Applicability of a Modified Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Loading and Characterization of Microspheres
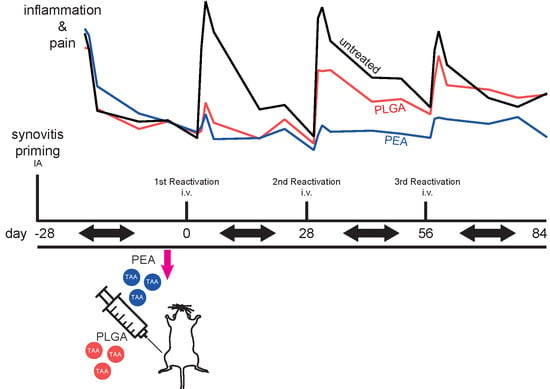
2.2. Modified Arthritis Model
2.2.1. Study Design
2.2.2. Joint Swelling
2.2.3. Referred Mechanical Hypersensitivity
2.2.4. Dynamic Weight Bearing
2.2.5. µCT Analyses
2.2.6. Histological Processing and Stainings
2.2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Observations
3.1.1. Systemic Effects of the PGPS Reactivations
3.1.2. Histological Joint Pathology
3.1.3. Course of Inflammation, Hyperalgesia and Weight Bearing in Untreated Animals in the Modified Arthritis Model
3.2. Polymer-Based Drug Delivery
3.2.1. PLGA and PEA Microsphere Characterization
3.2.2. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetics of PLGA and PEA Microspheres.
3.2.3. Effects of Locally Delivered TAA
3.2.4. Effects of TAA Delivery on Synovitis, Macrophage Subtypes and OA-Like Bone Phenotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woolf, A.D.; Pfleger, B. Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oikonomopoulou, K.; Diamandis, E.P.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Chandran, V. Proteinases and their receptors in inflammatory arthritis: An overview. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Lee, Y.C. Mechanisms for Joint Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): From Cytokines to Central Sensitization. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoof, R.; Willemen, H.; Eijkelkamp, N. Divergent roles of immune cells and their mediators in pain. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2018, 57, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, T.W.; Parkes, M.J.; Maricar, N.; Marjanovic, E.J.; Hodgson, R.; Gait, A.D.; Cootes, T.F.; Hutchinson, C.E.; Felson, D.T. Synovial tissue volume: A treatment target in knee osteoarthritis (OA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, N.; Campbell, J.; Robinson, V.; Gee, T.; Bourne, R.; Wells, G. Intraarticular corticosteroid for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodick, N.; Lufkin, J.; Willwerth, C.; Kumar, A.; Bolognese, J.; Schoonmaker, C.; Ballal, R.; Hunter, D.; Clayman, M. An intra-articular, extended-release formulation of triamcinolone acetonide prolongs and amplifies analgesic effect in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: A randomized clinical trial. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, M.B. Pharmaceutical Approval Update. P T 2017, 42, 733–755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudnik-Jansen, I.; Colen, S.; Berard, J.; Plomp, S.; Que, I.; van Rijen, M.; Woike, N.; Egas, A.; van Osch, G.; van Maarseveen, E.; et al. Prolonged inhibition of inflammation in osteoarthritis by triamcinolone acetonide released from a polyester amide microsphere platform. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Timur, U.T.; Woike, N.; Welting, T.J.; Draaisma, G.; Gijbels, M.; van Rhijn, L.W.; Mihov, G.; Thies, J.; Emans, P.J. Celecoxib-loaded PEA microspheres as an auto regulatory drug-delivery system after intra-articular injection. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinow, B.; Werling, J.; Bendele, A.; Gass, J.; Bogseth, R.; Balla, K.; Valaitis, P.; Hutchcraft, A.; Graham, S. Intra-articular (IA) ropivacaine microparticle suspensions reduce pain, inflammation, cytokine, and substance p levels significantly more than oral or IA celecoxib in a rat model of arthritis. Inflammation 2015, 38, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Bendele, A.M.; Blanks, R.C.; Bodick, N. Sustained efficacy of a single intra-articular dose of FX006 in a rat model of repeated localized knee arthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitlanadze, G.; Kviria, T.; Katsarava, R.; Chu, C.C. In vitro enzymatic biodegradation of amino acid based poly(ester amide)s biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minett, M.S.; Eijkelkamp, N.; Wood, J.N. Significant determinants of mouse pain behaviour. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, J.; Popov-Celeketic, J.; Steen-Louws, C.; Raoof, R.; Hack, E.; Eijkelkamp, N. Development of Recombinant Proteins to Treat Chronic Pain. J. Vis. Exp. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panahifar, A.; Jaremko, J.L.; Tessier, A.G.; Lambert, R.G.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Fallone, B.G.; Doschak, M.R. Development and reliability of a multi-modality scoring system for evaluation of disease progression in pre-clinical models of osteoarthritis: Celecoxib may possess disease-modifying properties. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, V.; Morawietz, L.; Burmester, G.R.; Kinne, R.W.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Muller, B.; Haupl, T. Synovitis score: Discrimination between chronic low-grade and high-grade synovitis. Histopathology 2006, 49, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, H.J.; Lippiello, L. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1970, 52, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companion Guide to Infectious Diseases of Mice and Rats; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [CrossRef]
- Dalldorf, F.G.; Cromartie, W.J.; Anderle, S.K.; Clark, R.L.; Schwab, J.H. The relation of experimental arthritis to the distribution of streptococcal cell wall fragments. Am. J. Pathol. 1980, 100, 383–402. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.Y.; Lau, C.S.; Elzorkany, B.; Hsu, P.N.; Praprotnik, S.; Vasilescu, R.; Marshall, L.; Llamado, L. Dosing down and then discontinuing biologic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: A review of the literature. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromartie, W.J.; Craddock, J.G.; Schwab, J.H.; Anderle, S.K.; Yang, C.H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J. Exp. Med. 1977, 146, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, K.; Seemann, S.; Konig, S.; Lenhardt, I.; Abdel-Tawab, M.; Koeberle, A.; Werz, O.; Lupp, A. Protective Effect of Casperome((R)), an Orally Bioavailable Frankincense Extract, on Lipopolysaccharide- Induced Systemic Inflammation in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, U.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chatterjee, M. Allylpyrocatechol attenuates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in a collagen-induced model of arthritis. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Arias, C.; Arias, C.F.; Zhang, M.; Herrero, M.A.; Acosta, F.J.; Tsuji, M. Modeling the effect of boost timing in murine irradiated sporozoite prime-boost vaccines. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnekave, M.; Bivas-Benita, M.; Gillard, G.O.; Sircar, P.; Hovav, A.H. A matter of timing: Unsynchronized antigen expression and antigen presentation diminish secondary T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guhad, F. Introduction to the 3Rs (refinement, reduction and replacement). Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2005, 44, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peters, T.; Kim, S.W.; Castro, V.; Stingl, K.; Strasser, T.; Bolz, S.; Schraermeyer, U.; Mihov, G.; Zong, M.; Andres-Guerrero, V.; et al. Evaluation of polyesteramide (PEA) and polyester (PLGA) microspheres as intravitreal drug delivery systems in albino rats. Biomaterials 2017, 124, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shive, M.S.; Anderson, J.M. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 28, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doty, A.C.; Weinstein, D.G.; Hirota, K.; Olsen, K.F.; Ackermann, R.; Wang, Y.; Choi, S.; Schwendeman, S.P. Mechanisms of in vivo release of triamcinolone acetonide from PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 2017, 256, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitlanadze, G.; Machaidze, M.; Kviria, T.; Djavakhishvili, N.; Chu, C.C.; Katsarava, R. Biodegradation of amino-acid-based poly(ester amide)s: In vitro weight loss and preliminary in vivo studies. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honore, P.; Rogers, S.D.; Schwei, M.J.; Salak-Johnson, J.L.; Luger, N.M.; Sabino, M.C.; Clohisy, D.R.; Mantyh, P.W. Murine models of inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer pain each generates a unique set of neurochemical changes in the spinal cord and sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2000, 98, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, V.B.; Conaghan, P.G.; Aazami, H.A.; Mehra, P.; Kivitz, A.J.; Lufkin, J.; Hauben, J.; Johnson, J.R.; Bodick, N. Synovial and systemic pharmacokinetics (PK) of triamcinolone acetonide (TA) following intra-articular (IA) injection of an extended-release microsphere-based formulation (FX006) or standard crystalline suspension in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, P.S.; Wright, P.K.; Van’t Hof, R.J.; Helfrich, M.H.; Ohshima, H.; Ralston, S.H. Immunolocalization of inducible nitric oxide synthase in synovium and cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Abnormality | No treatment | % | PLGA TAA | % | PEA TAA | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| granulomatous hepatitis | no–slight reaction (2/6) | 33 | no–slight reaction (3/6) | 50 | no–slight reaction (5/6) | 83 |
| moderate reaction (1/6) | 17 | moderate reaction (1/6) | 17 | |||
| severe reaction (3/6) | 50 | severe reaction (2/6) | 33 | severe reaction (1/6) | 17 | |
| granulomatous splenitis | no–slight reaction (2/6) | 33 | no–slight reaction (2/6) | 33 | ||
| severe reaction (4/6) | 67 | severe reaction (6/6) | 100 | severe reaction (4/6) | 67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudnik-Jansen, I.; Woike, N.; de Jong, S.; Versteeg, S.; Kik, M.; Emans, P.; Mihov, G.; Thies, J.; Eijkelkamp, N.; Tryfonidou, M.; et al. Applicability of a Modified Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020070
Rudnik-Jansen I, Woike N, de Jong S, Versteeg S, Kik M, Emans P, Mihov G, Thies J, Eijkelkamp N, Tryfonidou M, et al. Applicability of a Modified Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(2):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020070
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudnik-Jansen, Imke, Nina Woike, Suzanne de Jong, Sabine Versteeg, Marja Kik, Pieter Emans, George Mihov, Jens Thies, Niels Eijkelkamp, Marianna Tryfonidou, and et al. 2019. "Applicability of a Modified Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery Systems" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 2: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020070
APA StyleRudnik-Jansen, I., Woike, N., de Jong, S., Versteeg, S., Kik, M., Emans, P., Mihov, G., Thies, J., Eijkelkamp, N., Tryfonidou, M., & Creemers, L. (2019). Applicability of a Modified Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics, 11(2), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020070