, M.M.; Tosi, G.; Farid, R.M.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J.; Billa, N.; Hanafy, A.S. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for Alzheimer’s disease management: Technical, industrial, and clinical challenges. J. Control. Release 2017, 245, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, P.C.; Santos, A.O. Nanosystems in nose-to-brain drug delivery: A review of non-clinical brain targeting studies. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourganis, V.; Kammona, O.; Alexopoulos, A.; Kiparissides, C. Recent advances in carrier mediated nose-to-brain delivery of pharmaceutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Kumar, S.S.; Dutta, P.K. Stability-indicative HPLC determination of donepezil hydrochloride in tablet dosage form. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 45, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi da Silva, J.; Ferreira, S.B.S.; de Freitas, O.; Bruschi, M.L. A critical review about methodologies for the analysis of mucoadhesive properties of drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Figueiro, F.; de Fraga Dias, A.; Teixeira, H.F.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Koester, L.S. Kaempferol-loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion for intranasal administration reduces glioma growth in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.M.; Misra, M.; Shishoo, C.J.; Padh, H. Nose to brain microemulsion-based drug delivery system of rivastigmine: Formulation and ex-vivo characterization. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Abreu, M.; Espinoza, L.C.; Halbaut, L.; Espina, M.; García, M.L.; Calpena, A.C. Comparative Study of Ex Vivo Transmucosal Permeation of Pioglitazone Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Polymers 2018, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.; Bartos, C.; Bocsik, A.; Kiss, L.; Veszelka, S.; Deli, M.A.; Ujhelyi, G.; Szabo-Revesz, P.; Ambrus, R. Cytotoxicity of Different Excipients on RPMI 2650 Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.C.; Li, V.; Ng, Y.Z.; Chan, T.T.; Chang, R.; Wong, R. Systematic Review of Cholinesterase Inhibitors on Cognition and Behavioral Symptoms in Patients of Chinese Descent with Alzheimer’s Disease, Vascular Dementia, or Mixed Dementia. Geriatrics 2017, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, H.; Li, F.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Wu, W. An update on the role of nanovehicles in nose-to-brain drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovskaya, L.; Abou-Kaoud, M.; Stepensky, D. Quantitative analysis of drug delivery to the brain via nasal route. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.W., Jr.; Gad, S.C.; Julien, M. A review of the nonclinical safety of Transcutol(R), a highly purified form of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (DEGEE) used as a pharmaceutical excipient. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gue, E.; Since, M.; Ropars, S.; Herbinet, R.; Le Pluart, L.; Malzert-Freon, A. Evaluation of the versatile character of a nanoemulsion formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 498, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisal, S.S.; Paradkar, A.R.; Mahadik, K.R.; Kadam, S.S. Pluronic gels for nasal delivery of Vitamin B12. Part I: Preformulation study. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 270, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Khateb, K.; Ozhmukhametova, E.K.; Mussin, M.N.; Seilkhanov, S.K.; Rakhypbekov, T.K.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. In situ gelling systems based on Pluronic F127/Pluronic F68 formulations for ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, L.C.; Vacacela, M.; Clares, B.; Garcia, M.L.; Fabrega, M.J.; Calpena, A.C. Development of a Nasal Donepezil-loaded Microemulsion for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: In vitro and ex vivo Characterization. CNS Neurol Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 17, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnken, Z.N.; Smyth, H.D.; Watts, A.B.; Weitman, S.; Kuhn, J.G.; Williams, R.O., III. Formulation and device design to increase nose to brain drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, G.; Grossiord, J.L.; Agnely, F.; Chaumeil, J.C. A review of poloxamer 407 pharmaceutical and pharmacological characteristics. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Amalina, N.; Sengupta, P.; Kumar, U. Mucoadhesive Polymers and Their Mode of Action: A Recent Update. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Chatterjee, B. Potential and future scope of nanoemulgel formulation for topical delivery of lipophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzus, B.; Colombo, M.; Sahle, F.F.; Zoubari, G.; Staufenbiel, S.; Bodmeier, R. Comparison of different in vitro release methods used to investigate nanocarriers intended for dermal application. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Abreu, M.; Calpena, A.C.; Andres-Benito, P.; Aso, E.; Romero, I.A.; Roig-Carles, D.; Gromnicova, R.; Espina, M.; Ferrer, I.; Garcia, M.L.; et al. PPARgamma agonist-loaded PLGA-PEG nanocarriers as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5577–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, S.H.; Saliaj, E.; Wettig, S.D.; Dong, C.; Ivanova, M.V.; Huzil, J.T.; Foldvari, M. Effect of chemical permeation enhancers on stratum corneum barrier lipid organizational structure and interferon alpha permeability. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2248–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Xia, D.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhu, C.; Gan, Y. Comparative study of Pluronic((R)) F127-modified liposomes and chitosan-modified liposomes for mucus penetration and oral absorption of cyclosporine A in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 449, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonvico, F.; Clementino, A.; Buttini, F.; Colombo, G.; Pescina, S.; Staniscuaski Guterres, S.; Raffin Pohlmann, A.; Nicoli, S. Surface-Modified Nanocarriers for Nose-to-Brain Delivery: From Bioadhesion to Targeting. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Mucosal Applications of Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hanes, J. Mucus-penetrating nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to mucosal tissues. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.A.; Lim, J.L.; Kim, C.; Park, J.Y. Pharmacokinetic comparison of orally disintegrating and conventional donepezil formulations in healthy Korean male subjects: A single-dose, randomized, open-label, 2-sequence, 2-period crossover study. Clin. Ther. 2011, 33, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdo, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, A.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of intranasal delivery route of drug administration for brain targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengst, A.; Reichl, S. RPMI 2650 epithelial model and three-dimensional reconstructed human nasal mucosa as in vitro models for nasal permeation studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementino, A.; Batger, M.; Garrastazu, G.; Pozzoli, M.; Del Favero, E.; Rondelli, V.; Gutfilen, B.; Barboza, T.; Sukkar, M.B.; Souza, S.A.; et al. The nasal delivery of nanoencapsulated statins—An approach for brain delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6575–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Components (%) | DPZ-NE | DPZ-PNE |
|---|---|---|
| DPZ (6.25 mg/mL) | - | - |
| Capryol 90 | 6 | 6 |
| Labrasol | 20 | 20 |
| Transcutol-P | 20 | 20 |
| Water | 54 | 30 |
| Pluronic F-127 | - | 24 |
| Rotational Testing | DPZ-NE | DPZ-PNE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Better mathematical model for fitting | Ramp-up section | Newton r = 0.9998 | Ostwald de Waele r = 1 |
| Ramp-down section | Newton r = 0.9998 | Ostwald de Waele r = 1 | |
| Rheological behavior | Newtonian | Pseudoplastic | |
| Viscosity mean values | 10.69 ± 0.04 mPa·s | 315.40 ± 0.22 mPa·s | |
| Formulations | Jss (µg/(min/cm2)) | Kp (cm/min) 103 | Qret (µg DPZ/g tissue/cm2) | Css (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPZ-NE | 6.58 (5.22–7.83) | 1.05 (0.83–1.25) | 192.65 (108.44–266.26) | 0.09 (0.07–0.11) |
| DPZ-PNE | 13.30 (12.31–14.07) ** | 2.13 (1.97–2.25) ** | 295.50 (239.71–523.36) * | 0.19 (0.18–0.21) ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinoza, L.C.; Silva-Abreu, M.; Clares, B.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Halbaut, L.; Cañas, M.-A.; Calpena, A.C. Formulation Strategies to Improve Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020064
Espinoza LC, Silva-Abreu M, Clares B, Rodríguez-Lagunas MJ, Halbaut L, Cañas M-A, Calpena AC. Formulation Strategies to Improve Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(2):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020064
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinoza, Lupe Carolina, Marcelle Silva-Abreu, Beatriz Clares, María José Rodríguez-Lagunas, Lyda Halbaut, María-Alexandra Cañas, and Ana Cristina Calpena. 2019. "Formulation Strategies to Improve Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 2: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020064
APA StyleEspinoza, L. C., Silva-Abreu, M., Clares, B., Rodríguez-Lagunas, M. J., Halbaut, L., Cañas, M. -A., & Calpena, A. C. (2019). Formulation Strategies to Improve Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Donepezil. Pharmaceutics, 11(2), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020064